Neurons, Action Potentials, and Ion Channel Mechanisms in Neurophysiology
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What are neurons compared to in the context of circuits?
Neurons are compared to segments of wire that can be connected in multiple ways to drive various functions.
What is the function of the axon in a neuron?
The axon relays signals received on one end and releases neurotransmitters at the other end to communicate with other circuit components.
What is the synapse?
The junction between circuit components where signals are transmitted.
What role do dendrites play in neuron function?
Dendrites allow input from many different circuits to the cell body.
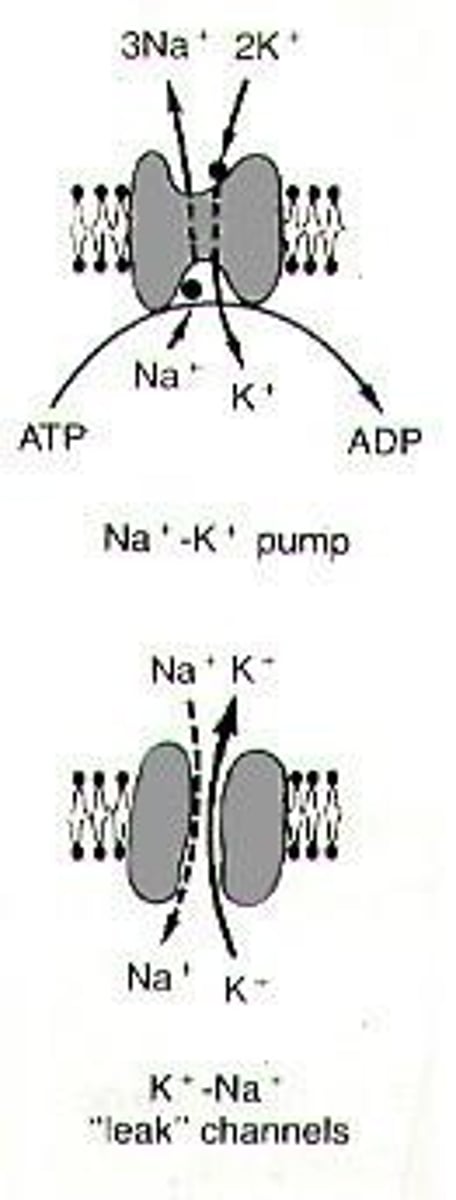
How does a neuron establish a resting potential?
By creating a polarized membrane with high intracellular concentrations of K+ and allowing some K+ to leak out, resulting in a negative charge inside the membrane.
What is the resting potential of a neuron?
The resting potential is -90 mV.
What is the role of the Na+-K+ pump in neurons?
The Na+-K+ pump establishes high intracellular concentrations of K+ by exchanging Na+ for K+, which is essential for maintaining the resting potential.
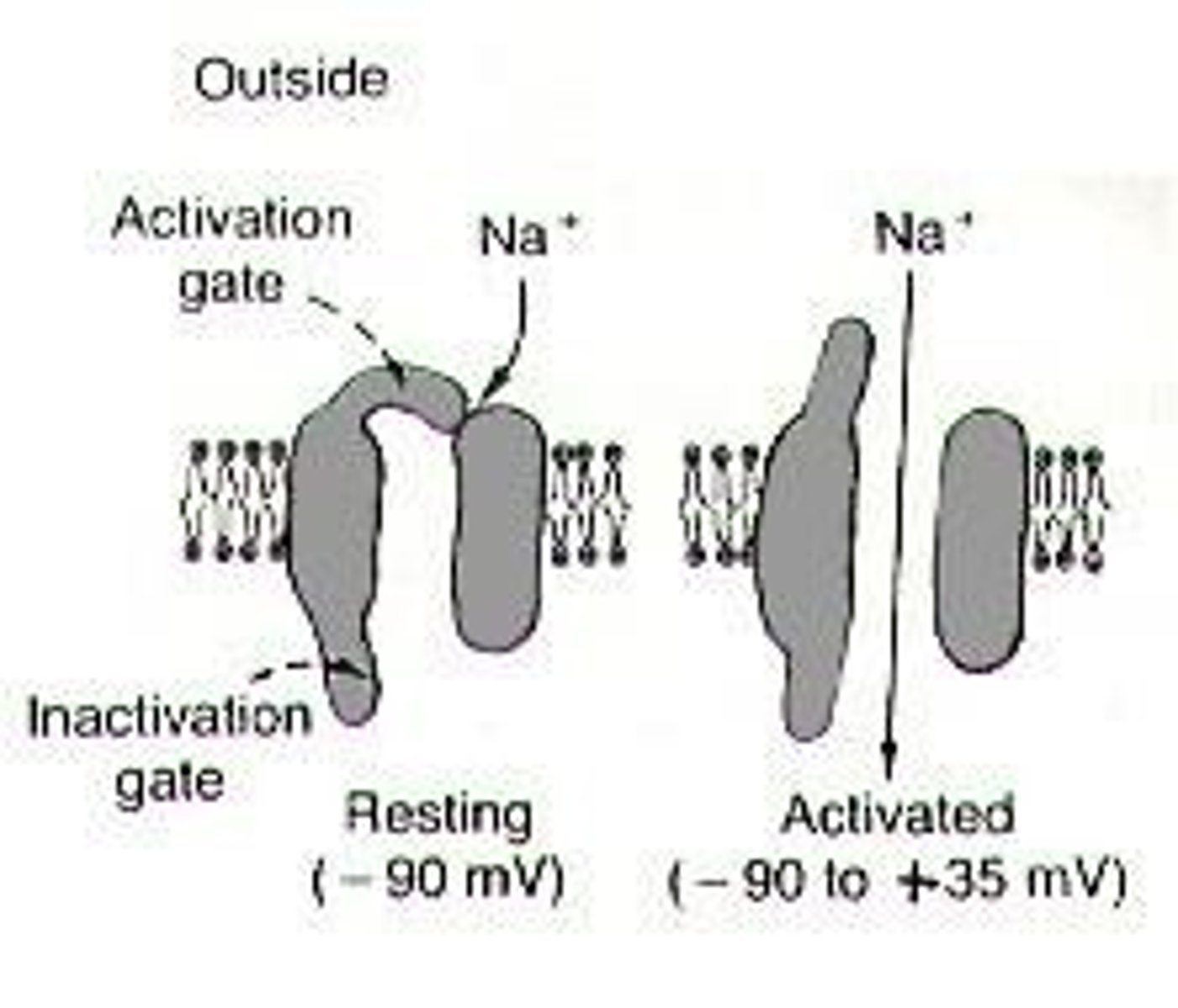
How does depolarization occur in a neuron?
Depolarization occurs when extracellular Na+ flows into the cell, reducing the negative charge and initiating an action potential.
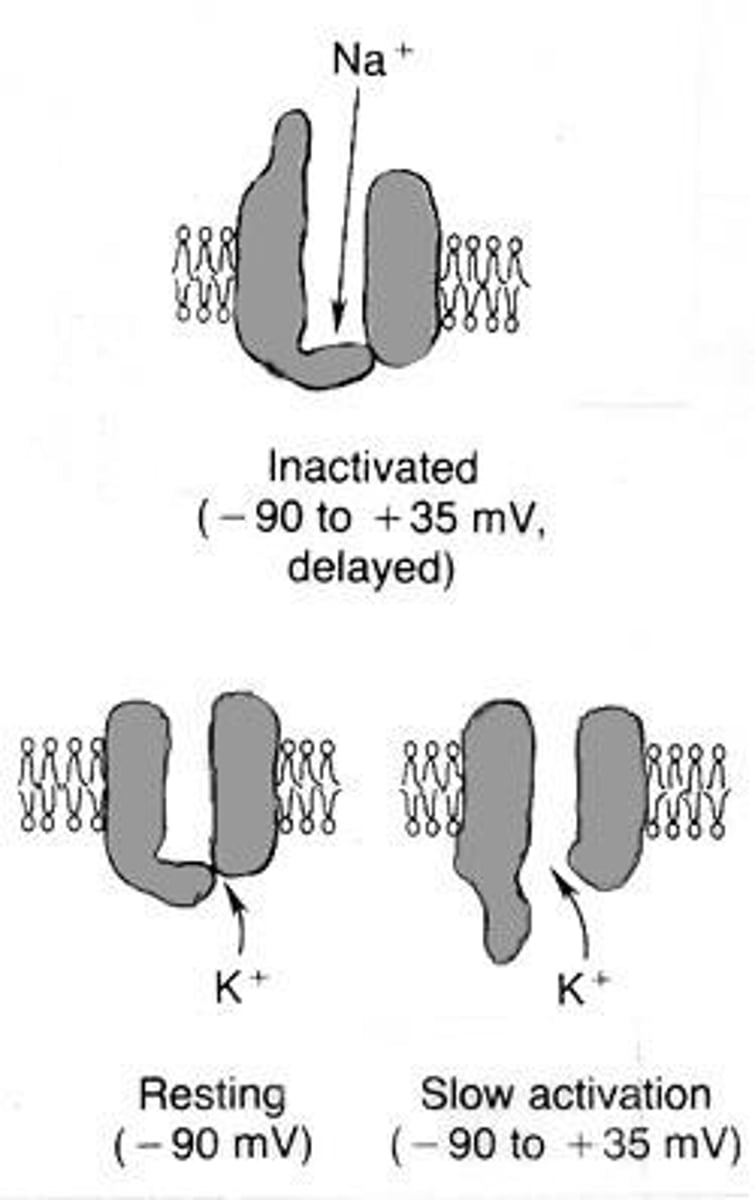
What triggers the opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels?
The membrane voltage reaching -50 mV triggers the opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels.
What initiates an action potential in neurons?
An action potential is initiated by the binding of neurotransmitters or other stimuli that reduce membrane charge.
What happens during the repolarization phase of an action potential?
Na+ channels close, K+ channels open, allowing K+ to exit the cell, restoring the resting potential.
What is the primary metabolic demand placed upon neurons?
The generation of ATP for Na+/K+ pumps is the predominant metabolic demand.
How much energy does the brain represent in relation to body mass and energy expenditure?
The brain represents 2% of total body mass but accounts for 15% of energy expenditure at rest.
What is the primary energy source for neurons?
Neurons utilize blood glucose almost exclusively for energy demands.
How do hypoglycemia and hypoxemia affect neuronal function?
They affect neuronal function significantly, even when disturbances in other cell types are not apparent.
What effect does increased extracellular K+ have on neurons?
Increased extracellular K+ diminishes the function of K+ leak channels, affecting the resting potential.
What role does Ca++ play in the function of voltage-gated sodium channels?
Ca++ stabilizes the outer gate of the voltage-gated sodium channel, preventing inappropriate opening.
What can cause a hyperexcitable state in neurons?
Reductions in serum Ca++ by 50% can lead to inappropriate opening of sodium channels, causing hyperexcitability.
What compounds are to be explained in the literature search assignment?
Lidocaine, agents of paralytic seafood poisoning (brevotoxin, tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin), and scorpion toxins.
What is the mechanism of action for lidocaine?
Lidocaine works by blocking voltage-gated sodium channels, preventing action potentials.
What is the effect of tetrodotoxin on neuronal function?
Tetrodotoxin blocks sodium channels, inhibiting action potential generation.
What is the role of brevotoxin in neuronal signaling?
Brevotoxin alters sodium channel function, leading to prolonged depolarization.
What is the effect of scorpion toxins on action potentials?
Scorpion toxins can modify sodium channel kinetics, leading to increased excitability.