ISLAMIC ARCHITECTURE
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Saracenic Architecture
A product of a religion with no special country (it was used widely and is an architecture based on a religion)
Saracen
term employed by the greeks and romans for the tribes occupying the deserts west of the Euphrates.
Sahara
The term Saracen was derived from what desert?
Ottoman Empire, Umayyad Calliphate, and Mughal Empire
The 3 major regions of the spread of Islamic Architecture
Marble, Stone, Brick, Plaster, and Wood
Local materials and methods of building used in Islamic Architecture
Stone
Material used in Indian-Islamic Domes
Brick and Plaster
(IN SPAIN) Principal materials responsible for the peculiar decorative surface treatment.
Marble and Red sandstone
these materials were more available in Central and Northern India
Small openings
The buildings for most part in Eastern or Southern climes used these openings in response to the HOT climate
Flexible and Adaptable
Character of Islamic Architecture that allows it to be used widely throughout different countries, adapting to the local culture
Muslim
Followers of Islam
Surrender
Islam means “_________” (Obedience to their God)
Allah
The God in Islam, It is not a specific term for God because the term God is generic
Prophet Muhammad
The prime looker of Islam, was born into a family belonging to a clan of Quarish, the ruling tribe of Mecca
Mecca
The city in the Hijaz region of north-western Arabia where muslims visit at least once in their lifetime; It is the Holiest city in the Islamic World
prohibited
In Islamic Architecture, images portraying Muhammad are _______. Body is allowed but the face must be covered with fabric
Koran/Quran
Sacred texts of islam
Apostles
The religion of Islam was spread by them
Sunni Muslims
Successors of Muhammad
Shia Muslims
Descendants of Muhammad
Sunni Muslims
Successors of Muhammad
4 Great Caliphs
Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali (They are the first four leaders of Muslim after the death of Muhammad)
Caliphate
Islamic nation ruled by a Caliph
Emirate
Lower kind of empire; Principality/territory ruled by an Emir who perceived their power as God Given
Sultanate
Principality/territory ruled by a Sultan
China
Not penetrated by the spread of Islam due to their strong influence of Buddhism
Aceh, Indonesia
The Birthplace of Islam in Southeast Asia. Arabians are known to be traders who spread the religion in this place
Mosque
A building associated with the presence of Islam
Hypostyle Mosque
unroofed enclosure approximating a parallelogram on plan. It is characterized by an open Courtyard with a fountain in the center surrounded by an enclosure
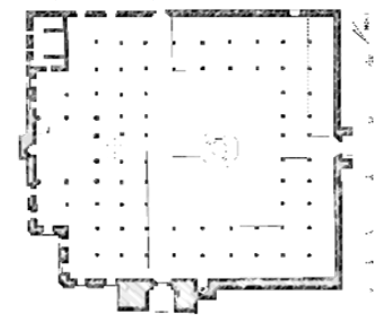
Mosque of the Sultan Hassan at Cairo/Iwan Plan
Cruciform in Plan, the center portion only being left open; It has 4 Entrances from Sahn (courtyard)
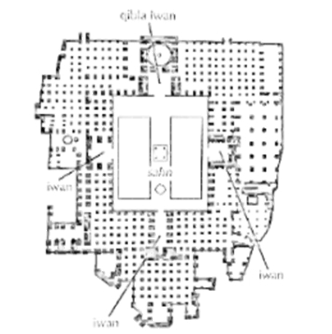
Iwan Plan
Another name of the Plan of the Mosque of the Sultan Hassan at Cairo
The founder’s tomb
On an Iwan type of plan, what is placed behind the Mihrab
A Dome
On an Iwan type of plan, what is the founder’s tomb crowned with or placed on top of?
Byzantine Model/Central Plan
A plan having a front courtyard, and a garden behind; the mosque proper being independent
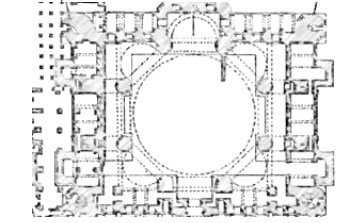
The Garden
In a Central plan/Byzantine Model, where is the founder’s tomb found?
Kiblah/Qibla
wall that indicates the direction of the Mecca/direction of the prayer which commemorates the presence of the Prophet
Fawwara/Meda
Fountain used for ablution and cleansing the spirit
Mihrab
The apse part of the mosque, it is also the most decorative part of the building
Dikka
a Tribune; a raised platform from which the repondents (qadi) repeat the ritual postures of the iman
Unam
reads passages from the Koran and intones the prayers
Minarets
A slim, bell tower, which is a distinctive traditional feature of a mosque; they are usually square in plan and transitions to a polygonal or circular shape in preceding storeys
For voicing out prayers during specific times of the day
Purpose of the Minarets
Domes
frequently constructed of brick plastered internally and externally; It is a feature of all Islamic Architecture both from Sassanian and Early Christian traditions
Cupola
A light structure on a dome or roof, serving as a belfry, lantern, or a belvedere
Sahn
Open courtyard at the center of a Mosque
Iwan
A vaulted hall or space, walled on three sides, with one endd entirely open
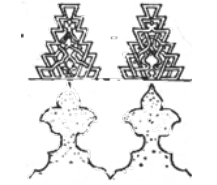
Muqaranas
The doorways were often surrounded with elaborate carved work (like a cave-dwelling), enclosed in a square frame, with stalactite cornices.
Arabic and Persian
Muqaranas is a type of corbel used as a decorative device in traditional _____________ Architecture.
Squinch
A structure, such as a section of vaulting or corbeling, set diagonally across the interior angle between two walls to provide a transition from a square to a polygonal or more nearly circular base on which to construct a dome
Riwaq/Liwanat
A colonaded or arcaded hall of the Hypostyle Mosque
Musalla
Prayer hall where no furniture is needed, as worshippers sit, kneel and bow directly on the floor
Mimbar
Pulpit entered by a flight of stairs
Khan
Hotels of Islamic Arc; they support Mosques and Mecca
chambers
Khans are often erected in the great cities, had an open court, round which were placed numerous _______ used by the merchants or travelers, who came from all parts to dispose of their goods
180
In Constantinople there are how many Khans (hotels)?
House
They are planned with interior courts in the Eastern manner, on to which the principal rooms face. The windows towards the street are small and strongly barred in the lower stories, those to the upper stories being often ornamented with lattice work.
Privacy
In Islamic Dwellings, Special regard is paid to _______ in the planning of the corridors and in the isolation of the harem or women’s apartments.
Principal court
There is generally a _________ in Islamic houses, approached from the entrance, in which is placed a summer-house and fountain.
Minute surface decoration
Walls in Islamic Architecture are constructed with local materials, what are they ornamented with? (either in plaster, precious stones, or glazed tiles)
Wall Crestings
A type of bold cresting often crowned the walls instead of a cornice. The noble type of entrance, specially used in India, consisting of a high fourcentered arch in a square frame, resembling a Tudor arch, and crowned by a semi-dome, has already been described. In later Mogul architecture the walls were divided into panels by perpendicular and horizontal inclosing lines
Tracery work
Windows/openings were often grouped together and occasionally had their entire surface fitted with elaborate ________ of marble and plaster, schemed into geometrical patterns the small open spaces being of colored glass.
Arches
Such forms are used for arcades, window and door openings. In arcades they either rest on columns or piers, and are frequently tied in at their springing by wooden beams or iron rods
Pointed
Identify the Type of Arch employed for Islamic Architecture

Ogee/Keel
Identify the Type of Arch employed for Islamic Architecture

Horseshoe
Identify the Type of Arch employed for Islamic Architecture

Multifoil/Scalloped
Identify the Type of Arch employed for Islamic Architecture

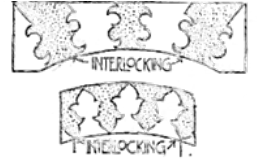
Voussoirs/Arch Voussoirs
Interlocking patterns used in Arches
Geometry/Geometrical Patterns
Architects and Artists of Islam were prohibited from illustrating Living things or Natural objects. Hence, what elements are used in their works?
Windows
often placed in the lower parts of the dome roof, which were occasionally ornamented with a fringe of sculptured foliage
Flat Timbers
Ceilings of undomed mosques were generally left with what? They are brilliantly colored and gilded
Roman and Byzantine buildings
Many of the earlier and later buildings in Islamic Arc have ready-made columns, these columns were erected from what? Causing the columns to be of different designs.
Mnemonic
Inscriptions type of ornamentation
Superposed
Arabesque ornamentation
Muqaranas
Stalactite-like ornamentation
Masjid
Arabic word for Mosque
Arabian Peninsula
Where is the origin of Mosques? Though they are found in all inhabited continents
Arabic
Oldest point of Islamic Architecture
Timurid
Most famous region of Islamic Architecture in Central Asia
Ottoman
(Turkey) adapted to Byzantine Architecture, use of tall and painted Minarets
Moorish
(Africa and Spain) Minarets are square, use of arch and columns
Mudejar
Also under Moorish; ISLAMIC + CHRISTIAN + SPANISH
Mughal
(India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh) use of Onion Domes
East Asia
(China, Indonesia, and Malay)
Great Mosque of Xi’an
Oldest mosque; best example of Islam Architecture blending to local culture
Menara Kudus Mosque
Rock cut Indonesian Mosque
Kampung Laut Mosque
Malaysian Mosque that adapts to local Arc
Dome of the Rock
Oldest Extant work of Islam Architecture
A Rock
In the Dome of the Rock, what is believed/prayed by the Muslims, Christians, and Jews?
Dome of the Chain
King David believed that the chain is used to identify which Solomon is the liar
Islamic Garden
Symbol of Paradise/Heaven. It is used for rest and reflection. The water should be flowing; use of wall screens and symmetry
Char Bagh
Persian Garden
Bustan
Inner court of the garden
Jannah
Islamic house
Rawdah
Vegetable Garden