L3 Microscopy (Light Microscopes VS Electron Microscopes)
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A Level Biology AQA
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
How does a light microscope work
Light passes through specimen (light bounces off mirror)
into magnifying lenses of microscope
into objective viewing lenses
What is the max magnification of a light microscope?
1500 X
What is resolution?
The ability to distinguish between two points
What is a light microscope’s max resolution?
200nm
Why might a light microscope be more useful than an electron microscope in some cases?
you can visualise specimens in their natural colour, rather than black and white
more widely available, and easy to use
you can use living cells and organisms, unlike electron microscopes which require them to be dead
less expensive than electron microscopes
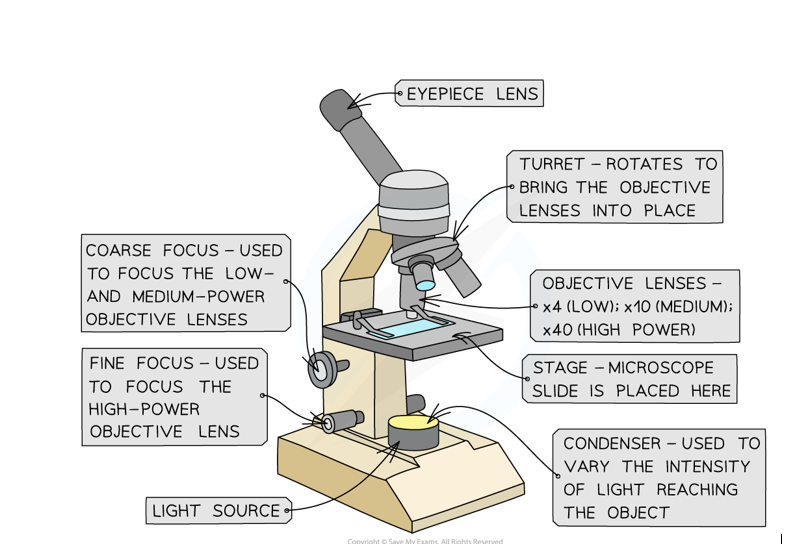
Label this diagram of a light microscope
How does an Electron Microscope work?
Electrons have properties of waves and particles
Starts with an electron gun, which is producing a beam of electrons
these electrons pass down the microscope
the inside of the microscope has a vacuum, so the electrons can pass through w/out bouncing off the molecules in the air
electrons have a negative charge, so you can focus the electron beam using electromagnets
these are called electromagnetic lenses
the specimen is placed in the path of the electron beam. Electrons can pass through some parts of the specimen more easily than others
Final image is produced on florescent screen
When was the electron microscope invented?
1931
What’s the electron microscopes maximum magnification?
TEM = around 50 million x
SEM = around 1,500,000 x
Compare resolution of Scanning and transmission electron microscopes
Transmission microscopes have a very high resolution, the scanning microscopes have a lesser resolution
What is the max resolution of an electron microscope?
around 20nm
Compare scanning and transmission electron microscopes magnification
TEM offers higher magnification, up to 50 million x
SEM is lower with up to 1-2million x
Compare scanning and transmission electron microscopes 2D VS 3D images
TEM offers 2D internal view, SEM offers 3D external view images
Compare scanning and transmission electron microscopes thickness of specimen that can be used
TEM= must be thinly sliced, SEM= not required to be thinly sliced
How does the transmission microscope work?
Electron beam passes through the specimen
In denser regions of the specimen, electrons are more easily absorbed, producing darker regions in the image
must be performed in a vacuum
How does a scanning microscope work?
Electron beam doesn’t pass through specimen, instead they are scattered from the surface of the specimen and detected.
Producing a 3D image
Requires specimen to be coated in metal such as gold —> leading to artefacts
What is an artefact (Electron microscope)? And what can cause them?
They are false images, and can be caused from the staining process, or the condition in the microscope