Accounting: 3 The Double Entry Model
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
1
New cards
Tell us about source documents.
* the starting point of the accounting system
* provide evidence of financial transactions - goods/services being bought or sold and money being paid or received.
* provide evidence of financial transactions - goods/services being bought or sold and money being paid or received.
2
New cards
What are the 8 source documents used by businesses?
● sales invoices
● purchase invoices
● credit notes
● cheque counterfoils
● paying-in slip counterfoils
● cash receipts
● till rolls
● bank statements.
● purchase invoices
● credit notes
● cheque counterfoils
● paying-in slip counterfoils
● cash receipts
● till rolls
● bank statements.
3
New cards
What is a sales invoice?
the document that a seller gives to a buyer when
supplying goods or services on credit.
supplying goods or services on credit.
4
New cards
What is a purchase invoice?
received by the buyer when goods or services
are bought on credit.
are bought on credit.
5
New cards
What is a credit note?
issued to show that goods have been returned and that
they do not need to be paid for.
they do not need to be paid for.
6
New cards
How is the term ‘credit note’ used by businesses?
* when goods have been returned by customers (sales returns)
* when goods received by the business have been returned to its suppliers (purchases returns)
* when goods received by the business have been returned to its suppliers (purchases returns)
7
New cards
What is a cheque counterfoil?
provides a record of money paid out by the business.
8
New cards
What is a paying-in slip counterfoil?
provides a record of cash and cheques banked by the business.
9
New cards
What is a cash receipt?
receipts for goods and services that have been paid for at
the time of purchase, whether by cash, cheque or debit card.
the time of purchase, whether by cash, cheque or debit card.
10
New cards
What is a till roll?
lists the amounts sold and paid for during a specific day and the total value of cash sales during that day.
11
New cards
What is a bank statement?
* sent to businesses by their banks
* show each individual receipt and payment to and from the bank account, as well as the balance at a given date.
* the source document for payments and receipts that are not recorded on counterfoils: standing orders, direct debits, debit card transactions, credit transfers, dishonoured cheques and bank charges and interest.
* show each individual receipt and payment to and from the bank account, as well as the balance at a given date.
* the source document for payments and receipts that are not recorded on counterfoils: standing orders, direct debits, debit card transactions, credit transfers, dishonoured cheques and bank charges and interest.
12
New cards
What is a standing order?
an instruction from a business to its bank to make fixed payments at regular intervals, e.g. a loan repayment.
13
New cards
What is a direct debit?
an arrangement where a business authorises its bank to allow another business to transfer money from its bank account on pre-arranged dates.
14
New cards
What is a debit card?
a convenient and quick way to make payments from
a bank account.
a bank account.
15
New cards
What is a credit transfer?
receipts or payments made electronically in or out
of a bank account.
of a bank account.
16
New cards
What is a dishonoured cheque?
* Cheques that have been returned by the bank because there is not enough money in the account to make the payment.
* These can either be cheques paid by the business or cheques received by the business.
* These can either be cheques paid by the business or cheques received by the business.
17
New cards
What are bank charges?
* Expenses to a business for using the bank account or interest for being overdrawn
* They are taken directly out of the bank account by the bank.
* They are taken directly out of the bank account by the bank.
18
New cards
What is a trade discount?
given for buying in bulk
19
New cards
What is a cash discount?
offered to encourage quick payment
20
New cards
What are the 6 books of prime entry?
● sales journal
● purchases journal
● sales returns journal
● purchases returns journal
● cash book
● general journal.
● purchases journal
● sales returns journal
● purchases returns journal
● cash book
● general journal.
21
New cards
What is a sales journal?
lists the invoices for credit sales.
22
New cards
What is the purchases journal?
lists the invoices for credit purchases.
23
New cards
What is the sales returns journal?
lists the credit notes issued by the business.
24
New cards
What is the purchases returns journal?
lists the credit notes received by the
business.
business.
25
New cards
What is the cashbook?
used to record bank receipts and bank payments, as well as cash discount allowed, and cash discount received.
26
New cards
What is the left side of the (three column) cashbook used to record?
● a positive bank balance at the start of the month
● amounts received by the business (e.g. payments from customers)
● cash discounts allowed to customers who have paid promptly.
● amounts received by the business (e.g. payments from customers)
● cash discounts allowed to customers who have paid promptly.
27
New cards
What is recorded at the right side of the (three column) cashbook?
● a negative bank balance at the start of the month
● amounts paid by the business (e.g. to its suppliers for goods received)
● cash discount received from suppliers for prompt payment.
● amounts paid by the business (e.g. to its suppliers for goods received)
● cash discount received from suppliers for prompt payment.
28
New cards
What is the general journal?
used to record non-routine transactions.
29
New cards
What is the receivables ledger?
includes T-accounts for each credit customer.
e.g. invoices, credit notes, payments, discounts and the amount owed by that customer.
e.g. invoices, credit notes, payments, discounts and the amount owed by that customer.
30
New cards
What is the payables ledger?
includes T-accounts for each credit supplier.
e.g. invoices, credit notes, payments, discounts and the amount owed to that supplier.
e.g. invoices, credit notes, payments, discounts and the amount owed to that supplier.
31
New cards
What is the general ledger?
ledger includes T-accounts for every item that will appear in the financial statements.
e.g. @@revenue, purchases, expenses and other items in the income statement, as well as the assets and liabilities, capital and drawings for the statement of financial position.@@
e.g. @@revenue, purchases, expenses and other items in the income statement, as well as the assets and liabilities, capital and drawings for the statement of financial position.@@
32
New cards
Each invoice or credit note will be entered in one of the books of (1) entry.
Each invoice or credit note will also be entered in either the (2) ledger or the (3) ledger.
The monthly total from each book of prime entry will be entered in the relevant section of the (4) ledger.
Each invoice or credit note will also be entered in either the (2) ledger or the (3) ledger.
The monthly total from each book of prime entry will be entered in the relevant section of the (4) ledger.
1. prime
2. receivables
3. payables
4. general
33
New cards
What is an asset? (with examples)
anything that is owned by a business
* physical objects such as land, buildings, vehicles, equipment, machinery, furniture and inventory
* cash or money in a bank account
* customers who owe money to the business (‘trade receivables’).
* physical objects such as land, buildings, vehicles, equipment, machinery, furniture and inventory
* cash or money in a bank account
* customers who owe money to the business (‘trade receivables’).
34
New cards
What is a liability? (with examples)
anything that is owed by a business
* amounts owed to suppliers (‘trade payables’)
* bank overdraft or bank loan.
* amounts owed to suppliers (‘trade payables’)
* bank overdraft or bank loan.
35
New cards
What are running costs?
costs involved in running the business
* purchases, carriage, rent, wages, rent, light and
heat, bills for electricity, gas and telephone, and any other expenses.
* purchases, carriage, rent, wages, rent, light and
heat, bills for electricity, gas and telephone, and any other expenses.
36
New cards
What is income?
includes sales revenue, capital, rent received, discount received and any other sources of income.
37
New cards
Do you debit or credit capital (personal savings)?
credit.
there is no T account for capital.
there is no T account for capital.
38
New cards
Do you debit or credit sales returns?
debit.
39
New cards
Do you debit or credit purchases returns?
credit.
40
New cards
Purchases of non-current assets such as vehicles or equipment are not ‘purchases’. Do you debit or credit ‘vehicles’ or ‘equipment’?
debit.
41
New cards
‘Drawings’ – money or goods taken out of the business by the owner. Debit or credit?
Debit.
Not an expense on IS
Not an expense on IS
42
New cards
Write out the layout for an income statement of a sole trader.
John Smith
Income statement for the year ended 30 June 20–8
Revenue
Sales returns (or ‘returns in’)
Opening inventory
Purchases
Purchases returns (or ‘returns out’)
Carriage in
Closing inventory
Cost of sales
Gross profit
Discount received
Expenses
Discount allowed
Carriage out
Rent
Wages and salaries
Other expenses
Depreciation
Profit for the year
Income statement for the year ended 30 June 20–8
Revenue
Sales returns (or ‘returns in’)
Opening inventory
Purchases
Purchases returns (or ‘returns out’)
Carriage in
Closing inventory
Cost of sales
Gross profit
Discount received
Expenses
Discount allowed
Carriage out
Rent
Wages and salaries
Other expenses
Depreciation
Profit for the year
43
New cards
What is cost of sales?
the cost to the business of buying or making the goods
that it has sold.
that it has sold.
44
New cards
What is carriage in?
* the cost of transporting goods purchased by the business
* is part of cost of sales
* is part of cost of sales
45
New cards
What is carriage out?
* the cost of transporting goods sold by the business
* is an expense
* is an expense
46
New cards
What is depreciation?
the decrease in the value of non-current assets
such as machinery and vehicles.
such as machinery and vehicles.
47
New cards
What is the statement of financial position?
* shows the financial situation of a business at a specific moment in time.
* summarises the assets (what a business owns), liabilities (what a business owes) and the capital of a business.
* summarises the assets (what a business owns), liabilities (what a business owes) and the capital of a business.
48
New cards
what are non-current assets?
* resources owned by the business that it intends to keep for more than one year, e.g. land, buildings, premises, machinery, equipment, vehicles, furniture, fixtures and fittings.
49
New cards
what are current assets?
* resources that are owned by a business and are already cash or are intended to become cash within the next 12 months.
* e.g. inventory, trade receivables, prepayments, cash in the bank and cash in hand.
* e.g. inventory, trade receivables, prepayments, cash in the bank and cash in hand.
50
New cards
what is inventory?
goods that are intended for resale but have not yet
been sold.
been sold.
51
New cards
what are trade receivables?
* customers that owe money to the business because they have bought goods on credit.
52
New cards
what are current liabilities?
* amounts owed by the business that must be repaid within one year.
* e.g. trade payables, accruals, bank overdraft and taxation.
* e.g. trade payables, accruals, bank overdraft and taxation.
53
New cards
what are trade payables?
suppliers that are owed money by a business because
they have sold goods to the business on credit.
they have sold goods to the business on credit.
54
New cards
How to calculate net current assets?
current assets - current liabilities
55
New cards
what are non-current liabilities?
* amounts owed by a business that will be fully repaid after more than one year.
* e.g. bank loans, mortgages and debentures.
* e.g. bank loans, mortgages and debentures.
56
New cards
how to calculate net assets?
Non-current liabilities + Net current assets – Non-
current liabilities
current liabilities
57
New cards
how to calculate capital?
Balance at start of the year + Capital introduced + Profit for
the year – Drawings
the year – Drawings
58
New cards
What are drawings?
money or goods taken out of the business by the owner.
59
New cards
Set out an statement of financial position.
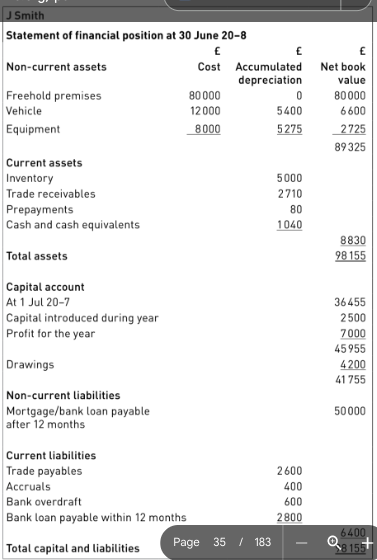
60
New cards
What is a prepayment?
* an expense that has been paid in advance. It is an expense that relates to the next accounting period.
* shown as a current asset.
* decreases the expense to which it relates.
* shown as a current asset.
* decreases the expense to which it relates.
61
New cards
What is the double entry for a prepayment?
* debit ‘prepayment’, credit the expense on the income statement (e.g.rent)
* will also be an additional current asset on sfp
* will also be an additional current asset on sfp
62
New cards
what is an accrual?
* an expense for services that have been used but not yet invoiced to the business at the end of the accounting period.
* shown as a current liability and it increases the expense to which it relates.
* shown as a current liability and it increases the expense to which it relates.
63
New cards
what is the double entry for an accrual?
* debit the expense on the income statement (e.g. ‘electricity’) and credit ‘accrual’ (a current liability).
* will be an additional current liability on SFP
* will be an additional current liability on SFP
64
New cards
what is irrecoverable debt?
* a debt that will not be paid – the business will not receive the amount owed by a customer who has been sold goods on credit.
* could be bc customer is bankrupt or company closed down
* could be bc customer is bankrupt or company closed down
65
New cards
what is the double entry for irrecoverable debt?
* Debit ‘Irrecoverable debts’ – an expense in the income statement.
* Credit ‘Trade receivables’ – this decreases this figure in current assets.
* Credit ‘Trade receivables’ – this decreases this figure in current assets.
66
New cards
what is depreciation?
decrease in value of non-current assets over a period of time.
67
New cards
what are the 2 formulae for straight-line method depreciation?
(Cost – Expected residual value) ÷ Expected years of useful life.
\
Cost × Percentage given.
\
Cost × Percentage given.
68
New cards
what is the formula for reducing balance method depreciation?
Depreciation = Percentage × Net book value
69
New cards
how to calculate nbv?
Net book value = Cost - Provision for depreciation
70
New cards
what is the double entry for depreciation?
* Debit ‘Depreciation’ (which is an expense on the income statement).
* Credit ‘Provision for depreciation’
\
\
* provdep is subtracted from the cost of the non-current assets on the statement of financial position.
* Credit ‘Provision for depreciation’
\
\
* provdep is subtracted from the cost of the non-current assets on the statement of financial position.
71
New cards
how to calculate profit/loss on disposal of nca?
what to know when calculating?
what to know when calculating?
Disposal proceeds - Net book value
\
* if figure is negative (i.e. the net book value is greater than the disposal proceeds), then the ‘loss on disposal’ is treated as expense on income statement
* if figure is positive (i.e. disposal proceeds are greater than the net book value), then ‘profit on disposal’ is shown as income after the gross profit on the income statement.
\
* if figure is negative (i.e. the net book value is greater than the disposal proceeds), then the ‘loss on disposal’ is treated as expense on income statement
* if figure is positive (i.e. disposal proceeds are greater than the net book value), then ‘profit on disposal’ is shown as income after the gross profit on the income statement.
72
New cards
What is accrued income (income due)?
* an amount due to a business that has not been received at the end of the financial year
73
New cards
What is the double entry for accrued income (income due)?
● Debit ‘income due’ (a current asset on the statement of financial position).
● Credit the source of income on the income statement (e.g. increase ‘rent receivable’).
* increases that item on the
income statement.
● Credit the source of income on the income statement (e.g. increase ‘rent receivable’).
* increases that item on the
income statement.
74
New cards
What is prepaid income (income received in advance)?
* payment received in advance of the accounting period to which it relates.
75
New cards
What is the double entry for prepaid income (income received in advance)?
* Debit the source of income on the income statement (e.g. decrease ‘rent receivable’).
* Credit ‘income received in advance’ (a current liability on the statement of financial position).
* decreases that item on the income statement.
* Credit ‘income received in advance’ (a current liability on the statement of financial position).
* decreases that item on the income statement.
76
New cards
What is irrecoverable debt recovered?
when a former trade receivable, whose account had been written off as an irrecoverable debt, makes a payment.
77
New cards
What is the double entry for irrecoverable debt recovered?
* Debit ‘Bank account’.
* Credit ‘Irrecoverable debts recovered’. This amount is added after gross profit on the income statement.
* Credit ‘Irrecoverable debts recovered’. This amount is added after gross profit on the income statement.
78
New cards
What is provision for doubtful debts?
* an estimate by a business of the likely amount of its trade receivables figure that may become irrecoverable.
79
New cards
What is the double entry when creating a prov for DD for the first time?
● Debit ‘Doubtful debts’ (an expense on the income statement).
● Credit ‘Provision for doubtful debts’ (which is subtracted from ‘Trade receivables’ on the statement of financial position).
● Credit ‘Provision for doubtful debts’ (which is subtracted from ‘Trade receivables’ on the statement of financial position).
80
New cards
What is the double entry when increasing a prov for DD?
● Debit ‘Increase in doubtful debts’ (an expense on the income statement).
● Credit ‘Provision for doubtful debts’ (increases the amount subtracted from ‘Trade receivables’ on the statement of financial position).
● Credit ‘Provision for doubtful debts’ (increases the amount subtracted from ‘Trade receivables’ on the statement of financial position).
81
New cards
What is the double entry when decreasing a prov for DD?
● Debit ‘Provision for doubtful debts’ (decreases the amount subtracted from ‘Trade receivables’ on the statement of financial position).
● Credit ‘Increase in doubtful debts’ (added after gross profit on the income statement).
● Credit ‘Increase in doubtful debts’ (added after gross profit on the income statement).