NURS 209: TOPIC 6 - RESPIRATORY
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
Related Health History:
What should be asked about cough type?
Determine whether the cough is dry, wet, or croupy.
Why ask about cough onset?
To know when the cough started, which helps identify acute vs chronic conditions.
Why is it important to ask about cough duration?
The length of time the cough has been present can indicate the severity or persistence of a respiratory issue.
What should be assessed regarding cough pattern?
Frequency, timing, and triggers of the cough to help identify underlying causes.
Why ask about cough severity?
Severe coughing may indicate significant respiratory distress or infection.
What should be asked about efforts to treat the cough?
Any treatments tried, including medications or home remedies, to assess response and effectiveness.
What should be asked about sputum production? (6)
Presence, amount, color, odor, pattern, and whether it contains blood.
Why ask about shortness of breath?
To evaluate respiratory function and detect possible airway or lung disease.
Why is it important to ask about chest pain with breathing?
May indicate conditions like pneumonia, pleuritis, pulmonary embolism, or cardiac issues.
What should be assessed regarding preferred breathing position?
Observing if the patient uses positions like the tripod position to ease breathing.
Why ask about history of respiratory infections or diseases?
Conditions like TB, CA, COPD, emphysema, asthma, bronchitis, PE, or pneumonia impact current respiratory health.
Why is smoking or vaping history relevant?
Tobacco or vaping can contribute to chronic lung disease, infections, and cancer risk.
What should be asked about exercise tolerance?
Ability to perform physical activity without SOB indicates respiratory and cardiovascular function.
Why ask about employment history?
Occupational exposures may affect respiratory health (e.g., dust, chemicals, fumes).
Why is residence history important?
Environmental exposures or living conditions can influence respiratory health.
Why ask about recent travel?
Travel to areas with prevalent respiratory illnesses can indicate risk of infection.
What should be asked about hobbies?
Certain hobbies may involve respiratory risks, such as exposure to dust, fumes, or allergens.
What does white or clear (mucoid) sputum indicate? (3)
It is associated with tracheobronchitis, asthma, or viral infections.
What does yellow or green sputum indicate?
It suggests a bacterial infection.
What does rust-colored or blood-tinged (hemoptysis) sputum indicate?
It may indicate pneumonia, pulmonary infection, or tuberculosis (TB).
What does black sputum indicate?
It is associated with black lung disease.
What does pink, frothy (bubbly) sputum indicate?
It indicates pulmonary edema.
What questions should be asked when assessing dyspnea or shortness of breath (SOB)?
Ask about onset, frequency, pattern, tolerance to activity, severity, associated symptoms such as cramping, nausea, or coughing, and the response to treatment.
What is orthopnea?
Shortness of breath or dyspnea that increases when lying down.
What is platypnea?
Shortness of breath or dyspnea that increases when upright; it is rare.
What are common causes of platypnea?
Multiple pulmonary embolisms (PE), abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), and cirrhosis.
What is paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea?
Attacks of severe SOB and coughing that usually occur at night, often awakening the person from sleep; commonly seen in COPD.
What questions should be asked when assessing chest pain?
Ask about onset, pattern, severity, duration, activity tolerance, associated symptoms, and relief measures.
What type of environment should the room be when preparing a patient for assessment?
The room should be warm and well-lit.
Why is it important for the room to be quiet and private during a patient assessment?
To ensure accurate assessment and maintain patient comfort and privacy.
How should the patient be prepared for the examination in terms of clothing?
The patient should undress to the waist and wear a gown that opens in the front.
What should you ensure about the stethoscope before using it on a patient?
The stethoscope should be warm and clean.
What position is the patient in for breathing?
Ask the patient about their preferred or most comfortable breathing position (e.g., sitting upright, leaning forward).
What does LOC stand for, and why is it assessed?
Level of Consciousness; it is assessed to determine the patient’s alertness and neurological status.
What should you look for on the skin and fingers as signs of hypoxia?
Look for pallor (paleness) and clubbing of the fingers, which indicate chronic oxygen deprivation.
What is the purpose of assessing respiratory rate?
To determine the number of breaths per minute and evaluate the patient’s respiratory function.
What does pulse oximetry measure?
It measures the oxygen saturation level (SpO₂) in the blood to assess how well oxygen is being delivered to the body.
What should you assess when inspecting the anterior chest for shape and configuration?
Assess for symmetry & equal movement, an AP to transverse diameter ratio of 1:2 (twice as wide as it is deep), ribs sloping downward, and a costal angle within 90 degrees or less.
What is the normal ratio of the anteroposterior (AP) diameter to the transverse diameter?
1:2 — the chest should be twice as wide as it is deep.
What should the ribs look like upon inspection of the anterior chest?
The ribs should slope downward.
What is the normal measurement for the costal angle?
Within 90 degrees or less.
What should be observed about respirations when inspecting the anterior chest?
Respirations should be regular, even, and within normal limits (WNL) for rate.
What indicates normal respiratory effort during inspection?
No use of accessory muscles during breathing.
What are examples of accessory muscle use that indicate abnormal breathing effort?
Use of chest and neck muscles, intercostal retractions, subcostal retractions, and nasal flaring.
What is the ratio of the anteroposterior (AP) diameter to the transverse diameter in a barrel chest?
1:1 ratio
Barrel chest is a sign of what respiratory condition?
COPD
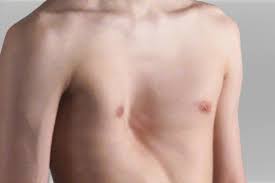
What is another name for funnel chest?
Pectus excavatum
In pectus excavatum, what happens to the xiphoid process?
It is sunken in
When can surgery be used to correct pectus excavatum?
Only if it affects breathing
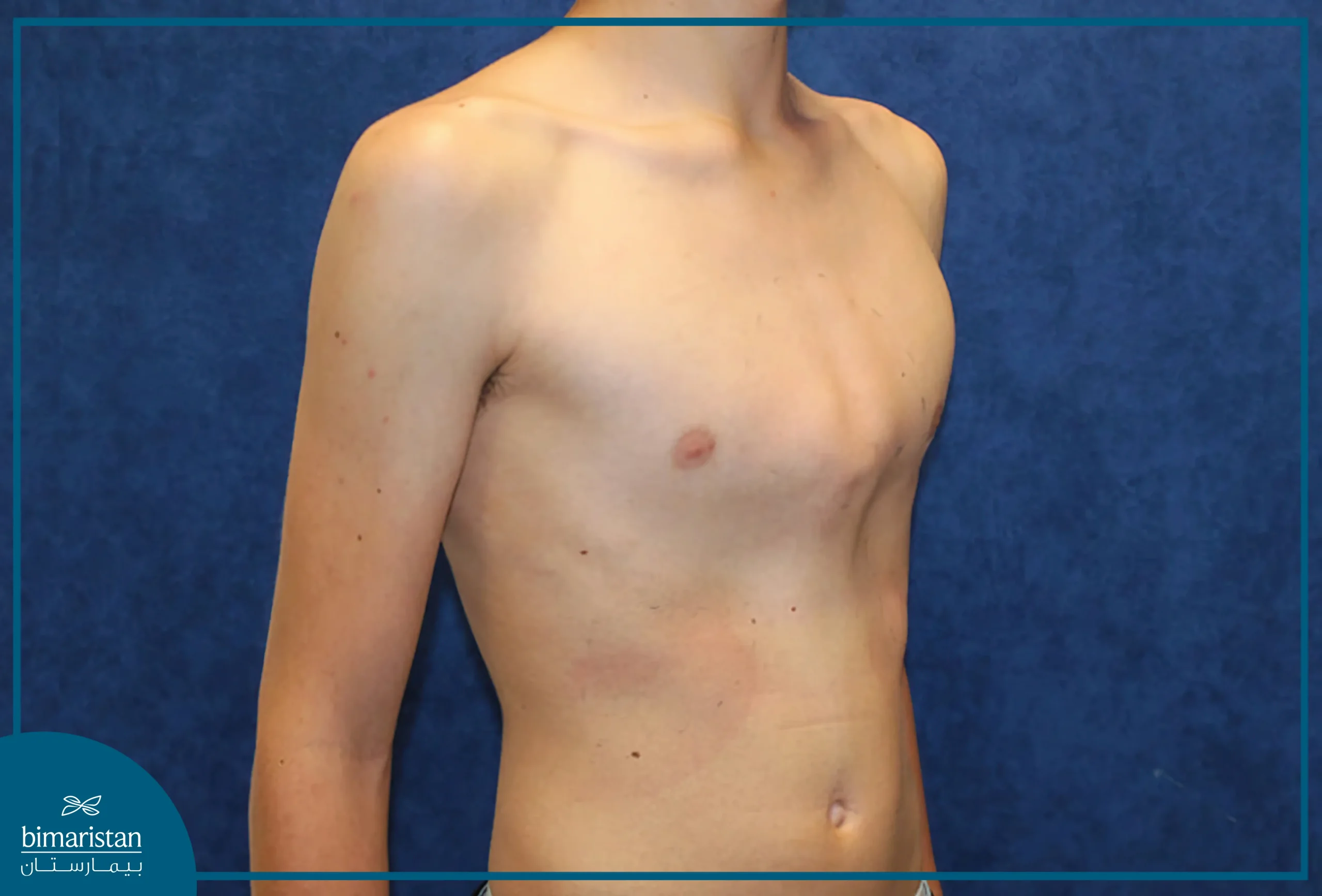
What is another name for pigeon chest?
Pectus carinatum
In pectus carinatum, what happens to the sternum?
It is pushed outward
When can surgery be used to correct pectus carinatum?
Only if it affects breathing
What pattern of respirations is typically seen in adult males and children?
Adult males and children are more diaphragmatic breathers, meaning the rise is seen in the stomach.
What pattern of respirations is typically seen in adult females?
Adult females are more thoracic breathers, meaning the rise is seen in the chest.
What is hypernea and when is it considered normal?
It is deep, rapid breathing and is normal during exercise.
What is an apneic episode?
It occurs when there is no breath for 20 seconds or more.
What characterizes Cheyne-Stokes breathing?
It involves shallow breaths followed by a period of no breathing (apnea), then returning to shallow breaths.
In which condition is Cheyne-Stokes breathing commonly seen?
It is commonly seen in people with head injuries.
What is Biot’s breathing pattern?
It consists of 3 normal breaths followed by a period of apnea.
Who typically exhibits Biot’s breathing?
It is often seen in people with head injuries.
What defines ataxic breathing?
It is a completely irregular pattern with periods of apnea, deep, and shallow breaths.
What does ataxic breathing evolve into?
It can evolve into agonal breathing.
What is agonal breathing?
It is not true breathing; it consists of gasps for air that are reflexive.
What does agonal breathing indicate?
It is a sign that the patient is near death.
What type of chest retractions are typically seen in infants?
Subcostal retractions, which occur under the ribs.
What type of chest retractions are typically seen in children?
Intercostal retractions, which occur between the ribs.
What type of chest retractions are typically seen in adults?
Intercostal retractions, which occur between the ribs.
What is flail chest and what causes it?
It is a trauma condition where a segment of the thorax moves independently due to ribs being fractured and not attached to the sternum or rest of the rib cage.
What are the main manifestations of flail chest?
Dyspnea, paradoxical chest movements, poor air exchange, crepitus, pain with breathing, and cyanosis.
What are paradoxical chest movements in flail chest?
Chest movements that are opposite of what is expected during breathing.
What is crepitus in the context of flail chest?
Air trapped within subcutaneous tissue, feels like bubble wrap under the skin.
Why might a patient with flail chest experience cyanosis?
Due to poor air exchange caused by the unstable chest segment.
What symptom in flail chest is associated with pain during breathing?
Pain with breathing, caused by rib fractures and chest trauma.
What should you assess during general light palpation of the entire chest? (5)
Temperature, sensation, tenderness, turgor, and crepitus (emphysema).
What should you check regarding bone and muscle during chest palpation?
Alignment, protrusions, and abnormalities of the thorax.
In what order should areas of pain, tenderness, or abnormality be palpated?
Palpate these areas last.
How is subcutaneous emphysema assessed?
By rolling palpation with the fingers.
Is crepitus considered normal or abnormal?
Always abnormal.
What are possible causes of subcutaneous emphysema in the chest? (3)
A nicked airway, air leaking around a chest tube site, or air from around a trach or endotracheal tube.
What is the proper technique for assessing symmetric chest expansion on the anterior chest?
Place thumbs along the costal margins pointing toward the xiphoid process, pinch the skin between the thumbs, have the patient take a deep breath, and observe if the thumbs move apart symmetrically.
What indicates normal symmetric chest expansion?
Thumbs move apart equally on both sides during deep inspiration.
How is tactile fremitus assessed on the anterior chest?
Use the palmar bases of fingers, the ulnar surface of the hand, or the ulnar surface of a fist, have the patient repeat “99” or “blue moon,” and palpate for vibrations.
What is considered normal tactile fremitus?
Vibrations should be perceptible and symmetrical on both sides of the chest.
What precaution should be taken when palpating tactile fremitus in females?
Avoid palpating directly over breast tissue.
What does increased tactile fremitus indicate?
They indicate consolidation, meaning there is blood or fluid within the lungs.
What does decreased tactile fremitus indicate?
They suggest a lung obstruction, effusion, pneumothorax, or emphysema.
What are rhonchal fremitus and what do they indicate?
They are vibrations caused by thick secretions in the lungs.
What is pleural friction fremitus and what does it indicate?
It occurs due to inflammation of the pleura, the lining of the lungs.
What should you do when percussing the anterior chest?
Compare side-to-side patterns.
How should you percuss around female breast tissue?
Percuss between the ribs and around the breast tissue.
Which part of the fingers should you use for percussion?
Use the middle fingers and tap right under the nail.
What sound should you hear when percussing over the lungs?
A resonance sound.
What is the normal percussion sound of the chest and how is it described?
Resonance; low-pitched, clear, hollow sound.
What is hyperresonance in chest percussion?
A low-pitched booming sound.
In which age group is hyperresonance commonly found and why?
Common in children; barrel chest is normal until adolescence.
What conditions can cause hyperresonance in adults?
Overinflated lungs such as in COPD, asthma, atelectasis, emphysema, or pneumothorax.
What does a dull percussion sound of the chest indicate?
Soft, muffled thud.
Where is dullness considered normal in chest percussion?
Over the liver or other visceral tissue.
What conditions can cause dullness in chest percussion?
Pulmonary fibrosis, pleural effusions, pulmonary edema, or tumors.
What does a flat percussion sound of the chest indicate?
Very soft sound; indicates collapsed lung, pleural effusions, or pneumonia with consolidation.