Prokaryotes
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are the similarities between Bacteria and Archaea?
Prokaryotes
single cell organisms
no nuclei
very small
What do bacteria have that archaea does not?
Cell wall have peptidoglycan which strengths them
What is a difference between bacteria and archaea?
machinery to replicate DNA is different
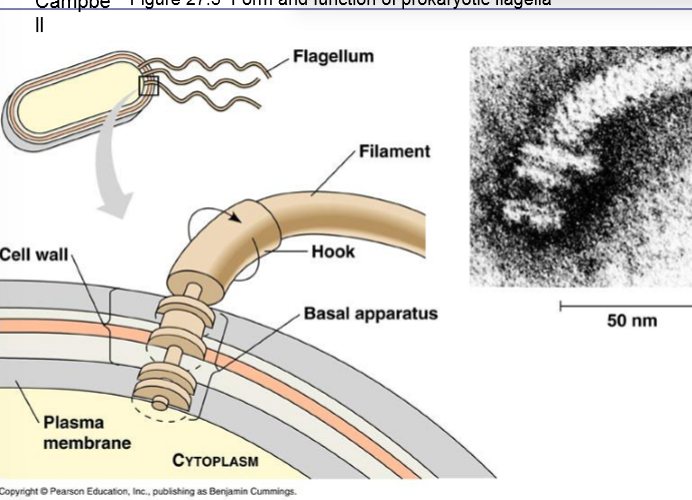
What are flagella?
have motor that are embedded into their cell wall that rotate the cell
like a propellor and created forward motion
How do prokaryotes use different types of metabolism?
Obligate anaerobes - don’t use oxygen
oxygen tends to stop their growth
tetanus
Facultative anaerobes
can survive with oxygen and without oxygen
Energy substrates
methane, benzene, sulfur, ammonia, petroleum
How do prokaryotes specifically bacteria survive extreme and diverse conditions?
bacteria can sense the environment and form a endospore ( thick protective structure/coat)
After an endospore forms, the bacterial cell that contains it breaks open, and the spore is released to the environment.
Metabolic activity ceases until the spore encounters favorable conditions, at which time metabolism resumes and the spore develops into an active bacterium.
How do prokaryotes reproduce and share in information?
Through binary fission
genetically identical copies of the original cell
essentially one cell splits into two
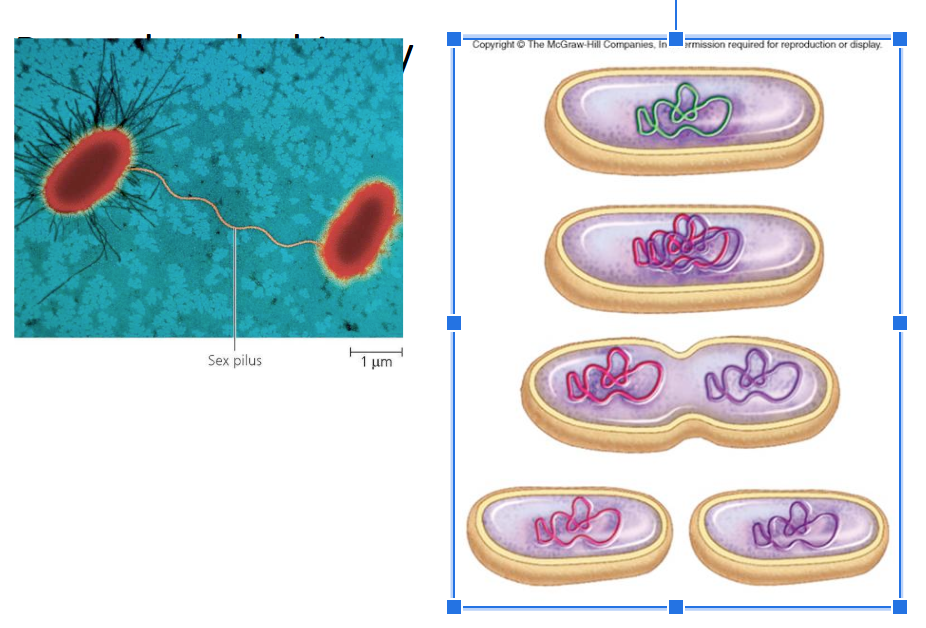
Conjugation
sharing genetic information through direct contact
plasma membranes of two conjugating prokaryotes fuse temporarily to form a cytoplasmic bridge across which DNA travels.
using a sex pili
critical to bacteria resistance against medicine
can share info about to improve function and survival of the bacteria
How is DNA seen in a Eukaryotes?
Linear strand within membrane bound nucleus
How is DNA seen in Prokaryotes?
single circle un nucleoid region (typically in the middle)
What is the typical size for a Eukaryotes?
5-100um
What is the typical size for a prokaryotes?
0.2-10 um
How are Eukaryotes organized?
multicellular
some have cell walls (no peptidoglycan)
How are prokaryotes organized?
usually single celled
some have peptidoglycan in cell walls
Do eukaryotes need oxygen to exist?
Yes
Do prokaryotes need oxygen to exist?
usually no but sometimes
What type of organelles do Eukaryotes have?
membrane bound organelles
example - mitochondria
Example of Eukaryotes
plants
animals
protists
fungi
What type of organelles do prokaryotes have?
actually have no organelles
different types of ribosomes
Examples of Prokaryotes
bacteria
archaea
What are four ways antibiotics stop/kill bacteria?
1. Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis
inhibiting protein production - causing death of bacteria
E.g. Penicillin, Amoxicillin, Ampicillin - mole derivatives that kill bacteria
2. Inhibits protein synthesis
E.g. Tetracycline, Clindamycin - inhibit all blanket proteins
3. Alters the cell membrane
E.g. Bacitracin
affects all cell membranes not only diseased
4. Inhibits nucleic acid synthesis
E.g. Cipro - not bacteria specific
How do bacteria resist antibiotics?
Antibiotic can’t get past the cell membrane or the cell wall
Antibiotic gets in but the bacteria pumps it right back out
The bacteria produces an enzyme/ protein that interferes with the antibiotic interacting with the target
Bacteria produce an enzyme that chews up the antibiotic
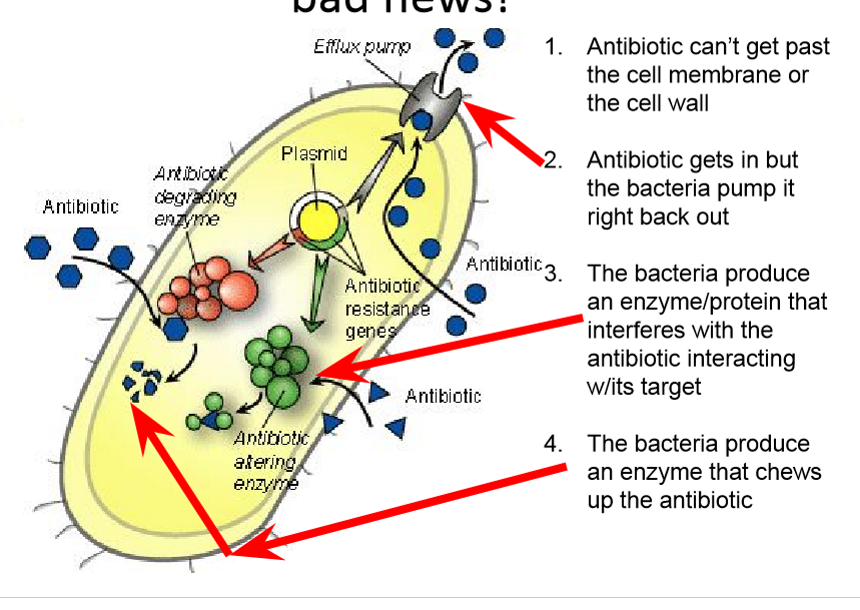

What is the bacteria doing to the antibiotic?
Bacteria pump is taking out the antibiotic out

What is the bacteria doing to the antibiotic?
The bacteria produces an enzyme/ protein that interferes with the antibiotic interacting with the target

What is the bacteria doing to the antibiotic?
Bacteria produce an enzyme that chews up the antibiotic
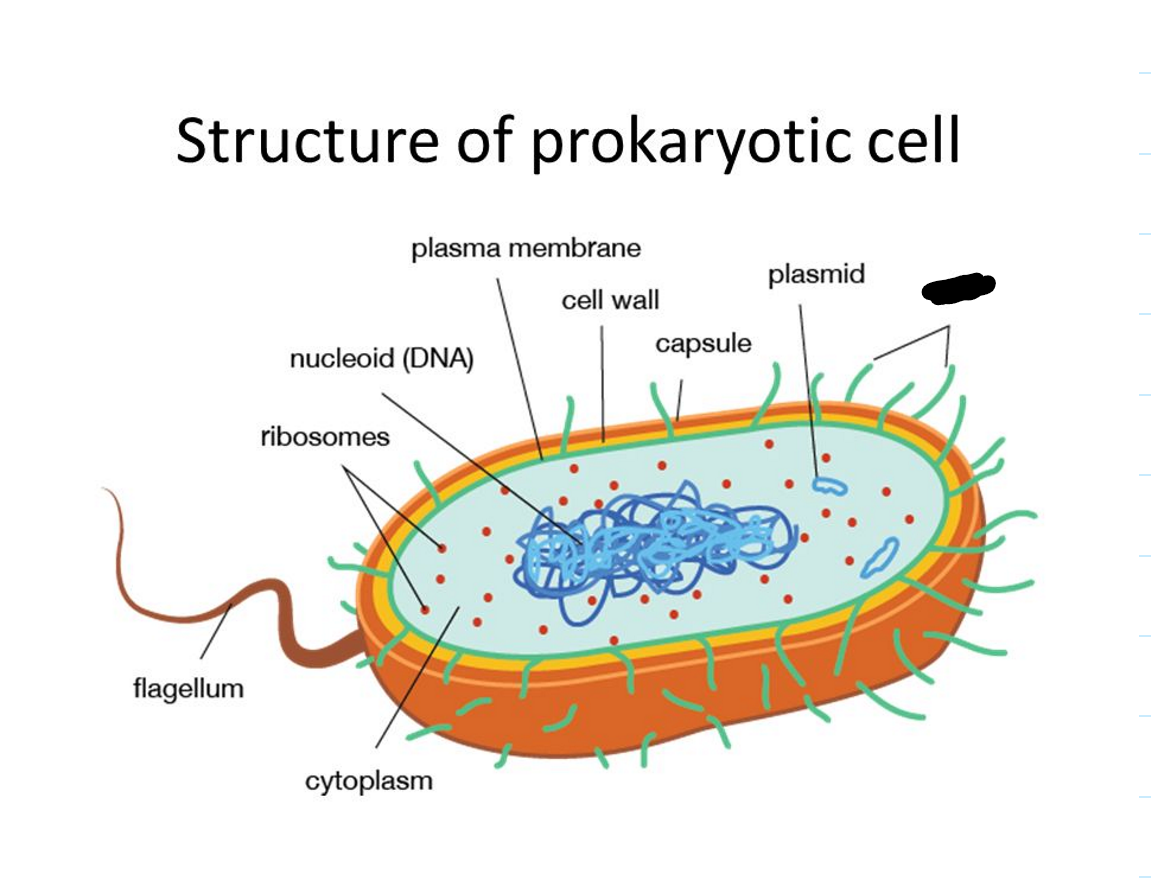
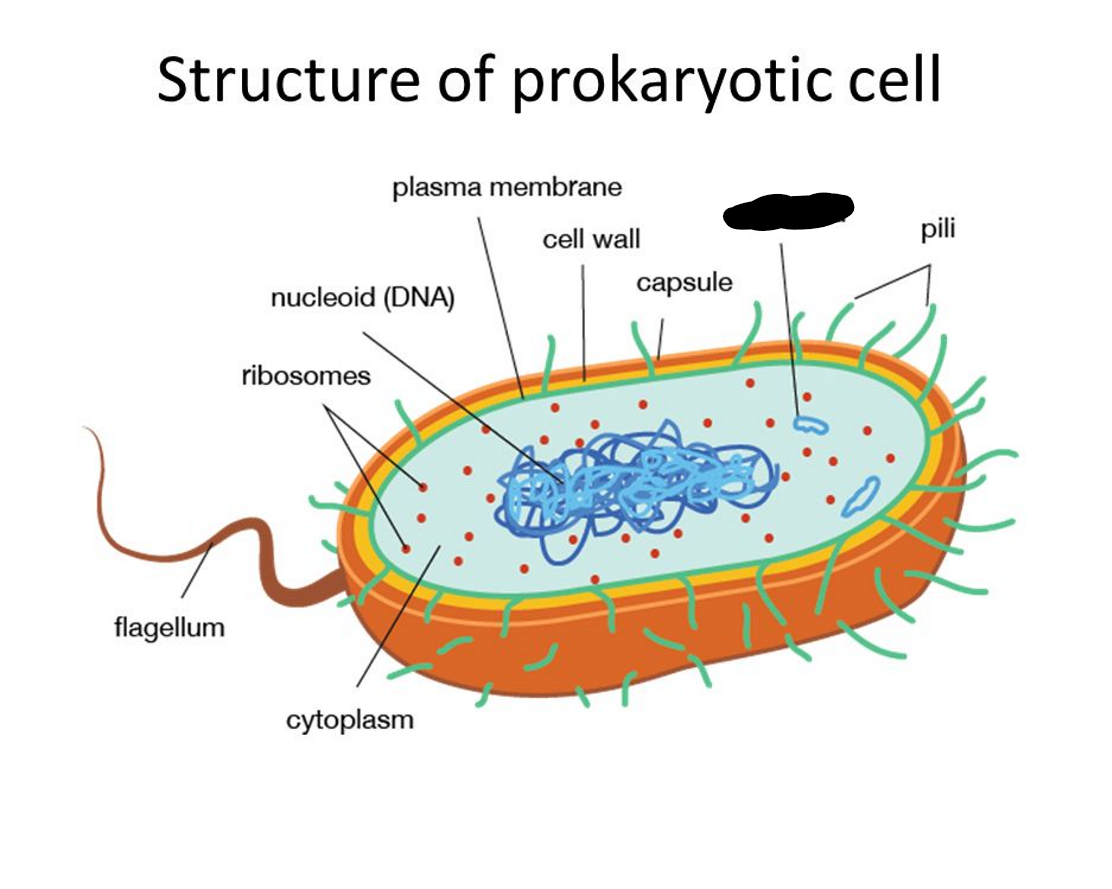
What is missing?
Pili
What is missing?
Plasmid
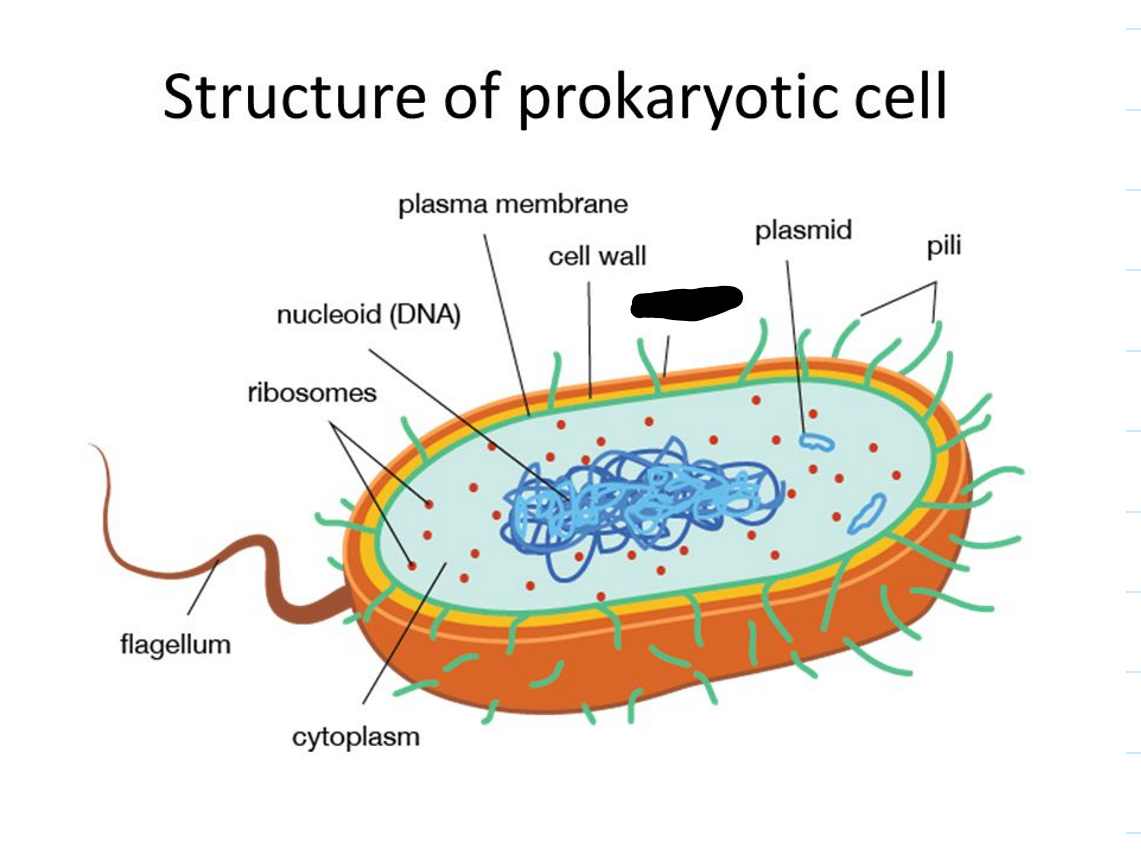
What is missing?
Capsule
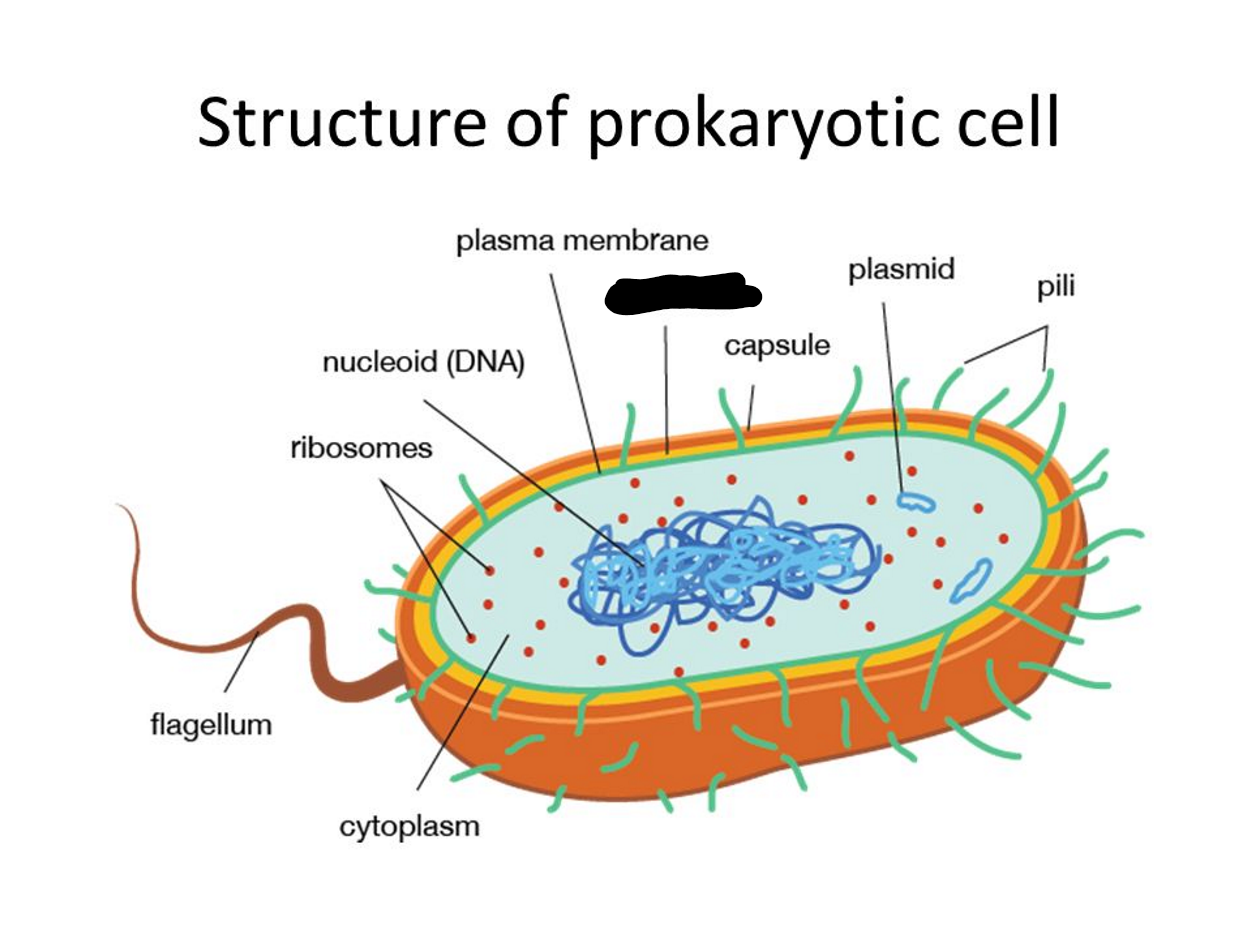
What is missing?
Cell Wall
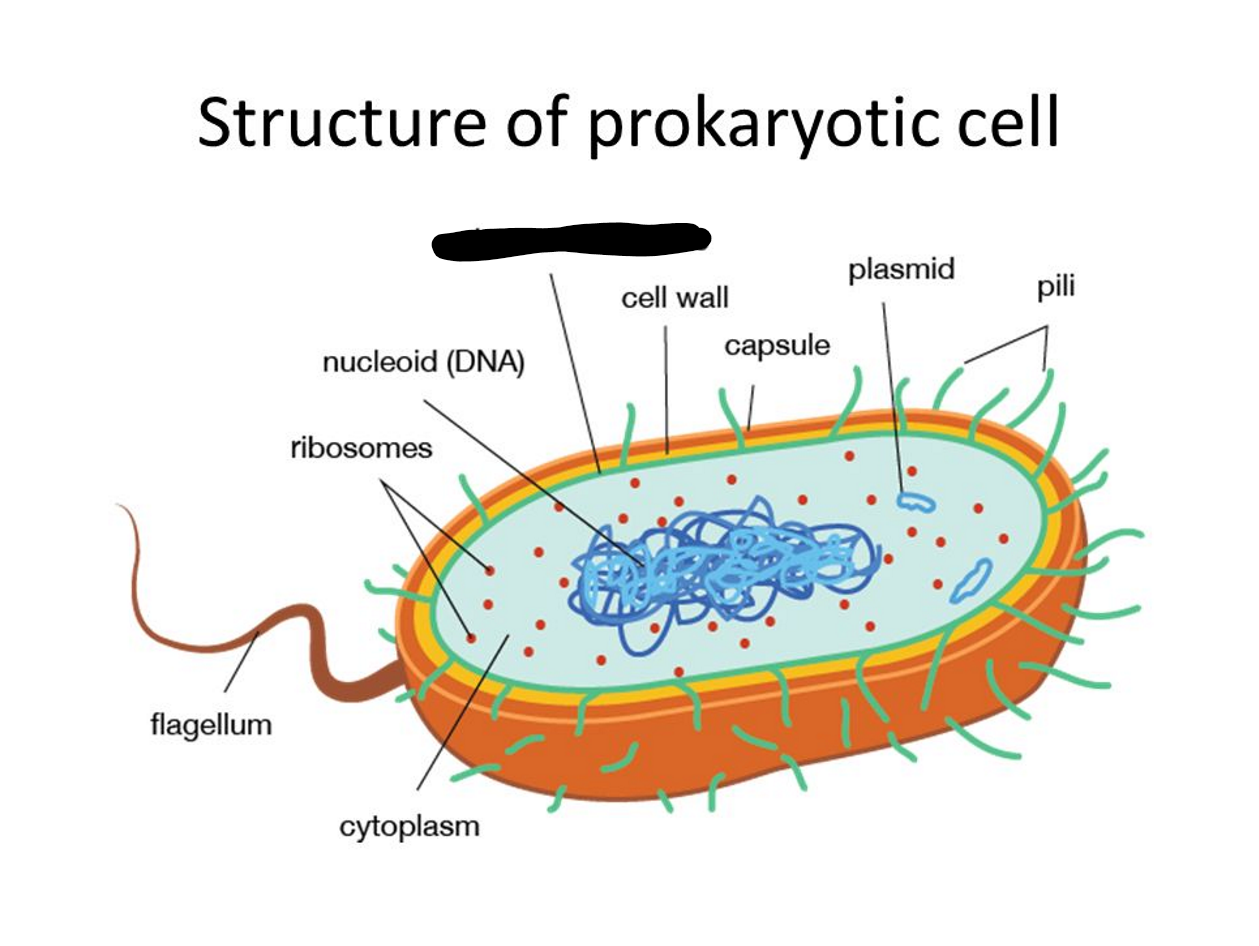
What is missing?
Plasma Membrane
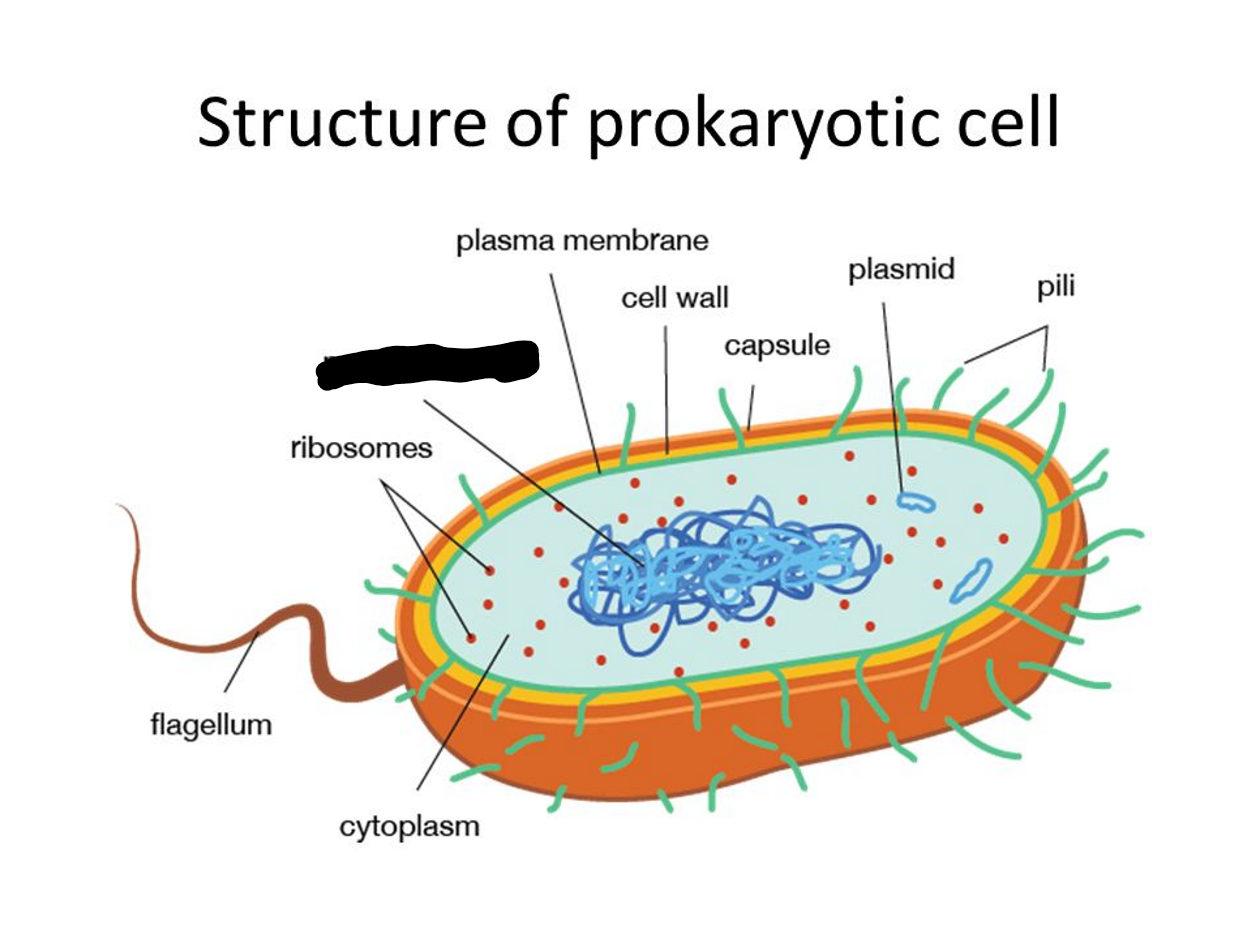
What is missing?
Nucleoid (DNA)
What is missing?
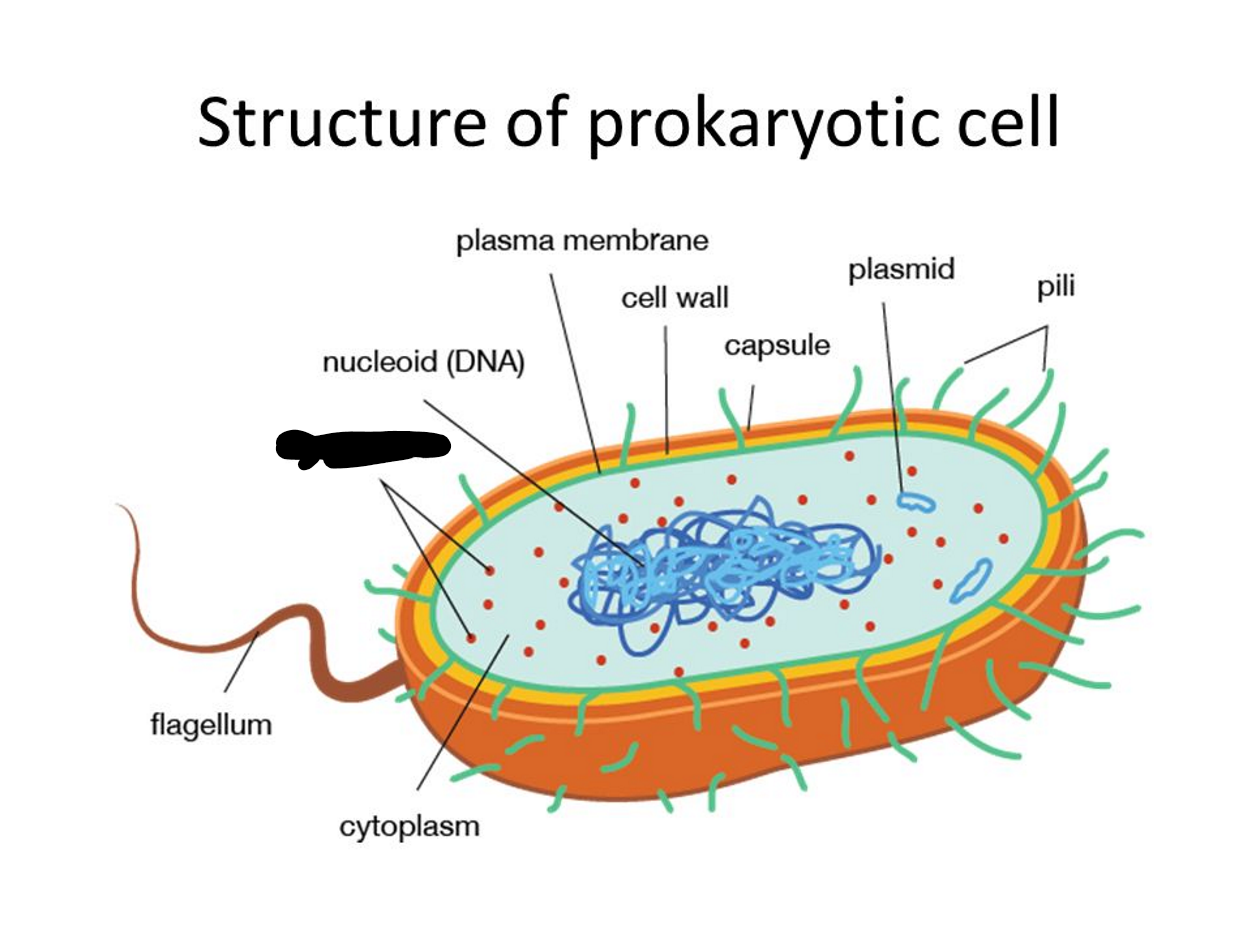
Ribosomes
What is missing?
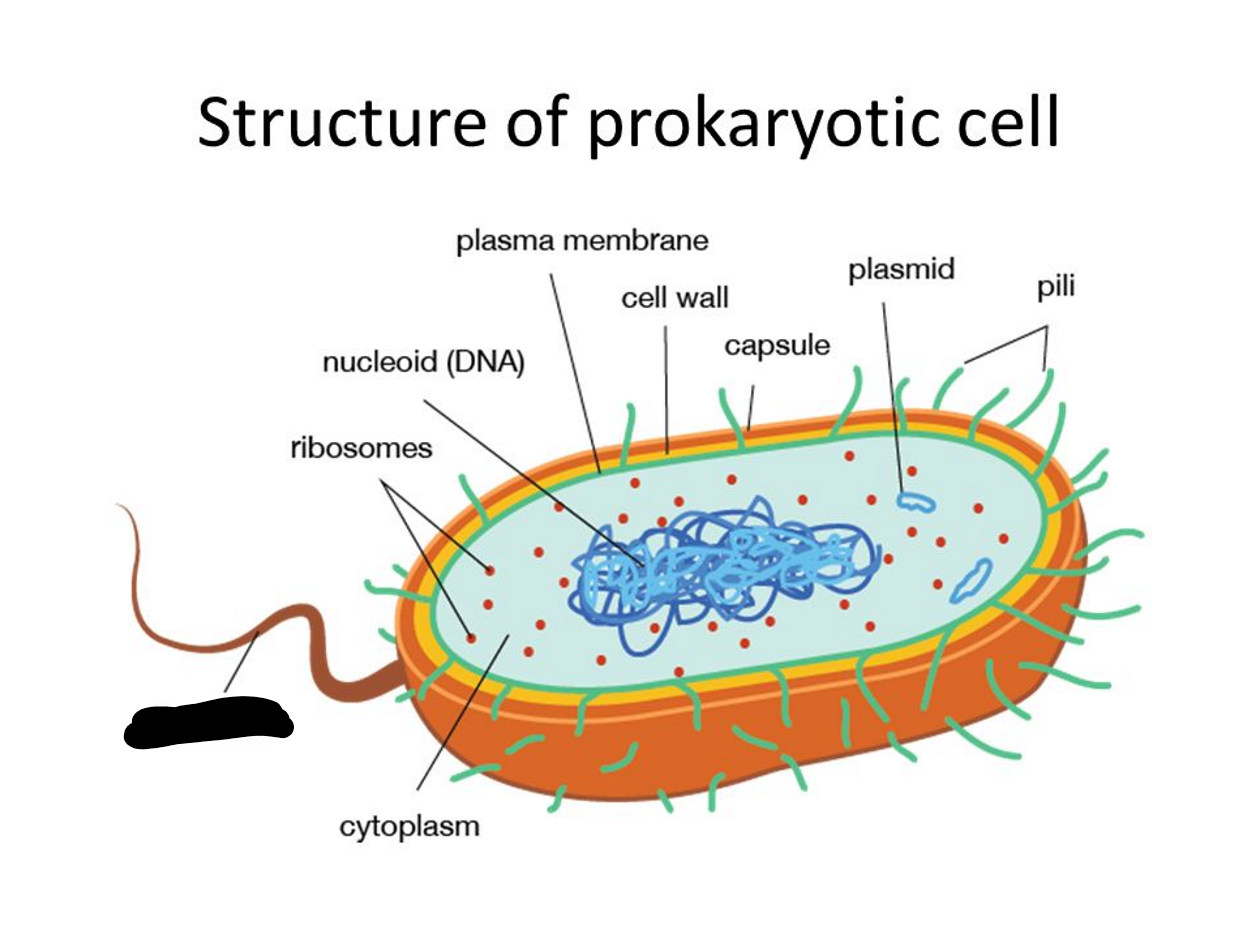
Flagellum
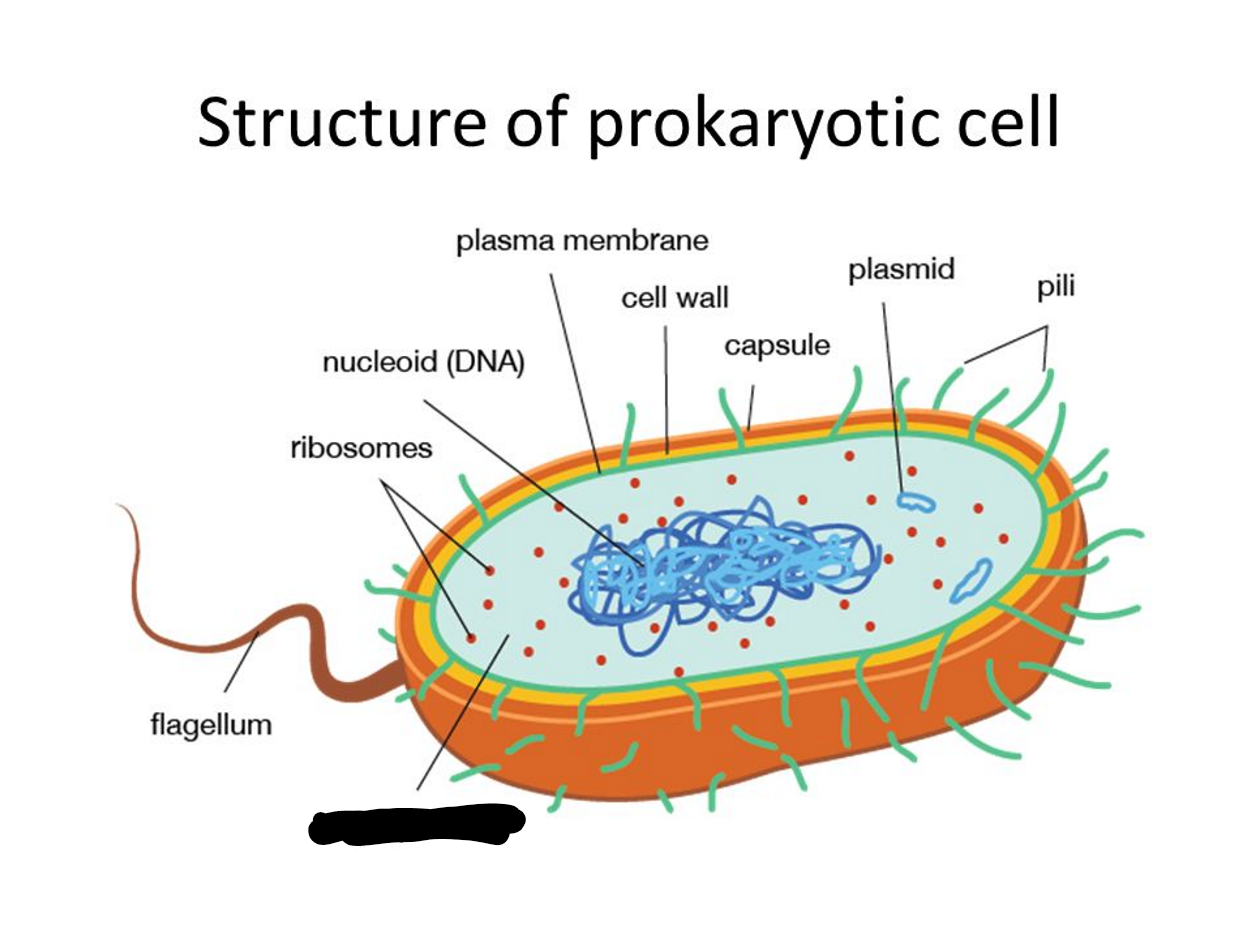
What is missing?
Cytoplasm
How do prokaryotes move?
Flagella
hair-like extensions that can rotate rapidly to propel the organism through its liquid environment
allows prokaryotes to disperse into new habitats, migrate toward nutrients, and leave unfavorable environments.
How do prokaryotes survive?
Biofilms
In a biofilm, one or more species of prokaryote aggregate to form a community that is typically surrounded by sticky protective slime
protects the prokaryote and helps them adhere to surfaces
What are some positive bacterial interactions?
Probiotics
Bacteria in our gut contributes to the production to vitamin K and B12
Nitrogen fixing bacteria
capture nitrogen gas (N2) from air trapped in the soil and combine it with hydrogen to produce ammonium
(NH4+), a nitrogen-containing nutrient that plants can use directly.
Bioremediation
stimulate breakdown of pollutants by living organisms
Oil eating bacteria to help clean up oil spills but the question is what do we do with the bacteria in environment after the oil spill is cleaned up?
What are some negative bacterial interactrions?
C. botulinum
Plague
Bubonic
Pneumonic
Septicemic
Tuberculosis
STDs
Cholera
Flesh-eating bacteria
MRSA
over colonization of staph bacteria that is antibiotic resistant
Red or tender skin around wound
swollen, painful, oozing boils
Necrotizing Fasciitis
flesh eating bacteria
very low chance in getting it
starts with a cut or insect bite then large sequence of events
chews up tissue and tissue dies