Carbonyls + Carboxylic acids + Esters
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is the functional group of carbonyls? Also what are examples of cabronyls?
Functional group: C=O
Aldehydes and ketones
Why is the position of the functional group for both aldehydes and ketones respectively?

What can be said about aldehydes and ketones boiling points compared to alcohols?
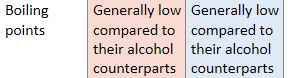
Why do aldehydes and ketones have low boiling points compared to alcohol?
Only have weak London forces and permananent dipole-dipole interactions due to polarity in the molecule
Alcohol has OH group and can interact with one another via hydrogen bonding, which is far stronger than bonding in carbonyls, hence higher boiling point
What can be said about aldehydes and ketones’ solubility?
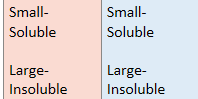
Why are only small carbonyls soluble in water?
The longer the non-polar hydrocarbon compoenent, the more disrupted the hydrogen bonding is with water molecules, hence only short carbonyls dissolve in water
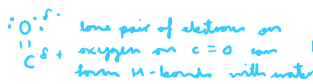
When will the carbonyl not dissolve in water?
This occurs when the cabronyl is large enough so that London forces between the non-polar hydrocarbon chain will be stronger than H-bonding between C=O and H on water molecule → won’t dissolve
What can be said about carboxylic acid’s ability to dissolve?
(same reasoning as carbonyls)

What can be said about the cabroxylic acid’s boiling point?
High
Why do carboxylic acids have high boiling points?
Carboxylic acids can form H-bonds with each other
+ due to dimers forming when there are pure, liquid forms of carboxylic acids hydrogen-bonding with another, the larger the dimer, the greater the intermolecular forces -> the higher the boiling point
How do you name esters?
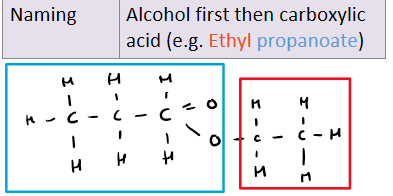
What do esters smell like?
Sweet (fruity)