Chem- chapter 5
2.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:18 AM on 2/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1
New cards
Specific heat capacity
the amount of energy needed to change 1 g of a substance by 1 °C.
2
New cards
Specific heat of water
4\.18
3
New cards
Calorimetry
the accurate and precise measurements of heat changes for chemical and physical processes.
4
New cards
Endothermic
process that absorbs energy
5
New cards
Exothermic
process that releases energy
6
New cards
enthalpy
the heat content for systems at a constant pressure (represented as H).
7
New cards
thermometer
instrument used to measure average kinetic energy
8
New cards
joule
SI unit for energy
9
New cards
calorie (lowercase c)
one calorie is the amount of energy needed to raise 1 g of water by 1 °C
10
New cards
kinetic energy
the energy of motion
11
New cards
potential energy
stored energy or energy of position
12
New cards
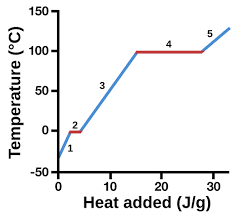
solid
1
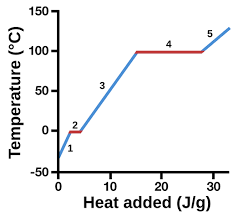
13
New cards
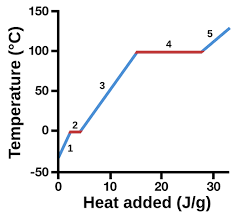
liquid
3
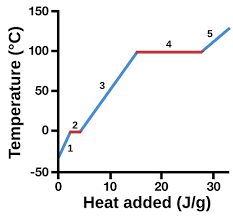
14
New cards
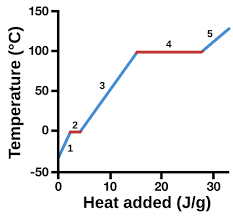
gas
5
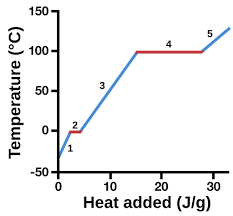
15
New cards
endothermic
Type of process
16
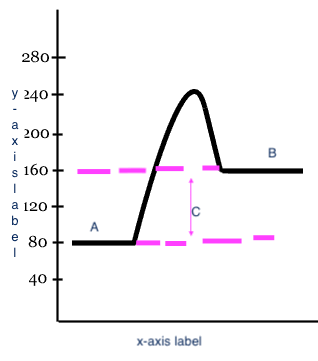
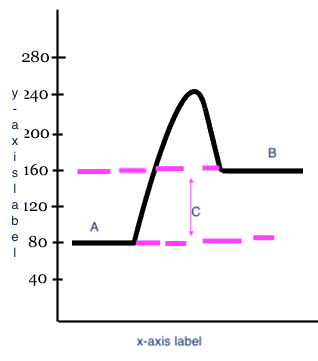
New cards
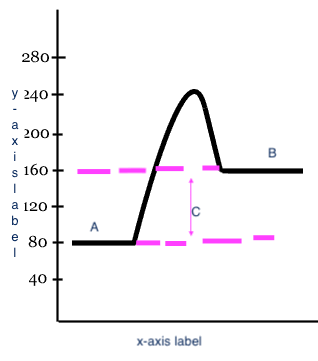
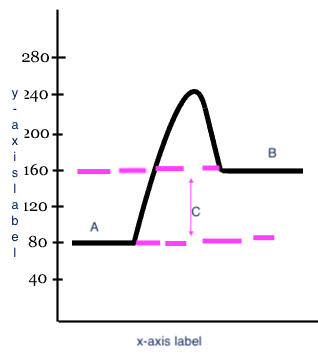
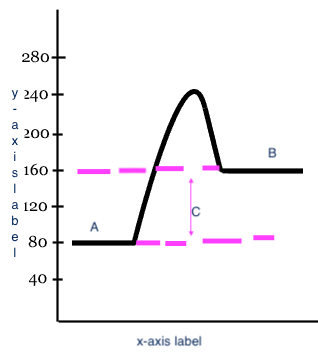
Reactants
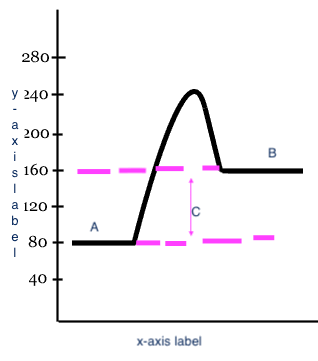
A
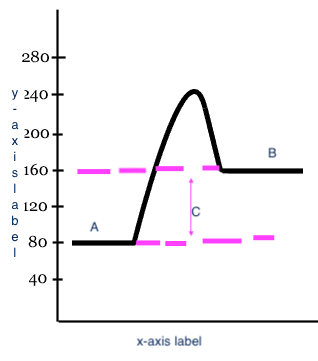
17
New cards
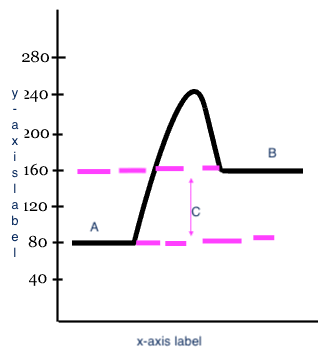
Products
B
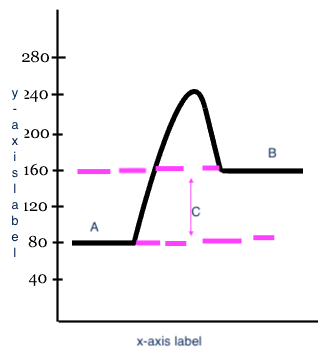
18
New cards
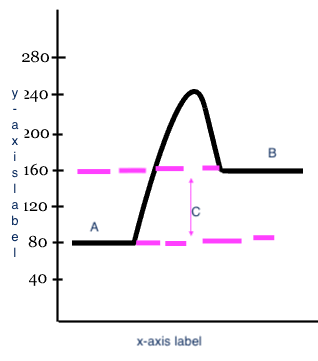
Heat change (delta H)
C
19
New cards
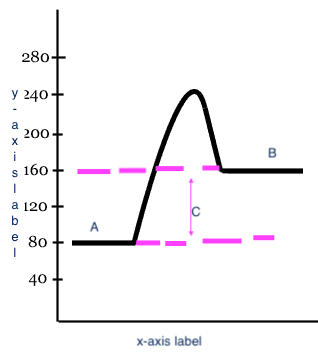
x-axis label
Reaction
20
New cards
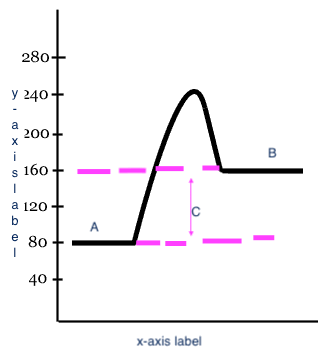
y-axis label
Potential Energy
21
New cards
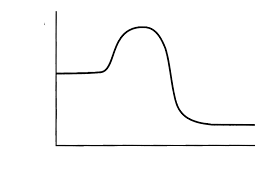
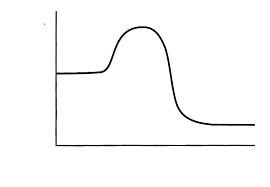
exothermic
Type of process?
22
New cards
1 Cal= 0.00418 J
Cal to Joules
23
New cards
1 cal= 4.18 J
cal to Joules
24
New cards
1000 cal= 1 Cal
cal to Cal
25
New cards

H°f
standard heat of formation

26
New cards
Standard temperature (STP)
0° C
27
New cards
Standard pressure (STP)
1 atm or 101.3 kPa
28
New cards
Law of conservation of energy
energy cannot be created nor destroyed
29
New cards
Temperature
the measurement of average kinetic energy
30
New cards
Work
moving matter against an opposing force
31
New cards
Energy
the capacity to do work
32
New cards
Thermochemistry
the study of heat changes that occur during chemical reactions and physical changes of state.
33
New cards
Heat capacity
the amount of energy needed to change the temperature of an object by 1 °C.
34
New cards
Calorimeter
device used to measure the heat absorbed or given off.
35
New cards
Thermochemical reactions
an equation including heat change (NOT q=mcAT).
36
New cards
Heat of reaction
the heat change for an equation as written.
37
New cards
molar heat of combustion
energy change when burning one mole of a substance.
38
New cards
molar heat of fusion
energy change when melting one mole of a substance.
39
New cards
Molar heat of solidification
energy change when freezing one mole of a substance.
40
New cards
molar heat of vaporization
energy change when vaporizing one mole of a substance.
41
New cards
molar heat of condensation
energy change when condensing (changing from gas to liquid) one mole of a substance.
42
New cards
molar heat of solution
energy change per mole of solute when making a solution.
43
New cards
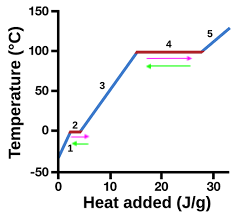
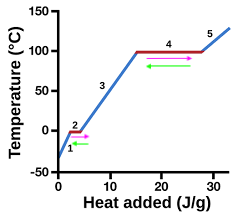
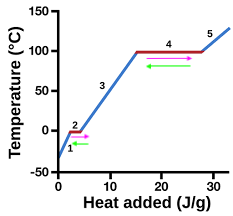
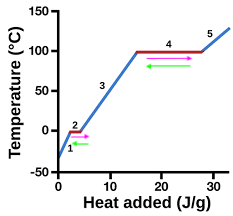
heating curve
represents heat vs. temp.
44
New cards
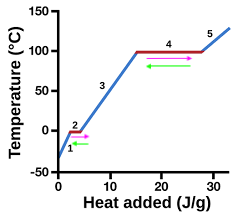
vaporization
4 (pink)
45
New cards
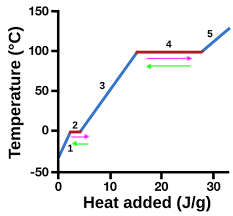
condensation
4 (green)
46
New cards
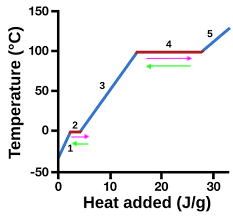
solidification
2 (green)
47
New cards
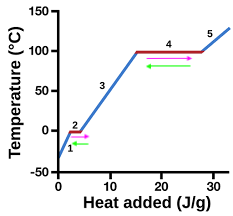
melting
2 (pink)
48
New cards
Chemical potential energy
energy stored in chemicals because of their compositions