NHA Practice Test (copy)
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
A phlebotomy technician is planning to collect a sputum specimen from a patient. Which of the following instructions should the technician give the patient?
A. Rinse your mouth with mouthwash before we collect the specimen
B. Gargle some water before we collect the specimen
C. Leave your dentures in during specimen collection
D. Breathe deeply and then cough up a specimen into the container
D. Breathe deeply and then cough up a specimen into the container
This increases the chances for obtaining a quality sputum specimen rather than saliva.
A phlebotomy technician is washing her hands at the beginning of her shift. Which of the following action should the technician take?
A. Turn the faucet off with her wet hand.
B. Use enough soap to form a lather.
C. Rub hands together for at least 5 seconds.
D. Hold hands with palms facing upward while rinsing.
B. Use enough soap to form a lather.
A phlebotomy technician is obtaining a blood specimen from a patient. The technician notices swelling and a large hematoma forming at the puncture site. Which of the following actions should the technician take?
Remove the tourniquet and needle.
Ask the patient to bend his arm at the elbow.
Apply a warm compress to the site.
Apply pressure to the site for no longer than 1 min.
Remove the tourniquet and needle.
A phlebotomy technician is collecting blood specimens from a patient for multiple blood assays. The technician should fill the tube that has which of the following additives first?
EDTA
Potassium oxalate
Heparin
Sodium citrate
Sodium citrate
A phlebotomy technician should identify that which of the following tube selections indicates the correct venipuncture?
Lavender, green, gray
Gray, green, lavender
Green, gray, lavender
Green, lavender, gray
Green, lavender, gray
During a routine venipuncture, a phlebotomy technician notices that a patient is becoming pale and diaphoretic. The technician should identify that the patient is at risk for which of the following conditions?
Syncope
Seizure
Nausea
Petechiae
Syncope
A phlebotomy technician is working with a patient who has a Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Which of the following transmission precautions should the technician use for this patient?
Droplet precautions
Airborne precautions
Radiation precautions
Contact precautions
Airborne precautions
A phlebotomy technician is processing a semen specimen. Which of the following actions should technician take?
Refrigerate the specimen.
Transport the specimen at room temperature.
Pour the specimen into a clean condom for transport.
Deliver the specimen to the laboratory within 2 hr.
Deliver the specimen to the laboratory within 2 hr.
A phlebotomy technician in an outpatient facility finds a patient who is in shock and bleeding profusely from his leg. Which of the following actions should the technician take first?
Keep the patient warm.
Seek support from other staff.
Raise the patient’s legs.
Apply direct pressure to the wound.
Apply direct pressure to the wound.
A phlebotomy technician is selecting a site for a blood draw from a patient. From which of the following veins should the technician attempt to draw first?
Median cubital
Basilic
Dorsal metacarpal
Cephalic
Median cubital
A phlebotomy technician obtains two readings of 17 mg/dL when performing a glucometer test for a patient. Which of the following action should the technician take?
Repeat the glucose test again until readings appear in range.
Perform a venipuncture draw to verify test results.
Repeat the test with the patient’s glucometer.
Perform a set of liquid controls
Perform a set of liquid controls
A phlebotomy technician is preparing to perform a blood draw on a patient who had a left-sided mastectomy and has an IV on her right side. In which of the following locations should the technician perform the draw?
Left median cubital vein
Above the IV
Left dorsal vein
Below the IV
Below the IV
A phlebotomy technician is preparing to obtain a blood specimen from a patient for an erythrocyte sedimentation rate test. The technician should select a collection tube that has a top with which of the following colors?
(A) Tiger tubes
(B) Gray tubes
(C) Yellow tubes
(D) Lavender tubes
(D) Lavender tubes
Which of the following is the proper cleansing technique when a phlebotomy technician is performing a routine venipuncture?
(A) Cleanse the site using back and forth friction.
(B) Cleanse the site by applying pressure for 5 seconds with an alcohol pad.
(C) Cleanse the site using a dry gauze pad.
(D) Cleanse the site with one downward wipe.
(A) Cleanse the site using back and forth friction.
Updated CLSI standards recommend cleaning the site using a back and forth friction motion
Coagulation studies are ordered for a patient whose veins require use of a butterfly assembly. Which of the following is true?
(A) A discard tube should be started first, then a light blue tube filled completely
(B) A discard tube should be started first, then a light green tube filled completely
(C) A light blue tube should be filled at least halfway
(D) A lavender tube should be filled completely
(A) A discard tube should be started first, then a light blue tube filled completely
If a tourniquet has been left on the arm for more than one minute, how long should it remain off the arm before it is reapplied?
(A) One minute
(B) Two minutes
(C) Three minutes
(D) Five minutes
(B) Two minutes
Which fingers are best suited for capillary blood collection? (Choose two.)
(A) The pinky
(B) The ring finger
(C) The middle finger
(D) The index finger
(E) The thumb
(B) The ring finger
(C) The middle finger
The anticoagulant action of this tube additive can be reversed with the addition of calcium:
(A) Sodium citrate
(B) Sodium fluoride
(C) EDTA
(D) Sodium heparin
(A) Sodium citrate
Which set of regulations deals with how laboratories are staffed and what tests they can perform?
(A) HITECH
(B) HIPAA
(C) CLSI
(D) CLIA
(D) CLIA
When a patient’s veins are difficult to access, how many attempts at venipuncture should a phlebotomy technician make before seeking help from other qualified personnel?
(A) Four
(B) Three
(C) Two
(D) One
(C) Two
Which of the following is a significant difference between midstream and routine urine specimens?
(A) The area around the urethra is cleaned before collecting a midstream specimen
(B) A routine urine specimen is collected first thing in the morning
(C) A midstream urine specimen is collected at a patient’s home
(D) A routine urine specimen is collected in a sterile container
(A) The area around the urethra is cleaned before collecting a midstream specimen
Hemoconcentration may be caused by
(A) Leaving a tourniquet in place for too long
(B) A patient eating a breakfast rich in fatty foods
(C) Using too narrow a needle
(D) Probing with the venipuncture needle
(A) Leaving a tourniquet in place for too long
Which of the following statements about patient identification is correct?
A. It's okay to draw blood if the patient's ID band is missing as long as they verbally confirm their identity.
B. The phlebotomist should compare the information on the requisition form to the patient's ID band.
C. The patient's bed number is sufficient for identification purposes.
D. The phlebotomist should identify the patient by their full name and date of birth.
D. The phlebotomist should identify the patient by their full name and date of birth.
Which of the following might indicate the need for a sputum (a type of non-blood specimen) culture?
A. Symptoms of a urinary tract infection
B. Symptoms of a throat infection
C. Symptoms of a lower respiratory infection
D. Symptoms of a gastrointestinal infection
C. Symptoms of a lower respiratory infection
Which of the following is an example of breaking the mode of transmission link in the chain of infection?
(A) Receiving a vaccination
(B) Taking an antiviral medication after being exposed to a confirmed case of influenza
(C) Washing hands
(D) An uninfected person wearing an N95 mask to avoid inhaling infectious microorganisms
(C) Washing hands
A very thin tube inserted into the bladder through the urethra is called a(n)
(A) Catheter
(B) Aspirant
(C) Irrigator
(D) Collection tube
(A) Catheter
Specific gravity measures the
_____________________ of urine.
(A) Temperature
(B) Concentration
(C) Acidity
(D) Bacterial content
(B) Concentration
When should a PBT conducting point-of-
care PT/INR testing make recommendations
regarding a patient’s warfarin dose?
(A) After checking the information on a repu-
table website
(B) After confirming it with a PBT colleague
(C) Only if the PBT has personal experience
taking warfarin and monitoring PT/INR
(D) This is beyond the PBT’s scope of practice
(D) This is beyond the PBT’s scope of practice
Why is newborn metabolic screening performed?
(A) Because it is harder to collect blood from older children
(B) Because these illnesses can be treated successfully in infancy
(C) Because parents are unlikely to bring children back for the tests when they are older
(D) Because these illnesses do not occur later in life
(B) Because these illnesses can be treated successfully in infancy
What is the name of the infection that may be
caused if a lancet strikes bone?
(A) Osteomyelitis
(B) Osteopathy
(C) Osteoporosis
(D) Osteonia
(A) Osteomyelitis
What must happen before a serum specimen is centrifuged?
(A) The patient’s doctor must call to authorize
it
(B) The PBT’s supervisor must approve it
(C) The specimen must be frozen
(D) The specimen must be allowed to clot
(D) The specimen must be allowed to clot
QNS stands for
(A) Quick nonsterile syringe
(B) Quantity not sufficient
(C) Quality not satisfactory
(D) Quantum non sequitur
(B) Quantity not sufficient
The most reliable way to locate a good site for
venipuncture is to
(A) Palpate the site
(B) Look at the site
(C) Ask the patient where other phlebotomists
have succeeded in drawing blood
(D) Choose a favorite site
(A) Palpate the site
What equipment would be best to use when
performing venipuncture on an elderly patient
currently undergoing chemotherapy?
(A) A winged collection set and syringe with a
23-gauge needle
(B) A winged collection set and evacuated
tubes with a 21-gauge needle
(C) A straight, 23-gauge multisample needle
and evacuated tubes
(D) A straight, 21-gauge multisample needle
and evacuated tubes
A) A winged collection set and syringe with a
23-gauge needle
A patient has orders for a blood culture and
coagulation studies. Which of these indicates
the proper order for drawing these specimens?
(A) Yellow-topped SPS tube/blood culture bottles, light blue-topped tube
(B) Light blue-topped tube, yellow-topped SPS
tube/blood culture bottles
(C) Yellow-topped ACD tube/blood culture
bottles, light green-topped tube
(D) Yellow-topped SPS tube/blood culture bottles, lavender-topped tube
(A) Yellow-topped SPS tube/blood culture bottles, light blue-topped tube
The substances studied in blood tests are called
(A) Analytes
(B) Materials
(C) Factors
(D) Activators
(A) Analytes
Collection tubes for capillary puncture usually have a volume of
(A) 1.0–3.0 mL
(B) 0.125–0.6 mL
(C) 1.8–2.2 mL
(D) 0.25–1.0 mL
(B) 0.125–0.6 mL
An enzyme called ____________ controls
platelet response when a blood vessel is
damaged.
(A) Fibrin
(B) Fibrinogen
(C) Plasmin
(D) Thrombin
(D) Thrombin
18. If a whole blood specimen is required for a
diagnostic test it should be collected in a tube
that
(A) Contains an anticoagulant additive
(B) Contains a clot-activating additive
(C) Has been prewarmed
(D) Contains no additive
(D) Contains no additive
Who is considered to be a universal blood
donor?
(A) A person with type A, Rh positive blood
(B) A person with type AB, Rh negative blood
(C) A person with type AB, Rh positive blood
(D) A person with type O, Rh negative blood
(D) A person with type O, Rh negative blood
B cells and T cells are varieties of
(A) Thrombocytes
(B) Megakaryocytes
(C) Lymphocytes
(D) Monocytes
Lymphocytes
Tests ordered to confirm pregnancy measure
the level of a pregnancy-related hormone
called
(A) Oxytocin
(B) Estrogen
(C) hCG
(D) ADH
(C) hCG
If a phlebotomy technician is told to perform
venipuncture distal to a patient’s IV, the veni-
puncture must take place
(A) Closer to the torso than the IV
(B) Farther away from the torso than the IV
(C) On the opposite side of the body from
the IV
(D) Alongside the IV
(B) Farther away from the torso than the IV
What does a dosimeter measure?
(A) Exposure to infected body fluids
(B) Exposure to radiation
(C) Exposure to toxic chemicals
(D) Exposure to excessive noise
(B) Exposure to radiation
There is a fire in a facility. The door to the
room where a PBT is located feels hot. There is
no window or other way out of the room. What
should the PBT do?
(A) Open the door using a wet towel or cloth-
ing to protect her hands
(B) Attempt to kick the door open
(C) Block the space under the door with a wet
towel or clothing and wait for help
(D) Pound on the door and shout until help
arrives
C) Block the space under the door with a wet
towel or clothing and wait for help
CLIA waived tests can be performed by the fol-
lowing healthcare personnel:
(A) Any healthcare personnel who have been
trained to perform them
(B) Medical technicians only
(C) Nurses and medical technicians only
(D) Physicians, nurse practitioners, and physi-
cian assistants only
(A) Any healthcare personnel who have been
trained to perform them
Which of the following tubes should a phlebotomy technician collect first when obtaining dermal samples?
Lavender top
Green top
Red top
Light blue top
Lavender top
A phlebotomy technician is preparing to draw a peak level for medication that was administered orally to a patient. After verifying when the patient received the medication, how long should the technician wait prior to attempting the draw?
30 min after administration
2 hr after administration
15 min after administration
4 hr after administration
2 hr after administration
How frequently should a phlebotomy technician perform a quality control test on a glucometer in the laboratory?
Every month the meter is used
Every week the meter is used
Every day the meter is used
Every 6 months the meter is used
Every day the meter is used
A phlebotomy technician is preparing a patient for a routine venipuncture. Which of the following antiseptic solutions should the technician use?
Providone-iodine
Hypochlorite solution
Chloramine
Isopropyl alcohol
Isopropyl alcohol
A phlebotomy technician is selecting a site to collect a blood specimen from a patient. After applying a tourniquet, the technician sees no apparent vein to use for venipuncture. Which of the following actions should the technician take?
Apply and inflate a blood pressure cuff to 60mm Hg
Puncture the area where the patient’s vein should be located
Tap the area repeatedly until a vein appears
Have the patient dangle her arm for 1 to 2 min.
Have the patient dangle her arm for 1 to 2 min.
Which of the following actions should a phlebotomy technician take when performing a venipuncture using an evacuated tube system?
A. Position the needle at a 30° angle in the same direction as the vein and with the bevel up.
B. Position the needle at a 15° angle near the vein and with the bevel up.
C. Position the needle at a 30° angle in the same direction as the vein and with the bevel down.
D. Position the needle at a 15° angle near the vein and with the bevel down.
A. Position the needle at a 30° angle in the same direction as the vein and with the bevel up.
A phlebotomy technician should identify that which of the following series of venipuncture steps is in the appropriate order?
A. Insert the needle, place the tourniquet, and label the tube.
B. Assess the site, cleanse the site, and insert the needle.
C. Identify the patient, cleanse the site, and assess the site.
D. Draw the specimen, remove the needle, and remove the tourniquet.
B. Assess the site, cleanse the site, and insert the needle.
A phlebotomy technician is collecting a patient's blood specimen in a lavender-topped tube. How many times should the technician gently invert the tube before setting it in the specimen collection tray?
A. Two to three times
B. Four to six times
C. Eight to ten times
D. Eleven to twelve times
Eight to ten times
The technician should invert the lavender-topped tube eight to ten times to ensure adequate mixing of the additive and the blood.
A phlebotomy technician is preparing to collect a blood specimen from a patient for a coagulation study. The patient states, "I faint every time I get my blood drawn." Which of the following statements should the technician make?
A. "Don't worry. I am well trained and you won't faint with me."
B. "Tell me if you feel like you're going to faint, and I will give you smelling salts."
C. "I will perform the draw while you are lying down."
D. "This procedure will be over before you know it."
C. "I will perform the draw while you are lying down."
Because the patient is prone to fainting, the technician should place him in a supine position to prevent injury from a potential fall.
A phlebotomy technician is performing a total cholesterol point-of-care test for a patient. Which of the following findings should the technician immediately report to the provider?
A. 300 mg/dL
B. 200 mg/dL
C. 180 mg/dL
D. 140 mg/dL
A. 300 mg/dL
The technician should identify that a finding of 300 mg/dL is above the reference range of 140 to 200 mg/dL for total cholesterol. The technician should immediately report this finding to the provider.
Prior to transport, which of the following specimens should a phlebotomy technician place in an ice bath within 30 min after collection?
A. Arterial blood gas
B. Cold agglutinin
C. Cryoglobulin
D. Blood culture
A. Arterial blood gas
The technician should immediately place an ABG specimen in an ice bath to stop the metabolic activity of the red blood cells for delivery to the laboratory.
A phlebotomy technician is collecting a blood specimen from a patient who has pneumonia. Besides gloves, which of the following pieces of personal protective equipment should the technician wear?
A. Goggles
B. Gown
C. Mask
D. N95 Respirator
C. Mask
The technician should wear a mask when collecting a blood specimen from a patient who has pneumonia, which requires droplet precautions. The technician should wear the mask when working within 3 feet of the patient.
A phlebotomy technician is collecting a blood specimen from a patient who has COVID-19. Besides gloves, which of the following pieces of personal protective equipment should the technician wear?
A. Goggles
B. Gown
C. Mask
D. N95 Respirator
D. N95 Respirator
A phlebotomy technician should identify that which of the following additives is used to prevent the breakdown of glucose?
A. Sodium citrate
B. Sodium floride
C. EDTA
D. Heparin
B. Sodium floride
The technician should identify that sodium fluoride is an additive used to prevent the breakdown of glucose.
Which of the following actions by a phlebotomy technician can result in a grossly hemolyzed specimen?
A. Following an incorrect order of draw
B. Using an incorrect needle gauge
C. Applying the tourniquet too close to the draw site
D. Failing to invert the tube
B. Using an incorrect needle gauge
If the technician uses a large-gauge needle to draw from a vein with a small lumen, it can cause a grossly hemolyzed specimen.
An unconscious patient is brought to the emergency department, and several blood tests are ordered. A phlebotomy technician should collect the patient's blood because he has received which of the following types of consent?
A. Implied consent.
B. Informed consent
C. Expressed consent
D. Explicit consent
A. Implied consent.
The technician should identify that implied consent can be obtained when a patient is unconscious and in an emergency situation.
A phlebotomy technician is preparing to collect a blood specimen from the antecubital site of a patient. Which of the following devices can be used to help stabilize the arm for the collection?
A. Supply clamp
B. Hand immobilizer
C. Phlebotomy wedge
D. Hand brace
C. Phlebotomy wedge
A phlebotomy wedge is a vinyl-covered device that stabilizes the patient's arm.
A phlebotomy technician is collecting blood from a patient for donation. The collection bag only fills halfway, and the vein collapses. Which of the following actions should the technician take?
A. Mark the collection bag as half full.
B. Use a new collection bag to draw a new unit of blood.
C. Continue filling the collection bag from an alternate site.
D. Combine two separate collection bags to make a whole.
B. Use a new collection bag to draw a new unit of blood.
The technician should use a new collection bag to draw a new unit of blood. The technician should take this action because collection bags have a specific amount of the additive citrate phosphate dextrose to prevent coagulation.
A phlebotomy technician is performing a venipuncture for a patient. The patient suddenly reports "feeling faint." After removing the tourniquet and the needle, which of the following actions should the technician take next?
A. Have the patient put her head between her legs.
B. Place a wet towel on the patient's forehead.
C. Offer the patient a cup of water or juice.
D. Monitor the patient for at least 15 min.
A. Have the patient put her head between her legs.
After removing the tourniquet and the needle, the technician should next have the patient put her head between her legs. This position helps prevent syncope.
A phlebotomy technician should identify that which of the following is an identifier for a specimen as long as it remains in the laboratory?
A. ICD-10 codes
B. Accession number
C. CPT code
D. Medical record number
B. Accession number
The accession number identifies a specimen as long as it remains in the laboratory.
A phlebotomy technician should identify that which of the following is an identifier for a service provided to the patient?
A. ICD-10 codes
B. Accession number
C. CPT code
D. Medical record number
C. CPT code
The Current Procedural Terminology code identifies a service provided to the patient.
A phlebotomy technician is collecting a blood specimen from a patient who has cutaneous diphtheria. Besides gloves, which of the following pieces of personal protective equipment should the technician wear?
A. Mask
B. Gown
C. Goggles
D. N95 respirator
B. Gown
The technician should wear a gown to protect the skin from infections that can be transmitted by contact. Because cutaneous diphtheria is spread through contact, the technician should wear a gown.
What is the maximum Total Blood Volume (TBV) for infants?
A. 60 mL per kilogram
B. 100 mL per kilogram
C. 40 mL per kilogram
D. 80 mL per kilogram
80mL per kilogram
A phlebotomy technician should identify that which of the following is the total blood volume of an infant who weighs 3.3 kg (7.3 lb)?
A. 350 to 390 mL
B. 125 to 230 mL
C. 240 to 330 mL
D. 405 to 450 mL
C. 240 to 330 mL
The technician should identify that an infant who weighs 3.3 kg (7.3 lb) has a total blood volume of approximately 240 to 330 mL.
3.3kg × 80 (maximum blood volume for infants per kilogram) = 264mL which is in between the range of 240 to 330 mL
Baby Lucas is an infant weighing 7 pounds. Several different specialists have been involved in his care, all of whom have ordered blood tests. Over the course of a week, accumulated orders have required draws of 0.5 mL, 1 mL, 0.25 mL, 0.5 mL, and 2 mL. Is Lucas likely to be in danger of iatrogenic anemia?
Remember that 80mL per kilogram is the maximum blood volume in infants.
No, Baby Lucas is not in danger of iatrogenic anemia.
According to the question, 0.5 mL + 1 mL + 0.25 mL + 0.5 mL, + 2 mL = 4.25 mL
The guideline of preventing iatrogenic anemia is to draw no more than 2.5% of a patient’s blood volume in 24 hours and 5% in 30 days. 1 kilogram (kg) = 2.2lbs
Baby Lucas weighs 3.1kg (7lbs); 7lbs/2.2lbs = ~ 3.1kg
Multiply the blood volume of infants (80) by the weight in kilograms.
3kg * 80mL = 248mL
Find 2.5% of 248mL; 248×2.5/100 = 6.2. The daily amount of draw for Baby Lucas is 6.2mL
How to find the percentage of a number?
Number * Percentage / 100
For example, find the 35% of 80?
80 × 35% / 100
80 × 35 = 2800
2800 / 100 = 28
What are the maximum percentages of a patient's blood volume that should be drawn within 24 hours and within 30 days to prevent iatrogenic anemia?
A. 1.5% in 24 hours and 2.5% in 30 days
B. 2.5% in 24 hours and 5% in 30 days
C. 3% in 24 hours and 5% in 30 days
D. 4% in 24 hours and 6% in 30 days
B. 2.5% in 24 hours and 5% in 30 days
The guideline of preventing iatrogenic anemia is to draw no more than 2.5% of a patient’s blood volume in 24 hours and 5% in 30 days.
A phlebotomy technician is interviewing a patient before performing a venipuncture. During the interview, the patient states that he lives nearby and ran to the facility to "get in some running time today." Which of the following precautionary actions should the technician take?
A. Offer the patient a high-carbohydrate snack before the venipuncture.
B. Place the patient in a reclining position for the venipuncture.
C. Have the patient rest comfortably for at least 15 min before the venipuncture.
D. Reschedule the venipuncture for another day.
C. Have the patient rest comfortably for at least 15 min before the venipuncture.
Because strenuous exercise affects coagulation, the technician should have the patient rest for 15 to 30 min before performing the venipuncture.
A phlebotomy technician is collecting a blood specimen from a patient. Which of the following techniques should the technician use to anchor the vein just before inserting the needle?
A. Use the thumb to anchor the vein 5 cm (2 in) below the puncture site.
B. Attach a 5 cm (2 in) piece of hypoallergenic tape 7.5 cm (3 in) below the puncture site to anchor the vein.
C. Anchor the vein 7.5 to 10 cm (3 to 4 in) above the puncture site.
D. Apply a flat tourniquet snugly 2.5 cm (1 in) below the puncture site to anchor the vein.
A. Use the thumb to anchor the vein 5 cm (2 in) below the puncture site.
Veins have a tendency to roll away from the needle, especially the basilic vein. The technician should hold the vein in place to help anchor it and prepare it for the puncture 2.5 to 5 cm (1 to 2 in) below the puncture site.
A technician should identify that which of the following is one of the Joint Commission's 2016 National Patient Safety Goals?
A. Identify the appropriate venipuncture site.
B. Identify patients correctly.
C. Identify the correct collection tubes for ordered assays.
D. Identify the appropriate needle gauges.
B. Identify patients correctly.
Technicians should use at least two forms of identification to identify patients correctly. The Joint Commission's National Patient Safety Goals help health care facilities address areas of concern regarding patient safety. The 2016 goals include identifying patients correctly, improving staff communication, using medicines safely, using alarms safely, preventing infections, identifying patient safety risks, and preventing mistakes in surgery.
Blood Types

What is the correct order to remove personal protective equipment (PPE) equipment?
A. Remove gown first, then gloves, goggles, and mask.
B. Remove gloves first, then goggles, gown, and mask.
C. Remove goggles first, then gown, gloves, and mask.
D. Remove mask first, then gown, gloves, and goggles.
B. Remove gloves first, then goggles, gown, and mask.
What is the correct order to put on personal protective equipment (PPE) equipment?
A. Put on gown first, then mask, goggles, and gloves.
B. Put on gloves first, then goggles, gown, and mask.
C. Put on goggles first, then gown, gloves, and mask.
D. Put on mask first, then gown, gloves, and goggles
A. Put on gown first, then mask, goggles, and gloves.
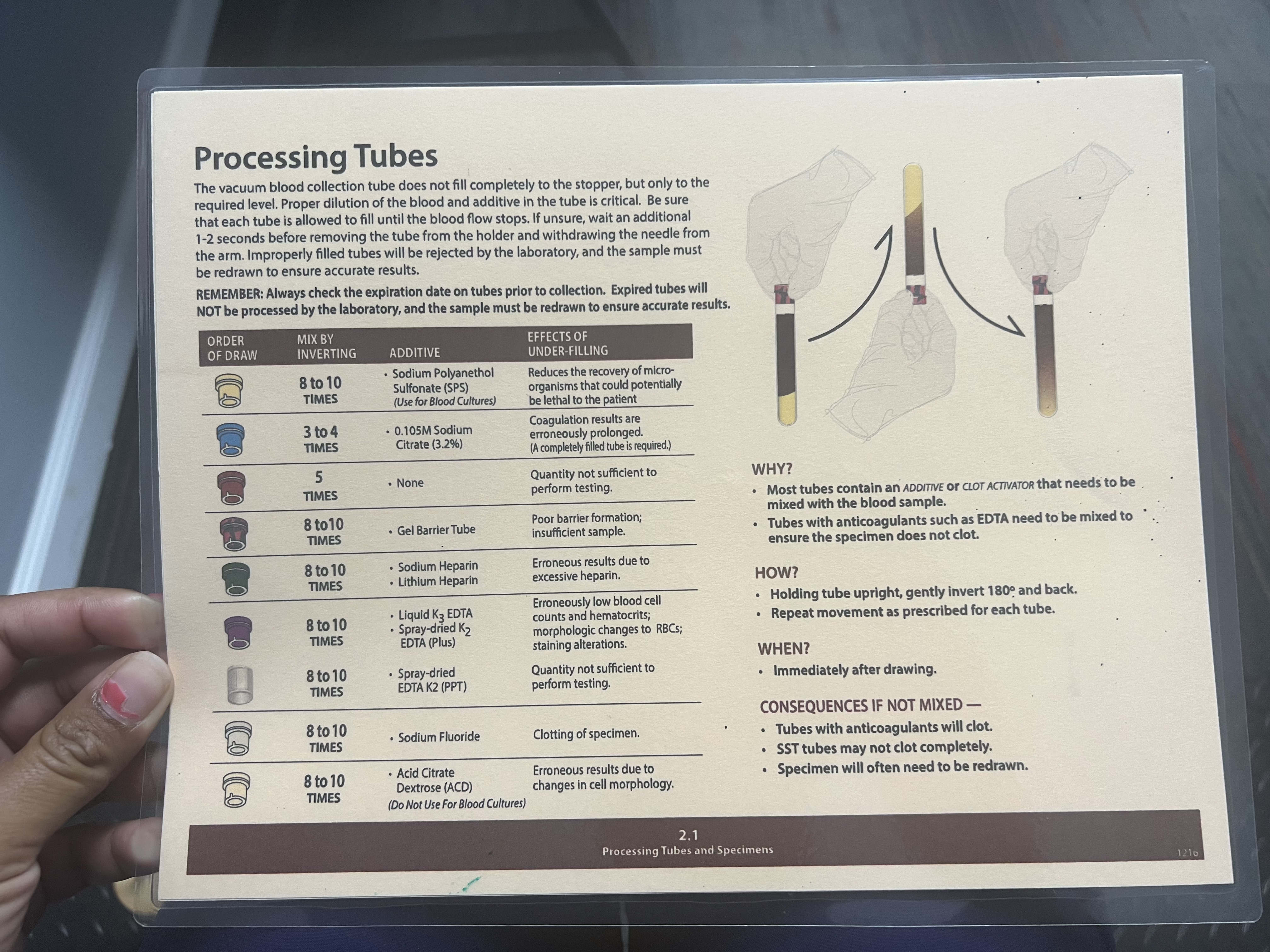
Order of Draw
Yellow
Light Blue
Red/Orange
Red & Gray (Tiger top)
Green
Lavender/Pink/White
Gray
Cream
Yellow Tubes
Mix by Inverting: 8-10 Times
Additive: Sodium Polyanethol Sulfonate (SPS) (Use for Blood Cultures)
Effects of Under-filling: Reduces the recovery of microorganisms that could potentially be lethal to the patient
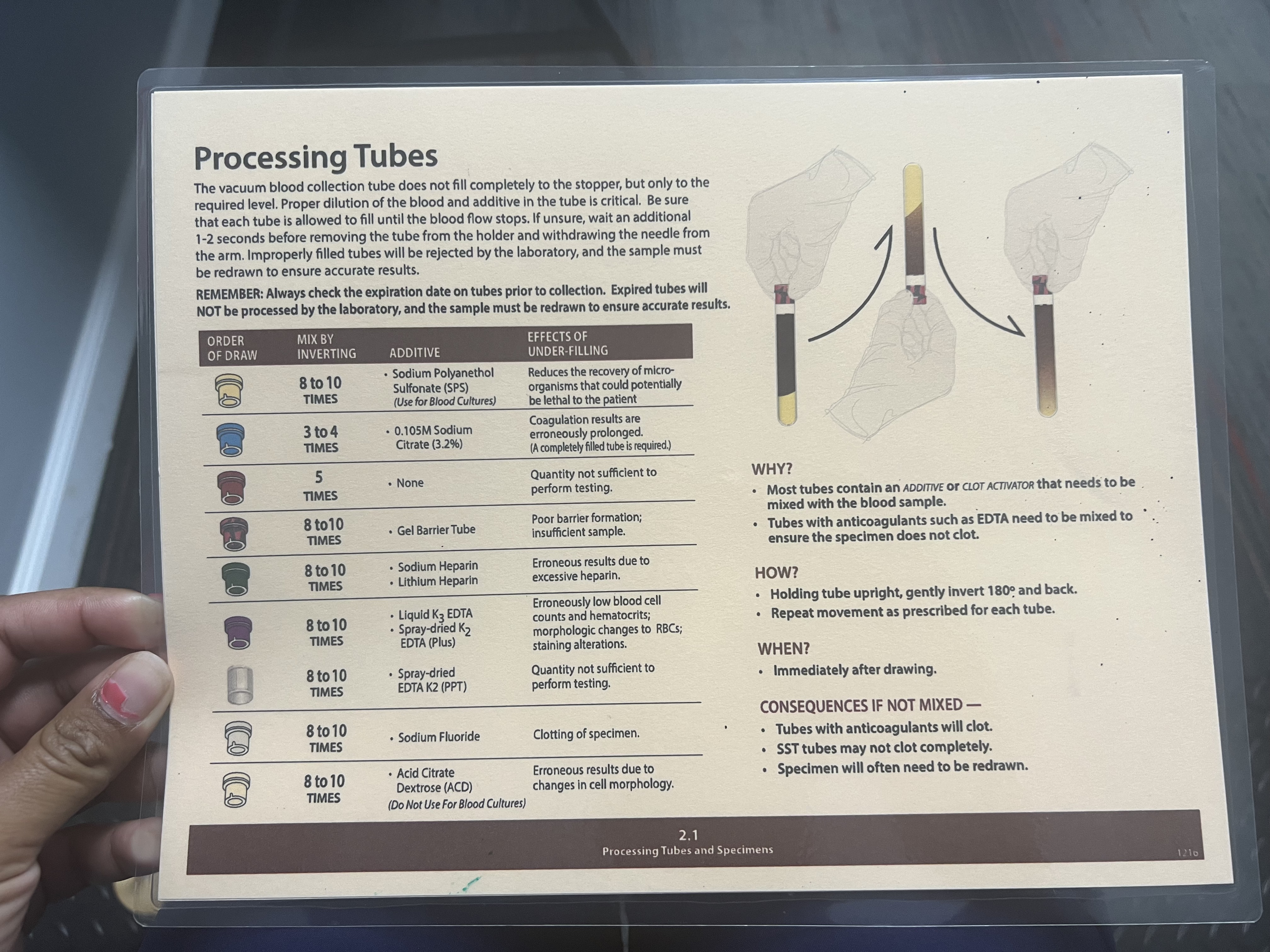
Light Blue Tubes
Mix by Inverting: 3-4 Times
Additive: 0.105M Sodium Citrate (3.2%)
Effects of Under-filling: Coagulation results are erroneously prolonged. (A completely filled tube is required.)
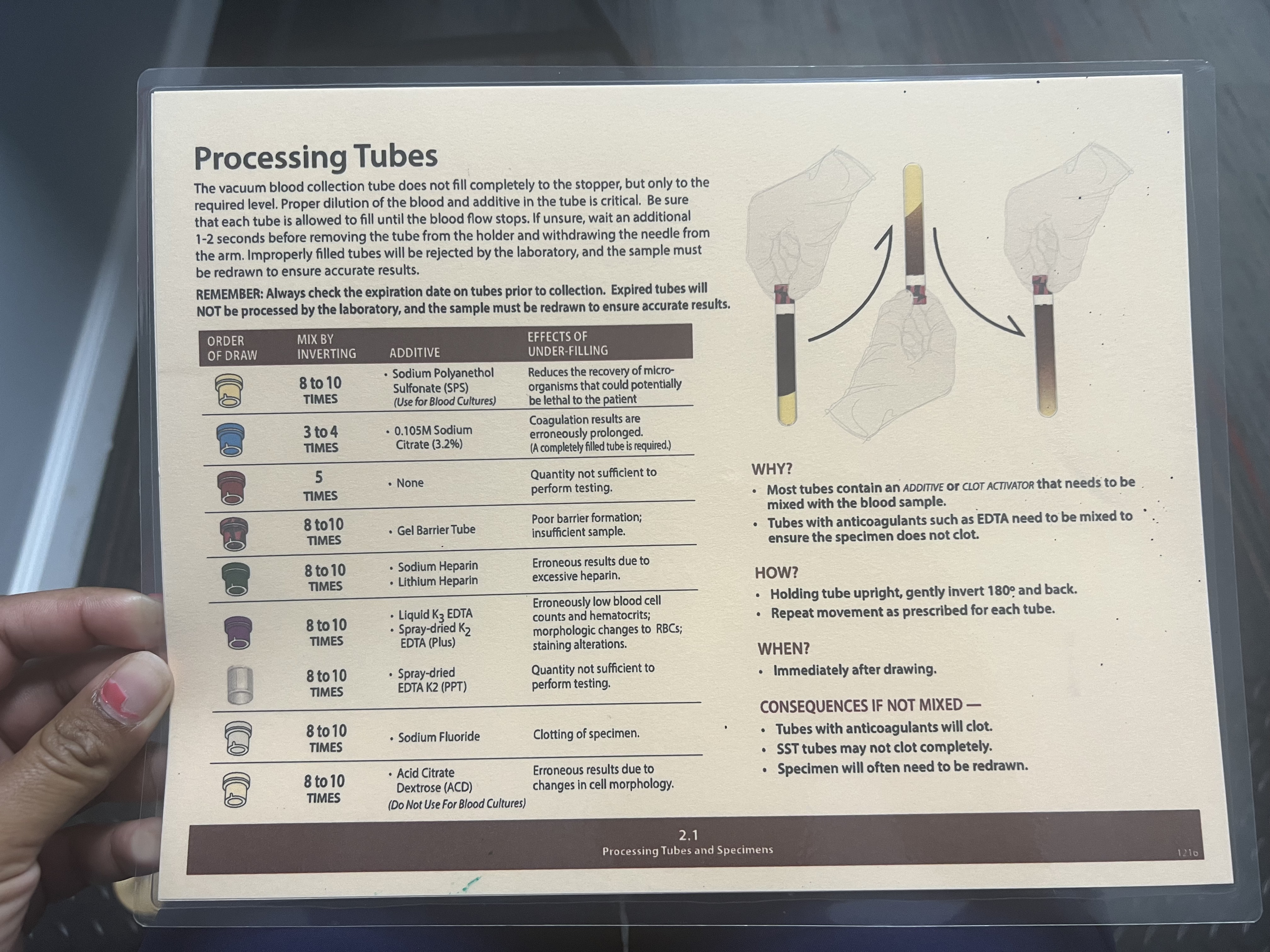
Red/Orange Tube
Mix by Inverting: 5 Times
Additive: None
Effects of Under-filling: Quantity not sufficient to perform testing.
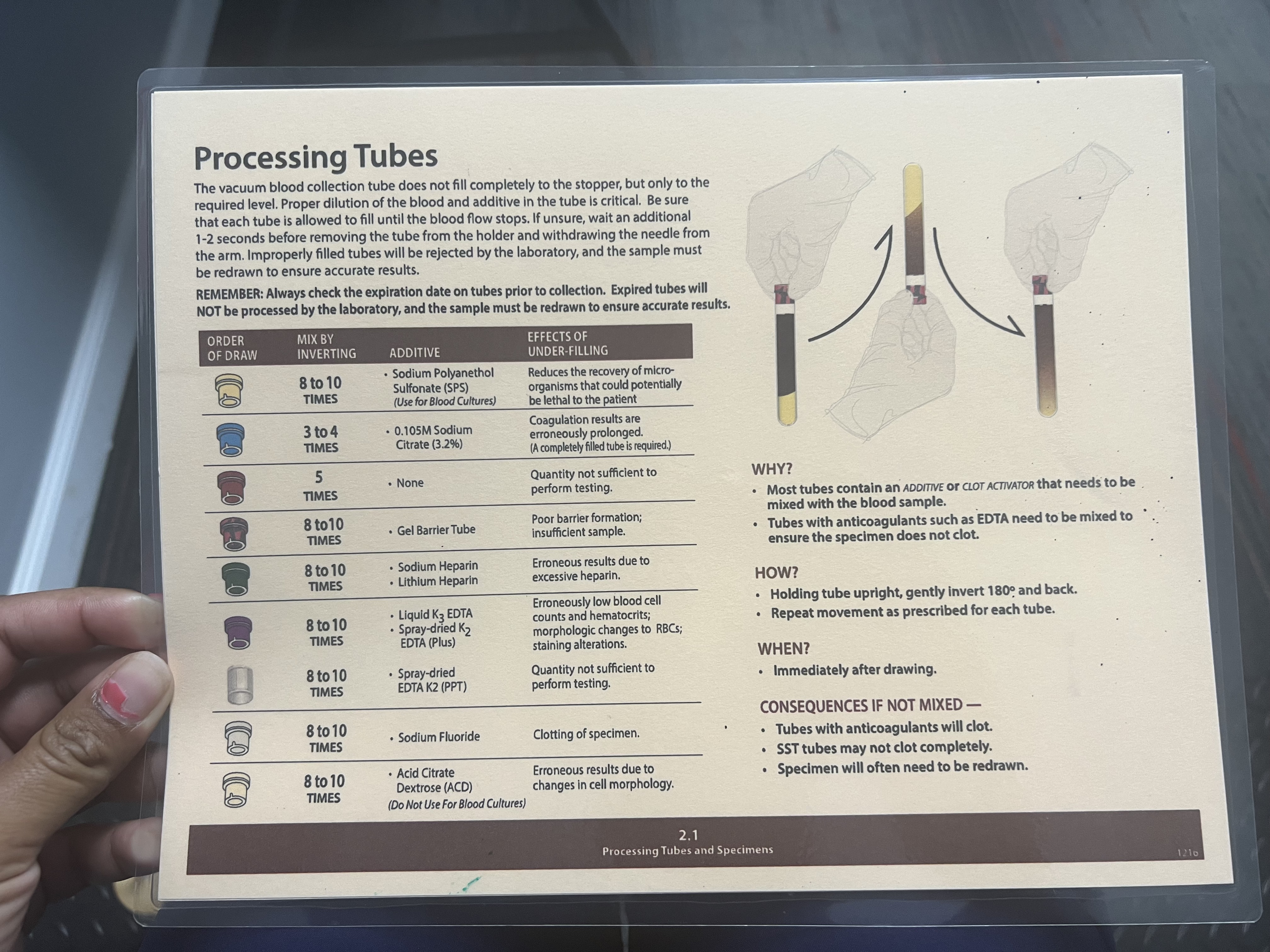
Red + Gray (Tiger tops) Tubes
Mix by Inverting: 8-10 Times
Additive: Gel barrier tube
Effects of Under-filling: Poor barrier formation; insufficient sample.
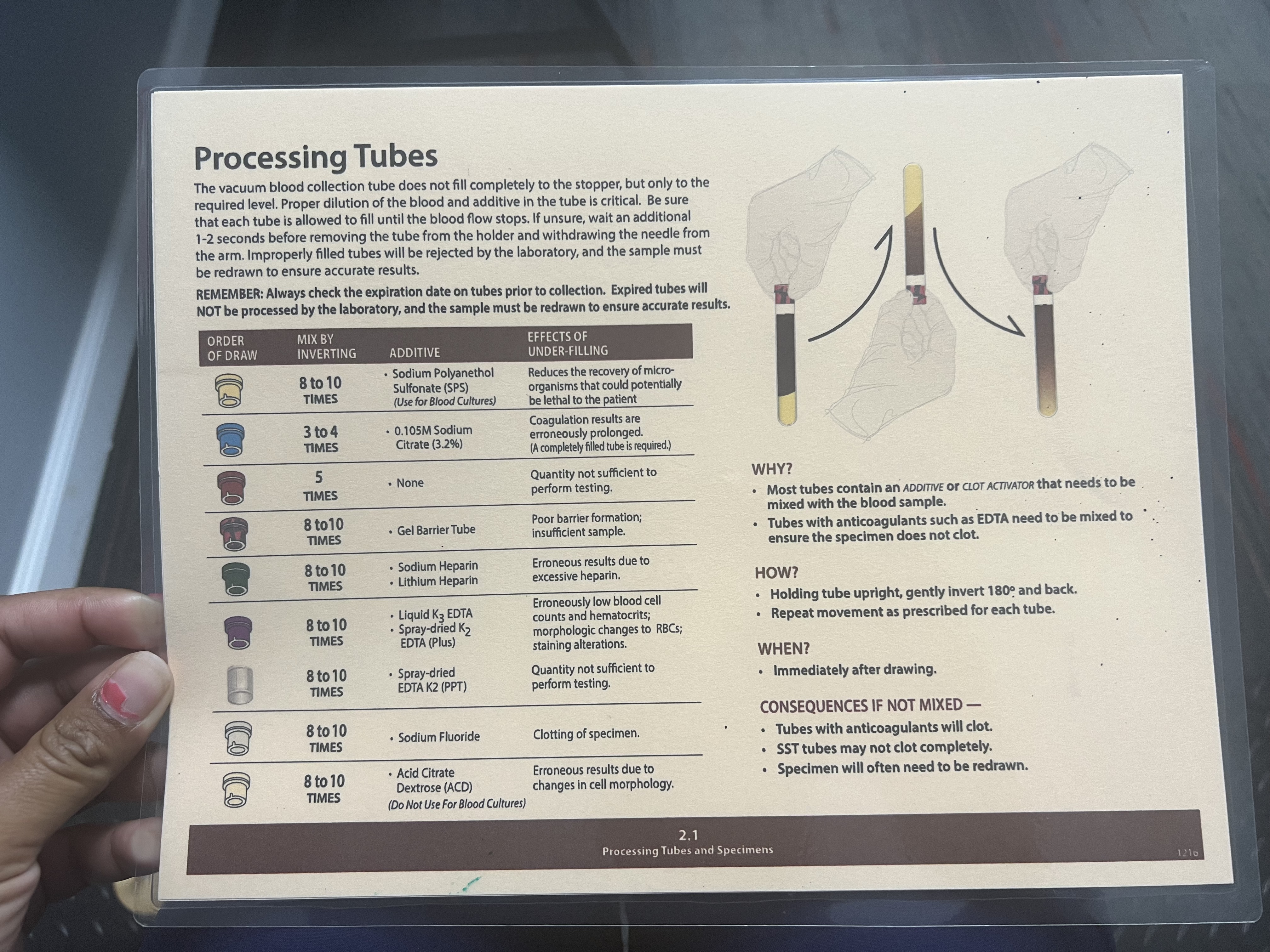
Green Tubes
Mix by Inverting: 8-10 Times
Additive: Sodium heparin or lithium heparin
Effects of Under-filling: Erroneous results due to excessive heparin.
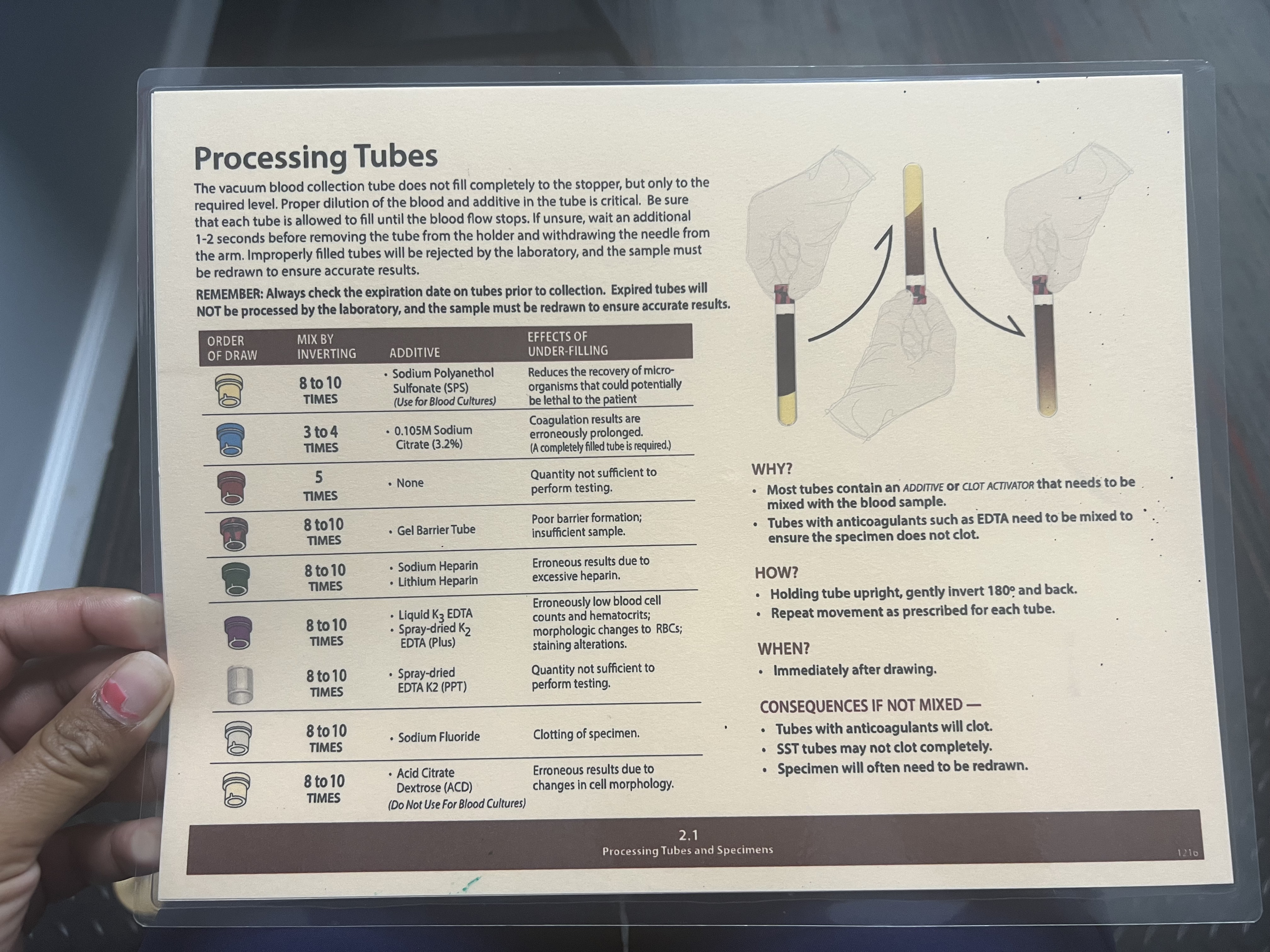
Lavender/Pink Tubes
Mix by Inverting: 8-10 Times
Additive: Liquid K3 EDTA; Spray-dried K2 EDTA (Plus)
Effects of Under-filling: Erroneously low blood cell counts and hematocrits; morphologic changes to RBCs; staining alterations.
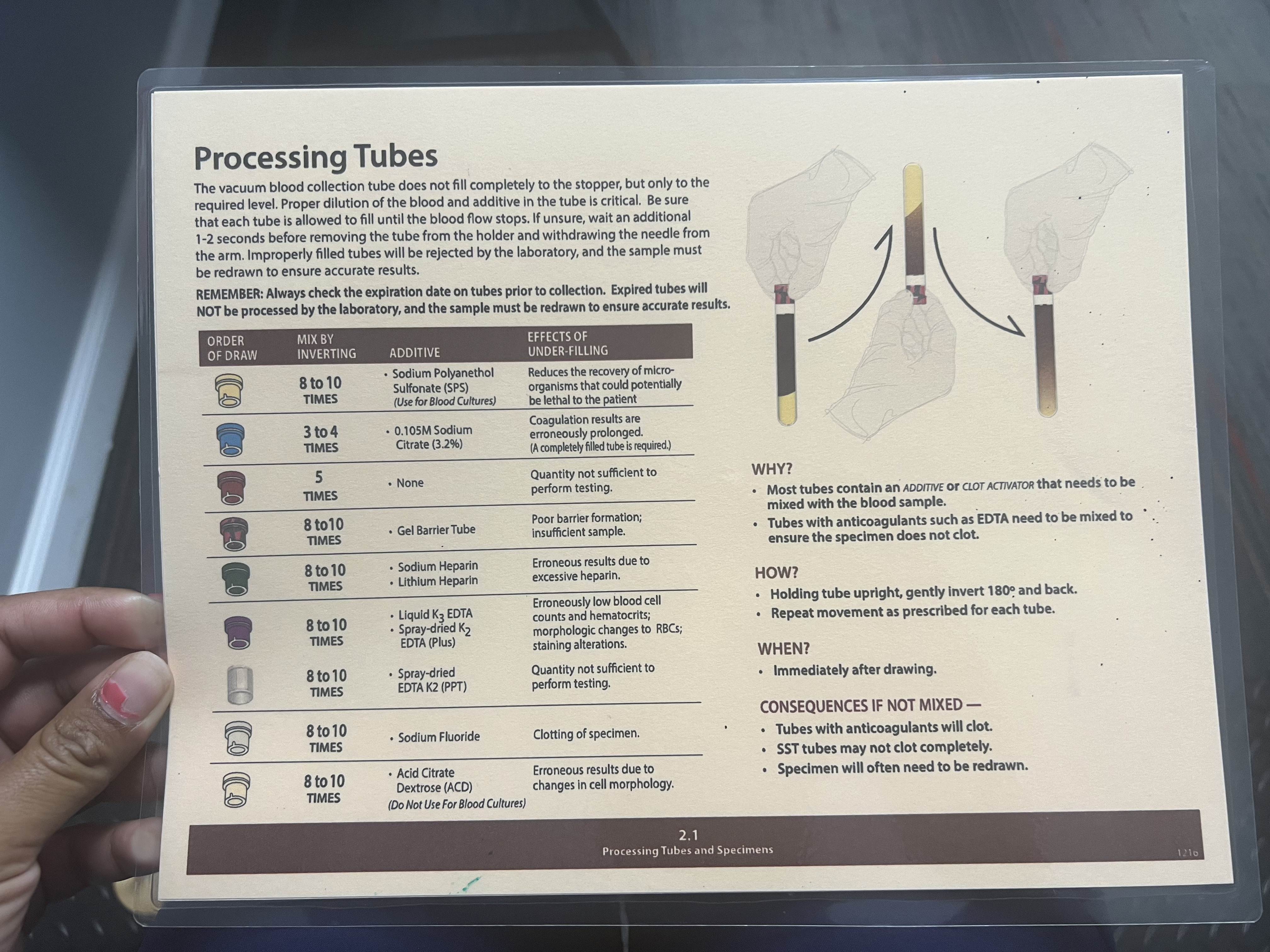
White Tubes
Mix by Inverting: 8-10 Times
Additive: Spray-dried EDTA K2 (PPT)
Effects of Under-filling: Quantity not sufficient to perform testing.
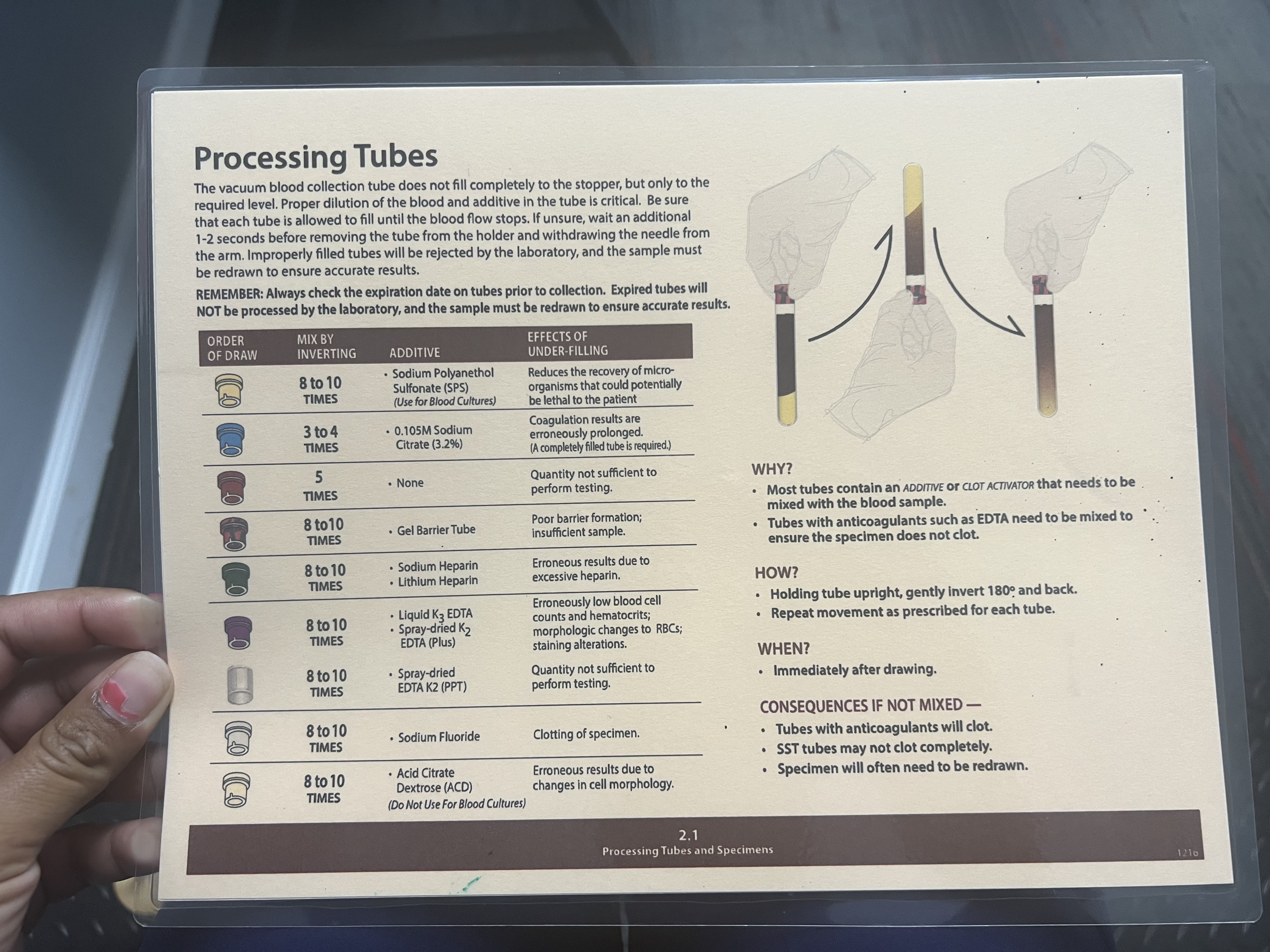
Grey Tubes
Mix by Inverting: 8-10 Times
Additive: Sodium Fluoride
Effects of Under-filling: Clotting of specimen
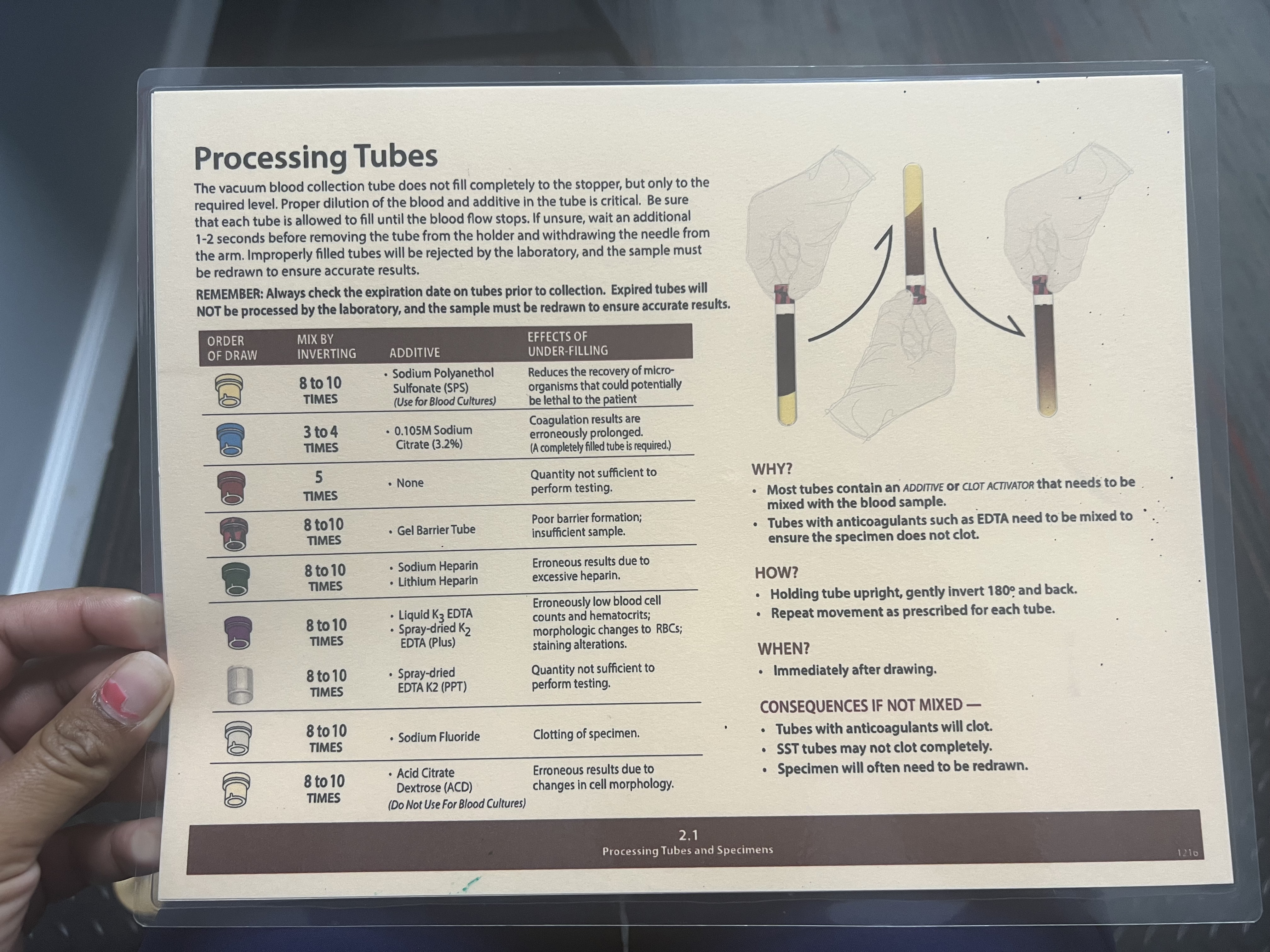
Cream/Tan Tubes
Mix by Inverting: 8-10 Times
Additive: Acid Citrate Dextrose (ACD) (Do Not Use For Blood Cultures)
Effects of Under-filling: Erroneous results due to changes in cell morphology.
A phlebotomy technician should ensure that which of the following specimens is protected from light?
A. Bilirubin
B. Triglyceride
C. Lead
D. Amylase
A. Bilirubin
Bilirubin is photosensitive, therefore it should be protected from light by wrapping it in aluminum foil
A phlebotomy technician is preparing to collect a patient’s troponin T level. Which of the following troponin T levels should the technician immediately report to the provider?
A. 0.3ng/mL
B. 0.2ng/mL
C. 0.03 ng/mL
D. 0.02 ng/mL
A. 0.3ng/mL
The technician should identify that a troponin T level of 0.3 ng/mL is above the expected reference range of 0 to 0.2 ng/mL and is therefore a critical value. The technician should immediately report this finding to the provider.
After placing a tourniquet on a patient's arm, a phlebotomy technician notices small red spots below the tourniquet. Which of the following terms describes these spots?
A. Hemoconcentration
B. Edema
C. Urticaria
D. Petechiae
D. Petechiae
The technician should identify that the small red spots are called petechiae, which are microcapillary bleeds that are associated with coagulation abnormalities.
A phlebotomy technician is preparing to perform a lactic acid test. Which of the following actions should the technician take?
A. Collect the specimen in a gray-topped tube
B. Protect the specimen from light
C. Protect the specimen from cold
D. Collect the specimen in a royal blue-topped tube.
A. Collect the specimen in a gray-topped tube
The technician should collect a lactic acid specimen in a gray-topped tube.
Before collecting blood from a patient in an inpatient setting, a phlebotomy technician notices that the patient does not have a wristband on his wrist, but there is one attached to the patient's IV stand. Which of the following actions should the technician take?
A. Hold the draw until the nurse has attached a wristband to the patient.
B. Write "unable to draw" on the requisition form.
C. Verify the patient's identity with the wristband on the IV stand
D. Ask the patient to confirm his identity.
A. Hold the draw until the nurse has attached a wristband to the patient.
The technician should not perform a blood draw on this patient until the nurse has attached a wristband to the patient.
The Joint Commission recommends using the patient's full name and which of the following pieces of information to ensure accurate inpatient identification?
A. Insurance carrier.
B. Medical record number
C. Laboratory requisition number
D. Provider's name
Medical record number
The patient's medical record number, a number assigned to the patient by a facility, is an acceptable form of patient identification. The patient's birthdate and home address are also acceptable patient identifiers.
Blood cultures have been ordered on an adult patient in an intensive care unit. A nurse calls a phlebotomy technician to bring the appropriate material. Which of the following materials should the phlebotomy technician bring?
A. Two aerobic bottles
B. Two anaerobic bottles
C. An aerobic bottle and an SPS tube
D. An aerobic bottles and an anaerobic bottle
D. An aerobic bottles and an anaerobic bottle
The technician should bring a set that includes both an aerobic bottles and an anaerobic bottle
Which of the following information should a phlebotomy technician document when adhering to chain of custody guidelines?
A. Identity of everyone who had possession of the specimen
B. Identity of the officer in charge
C. Identity of lawyers involved
D. Identity of the judge involved
A. Identity of everyone who had possession of the specimen
The technician should ensure that all personnel who had possession of the specimen are documented, as well as the time of transfer.
When performing a hand draw, which of the following steps should a phlebotomy technician take before removing the needle?
A. Ask the patient to release his fist.
B. Apply pressure to the site.
C. Disengage the tube from the adapter.
A. Reapply the tourniquet.
Disengage the tube from the adapter.
The technician should disengage the tube from the adapter before removing the needle. This prevents contamination and the dripping of blood.
A phlebotomy technician is instructing a patient about how to collect a 24-hr urine specimen. Which of the following instructions should the technician include?
A. Transport the specimen to the laboratory within 48 hr.
B. Restrict fluid intake.
C. Discard the first void of the morning.
D. Keep the specimen at room temperature.
D. Discard the first void of the morning.
The technician should instruct the patient to discard the first void of the morning and collect all subsequent voids until the next morning
A phlebotomy technician is removing a bag of contaminated items from a collection area. Which of the following actions should the technician take to properly dispose of the items?
A. Transfer the contents of the bag into a different hazardous waste bag.
B. Transfer the contents into a large trash bin.
C. Take the items directly to the dirty utilities room.
D. Place the bag inside a second hazardous waste bag outside of the room.
D. Place the bag inside a second hazardous waste bag outside of the room.
This method of disposal is called double-bagging and is the proper procedure for disposing of biohazardous waste. This process limits the risk for cross-contamination.