1.1 - What is Economics?
1/27
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
economics as a social science
studies the behaviours of individuals and societies
uses the scientific method to model the behaviour of economic agents
microeconomics
studies the behaviors of individuals and firms in particular markets
macroeconomics
studies the behavior of the government and the economy as a whole
basic economic problem
how to allocate scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants
What to produce?
How to produce?
For whom to produce for?
factors of production
refers to the resources that are required to produce goods and services
capital
refers to any machinery or man made resources used in the production of goods or services
factor income = interest
enterprise
refers to the skill of organizing the three other factors of production
factor income = profit
land
refers to natural resources
factor income = rent
labor
refers to human resources
factor income = wages
factor income
factor income is the income earned by individuals or households for their contribution to the production process
sustainability
refers to the ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.
scarcity
Refers to the situation in which there are finite amount of resources, whereas wants are infinite
Scarcity is a relative concept, therefore it depends on the scenario
e.g water is scarce in a desert but not in a river.
scarcity & sustainability
Sustainability refers to the ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.
scarcity is a threat to sustainability
threats to sustainability arise due to scarce resources.
therefore, choices on the allocation of our scarce resources allows us to meet our present needs without compromising the ability to meet future needs
e.g China, US, and India use more fossil fuels than the world combined (>50%), fossil fuels are not renewable, thus the consumption of fossil fuels is a threat to sustainability.
opportunity cost
the value of the next best alternative forgone when a choice is made
note that it refers to the next best alternative, therefore if there are multiple options, it refers to the single next best alternative, not the other choices combined
how do opportunity costs arise
Opportunity costs arise due to the scarcity of resources and the necessity to make choices.
When resources are limited, stakeholders decide how to allocate these resources among alternative choices.
Therefore, when a choice is made, the opportunity cost is incurred because resources used for that choice cannot be used for the next best alternative.
economic goods
resources and products that are limited in supply and have economic value to society, most goods are economic goods.
free goods
naturally abundant, and the quantity is sufficient to satisfy all human wants, hence does not incur any opportunity costs
free market economy
allocation of resources is determined by market forces, e.g producers and consumers (private sector)
mixed economy
allocation of resources is
determined by
consumers, producers,
and the government.
controlled/planned economy
allocation of resources is determined by the government (public sector)
Distribution is based on communal needs e.g, a pregnant mother of 10 needs a house more than a single man
Aims to meet societal needs holistically, rather than maximizing profits like the private sector
Prices, rations, and quotas are assigned by the government
advantages of the private sector
absence of price mechanisms in the public sector
price mechs. are systems of feedback and signals which illustrate consumer preferences. therefore resource allocation is not aligned with the public’s best interest
profit driven maximisation
priv sector has a strong incentive to minimize costs and maximize profits, causing them to be more efficient and innovative
competitive pressures
forces firms to remain efficient and innovative to meet consumer demands + keep their competitive edge within the market
PPC assumptions
There is a fixed amount of resources (FOP)
Assumes that there are only 2 goods available to produce
Efficiency and production techniques remain fixed or don’t innovate
All resources are used efficiently
Concave/curved PPC
Increasing opportunity cost
Occurs due to specialization.
Causes it to be harder to change production from good a to b, as they may require different labor skills or machinery (capital)
Resources are not equally suitable to produce different goods
e.g farmers and engineers have very different skill sets. To shift from producing more strawberries to producing more cars, the farmers need to learn math and engineering skills, therefore they are less specialized
Linear PPC
Constant opportunity cost
Occurs when the products have very similar FOPs.
"shoe leather costs" may be less pronounced due to the smoother transitions in production as the FOPs for both goods are very similar.
e.g green apple and red apple farmers have very similar skill sets, therefore if they want to shift to making more red apples and less green apples, the green apple farmers are likely quite specialized already in farming red apples
pareto efficiency
it is impossible to allocate resources in such a way that makes another party better off without making someone worse off
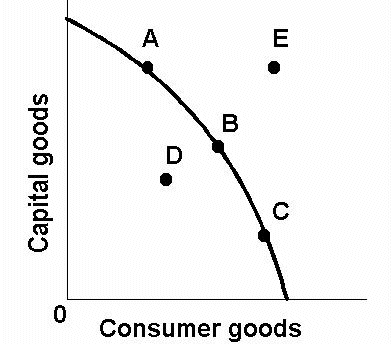
PPC diagram - pareto eff, max eff, min eff, actual growth, unattainable
A,B,C are pareto efficiency, max efficiency
E is unattainable currently
D is unemployment of resources/inefficiency
D to B is actual growth
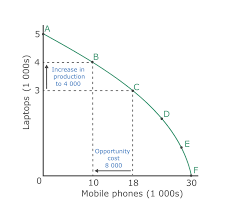
PPC - opportunity cost
Opportunity cost can be visualized on the PPC 10<x<18
what the ppc represents
model which illustrates the different combinations of goods and services that a firm or economy can produce