hmmm speed run
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
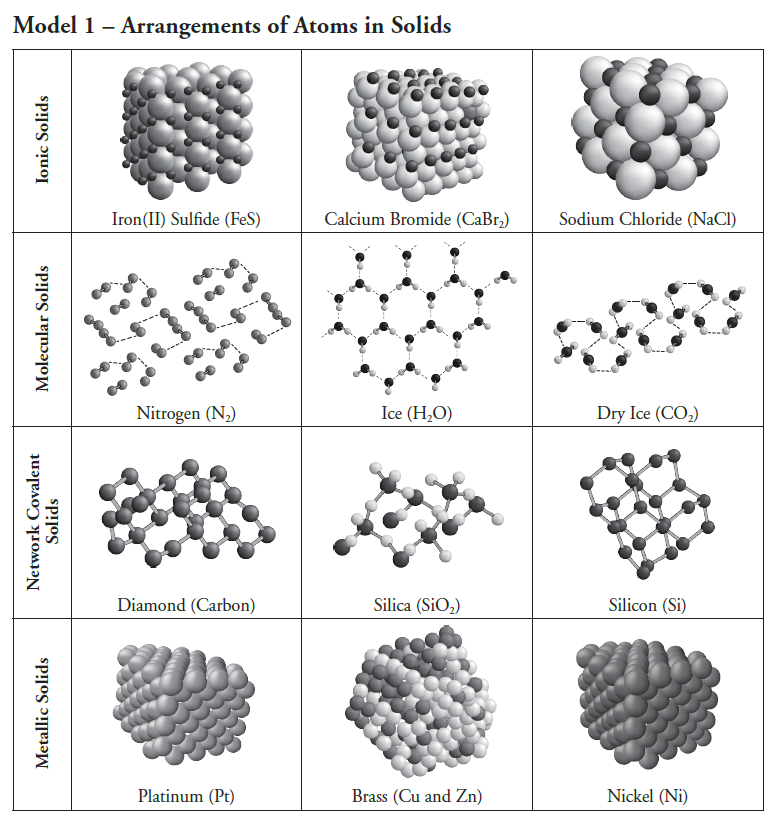
lattices
PE diagram
bonds form when minimun PE
blond length is the distance of the lowest point on the curve
geometry
Molecular Geometry & Bond Angles (VSEPR)
Bond Angles:
Linear = 180°
Trigonal planar = 120°
Tetrahedral = 109.5°
Trigonal pyramidal ≈ 107°
Bent ≈ 104.5°
hybridization changes during a reaction
Addition reaction: C=C double bond (sp²) → becomes sp³.
lone pairs push bonds close tg
decreasing angles
bond length is shorter w
strong bonds
ionic
lattices of alternating cation and anion
high mp
hard
free floating = yes 2 conductivity
solid = none
molecular
molecular hmph - imf
held by IMF, dipole dipole
low mp
soft
dont conduct
covalent solids (bonds = nonmetals)
hella high
atoms = covalently bonded
high mp
hard
dont conduct - molecular
metalic
metalicsea
metal cations in a sea of electrons
mp depend on metal
ductile
good conducters
polar lewis structure
central atoms have lone pair = polar
If the outer atoms are different (for example, COCl₂ with O and Cl attached to the same C)
electronegativity difference
polar bonds arragned sym cancel dipoles out
The particle must be a cation because the negative end of each water molecule is pointed toward it.
the Br—F molecule is the most polar
larger electronegativity difference (so the larger bond dipole), making it the most polar.
Propanoic acid — because it can form intermolecular hydrogen bonds strongly
intermolec force from temp dipoles
trans isomer = dipole dipole interaction
cisometer = london
brittle water
london disp in cl4
The carbon atoms in C₂H₂ are sp hybridized (triple bond), and in C₂H₃Cl₂ they change to sp³ hybridization (single bonds), so answer b is correct.
smallest O-S-O bond angle at approximately 109.5° in its tetrahedral structure
The Cl-Cl bond is stronger than the Br-Br bond because chlorine atoms are smaller, allowing for better orbital overlap and a stronger covalent bond, making answer d correct.