Spinal Cord and PNS
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
reflexive
The spinal cord carries out ________________ actions
sensory
Are ascending axons motor or sensory?
motor
Are descending axons motor or sensory?
conduction, integration, automation
What are the three principal functions of the spinal cord?
both
Do spinal neurons receive ascending or descending inputs?
motor neurons, interneurons (central pattern generators)
During automation, input are converted to reflexive outputs by what two things?
Medullary cone
tapered tip of spinal cord
L1 adult, L3 birth
What level of the spine does the spinal cord terminate?
cauda equina
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord in the lumbar cistern
cervical thoracic lumbar sacral coccygeal
Name the levels of the spinal cord in order
8, 12, 5, 5, 1
List the # of pairs of spinal nerves in each of the spinal cord segments from cervical to coccygeal
cervical, lumbosacral
List the enlargements found in the spine
upper limbs
The cervical enlargement correspond to the nerve plexus innervating the __________________
lower limbs
The lumbosacral enlargement correspond to the nerve plexus innervating the __________________
epidural space, thick pia mater anchor, no periosteal layer
Menigeal characteristics unique to the spinal cord
dentate ligaments
extensions of the pia that extend out from the spinal cord surface to attach and anchor the spinal cord to the dura
filum terminale
fibrous extension of the pia mater and dura mater that anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx
inside
Gray matter is on the ____________ of the spinal cord
sensory interneurons
Neurons located in the posterior horns of the spinal cord
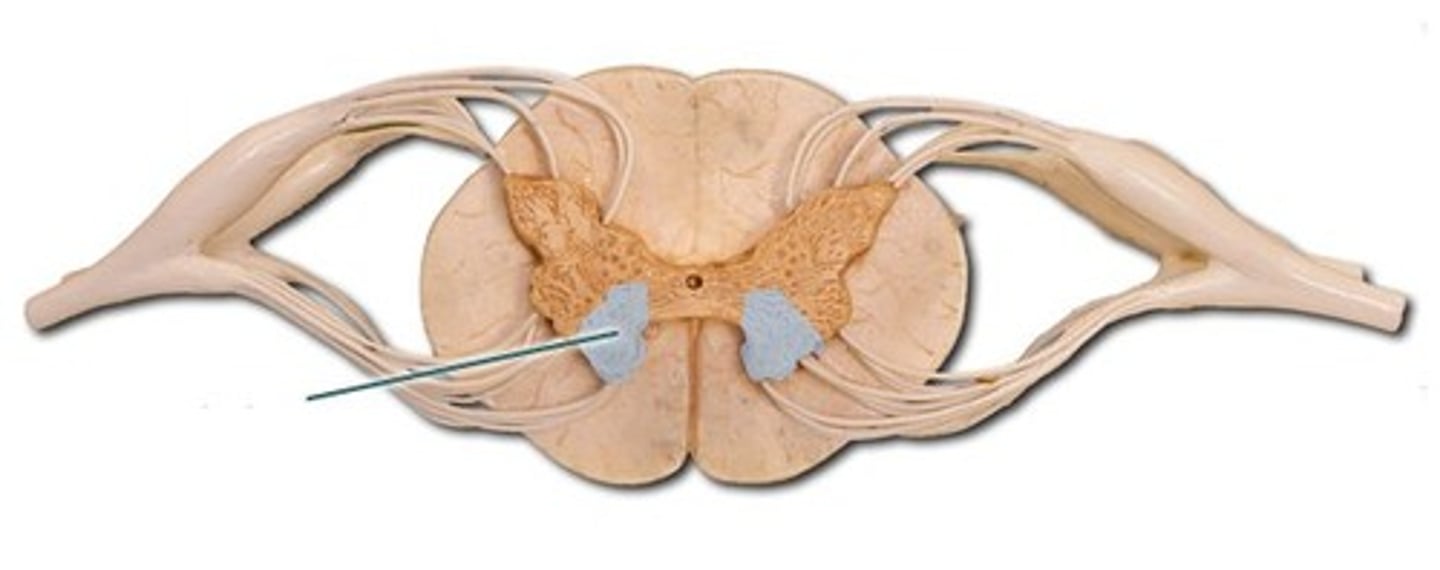
motor neurons
Neurons located in the anterior horns of the spinal cord
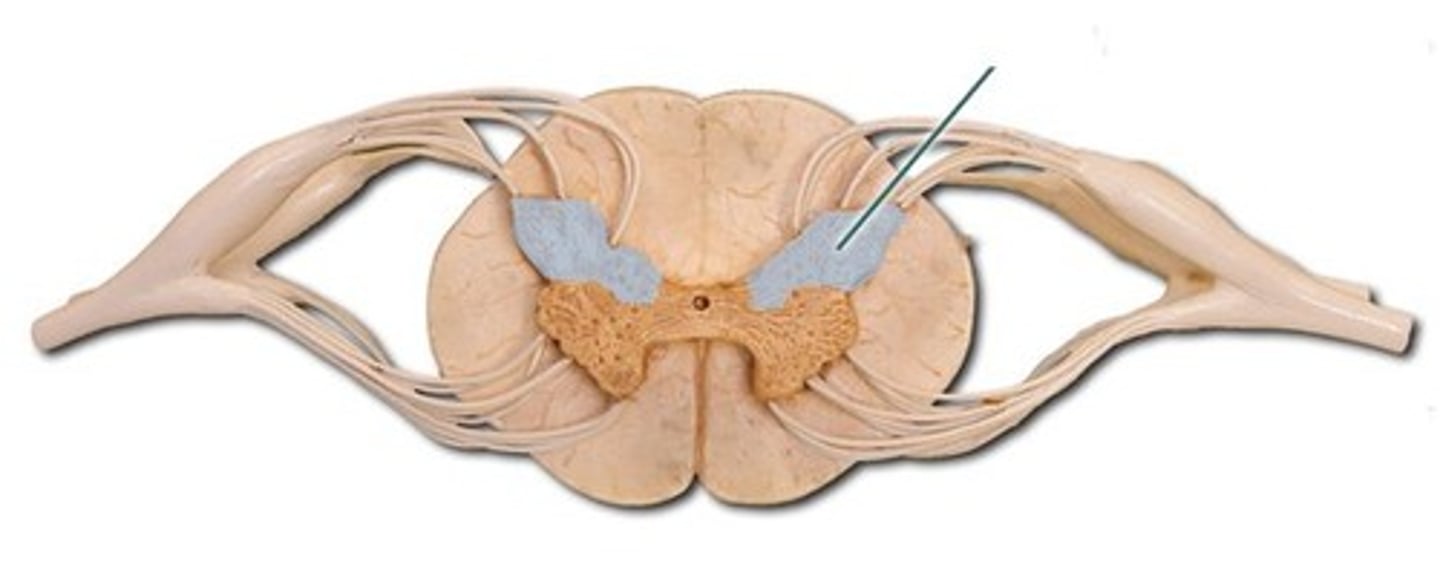
autonomic neurons
Neurons located in the lateral horns of the spinal cord
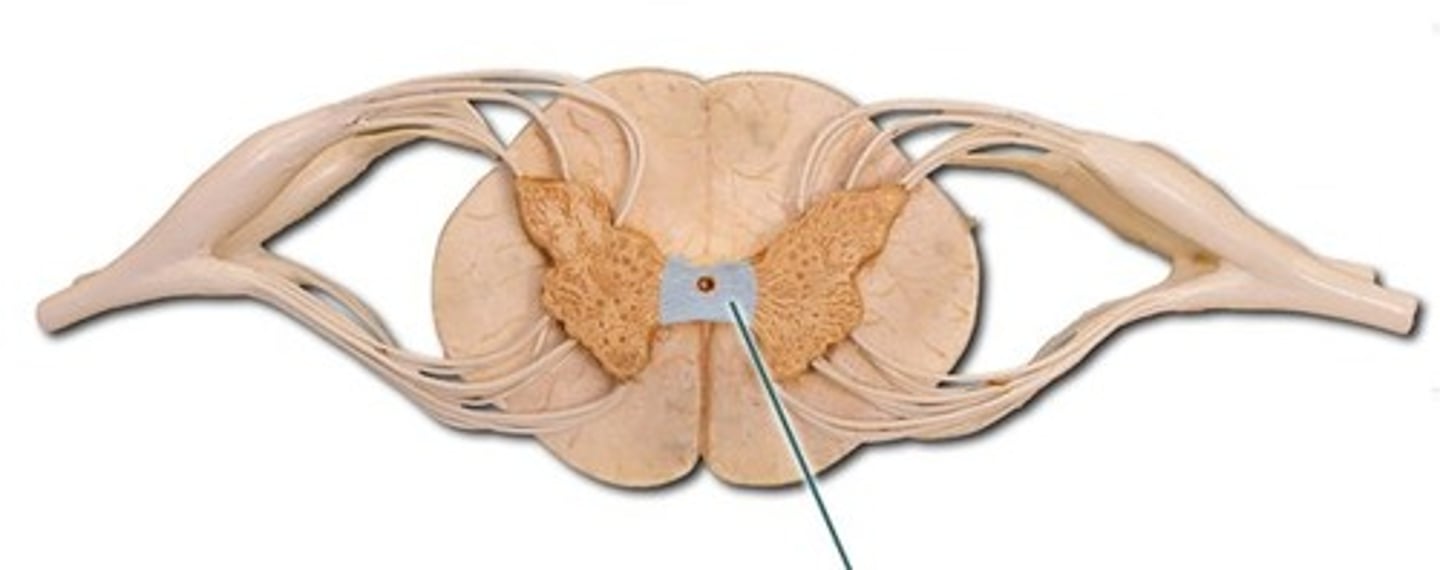
gray commissure
A strip of gray matter interneurons with unmyelinated axons to connect both sides of the spinal cord
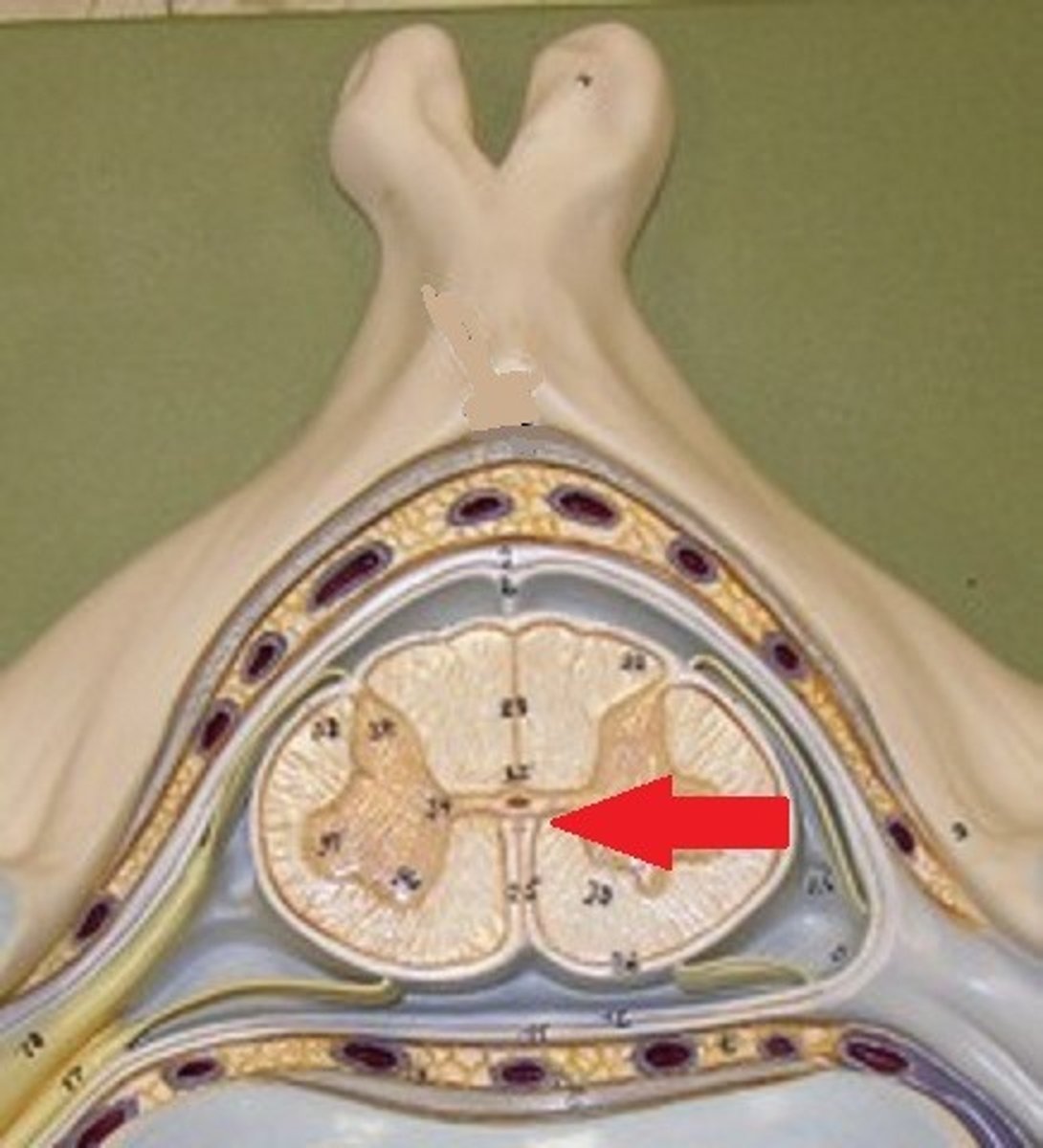
central canal
A tiny channel found within the spinal cord's gray matter, existing as an extension of the fourth ventricle
funiculi
Another name for long-range tracts, found in white matter
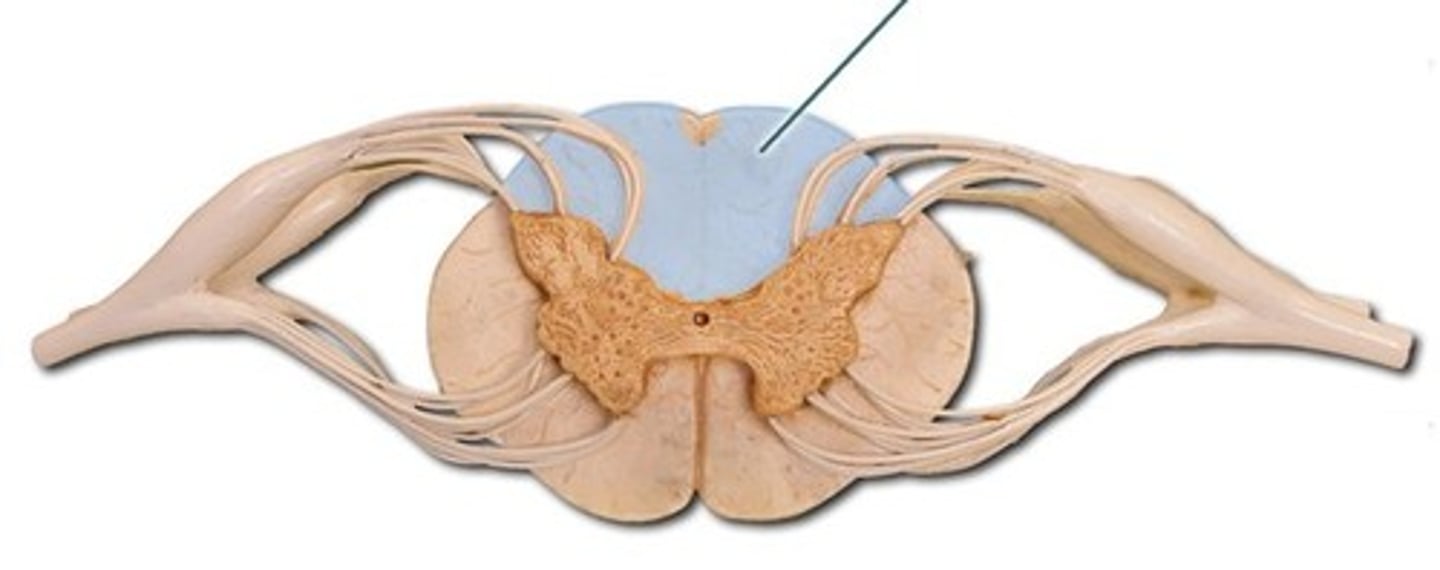
posterior funiciuli
white matter containing the posterior column's fibers, which transmit information concerning tactile sense from the body to the brain through 1º afferents
anterior funiculus
the white matter of the spinal cord transmitting motor control information
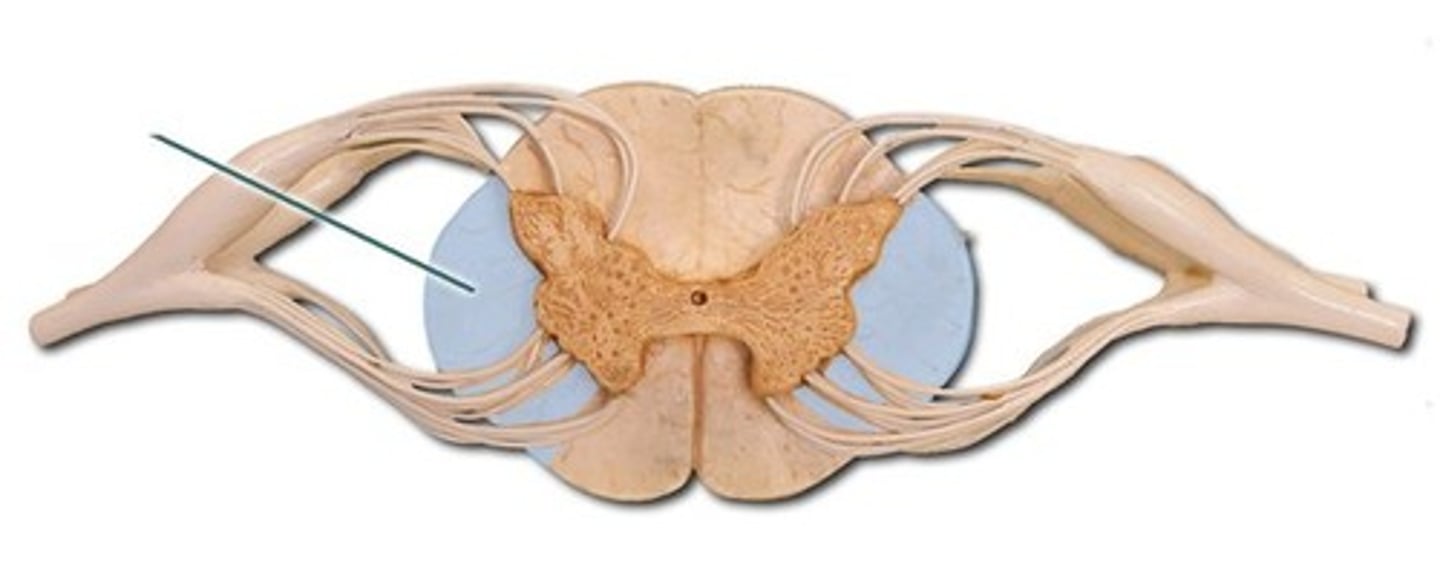
lateral funiculus
white matter region on each lateral side of the spinal cord composed of sensory AND motor tracts
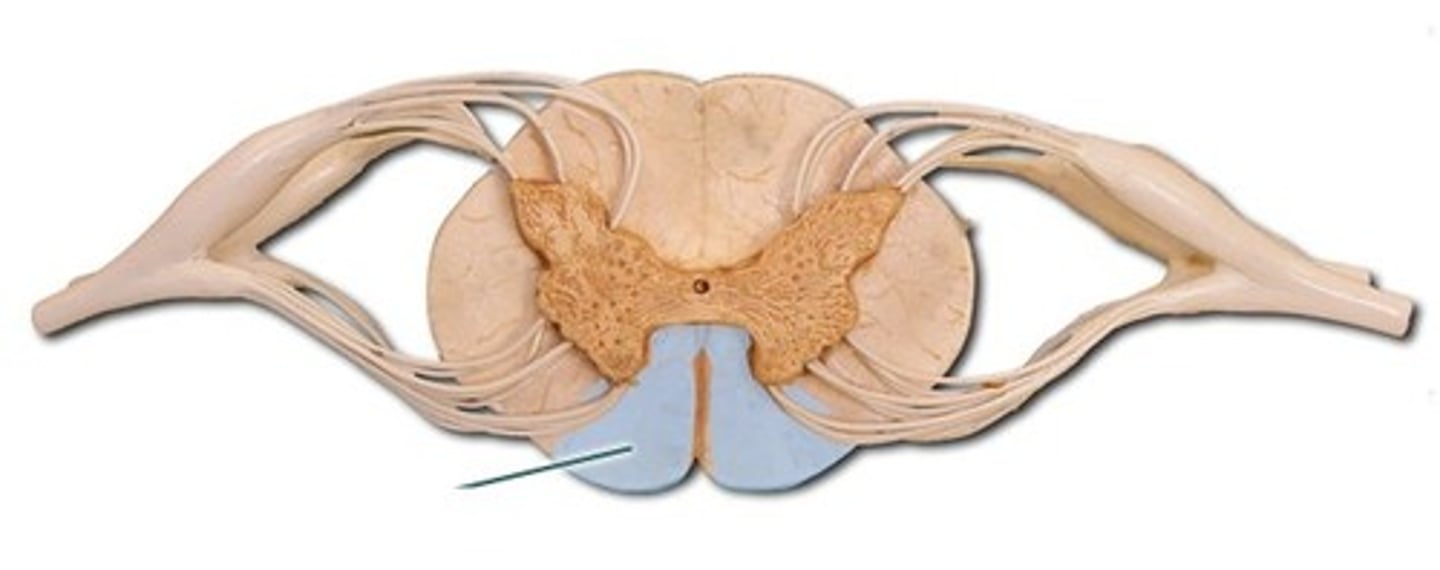
white commissure
connects the white matter of the right and left sides of the spinal cord
white commissure
Where do myelinated tracts in the spinal cord decussate?
spinothalamic tract
Tract containing sensory fibers to transmit pain and temperature information to both sides of the both
anterior corticospinal tract
division of the corticospinal pathway that travels through the ventral (anterior) column of the spinal cord and controls axial musculature through the medial motor neurons in the ventral (anterior) horn
decreases
White matter in the spinal cord __________________ from top to bottom
dorsal root ganglia
Ascending tract first order neuron resides here
decussate
Ascending tract second order neurons always ___________
thalamus
Ascending tract third order neurons are always here
2
Descending spinal tracts are composed of what number of neurons?
upper motor, lower motor
The types of neurons in the descending spinal tract
upper motor
Which neurons in the descending tracts decussate?
muscle
Lower motor neurons have map to _________________
contralateral tactile sensation
The PCML spinal tract conveys:
Fasciculi
PCML first order comes from:
medulla, medial lemniscus
PCML second order neurons are found in the _____________, decussate, and form the ___________________
ventral posterior thalamus
PCML third order neuron are found here
anterolateral spinal tracts
conveys contralateral pain and temperature sensation
dorsal horn
anterolateral spinal tract first order neurons synapse here
anterolateral tracts (anterior and lateral funiculi)
anterolateral spinal tract second order neurons decussate and form ________________________
ventral posterior thalamus
anterolateral spinal tract third order neurons are found here when coming from spinothalamic tracts
brainstem
anterolateral spinal tract third order neurons are found here when coming from spinoreticular tracts
conveys ipsilateral nonconscious proprioception
What do we need to remember about the spinocerebellar tract?
contricospinal tracts
tract conveying contralateral conscious movement
pyramidal decussation
location at which corticospinal tract fibers cross the midline and segregate into the anterior and lateral divisions of the pathway
contralateral limbs
in the corticospinal tract, lateral divisions of the pathway control:
bilateral axial
in the corticospinal tract, anterior divisions of the pathway control:
tectospinal tract
motor tract responsible for contralateral postural muscle tone associated with turning head to auditory/visual stimuli
reticulospinal tract
motor tract responsible for bilateral routine movements through extensors and flexors
vestibulospinal tract
motor tract for ipsilateral and bilateral gross postural adjustments subsequent to head movements to maintain balance
rubrospinal tract
motor tract responsible for motor input of gross postural tone, facilitating contralateral activity of flexor muscles, and inhibiting the activity of extensor muscles
decorticate posture
The body is rigid, the arms are stiff and bent, the fists are tight, and the legs are straight out; a result of no corticospinal tract control
decerebrate posture
The arms and legs are out straight and rigid, the toes point downward, and the head is arched backward; a result of no CST or rubrospinal tract control
reticulospinal
What tract was responsible for routine movements and spinal pattern generators?
spinal roots
a bundle of axons surrounded by connective tissue that occurs in pairs, which fuse and form a spinal nerve
motor
Ventral roots are motor or sensory?
sensory
Dorsal roots are motor or sensory?
spinal nerves
Dorsal and ventral roots form:
intervertebral foramen
Where do spinal nerves exit?
ganglia
Collection of somas outside the CNS
epineurium
Dense connective tissue that surrounds entire nerve including the ganglia
nowhere, nonexistent
Where are ventral root ganglia?
Mesoneurium
connective tissue that surrounds epineurium
perineurium
coarse connective tissue that surrounds the fascicles to form a nerve-tissue barrier
endoneurium
delicate connective tissue around individual nerve fibers in nerve: "jello for the axons to float in"
Fascicles
bundles of axons, usually being a mix os sensory and motor
fenestrated
Blood vessels are ____________ outside of the perineurium
blood-nerve barrier
Similar to blood brain barrier, but found in PNS. Contains tight junctions between vascular endothelial cells
meningeal branch
spinal nerve branch that innervates the anterior dura mater and contributes to back pain
communicating rami
carry visceral motor (sympathetic) and visceral sensory neurons to and from the sympathetic chain
white
Communicating rami which allows passage for preganglionic sympathetic neurons
gray
Communicating rami which allows passage for postganglionic sympathetic neurons
dorsal rami
branch of spinal nerve that supplies nerves to muscle of the back and the skin
ventral rami
branch of spinal nerve that supplies limbs and anterior trunk
intercostal nerves
Ventral rami in the thoracic region are termed:
plexuses
Ventral rami in any other region but the thoracic region are termed:
C1-C4
Cervical plexus, innervating the neck, shoulders, and diaphragm run from:
C5-T1
Brachial plexus, innervating the upper limbs, runs from:
L1-L4
Lumbar plexus, innervating the anterior pelvis and proximal legs, runs from:
L4 - S4
Sacral plexus, innervating the posterior pelvis and distal legs, runs from:
S4-Co1
Coccygeal plexus, innervating the post-anal region, runs from:
Dermatomes
an area of the skin supplied by nerves from a single spinal root
50%
Dermatomes overlap by what percentage?
level of injury
Dermatomes are useful for identifying what?
reflexes
Synaptic connections within the spinal cord create:
stimulated, quick, involuntary, stereotyped
4 properties of reflexes
visceral, somatic
Two types of reflexes
motor, skeletal
Somatic reflexes are mostly conscious, involving ___________ neurons and ___________ muscle
autonomic, smooth/cardiac
Visceral reflexes are mostly unconscious, involving _____________ neurons and ____________ muscle
reflex arcs
neural circuits that control reflexive behavior
sensory receptor, sensory afferents, integration center (optional interneurons), motor efferents, effector cells
the order of reflex arcs
extrafusal muscle fibers
bulk of muscle is:
alpha motor neurons
What innervates the extrafusal muscle fibers?
intrafusal muscle fibers
specialized muscle fibers with sensory fibers in the middle (without sarcomeres) and sarcomeres at the ends with gamma motor neurons