Unit 2 - Cell Structure and Function
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Prokaryotic cells
cells with no membrane bound organelles
Eukaryotic cells
cells with membrane bound organelles
Nucleoid
where the genetic material in prokaryotic cells are stored.
Plasmids
small circular DNA molecules
Primary cell wall
the outermost layer of a plant cell, thin and flexible layer that provides structural support.
Secondary cell wall
thick and strong layer in a plant cell, ex:- Wood
Middle Lamella
thin layer that acts like a glue between adjacent plant cells.
Plasmodesmata
channels in the cell walls of plants that allow substances to get from one plant cell to the next.
The extracellular matrix (ECM)
a network of proteins and carbohydrates that are outside the animal cell that provide support, adhesion, movement and regulation.
Tight Junctions
holds the plasma membrane of cells tightly together, like a zipper
Desmosomes
structures that connect cells, providing strength by anchoring them together.
Gap Junctions
channels that allows small molecules to pass between cells.
The Endomembrane System
network in eukaryotic cells for making, modifying, and transporting proteins and lipids.
Nucleus
The control center of the cell, contains the DNA and genes
Nucleolus
a structure inside the nucleus that makes rRNA
Nuclear Envelope
a double membrane that has pores that allow RNA and other molecules to pass in and out of the nucleus
Chromatin
the uncoiled form of chromosomes
Ribosomes
cellular structures made up of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins, and their main job is to carry out protein synthesis
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
a network connected to the nuclear envelope made of tubes and sacs that help move substances around the cell
Smooth ER
makes lipids and detoxifies. no ribosomes.
Rough ER
makes and folds proteins. covered with ribosomes.
Glycoproteins
proteins attached to carbohydrates
Golgi Apparatus
modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport.
Lysosomes
digestive organelles that break down waste and cellular debris.
Autophagy
process where cells recycle their own components and break down damaged organelles.
Phagocytosis
process where cells engulf and digest large particles or pathogens.
Apoptosis
Cell death
Vacuoles
storage sacs in cells for nutrients, waste, and water.
Food Vacuoles
Stores and digests food particles in cells.
Contractile Vacuoles
Expels excess water from cells to maintain osmotic balance.
Tonoplast
the membrane that surrounds the vacuole
Turgor pressure
pressure from water inside plant cells that maintains their shape and rigidity
Hypertonic
solution with a higher solute concentration than inside the cell, causing the cell to lose water.
Hypotonic
solution with a lower solute concentration than inside the cell, causing the cell to gain water.
Isotonic
solution with equal solute concentration inside and outside the cell, resulting in no net water movement.
Mitochondria
the powerhouse of the cell; produces energy (ATP) through cellular respiration.
Cristae
folds of the inner membrane inside the mitochondria that enhances surface area
Chloroplasts
organelles in plant cells that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis.
Plastids
organelles in plant cells for storage and synthesis; include chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and leucoplasts.
Amyloplasts
plastids that store starch in plant cells
Chromoplasts
plastids that contain pigments for color
Peroxisomes
small membrane-bound organelles that break down harmful & poisonous substances in the cell like hydrogen peroxide.
Cytoskeleton
a network of fibers that provides structural support in animal cells
Microtubules
hollow rods that are made of the protein tubulin
Centrosomes
structures located near the nucleus of a cell where microtubules are produced
Centrioles
organelles that assist in organizing the microtubules during cell division
Microfilaments
Solid rods composed of the protein actin
Intermediate filaments
stable and sturdy filaments made of keratins
Stomata
tiny openings located on the surface of leaves that aid in gas exchange.
The plasma membrane
a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds and protects the cell, which control what goes in and out of the cell
Phospholipid molecules
the main building blocks of the plasma membrane, forming a double layer called the phospholipid bilayer
Integral Proteins (Transmembrane Proteins)
proteins embedded in the cell membrane that span its entire width
Peripheral Proteins
proteins located on the surface of the cell membrane
Glycolipids
molecules where carbohydrates attach to lipids.
Aquaporins
special channel proteins that facilitate the rapid movement of water across the membrane
A concentration gradient
the difference in the concentration of a substance between two regions.
Diffusion
molecules move from high to low concentration until equilibrium is reached.
Passive Transport
movement of molecules across the membrane without energy, from high to low concentration.
Active transport
movement of molecules across the membrane with energy (ATP), from low to high concentration.
Facilitated diffusion
diffusion though channels or carrier proteins.
Osmosis
water movement across a membrane from high to low concentration.
Osmoregulation
process of controlling water
Plasmolysis
shrinking of a plant cell’s membrane away from the cell wall due to water loss.
Flaccid
when a plant cell loses water, causing it to become soft and limp.
Exocytosis
moving large molecules out of the cell via vesicles
Endocytosis
taking in large molecules into the cell forming a vesicle
Phagocytosis
engulfing large particles like food or bacteria
Pinocytosis
engulfing extracellular fluid containing dissolved substances
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
receptors on the cell membrane that target and bring in specific molecules
Gated Channels
membrane channels that open or close in response to signals, controlling ion flow in and out of cells.
Cystinuria
A genetic disorder that is caused by the absence of a carrier protein that transports cystine.
Cotransport
transport of two substances across a membrane together, using one molecule’s gradient to move the other.
Symporter
a protein that moves two molecules in the same direction across the cell membrane.
Antiporter
a protein that moves two molecules in opposite direction across the cell membrane
The sodium-potassium pump
active transport process that moves sodium (Na⁺) and potassium (K⁺) ions across the cell membrane
Chemical Force
ions naturally want to move from areas of high concentration to low concentration
Electrical Force
ions naturally move towards areas with opposite charges
Electrogenic Pumps
special transport proteins that create a voltage difference across cell membranes.
Voltage gradient
difference in voltage
Proton pump
protein pump that actively transports protons (H⁺ ions) out of the cell, generating a voltage across the membrane. (found in plants, bacteria and fungi)
Osmolarity
The total concentration of all solutes in a solution, regardless if they can cross the membrane or not
Tonicity
The concentration of non-permeable solutes that cannot cross into the membrane
Water Potential
the tendency of water to move from one place to another
Water Potential Formula
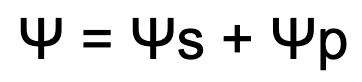
Solute Potential Formula
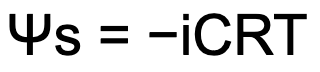
Compartmentalization
the separation of the cell’s interior into distinct areas
Endosymbiosis
theory that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated from engulfed prokaryotes that formed a symbiotic relationship with host cells.