World War 1 and 2
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
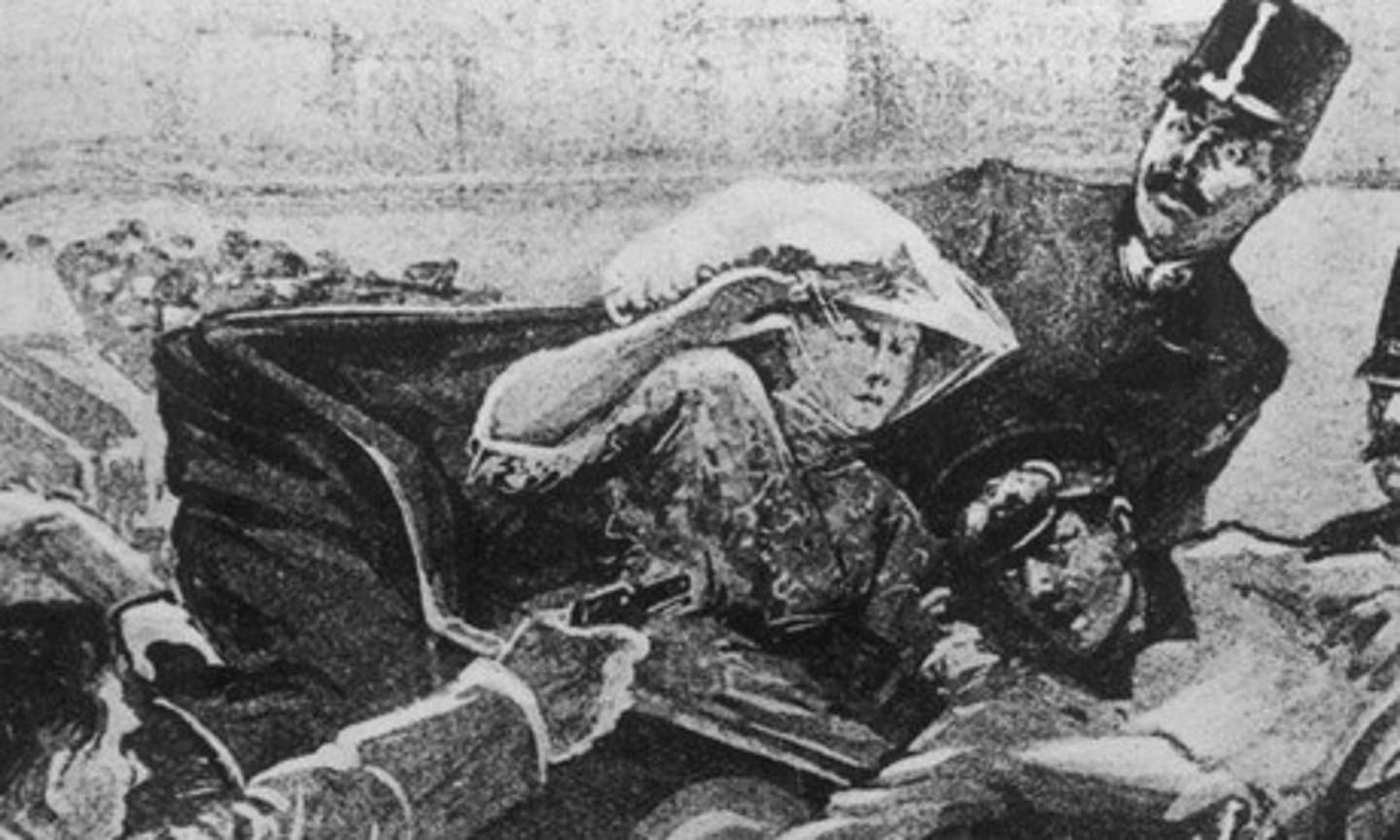
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
This was the spark that started World War I. Archduke Ferdinand, the Austrian crown prince, was murdered on June 28, 1914, by a Serbian nationalist while visiting Sarajevo, Bosnia. Germany urged Austria-Hungary to fight and they went to war against Serbia; all of this due to Serbia wanting to expand
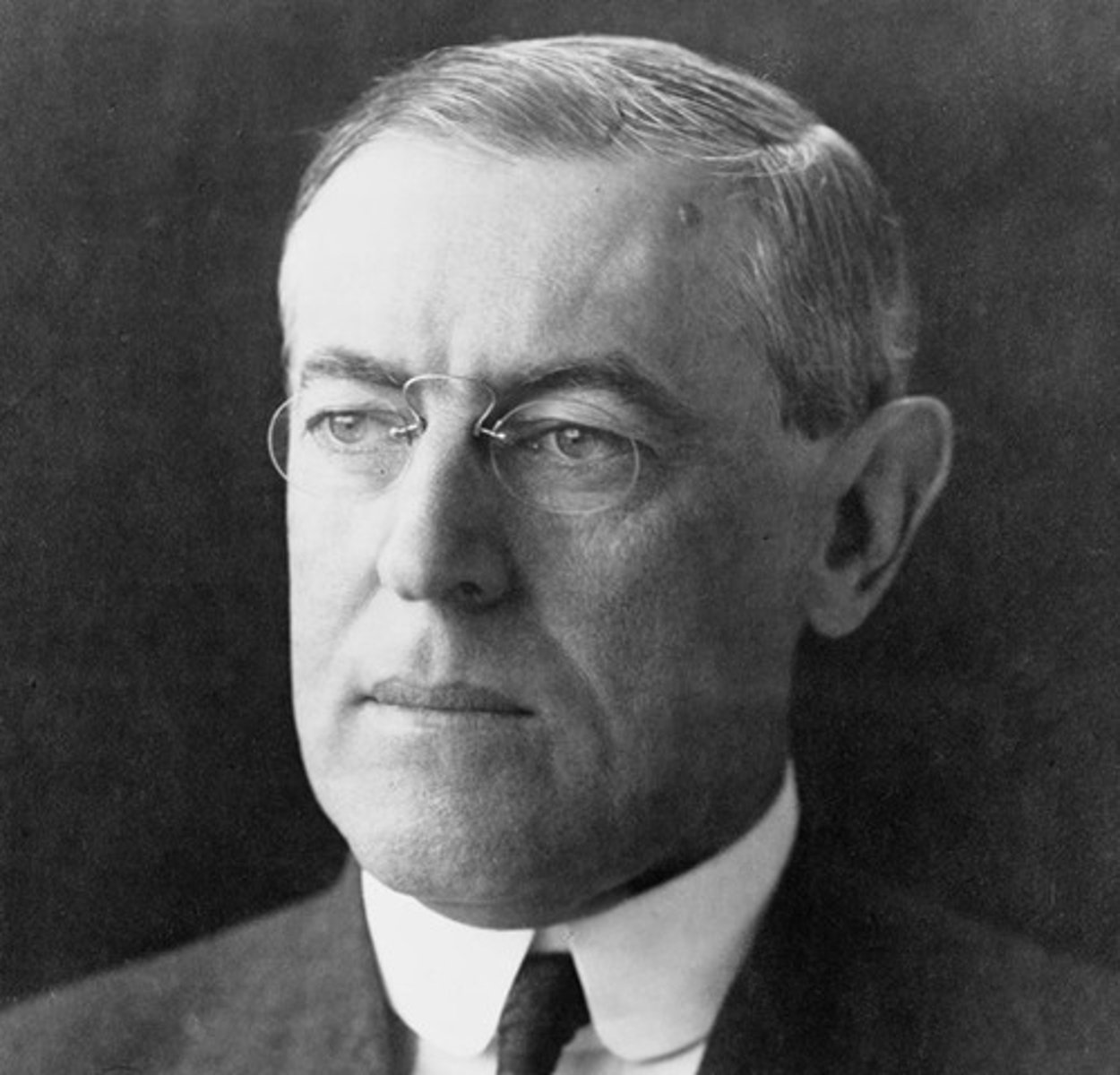
Woodrow Wilson
This was the president who was elected in 1912, and led the US into WWI. Later wrote a plan for post-WWI peace known as the Fourteen Points.

Austria-Hungary
This Central Power empire during WWI, started the war with their invasion of Serbia after the assassination of Archduke Ferdinand on June 28, 1914 . It was made up of Austria, Hungary and several other nations and territories. After World War I it split up into several nations.
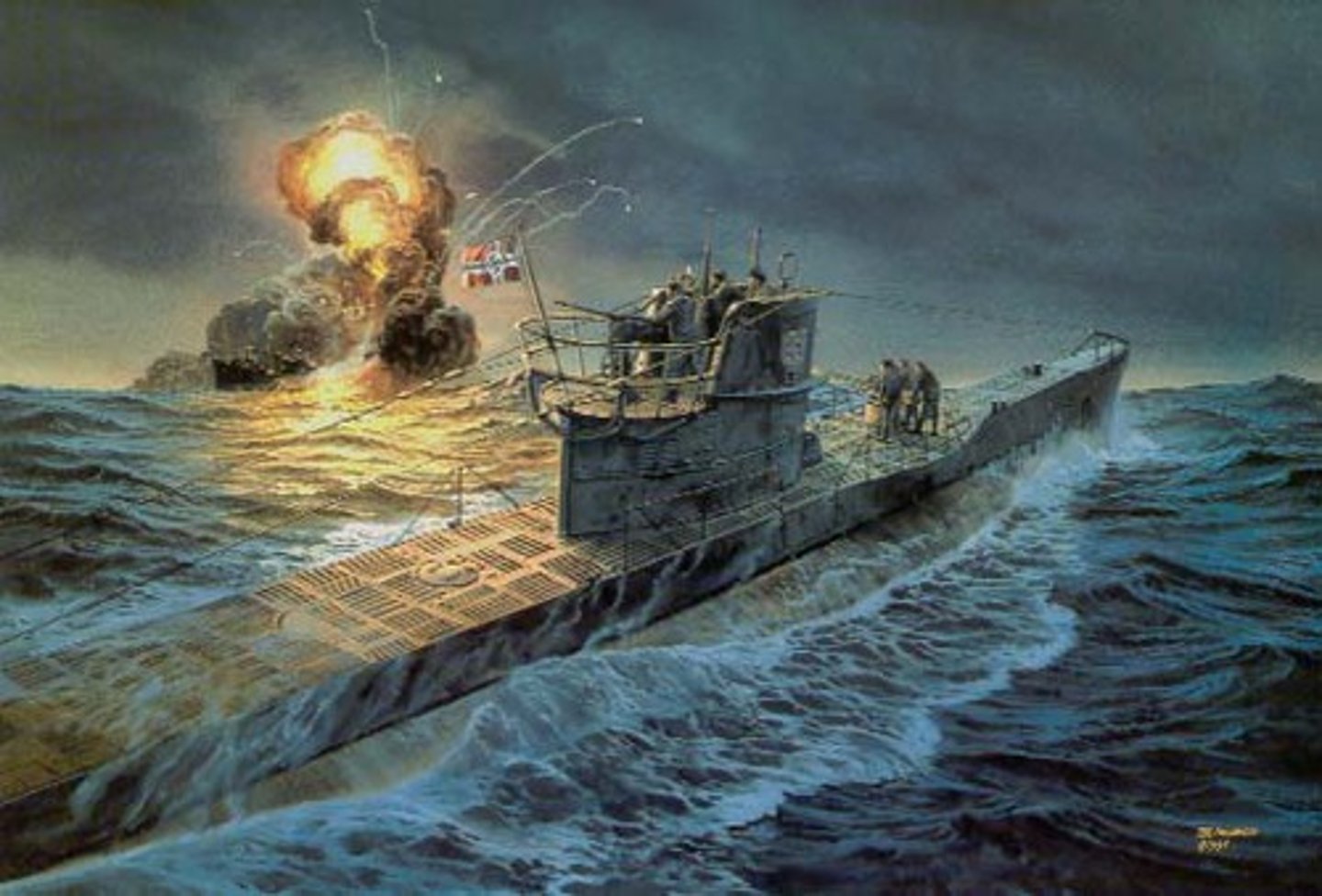
U-boats
This new machinery used by the Germans in sea warfare, to attack British and American supply ships in the North Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.

Nationalism
This cause of World War I was based on an intense pride in one's nation.

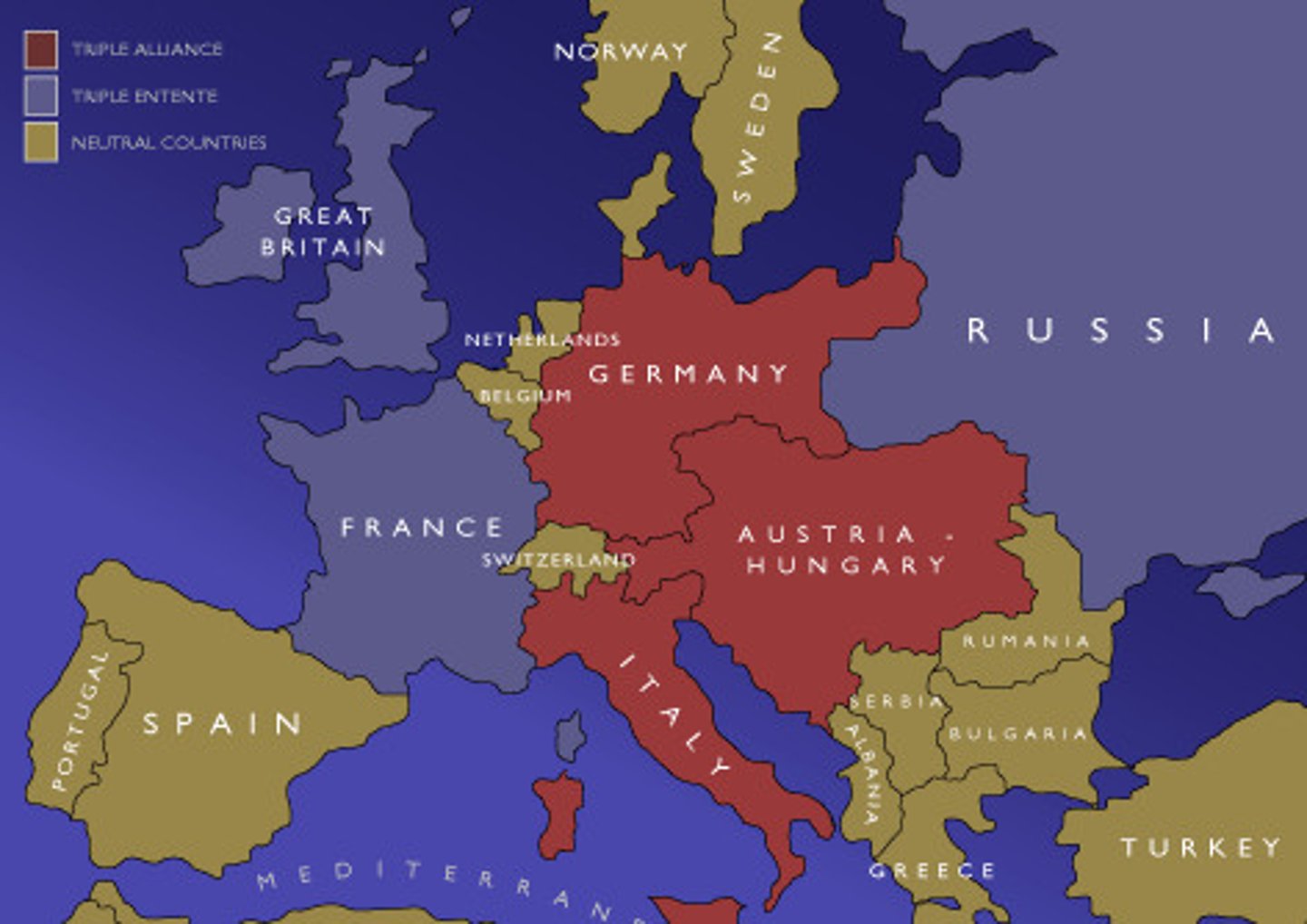
Allied Powers
This alliance during WWI included the United States, Great Britain, France, Russia and Italy (switched to the Allied Powers in 1915). (The blue countries of the East and West on map above)
Wilson's Fourteen Points
This is the plan for post-World War I outlined by President Wilson in 1918. This plan called for self-determination (countries in Africa and Asia govern themselves), freedom of the seas, free trade, end to secret agreements, reduction of arms and a league of nations.

Zimmerman Telegram
This intercepted note from the German foreign minister to the Mexican government offered, territories in Texas, Arizona and New Mexico for Mexico. The note also confirmed the new policy of unrestricted submarine warfare by Germany against the Allied Powers. This helped turn Americans against Germany in WWI.

Lusitania
This British passenger ship was sunk by German U-boats in 1915, carrying civilians and ammunition to Britain from the U.S. The event turned American opinion against Germany.

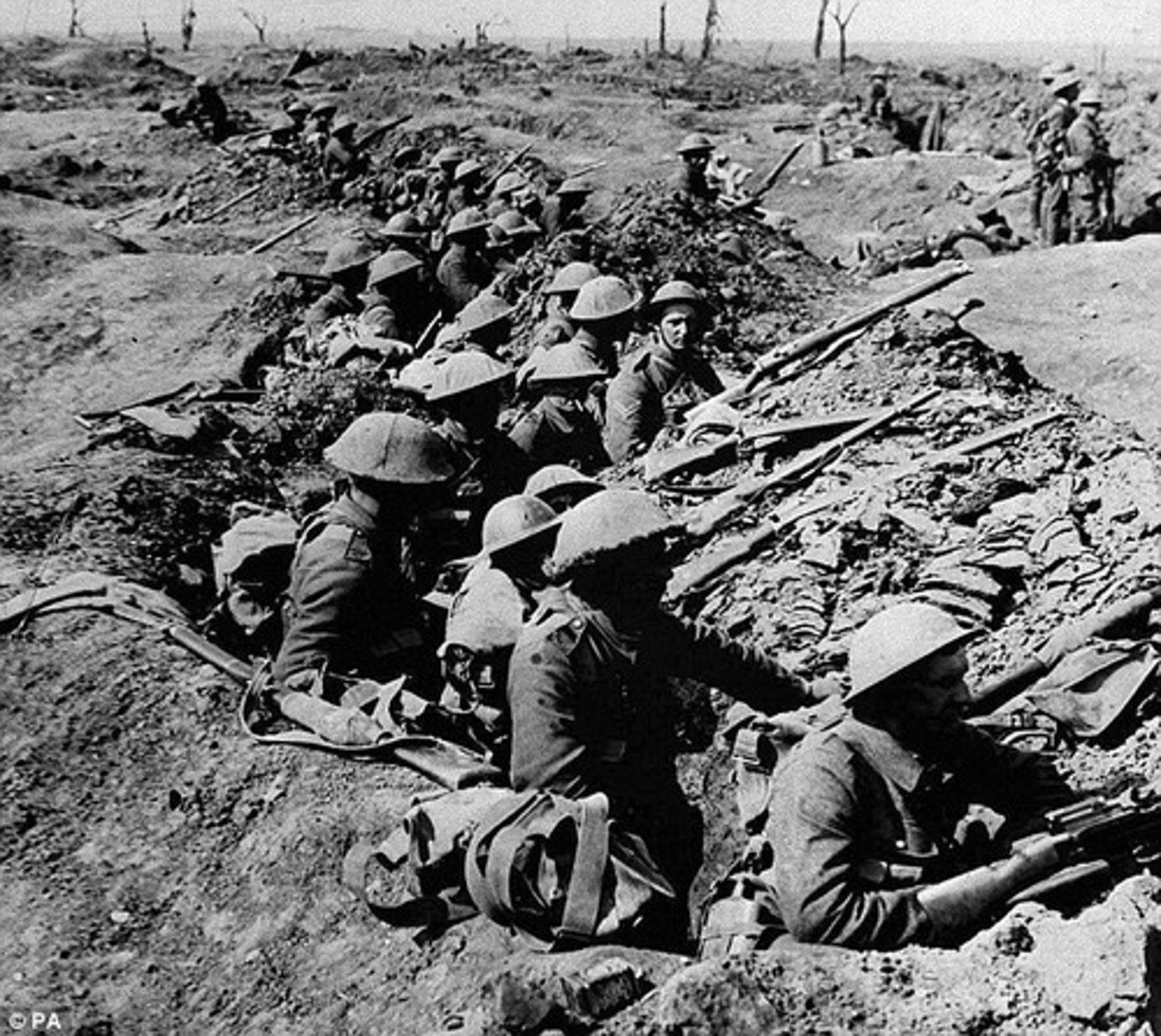
Trench Warfare
This style of warfare was common in WWI, due to the invention of the machine gun and heavy artillery. It included digging long trenches, separated by barbed wire and a no mans land.

Armistice, 1918
This was the agreement between the Allies and Central Powers that ended the fighting after WWI. It began at 11/11/1918 at 11:11 am. This marked a victory for the Allies and stated that the Central Powers lost. Germans would later look at this as "the stab in the back."

Reparations
This term refers to the payments and transfers of property that Germany was required to make under the treaty of Versailles.

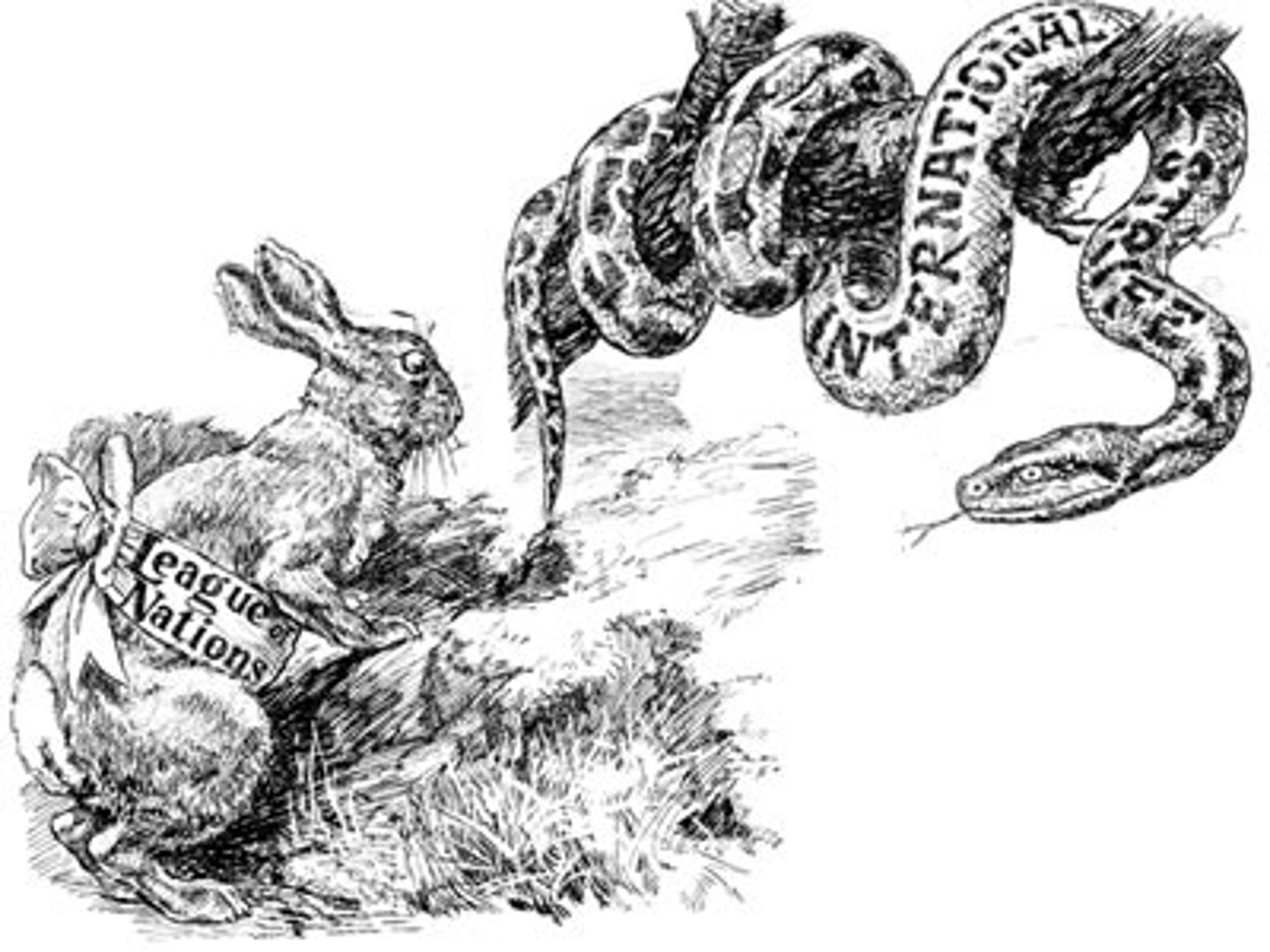
League of Nations
This intergovernmental organization lasted from 1919-1946, was founded after the Paris Peace Conference. It did not work effectively to prevent WWII.

Imperialism
This cause of World War II resulted from the competition among European nations for colonies in Africa and Asia from 1880-1914. This created tension, especially between Germany and Great Britain.

Alliances
This was a major cause of WWI. Two major alliances formed the Triple Alliance (Germany, Austria, Italy) and the Triple Entente (France, England, Russia). This alliance system made world war likely, by drawing all countries into a small war.
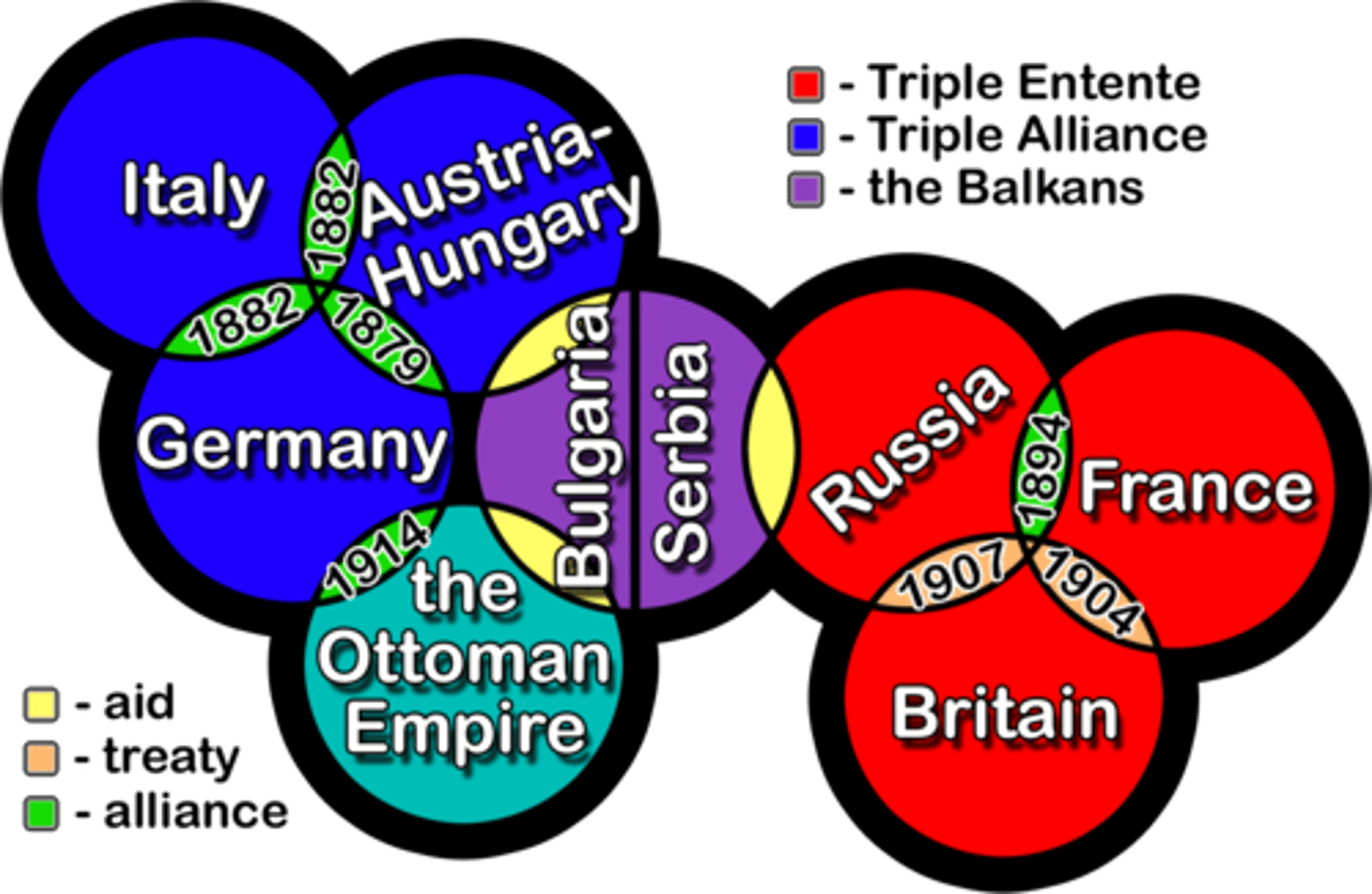
Triple Alliance
This alliance was made Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy in the years before WWI. IN RED ABOVE
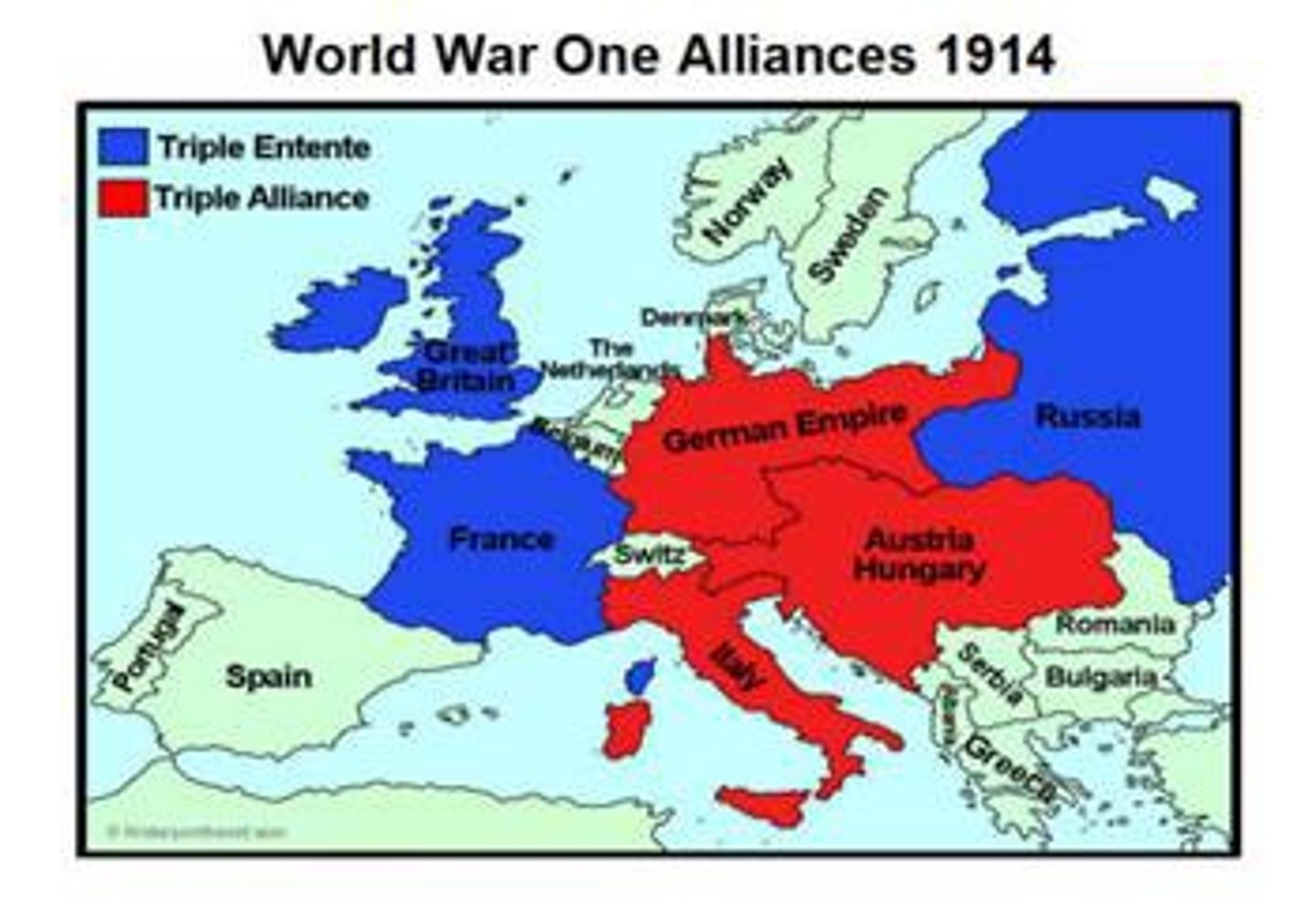
Triple Entente
This alliance between Great Britain, France and Russia in the years before WWI. IN BLUE ABOVE
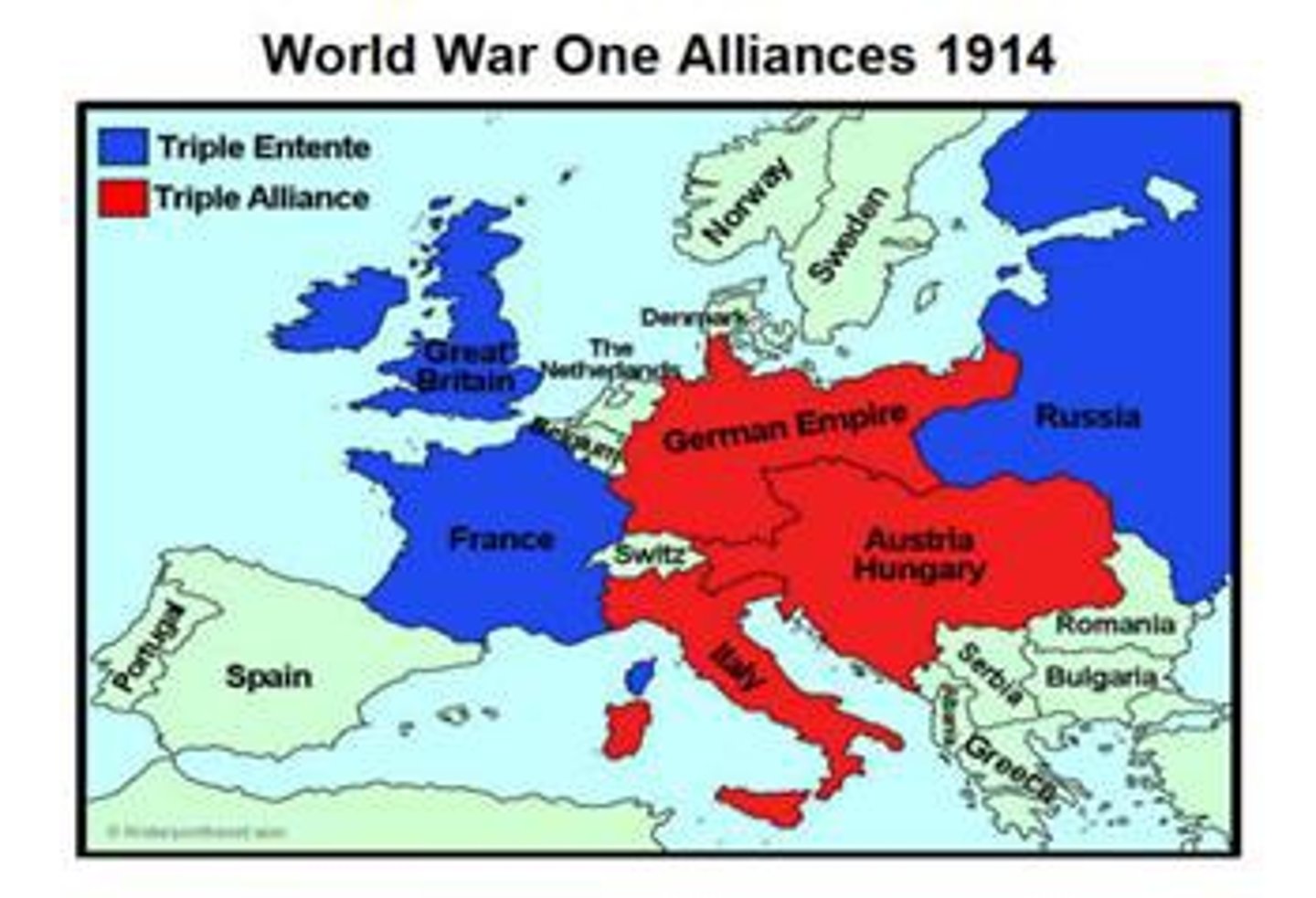
Central Powers
This was a major alliance at the 'center' of Europe during World War I, made up of Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and Ottoman Empire. It was formerly known as the Triple Alliance before the war. SHOWN ABOVE IN RED.
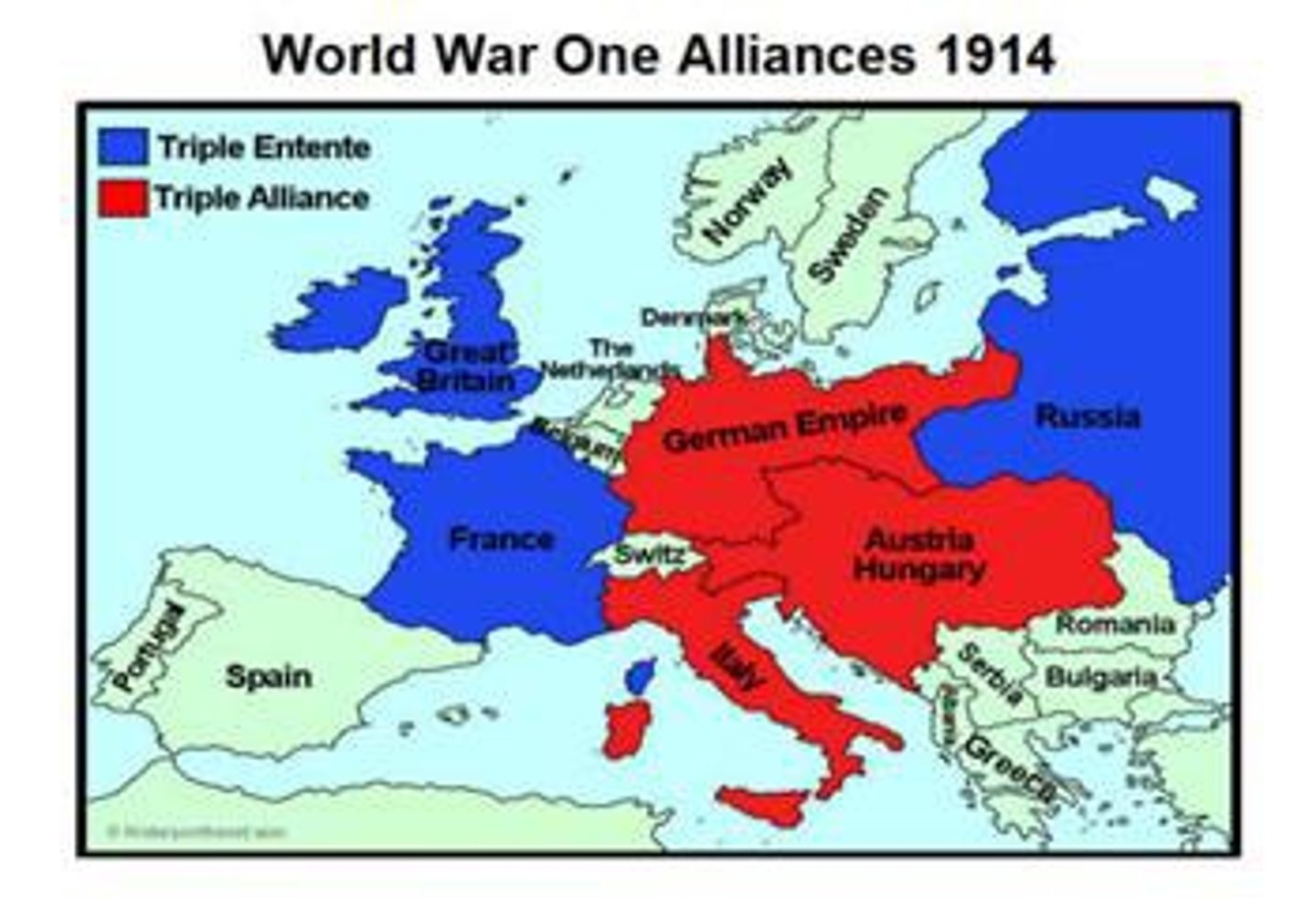
Allied Powers
This was a major alliance during World War I made up of Britain, France, Russia, and the United States. It was know n as the Triple Entente(a French word) before the war.
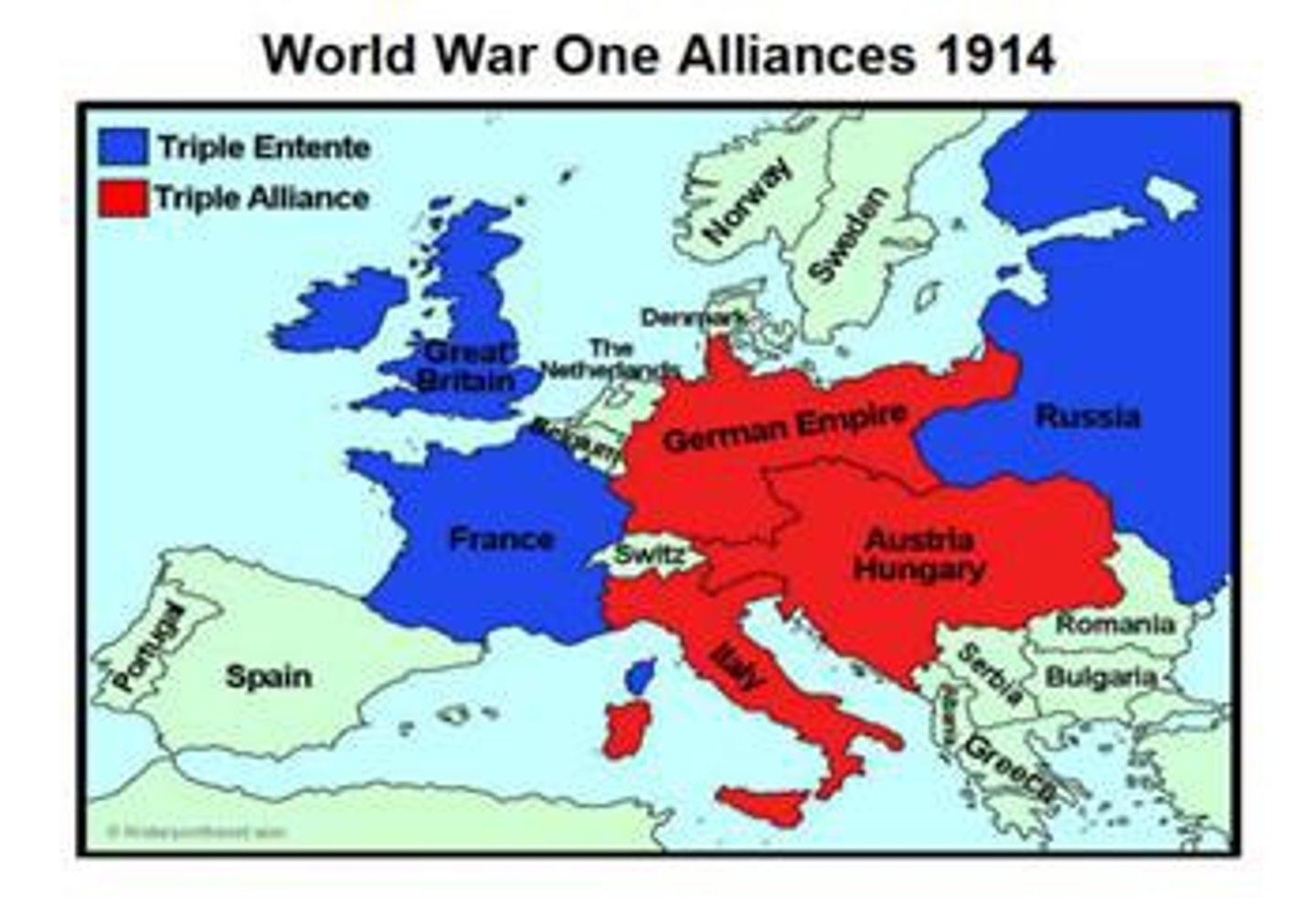
Unrestricted Submarine Warfare
A policy that the Germans announced on January 1917 which stated that their submarines would sink any ship in the British waters. Resulted in entry of the US into World War I.
Militarism
This cause of World War I was a policy of building up strong armed forces to prepare for war.
Treaty of Versailles
Treaty which ended World War I that included large reparations from Germany, the formation of the League of Nations, and the mandate system.

Adolph Hitler
german leader of Nazi Party. 1933-1945. rose to power by promoting racist and national views
Benito Mussolini
Fascist Dictator of Italy that at first used bullying to gain power, then never had full power.
fascism
an authoritarian and nationalistic right-wing system of government and social organization.
totalitarian
referring to a form of government in which one person or party holds absolute control
propaganda
Ideas spread to influence public opinion for or against a cause.
Joseph Stallin
Agreed to let Hitler take western Poland and was the Soviet Union's dictator
Aggression
the practice of making unproviked attacks or other military encroachments on the territory of another country
militarism
A policy of glorifying military power and keeping a standing army always prepared for war
Sanction
a threatened penalty for disobeying a law or rule.
Axis Powers
Alliance of Germany, Italy, and Japan during World War II.
Appeasement
Accepting demands in order to avoid conflict
Munich Pact
A 1938 agreement between Great Britain and Germany to appease Hitler
Embargo
an official ban on trade or other commercial activity with a particular country.
Isolationism
A policy of nonparticipation in international economic and political relations
Blitzkrieg
"Lighting war", typed of fast-moving warfare used by German forces against Poland in 1939
Atlantic Charter
a 1941 program developed by the United States and Britain that set goals for the postwar world - became the foundation for the United Nations
Ghetto
a part of a city, especially a slum area, occupied by a minority group or groups.
D-Day
Allied invasion of France on June 6, 1944
Holocaust
Mass murder of Jews under the Nazi Regime
A-Bomb
fission, splitting atoms, colliding them, used on hiroshima and nagasaki
War crime
a violation of internationally accepted practices related to waging war
Nuremberg Trials
Trials of the Nazi leaders, showed that people are responsible for their actions, even in wartime
Sovereignty
Ability of a state to govern its territory free from control of its internal affairs by other states
Winston Churchill
Prime Minister of Great Britain during WWII
Harry S Truman
Became president when FDR died; gave the order to drop the atomic bomb
The Big Lie
telling a complete falsehood with such confidence that people believe it. Examples - Jewish World Conspiracy, Rigged US Election claims of 2020
Franklin D. Roosevelt
President of the United States during most of the Depression and most of World War II.
Manhattan Project
A secret U.S. project for the construction of the atomic bomb.
Battle of Stalingrad
(1942) World War II battle between invading German forces and Soviet defenders for control of Stalingrad; each side sustained hundreds of thousands of casualties; Germany's defeat marked turning point in the war
Midway Battle
Battle between US and Japan at Midway Island. US victory here gave Allies control of the "central" Pacific; proved to be the turning point in the war in the Pacific with Japanese fleet destroyed.
Battle of the Bulge
A 1944-1945 battle in which Allied forces turned back the last major German offensive of World War II.
Milgram Experiment
an experiment devised in 1961 by Stanley Milgram, a psychologist at Yale University, to see how far ordinary people would go to obey a scientific authority figure
Stanford Prison Experiment
Philip Zimbardo's study of the effect of roles on behavior. Participants were randomly assigned to play either prisoners or guards in a mock prison. The study was ended early because of the "guards'" role-induced cruelty.
Geneva Convention
international agreement governing the humane treatment of wounded soldiers and prisoners of war
United Nations
An international organization formed after WWII to promote international peace, security, and cooperation.
Declaration of Human Rights 1948
Policy adopted by the United Nations following the violations of human rights during the second World War.