Endo/Repro Exam 1: Medicine Endocrine conditions (Dr. Siegel)
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Total lack of insulin along with high glucagon leads to _______________
ketoacidosis (DKA)

What are six signs and symptoms of diabetes mellitus when not well controlled?
- Polyuria
- Polydipsia
- Polyphagia
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Weight loss

Diagnosis of Diabetes: HbA1C >______%
6.5

Diagnosis of Diabetes: Fasting blood sugar > _____ mg/dl
126

Diagnosis of Diabetes: Casual blood sugar > ____ mg/dl
200

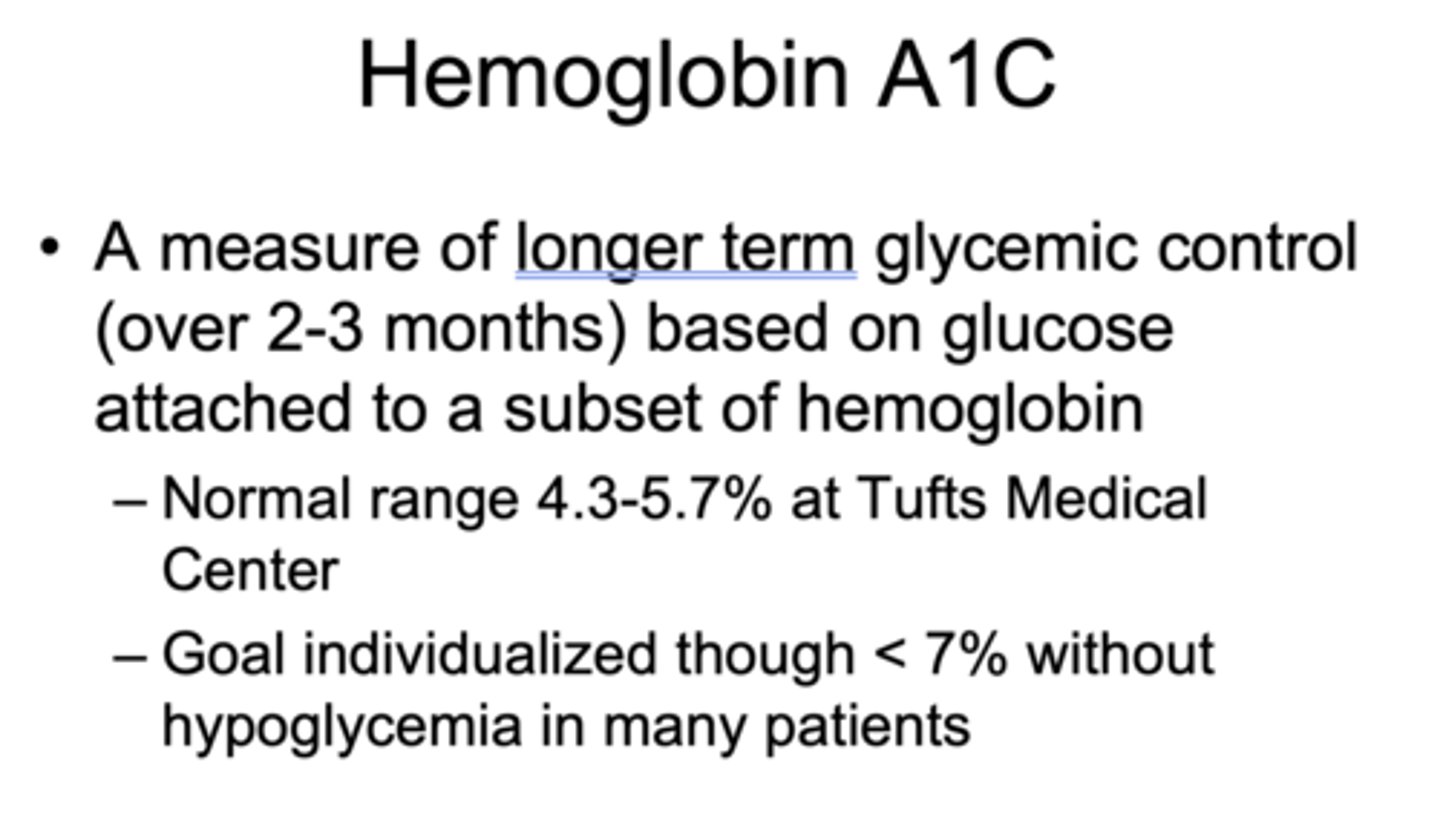
What is a measurement of longer term glycemic control (over 2-3 months) based on glucose attached to a subset of hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin A1C
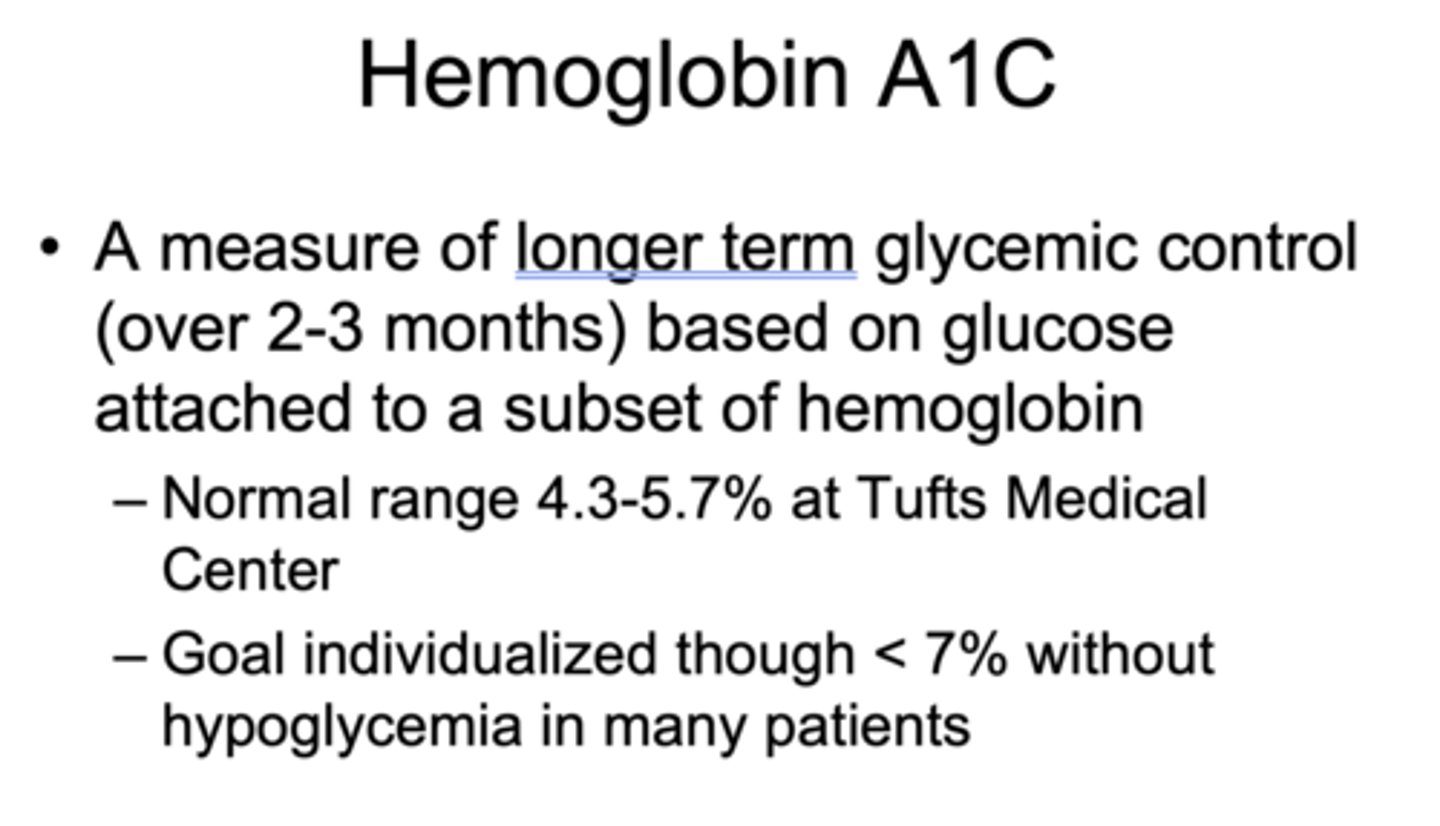
What is the normal Hemoglobin A1C range at Tufts Medical Center?
4.3-5.7%
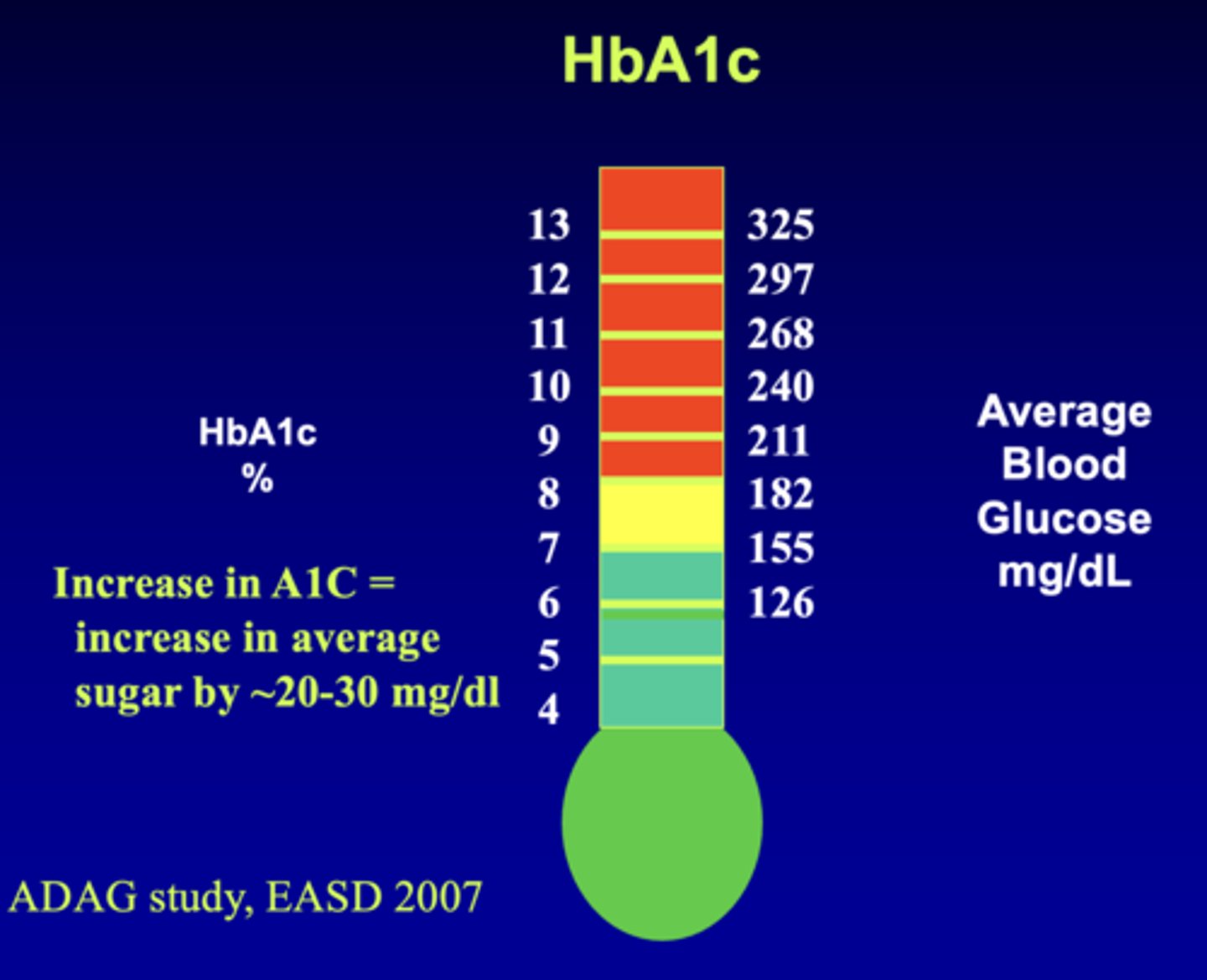
Increase in A1C = increase in average sugar by ______-______ mg/dl
20-30 mg/dl
What has the following characteristics?
- Associated with poor glycemic control, increased risk of death from cardiovascular and renal disease in diabetes
- Higher levels of C-reactive protein (CRP)
Periodontitis

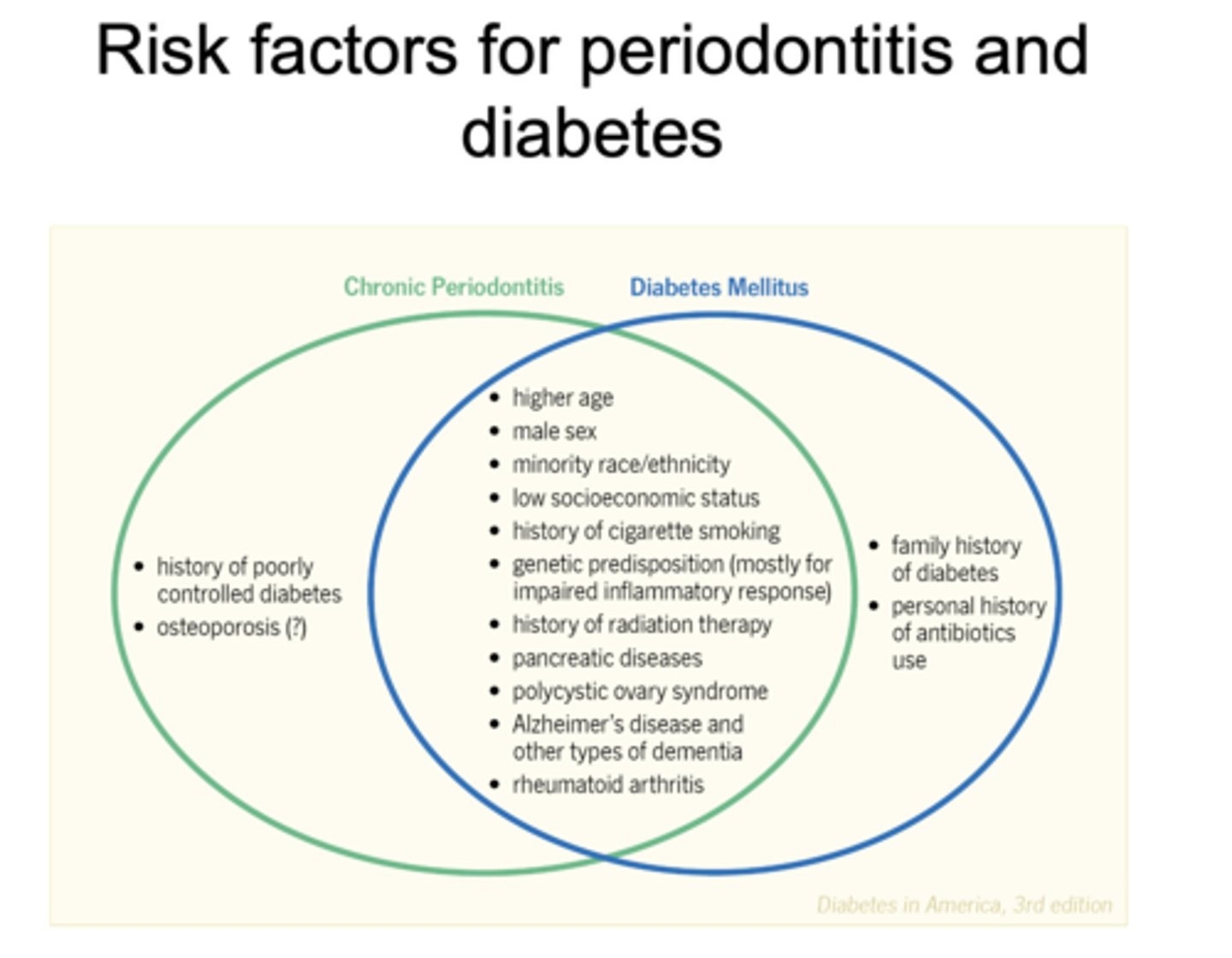
All of the following are risk factors for what?
- Higher age
- Male sex
- Minority race/ethnicity
- Low socioeconomic status
- History of cigarette smoking
- Henetic predisposition (mostly for impaired inflammatory response)
- Gistory of radiation therapy
- Pancreatic diseases
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Alzheimer's disease and other types of dementia
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Chronic periodontitis
- Diabetes mellitus
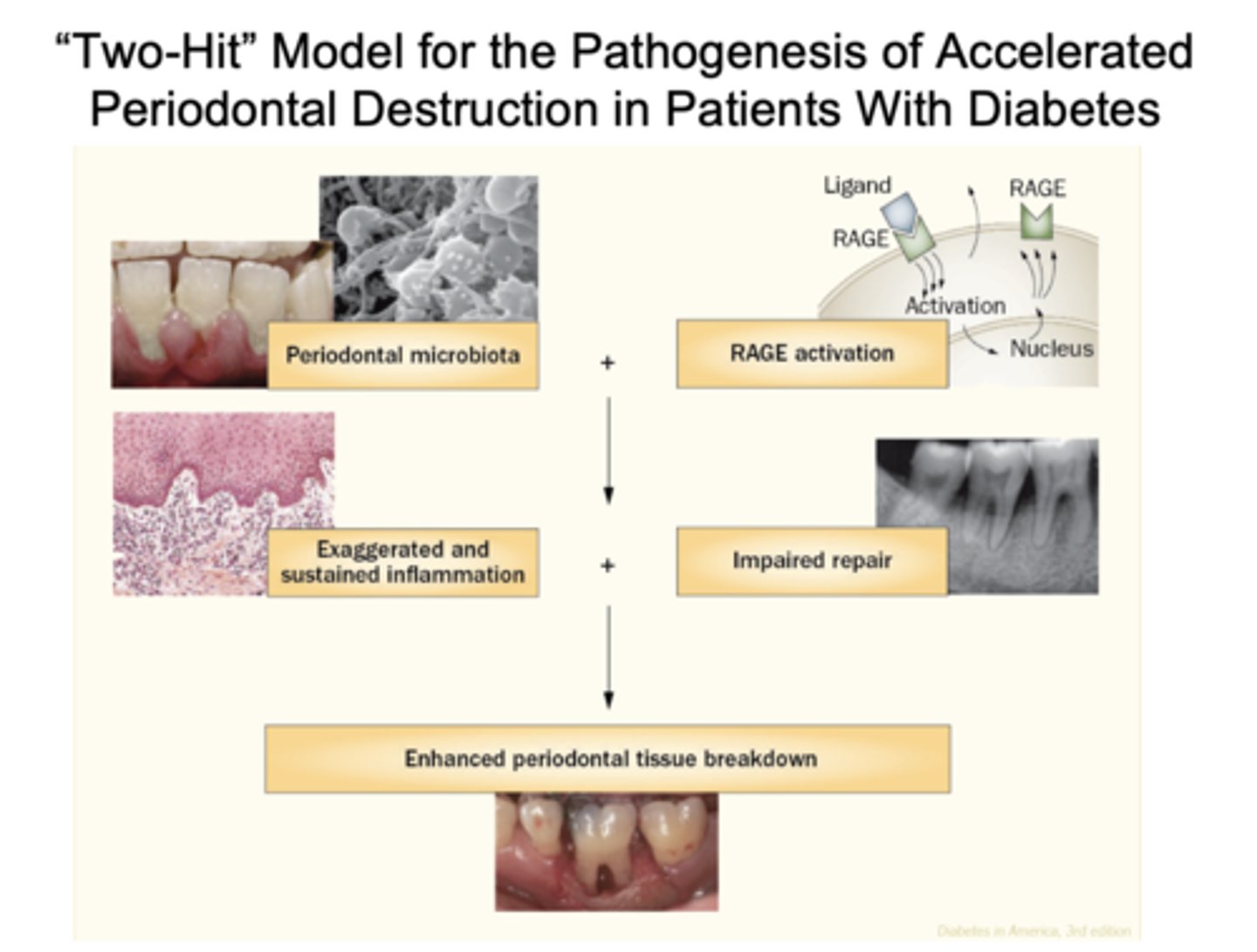
What is the "Two-Hit" Model for pathogenesis of accelerated periodontal destruction in patents with diabetes?
Periodontal microbiota and RAGE activation resulting in exaggerated and sustained inflammation and impaired repair, resulting in enhanced periodontal tissue breakdown
Is periodontal disease a precursor for diabetes and metabolic syndrome?
Yes!

What includes:
- High waist circumference
- Low HDL, high triglycerides
- Hypertension
- Elevated fasting glucose
Metabolic syndrome

In the 2022 Chochrane Review, they said "Moderate-certainty evidence to support gum disease treatment for controlling blood sugar levels in people with periodontitis and diabetes up to 12 months after the start of the periodontal treatment” which showed HbA1C improving by about ______%
0.4

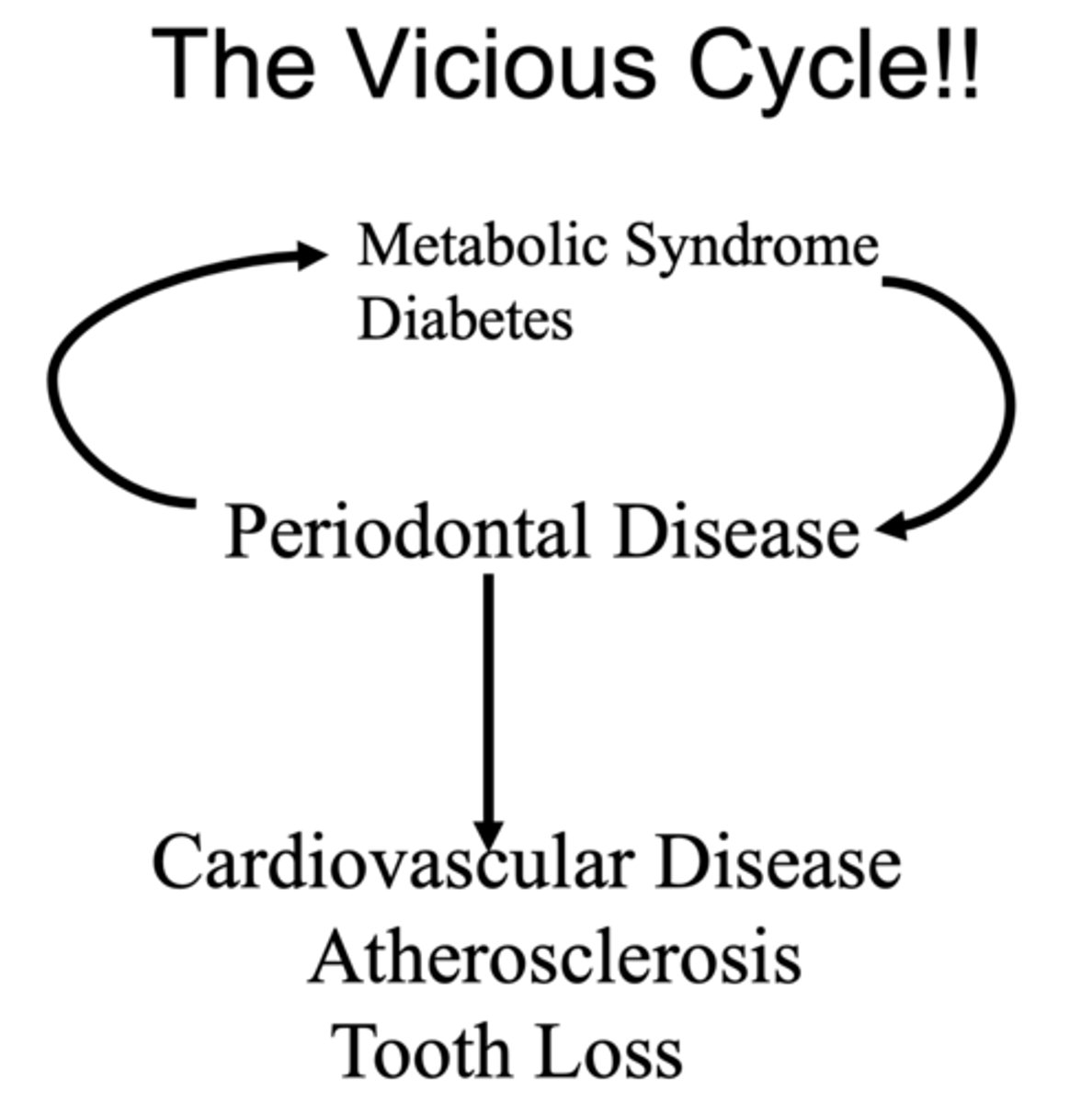
Metabolic syndrome disease and periodontal disease can ultimately lead to what three things?
- Cardiovascular disease
- Atherosclerosis
- Tooth loss
Which of the following is not an oral manifestations of diabetes?
A. Mucosal diseases (lichen planus/lichenoid drug reactions)
B. Xerostomia
C. Altered taste
D. Parotid gland enlargement
E. None of the above
E. None of the above

What are the 5 chronic complications of diabetes?
- Nephropathy
- Neuropathy
- Retinopathy
- Vascular disease
- Skin/mucosal infections

What is the leading cause of blindness?
Retinopathy from diabetes

what are glycemic goals?
premeal sugars:
postprandial sugars:
premeal sugars: 80-130 mg/dl
postprandial sugars: under 180 mg/dl
avoid hypoglycemia
higher ranges may be appropriate for some patients
_____________ is new glucometric with a >70% goal for 70-180 mg/dl
Time in range

What are three ways to manage type I diabetes?
- Coordination of diet, activity and insulin
- Basal and bolus insulin using vials, pens
- Insulin pump therapy working toward the concept of the closed loop

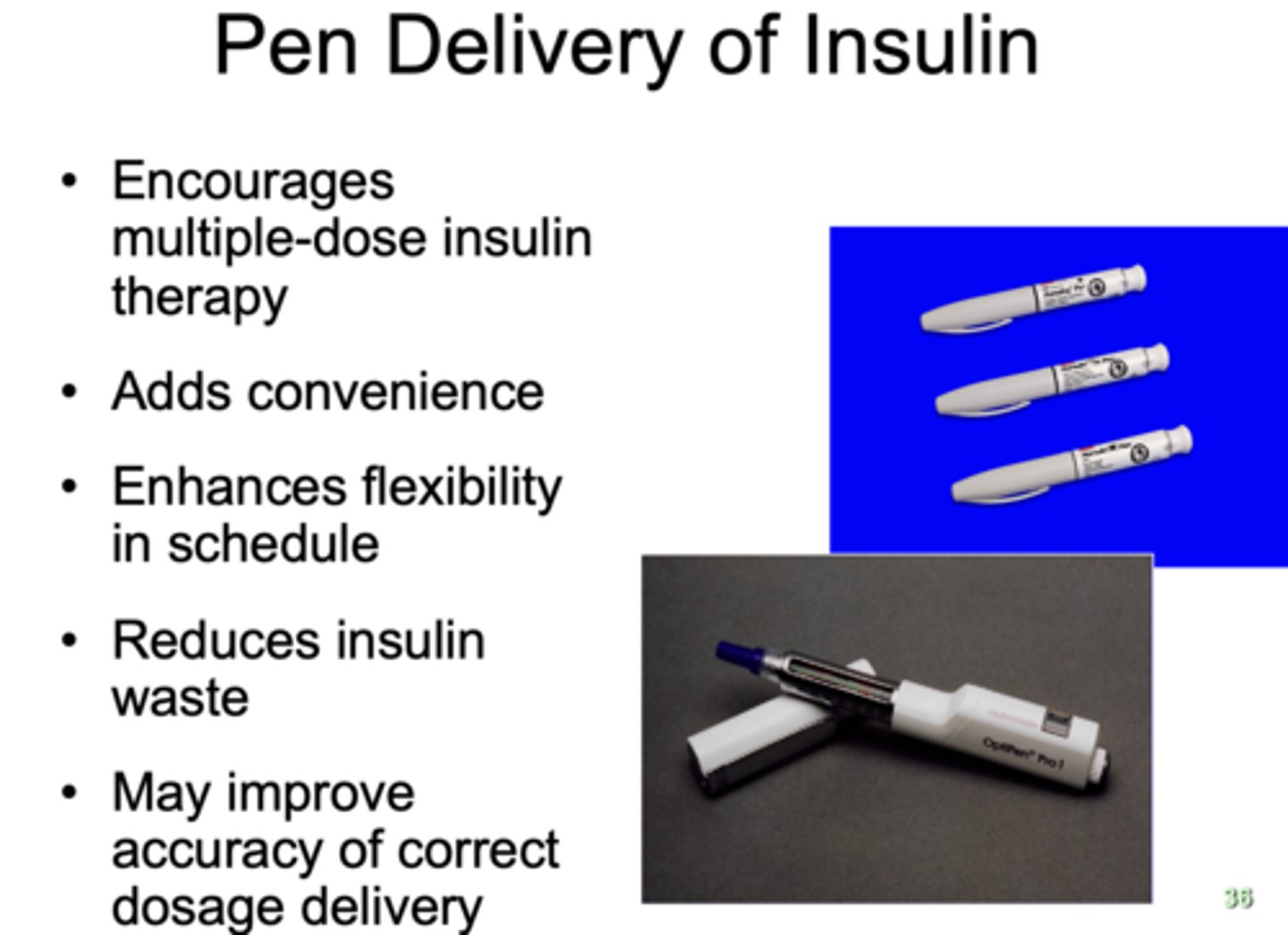
What has the following characteristics?
- Encourages multiple-dose insulin therapy
- Adds convenience
- Enhances flexibility in schedule
- Reduces insulin waste
- May improve accuracy of correct dosage delivery
Pen delivery of insulin
What are four ways to manage type 2 diabetes?
- Lifestyle management - diet and exercise
- Non-insulin oral and injectable agents
- Insulin
- Bariatric surgery - sleeve gastrectomy, gastric bypass

What are three things that you should know about patients with diabetes before dental procedures?
- Type and duration of diabetes
- How patient is being treated
- Degree of control of disease

Management for Dental Procedures: which types of medications are with held NPO?
- Bolus insulins
- Oral meds which stimulate insulin release

Management for Dental Procedures: which types of medications are NOT with held NPO?
basal insulin on type 1 diabetic

Postpone elective procedures on people with diabetes with suboptimal glucose control unless what?
Problem is contributing to poor control (infection)

t/f: procedures are safe on unstable diabetics
false, try to avoid procedures on unstable diabetics

What are the four symptoms of hypoglycemia?
- Tachycardia
- Sweating
- Confusion
- Bizarre behavior

treatment for hypoglycemic patient:
- PO juice, crackers, glucola
- IV D5 or D10
- SQ, nasal glucagon (1 mg), epinephrine (0.5 mg of 1:1000)

Hyperglycemia symptoms (3):
- Ketoacidosis
- Severe volume depletion
- Acetone breath

treatment for hyperglycemic patient:
- Get to ER
- Fluids with potassium and insulin Rx

The goal intake of Calcium is ______ mg daily
800-1200

What has the following characteristics?
- From the parathyroid glands
- Needed to activate vit D, affects bones and kidneys
PTH

What has the following characteristics?
- Converted to active form by kidneys
- Most produced by the skin (none in N.E. from Nov-May)
Vitamin D

What has the following characteristics?
- High Ca, PTH
- Usually adenoma, may be 4 gland hyperplasia
- Bones of the mouth are less radiodense
- Lamina dura may be absent; radiolucent areas may appear
- Central giant cell granulomas from osteoclasts may be present
Hyperparathyroidism

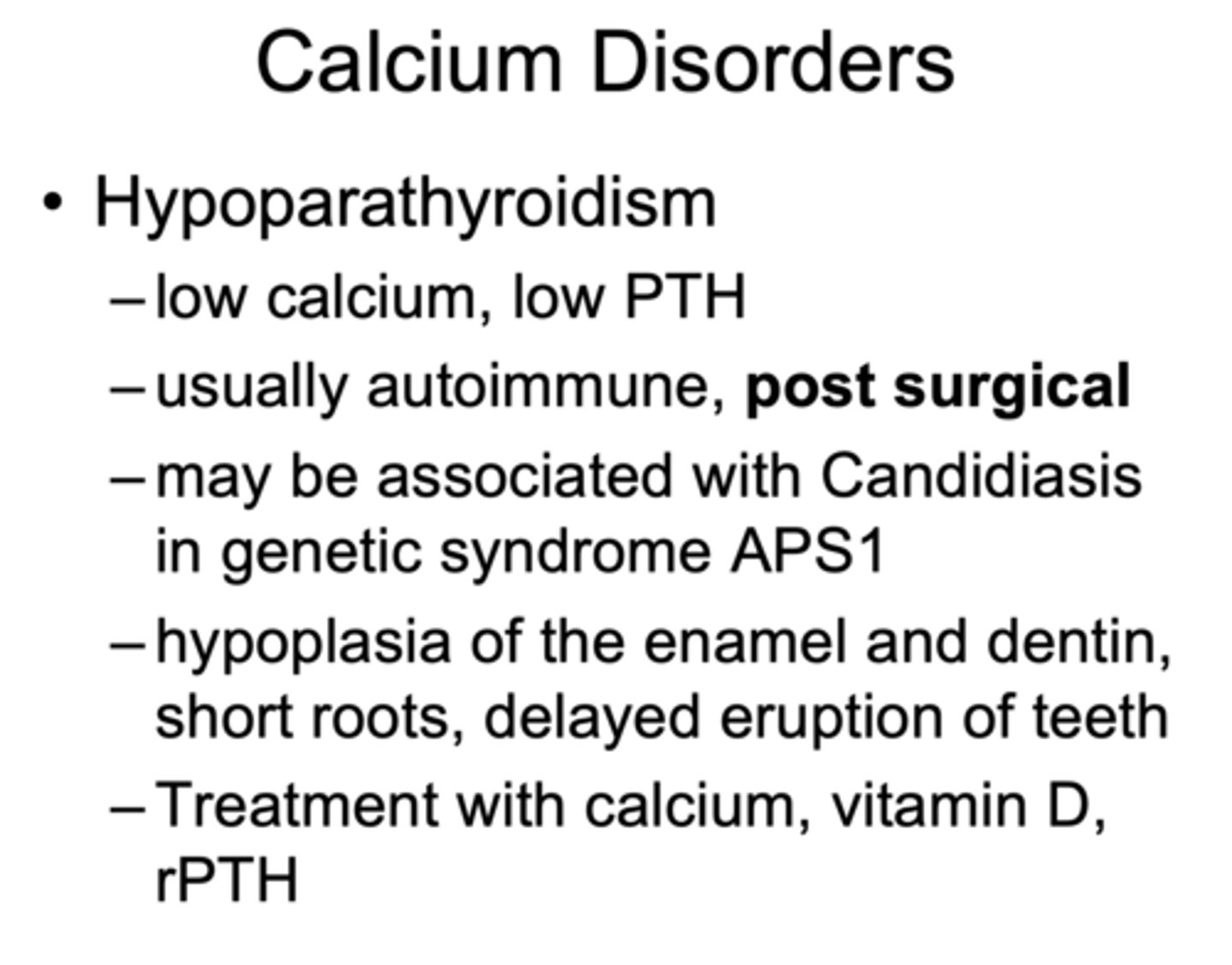
What has the following characteristics?
- Low calcium, low PTH
- Usually autoimmune, post surgical
- May be associated with Candidiasis in genetic syndrome APS1
- Hypoplasia of the enamel and dentin, short roots, delayed eruption of teeth
- Treatment with calcium, vitamin D, rPTH
Hypoparathyroidism
What has the following characteristics?
- Poor mineralization of bone
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Higher vitamin D levels associated with less bleeding on gingival probing
- Familial or acquired
- Rickets: Hypocalcification of dentin, enamel and alveolar bone
Osteomalacia
What has the following characteristics?
- Prone to accelerated alveolar bone loss
- Form of calcium disorder
renal osteodystrophy

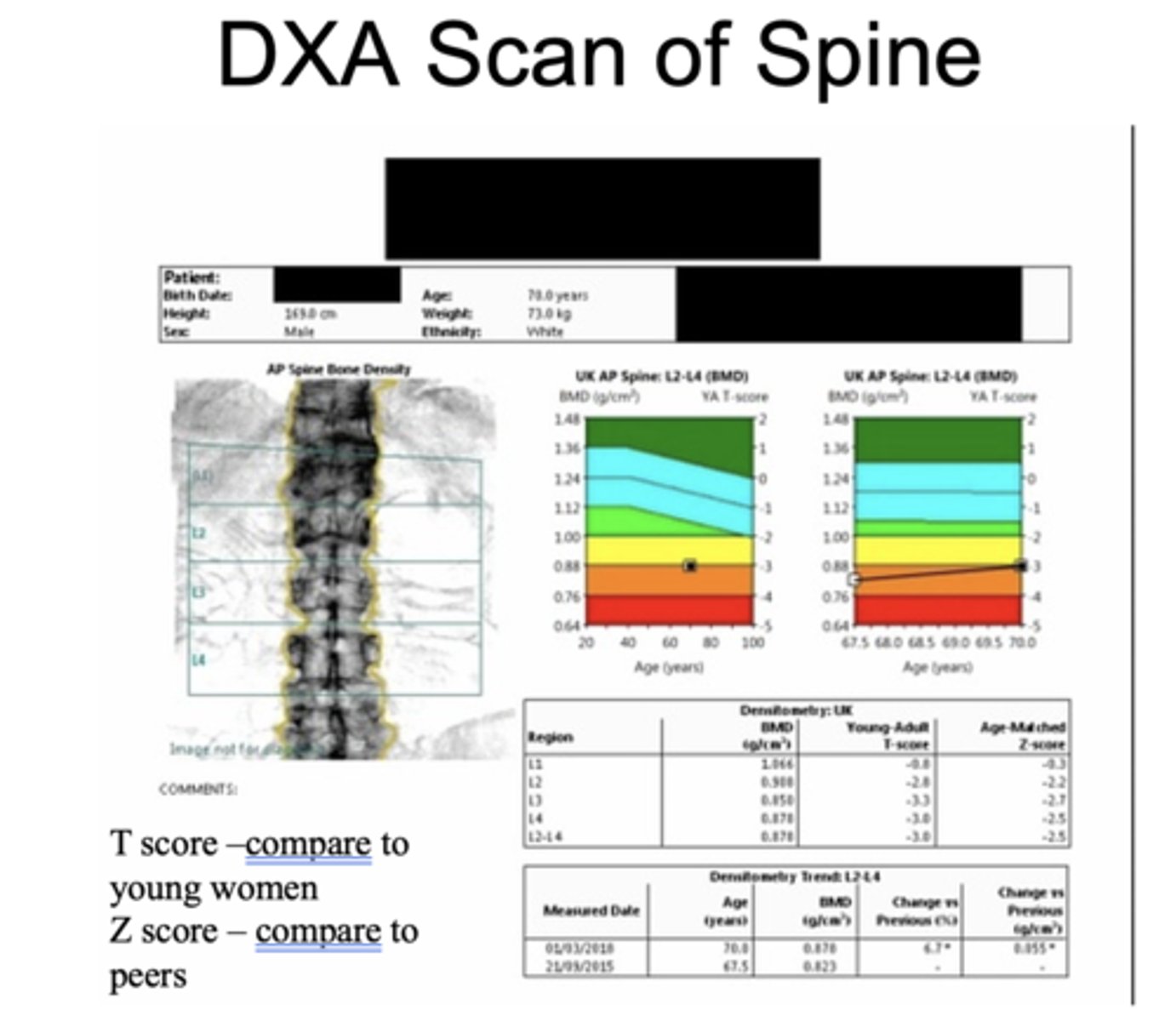
what tools can be used to assess osteoporosis?
DXA scan, FRAX risk calculator

what treatments are prescribed for osteoporosis?
- Prescribe with calcium, vitamin D, antiresorptive agents, anabolic agents
what are some risk factors for osteoporosis?
genetics, thin body habitus low calcium ntake, hypogonadism, hyperthyroidism
osteoporosis is most common in what groups of pts?
postmenopausal women but also seen in men
What is the T score vs Z score in the DXA scan?
T score - Compare to young women
Z score - Compare to peers
What has the following characteristics?
- Condition seen mostly in patients with cancers such as multiple myeloma and breast cancer receiving antiresorptive therapy for bone metastases or high calcium (Occasionally seen in patients with osteoporosis)
- Other risk factors include corticosteroids, chemotherapy, oral surgery
osteonecrosis of the jaw
Should antiresorptive therapy be stopped for patients needing dental surgery?
No validated diagnostic technique exists to determine which patients are at increased risk of developing MRONJ

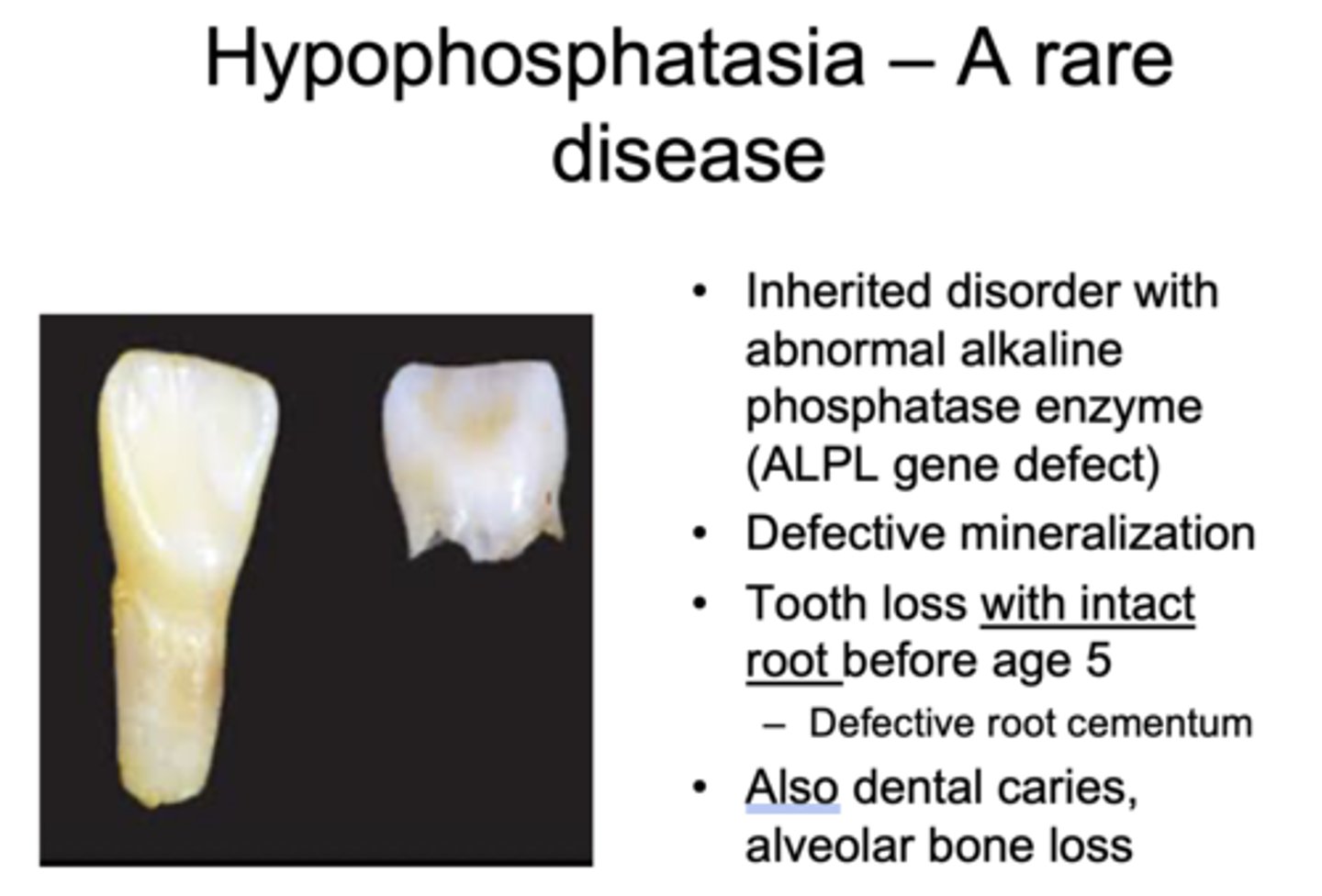
What has the following characteristics?
- Inherited disorder with abnormal alkaline phosphatase enzyme (ALPL gene defect)
- Defective mineralization
- Tooth loss with intact root before age 5
– Defective root cementum
- Also dental caries, alveolar bone loss
Hypophosphatasia
What condition is caused by:
- Graves' disease (autoimmune)
- Toxic nodular goiter
- Toxic adenoma
- Exogenous from excess thyroid hormone medication
hyperthyroidism

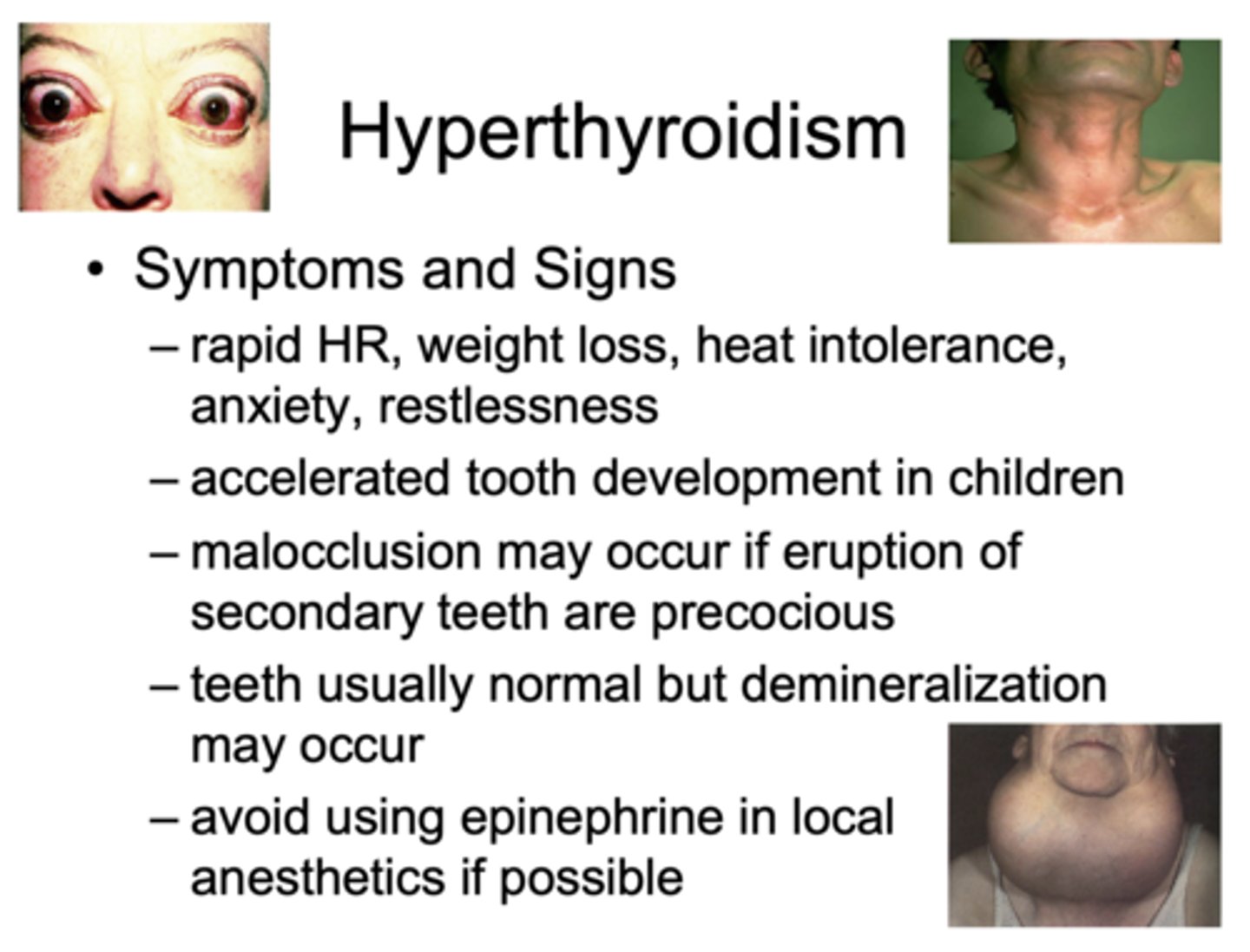
The following are symptoms and signs of what?
– Rapid HR, weight loss, heat intolerance, anxiety, restlessness
– Accelerated tooth development in children
– Malocclusion may occur if eruption of secondary teeth are precocious
– Teeth usually normal but demineralization may occur
– Avoid using epinephrine in local anesthetics if possible
hyperthyroidism
Diagnosis of primary hyperthyroidism
- High T4 and T3
- Low TSH
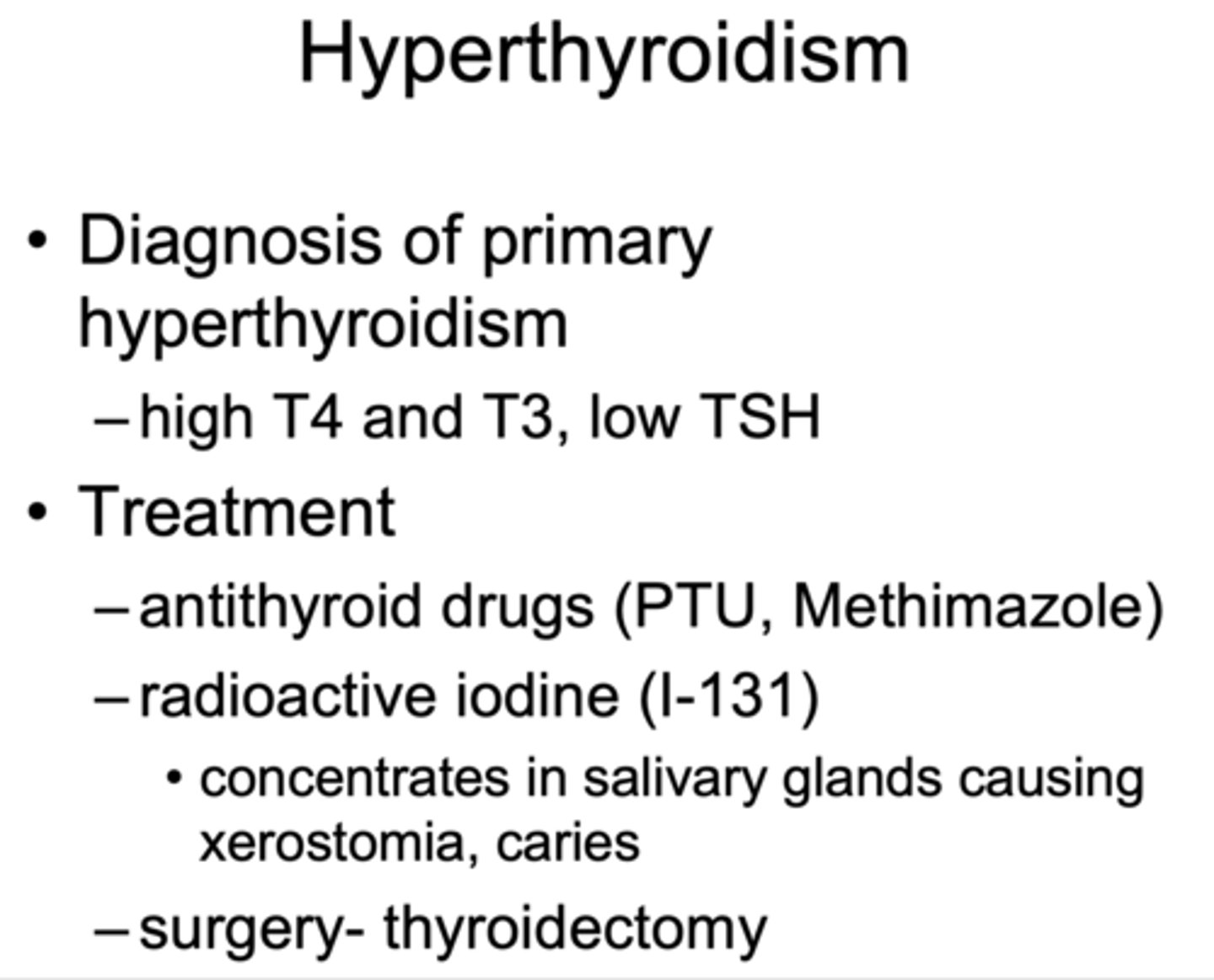
What are the three main treatments of hyperthyroidism?
- Antithyroid drugs (PTU, Methimazole)
- Radioactive iodine (I-131)
- Surgery- thyroidectomy

what are some causes of hypothyroidism?
- Autoimmune hasimoto thyroiditis
- Post radioactive iodine therapy
- Post surgery
- Meds including immune checkpoint inhibitors

The following are symptoms and signs of what?
- Fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, dry skin
- Congenital hypothyroidism- maxillary prognathism, retarded tooth development
- Excessive dental caries
- Macroglossia and swollen lips when advanced (myxedematous)
- Exaggerated response to narcotics and barbiturates
hypothyroidism

Diagnosis of hypothyroidism
- Low T4
- High TSH

What are the treatments of hypothyroidism?
- Levothyroxine therapy (Synthroid, Levoxyl)
- Screening done at birth with T4 and TSH

What has the following characteristics?
- Extremely common, many found incidentally on imaging
- Workup includes functional assessment with TSH, thyroid ultrasound
- Fine needle aspirate may be done based on ultrasound appearance
- Overall 5 year survival rate is 98%
Thyroid nodules and cancer

what are signs of acromegaly?
- Everything is big!!!
– Gigantism- large hands, feet, skin tags, excess sweating, colonic polyps
- Accelerated tooth eruption in children
- Enlarged jaw with prognathism – teeth are spaced and tipped outward

what causes acromegaly?
- Excess of GH from a pituitary tumor
What has the following characteristics?
- Coarsened facial features
- Macroglossia with obstructive sleep apnea
- Larger maxillary sinuses
- Excess deposition of cementum on the roots of tooth
acromegaly

what are some treatment options for acromegaly?
surgery, radiation, somatostatin therapy, GH receptor blockade
what are some signs of Cushing’s syndrome?
- Hypertension, central obesity, easy bruising, osteoporosis
- Increased periodontitis, oral candidiasis
- Gums bleed easily and may be swollen

what are some causes of Cushing syndrome?
- Excess cortisol production
- - Endogenous: pituitary, adrenal or ectopic tumor
- - Exogenous: too much therapeutic steroid
- Low cortisol and aldosterone, high ACTH is a sign of…?
Addison's Disease
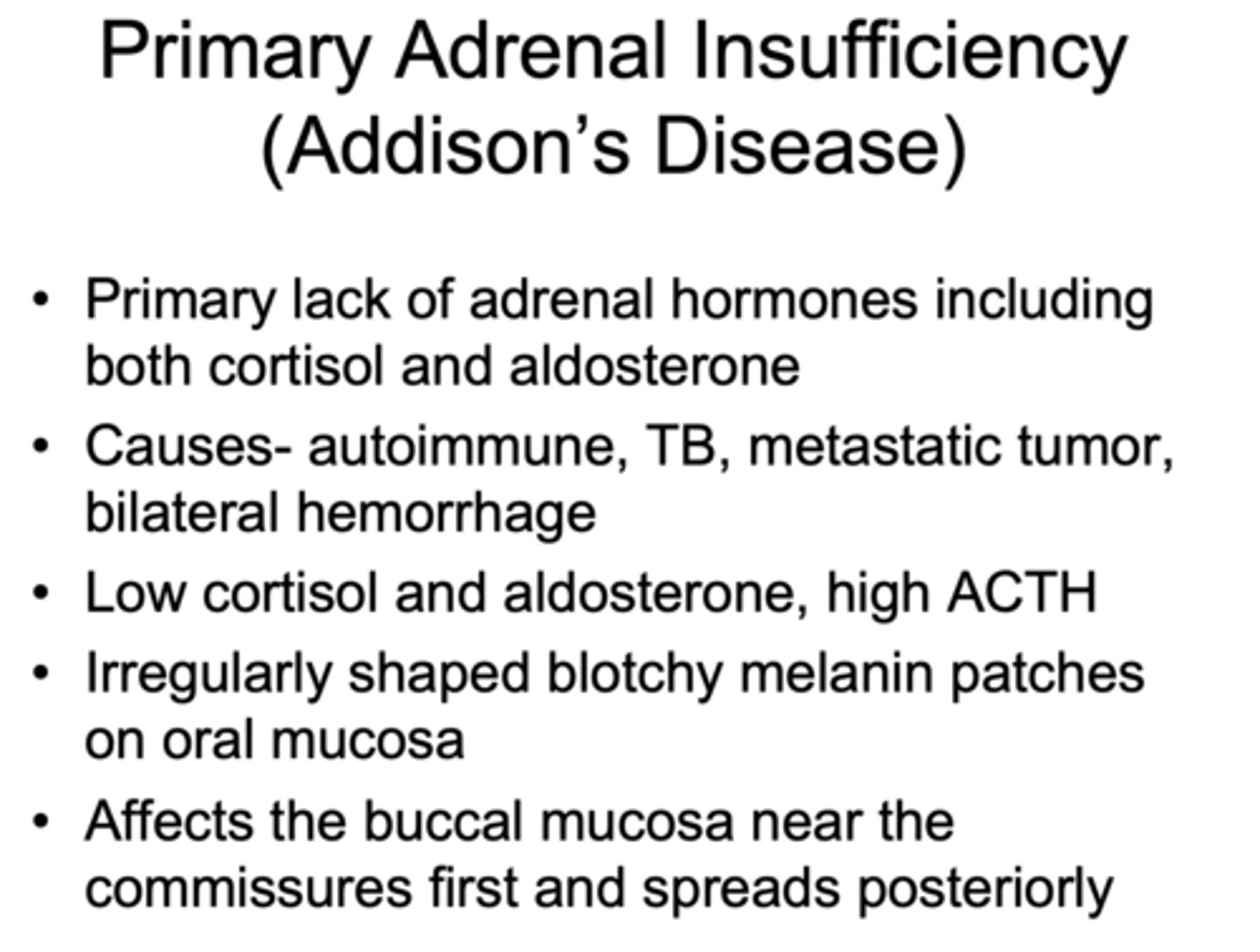
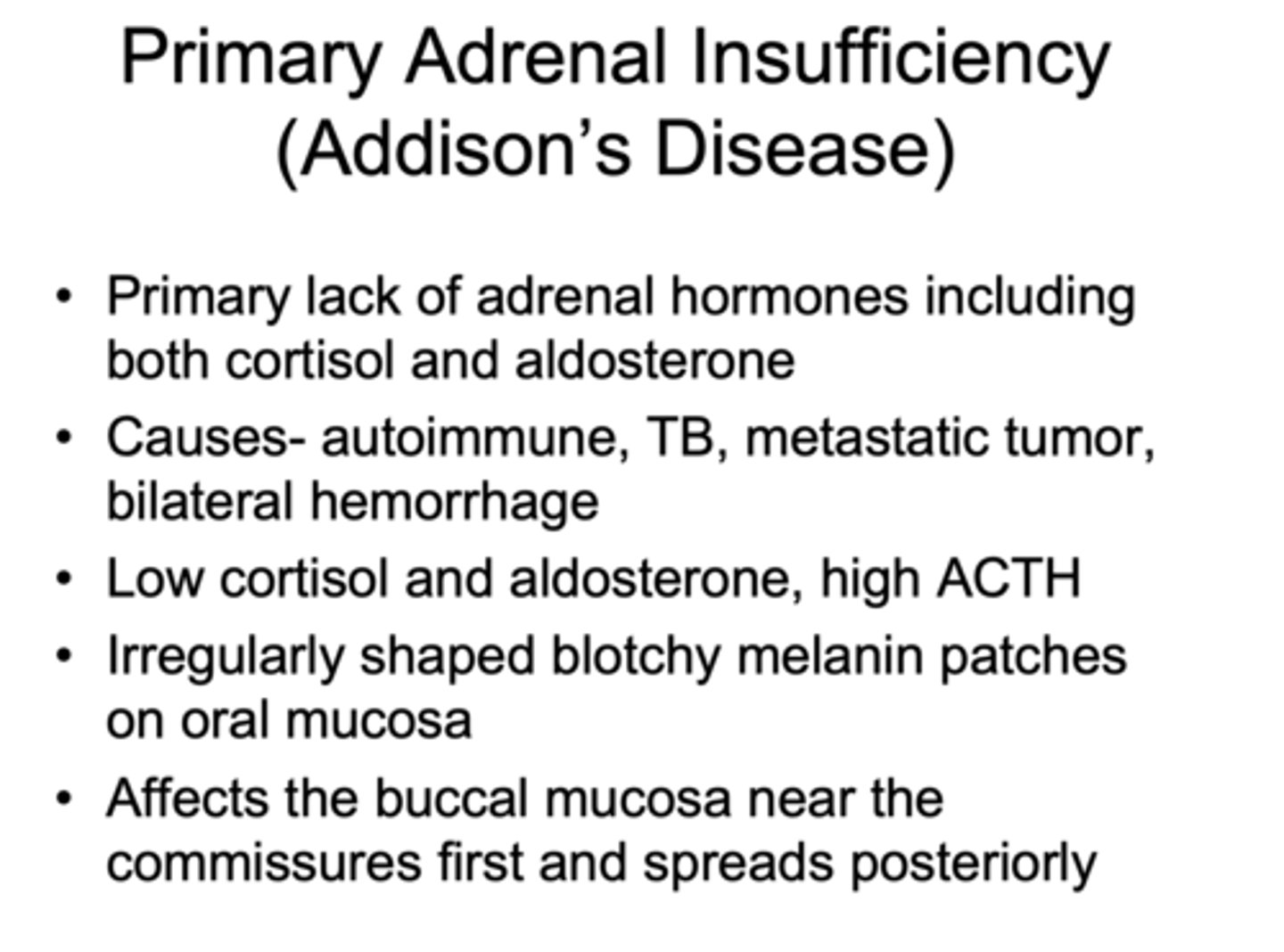
what are signs of Addison’s disease?
- Low cortisol and aldosterone, high ACTH
- Irregularly shaped blotchy melanin patches on oral mucosa
- Affects the buccal mucosa near the commissures first and spreads
what causes Addison’s disease?
- Primary lack of adrenal hormones including both cortisol and aldosterone
What condition has the following causes?
- Autoimmune, TB, metastatic tumor, bilateral hemorrhage
Addison's Disease

What disease is characterized by low cortisol and aldosterone and high ACTH?
Addison's Disease
t/f: Patients taking steroids for more than 2 weeks may be adrenally insufficient and may require steroid coverage for up to a year after treatment
true

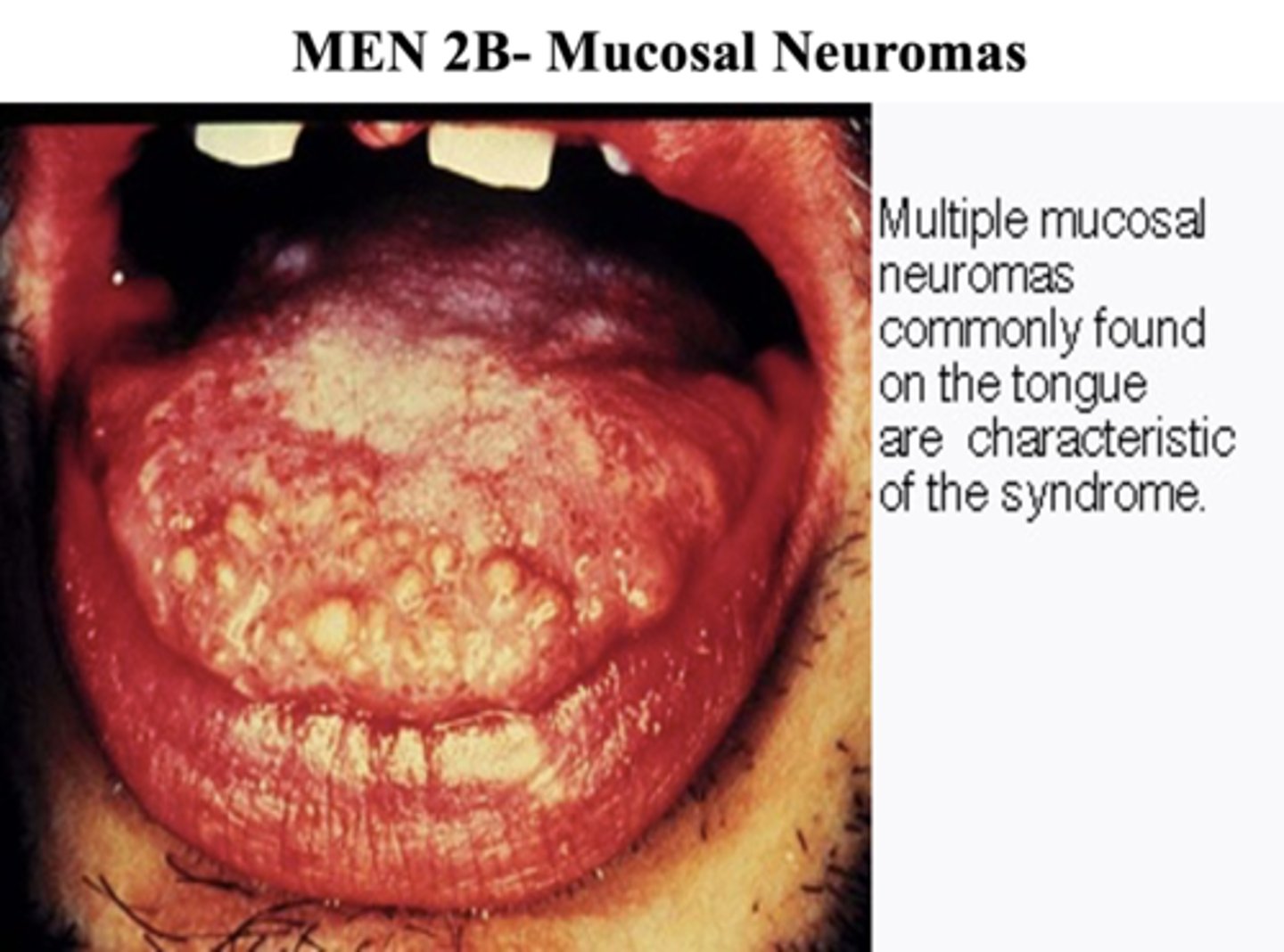
mucosal neuromas commonly found on the tongue are characteristic of ________
MEN2B
Key concept:
_____________ is a heterogeneous disease. For your patient, try to understand their underlying pathophysiology, glycemic control and treatment.
Diabetes mellitus

Key concept:
Ideally, blood sugars should be under ________mg/dl (A1C under 8%) for optimal healing with dental procedures though sometimes blood sugars may be elevated due to infection or inflammation in the mouth. In this situation, dental treatments may improve blood sugar control.
180

Key concept:
____________ is strongly associated with diabetes and is a risk factor for cardiovascular and renal morbidity and mortality. Treatment of ____________ may improve glycemic control.
Periodontal disease

Key concept:
For patients on insulin, __________ (intermediate or long acting) should never be held for a procedure. The dose may need adjustment prior to a procedure
Basal insulin

Key concept:
Holding basal insulin in patients dependent on insulin (such as autoimmune diabetes) can lead to _____________
Ketoacidosis

Key concept:
_____________ (short acting, mealtime) will be held if a patient will be skipping a meal
Bolus insulin

Key concept:
Among oral medications, _______________(such as glipizide, glimepiride, repaglinide) should be held if a patient will fasting for a procedure. This will avoid hypoglycemia. All other oral medications (as well as injectable GLP-1 agonists) can be continued as they do not cause hypoglycemia.
insulin secretagogues

Key concept:
Nausea, vomiting and fruity breath are symptoms and signs of ____________. In ____________, counterregulatory hormones including glucagon may be very high in association with low insulin levels. Patients with diabetic ketoacidosis require emergency treatment with IV fluids, insulin, potassium along with treatment for any underlying cause.
ketoacidosis (DKA)

Key concept:
Symptoms of ______________ include sweating, tremor, palpitations and possibly confusion. Treatment may include oral glucose, IV dextrose and subcutaneous glucagon if severe. Epinephrine can also help to reverse this.
hypoglycemia

Key concept:
Common disorders of calcium metabolism include what three things?
- Primary hyperparathyroidism
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Chronic kidney disease

Key concept:
_____________ is very common in older adults. It is diagnosed either by a bone density scan (DXA scan) or in a patient who has had a fragility (low trauma) fracture
Osteoporosis

Key concept:
Along with adequate calcium, vitamin D and weight bearing exercise, antiresorptive medications including bisphosphonates and denosumab are the most common class of medication used to treat ______________. A very rare side effect is osteonecrosis of the jaw (usually seen in patients with other risk factors such as cancer). Ideally, a patient requiring a dental procedure should have the procedure and heal up prior to starting an antiresorptive medication.
osteoporosis

Key concept:
Common _____________ disorders include hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism and thyroid nodules. In primary hyperthyroidism, TSH is very low and thyroid hormones (T4, T3) are elevated. In primary hypothyroidism, TSH is elevated and thyroid hormones are low normal or low. The _____________ should be shielded during dental xrays.
Thyroid

Key concept:
_______________ may present in the dental office with malocclusion, prognathism and teeth which are spaced and tipped outwards. It is caused by a growth hormone producing pituitary adenoma in almost all cases.
Acromegaly

Key concept:
_______________ is caused by an excess of glucocorticoids. The most common cause is chronic therapeutic steroids such as may be used for diseases including asthma and post transplant. Endogenous _____________ can be from pituitary adenomas, adrenal adenomas and certain ectopic tumors. It can lead to periodontitis and bleeding gums.
Cushing’s syndrome

Key concept:
_______________ is the name often used for primary adrenal insufficiency. The most common cause is autoimmune disease. Patients are deficient in cortisol and aldosterone which require replacement. Untreated, it is associated with pigmentation of the skin and mucous membranes including the mouth due to high levels of ACTH (and MSH).
Addison’s disease

Key concept:
All patients on long term ______________ (usually Hydrocortisone or Prednisone) for primary adrenal insufficiency, hypopituitarism or a non-endocrine disease require "stress" doses for infections and significant dental procedures. For most outpatient procedures, doses may be doubled for 1 or more days. For inpatient surgery, higher oral doses or IV hydrocortisone may be given. Patients should resume their usual daily dose as soon as their stress has resolved.
Glucocorticoid therapy
