natural monopoly
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
what is a natural monopoly
what characteristics do natural monopolies have
huge fixed costs
enormous potential for economies of scale
rational for 1 firm to supply the entire market (competition is undesirable)
competition would result in wasteful duplication of resources and non exploitation of full economies of scale (allocative and productive inefficiency)
why is there enormous potential for economies of scale
because it will take a very large quantity to minimise average costs, due to fixed cost and total cost being extremely high
the long run average cost curve is…
downward sloping
what is quantity like at the minimum efficient scale point where all economies of scale are fully exploited
very high
why is competition in a natural monopoly undesirable
because it would result in a wasteful duplication of resources because the first firm to enter the market will have the economies of scale advantage, allocative inefficiency will take place
why would economies of scale not be fully exploited if there was competition
there will be productive inefficiency because firms will not be the greatest size possible if there is competition compared to if they are a monopoly
in this market, a natural monopoly is positive as it results in…
productive and allocative efficiency
lrac diagram natural monopoly
natural monopoly diagram
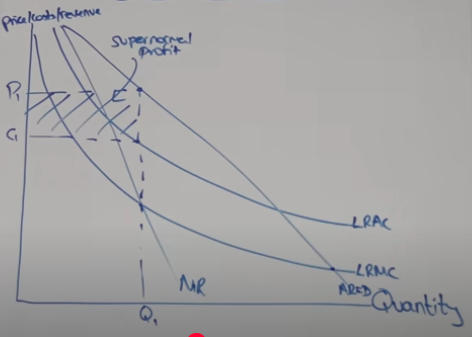
what would be the point of regulation
AR = MC
what will happen to quantity as a result of regulation
increase
what will happen to price as a result of regulation
decrease
what is the problem with natural monopolies being regulated at ar = mc
average cost is higher than average revenue, so subnormal profit is being made
natural monopolies being regulated diagram
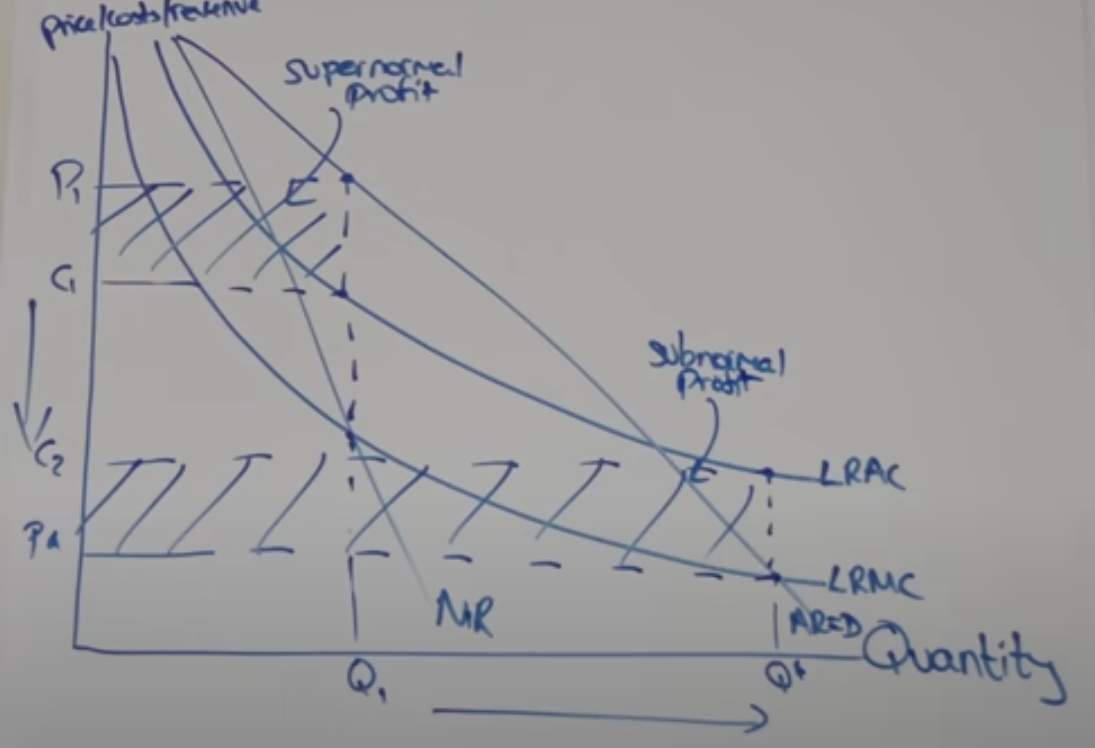
what is done when a private natural monopolist is being forced to produce at ar = mc
a subsidy is given to cover the losses
the subsidy given is equal to the…
loss per unit