MS_Week 1_Function of the Heart
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Cardiac conduction system
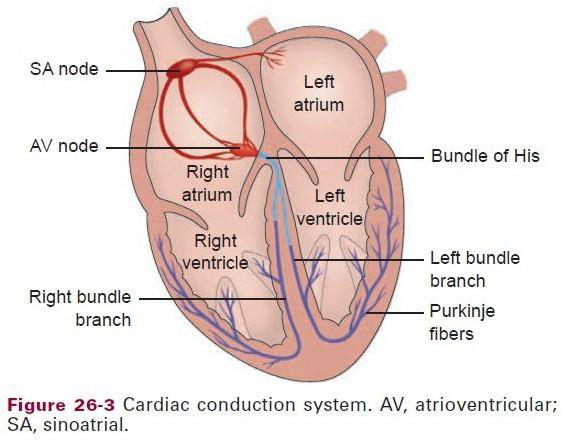
cardiac conduction system
generates and transmits electrical impulses that stimulate contraction of the myocardium
Automaticity
Excitability
Conductivity
three physiologic characteristics of two types of specialized electrical cells, the nodal cells and the Purkinje cells, provide this synchronization:
Electrophysiologic Properties of the Heart
Automaticity
Excitability (depolarization)
Conductivity
Contractility
Refractoriness
Automaticity
ability to initiate an electrical impulse spontaneously and repetitively
Excitability (depolarization)
ability to respond to an electrical impulse
Conductivity
ability to transmit an electrical impulse from one cell to another
Contractility
Contract
Refractoriness
inability to respond until repolarization
Conduction system of the heart
SA Node
AV node
Bundle of His
R & L bundle branches
Purkinje fibers
Conduction system of the heart (mnemonic)
Sending Angel Brings L&R Prosperity
composition of both the sinoatrial (SA) node and the atrioventricular (AV) node
nodal cells
sinoatrial (SA) node
primary pacemaker of the heart, is located at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium
inherent firing rate of sinoatrial (SA) node in a normal resting adult heart
60 to 100 impulses/min
inherent firing rate of atrioventricular (AV) node in a normal resting adult heart
40 to 60 beats/min
inherent firing rate of purkinje fibers in a normal resting adult heart
20 to 40 beats/min
Cardiac cycle
refers to the events that occur in the heart from one heartbeat to the next. These events cause blood to flow through the heart due to changes in chamber pressures and valvular function during atrial and ventricular diastole and systole.
atrial and ventricular diastole
heart chambers are relaxed
Diastole
relaxation - filling of ventricles
Systole
Contraction - emptying
Cardiac Output
the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle during a given period.
The cardiac output in a resting adult
about 5 L/min but varies greatly depending on the metabolic needs of the body
Cardiac output formula
Cardiac Output = Heart Rate x Stroke Volume
Stroke volume
the amount of blood ejected per heartbeat
average resting stroke volume
70 mL
normal heart rate
60 to 80 bpm
Changes in heart rate are accomplished by
reflex controls mediated by the autonomic nervous system, including its sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.
parasympathetic impulses,
travel to the heart through the vagus nerve, can slow the cardiac rate,
sympathetic impulses
increase cardiac rate
Baroreceptors
specialized nerve cells located in the aortic arch and in both right and left internal carotid arteries (at the point of bifurcation from the common carotid arteries).
Are sensitive to changes in blood pressure (BP).
three factors that primarily determine stroke volume
Preload
Afterload
contractility
Preload
refers to the degree of stretch of the ventricular cardiac muscle fibers at the end of diastole.