Industrial Sectors and Markets
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Market
A place where buyers and sellers come together for buying and selling goods.
Factors of Demand
Elements influencing consumer purchasing behavior.
Goods
Tangible items satisfying human wants.
Services
Intangible acts paid for by customers.
Primary Sector
First stage of production involving raw materials.
Secondary Sector
Manufacturing stage of production for finished goods.
Tertiary Sector
Final stage providing services to consumers.
Interdependence
Mutual reliance among industrial sectors.
Factor Markets
Markets for buying and selling factors of production.
Product Markets
Markets for buying and selling goods/services.
Derived Demand
Demand for a good due to another good's demand.
Specialisation
Focus on specific tasks or products by workers.
Specialisation pros for workers
Increased productivity - faster and more accurate work
Potentially higher wages - high demand for greater expertise may lead to higher pay
Increased morale and pride - workers feel more confident and fulfilled from their well-completed work
Increased efficiency - optimised utility of resources leading to greater efficiency
Specialisation cons for workers
Limited career flexibility - restrict worker’s ability to take on new roles, tasks and skill sets
Boredom - repetitive tasks can lead to dissatisfaction and burn out
Low skill set ranges - less likely to practise skills outside of specialisation
Reliance on specialised career - if demand for skills falls, worker may experience unemployment as they have restricted skill sets
Specialisation pros for producers
Increased productivity and efficiency - workers become highly skilled and efficient
Lower costs - increased productivity and economics of scale may lead to reduced costs
Economies of scale - make production increase easier and benefit from reduced costs
Higher quality products - focus on specific tasks leads to better control and consistency
Lowered training costs - workers already experienced and efficient
Specialisation cons for producers
Dependency - reliance on specialised workers can make producers vulnerable when faced with issues involving workers
Limited skilled and knowledge - limited workers’ ability to adapt to new situations and problems
Potential reduced worker motivation - workers may become bored and inefficient
Division of Labour
Breaking production into separate tasks for efficiency.
Demand
Willingness and ability to buy a good or service in a given time and price.
Law of Demand
Higher prices lead to lower quantity demanded, and lower prices lead to higher quantity demanded.
Individual Demand
Demand for a good by an individual or household.
Market Demand
Total demand from all buyers in a market.
Demand Curve
Graph showing relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Complementary Goods
Goods that are consumed together; as demand for one increases, the demand for other also increases.
Substitute Goods
Goods that replace each other; as demand for one increases, the demand for other decreases.
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
Responsiveness of demand to price changes.
Elastic Goods
Demand changes significantly with price changes.
Inelastic Goods
Demand changes little with price changes.
Unit Elastic
Demand changes proportionately with price changes.
PED = 1
Perfectly Inelastic
Demand remains constant regardless of price changes.
PED = 0
Revenue
Income gained by a producer through the sales of a product/service.
Basic Economic Problem
Scarcity of resources versus unlimited human wants.
Consumers
Individuals using goods or services.
Producers
Entities creating goods or services.
Factors of Production
Inputs used to produce goods and services.
Capital
Investment goods aiding future production. E.g. sewing machines, tools, tables
Enterprise
Idea for utilizing factors of production in business / to start a business.
Land
Space for business operations and resource extraction.
Labour
Human input in business operations.
Opportunity Cost
Value of the next best alternative.
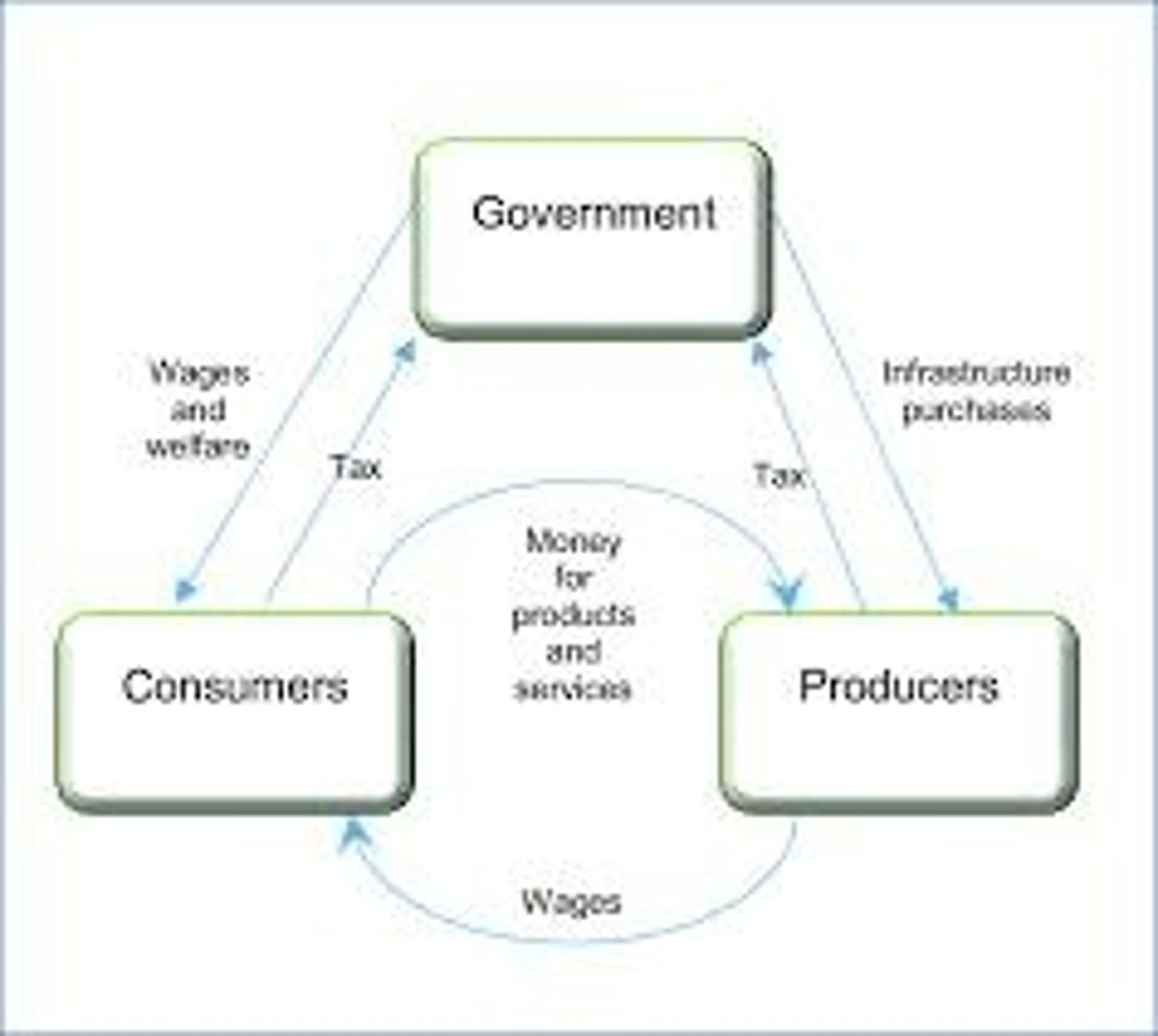
Economic Groups
Consumers, producers, and government.
PASIFIC (factors impacting demand)
Population
Advertisement
Substitutes
Income
Fashion and Taste
Income tax
Cost
Advertising
Promotional activities to influence consumer behavior.
Income Tax
Tax on individual or corporate earnings.
Fashion and Taste
Consumer preferences influencing demand.
Weather and Disease
Good/Bad weather impacting agricultural production.
Market Share
Percentage of total sales in a market held by a firm.