BIOL1030 - Wk1: Review
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This covers materials from Week 1 lecture, in-class iClicker and quiz, as well as material from the textbook.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
High body temperature in mammals reflexively causes a change in blood flow and sweating, which act to reduce the temperature.
This is a ____ feedback loop because response to the signal results in a(n) ____ of that signal.
negative; decrease
Which of the answer choices is an example of the effector’s role in maintaining homeostasis?
Increased sweating on a hot summer day
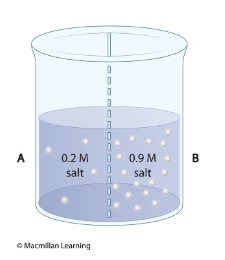
The breaker in the illustration contains two solutions of salt with different concentrations (measured by molarity, M). The two solutions are separated by a membrane that is permeable to water but not to salt. What will occur in this container?
Diffusion of water from A to B but no diffusion of salt
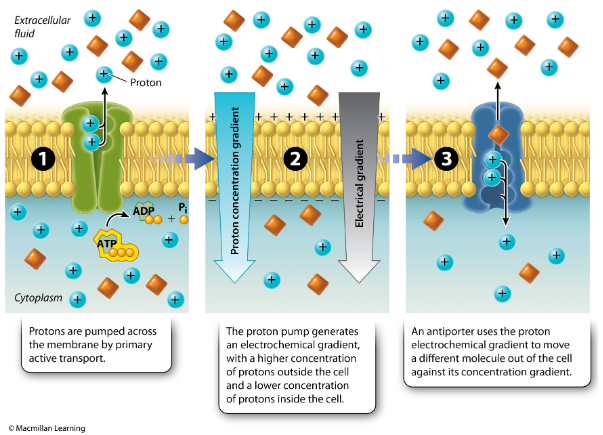
In the example of secondary active transport, what would happen if ATP suddenly became unavailable for Step 1 of the figure shown?
The movement of the molecules through the antiporter would continue for a while until the proton gradient was depleted
The cell membrane contributes to the homeostasis of the cell by:
acting as a selective barrier
Why does active transport of molecules across a membrane require ATP?
An input of energy is needed to drive the movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to one of higher concentration
Circulating blood sugar levels are tightly maintained in the body. After a meal, blood sugar levels rise, and specialized cells in the pancreas release insulin to lower circulating levels of blood sugar. Some diabetics are unable to produce insulin.
Which statement reflects how this would disrupt the feedback loop to decrease the blood sugar levels?
Pancreatic cells do not produce insulin; therefore, the effector is broken
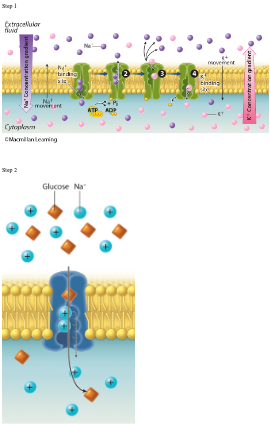
In the kidney, glucose transport across the cell membrane is the result of a combination of two steps of active transport. Refer to the figures shown. The first step involves a primary active transport system performed by the sodium-potassium pump. It uses the energy from ATP hydrolysis to move sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell. The second step involves a secondary active transport symporter that uses the energy in the sodium gradient created by the first step. This second step moves glucose, as well as sodium ions that move down their concentration gradient, into the cell.
The sodium-potassium pump would make less of a sodium gradient, so less glucose could be transported across the membrane
Which lipid composition option has the least membrane fluidity?
Phospholipids with long-chain, saturated fatty acids
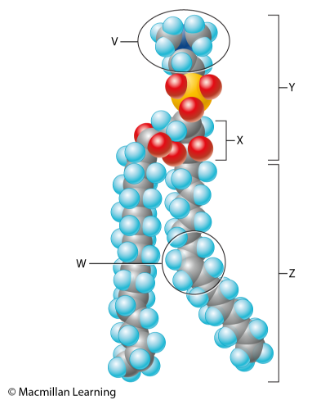
Which lettered part of the space-filling molecular model in the figure represents the hydrophobic portion?
Z