Stomach Stuff
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Gastritis, Peptic Ulcer Disease, Pyloric Stenosis, Neoplasms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Gastritis
Inflammation, infection, or damage to the stomach’s mucosal lining
Nonerosive, Erosive/hemorrhagic, infectious disease states
Categories of Gastritis
Nonerosive Gastritis
Gastric irritation and atrophy caused by cellular changes or weakened host mechanisms
Pernicious anemia, H. plyori (body)
Types of Nonerosive gastritis
Pernicious anemia
An autoimmune condition resulting in B12 malabsorption due to decreased intrinsic factor (loss of parietal cells - antibody mediated 70%)
Parenteral B12, PPI
Treatment plan for Pernicious Anemia related Gastritis gastritis
H. plyori
A Gram neg bacillus that secretes ammonia as a buffer to gastric acid and is spread via oral-oral or fecal-oral
Family hx of ulcers, similar symptoms, or H. plyori
Risk factors for H.plyori
Fecal antigen immunoassay (sens/spec 95%), Urea breath test (sens/spec 95%), Serological ELISA
Patient presents to the ER for abdominal pain for the last 3 days. She states that is so mad she doesn’t want to eat and also reports N/V. On a physical exam you note mid-epigastric tenderness. Family Hx is positive for PUD. What labs do you want?
No PPI for 7 days, Abx for 28
What are the rules for running fecal and breath test for H. plyori
Actively bleeding ulcer, recent PPI/abx use, endoscopic abnormality requiring biopsy, or failure of other treatment
When should you get a upper endoscopy on a patient with possible H.plyori (sen 90%/spec 95%)?
14 days (at least 7) of PPI, Clarithromycin, Amoxicillin (metro for PCN allergy), test for eradication in 4 weeks; Preferred treatment is the Bismuth Quad
Patient presents to the ER for abdominal pain for the last 3 days. She states that is so mad she doesn’t want to eat and also reports N/V. On a physical exam you note mid-epigastric tenderness. Family Hx is positive for PUD. Urea breath test and fecal antigen testing are consistent with H. plyori, what is the game plan team?
Erosive/Hemorrhagic gastritis
Gastric mucosal erosion due to inhibition of normal mucosal defenses allowing gastric fluids to damage tissues OR local damage from ingested items
Meds (NSAIDs), H. Plyori (Antrum), EtOH, Stress, Portal HTN, Consumed irritants (takis ☹ )
Common causes of erosive/hemorrhagic gastritis
Chronic NSAID usage, severe medical illness/injury, chronic/binge drinking, family hx, liver disease, spicy/acidic foods
Risk factors for erosive/hemorrhagic gastritis
Upper endoscopy (#1 draft pick), CBC (anemia if chronic), urea breath test, fecal antigen test, fecal occult blood
Patient presents to the ER for abdominal pain. He reports that he has loss his appetite as well as nausea. He also reports that his stools have been dark and tarry. On a physical exam you mote mid-epigastic tenderness and a coffee ground blood on NG suction. What diagnostics do you want?
Continuous PPI infusion, PO sucralfate suspension, possible endoscopic repair
Patient presents to the ER for abdominal pain. He reports that he has loss his appetite as well as nausea. He also reports that his stools have been dark and tarry. On a physical exam you mote mid-epigastic tenderness and a coffee ground blood on NG suction. Upper endoscopy is positive for erosive gastritis, let’s say stress induced, what is your treatment plan?
PPI PO/IV prophylactically
How can we avoid stress-induced erosive gastritis in our severely ill/injured peeps?
Stop the NSAID (or drop the dose) switch to COX2 inhibitors (celecoxib), educate patients to take meds with food, Begin PPI for 2-4 weeks (if no improvement endoscopy)
Patient presents to the ER for abdominal pain. He reports that he has loss his appetite as well as nausea. He also reports that his stools have been dark and tarry. On a physical exam you mote mid-epigastic tenderness and a coffee ground blood on NG suction. Upper endoscopy is positive for erosive gastritis, let’s say NSAID induced, what is your treatment plan?
Stop eating hot chip and lie, Stop alcohol, Start PPI/H2/sucralfate for 2-4 weeks
Patient presents to the ER for abdominal pain. He reports that he has loss his appetite as well as nausea. He also reports that his stools have been dark and tarry. On a physical exam you mote mid-epigastic tenderness and a coffee ground blood on NG suction. Upper endoscopy is positive for erosive gastritis, let’s say EtOH and Takis induced, what is your treatment plan?
Propanolol, Treat liver disease, PPI/sucralfate for symptomatic relief
Patient presents to the ER for abdominal pain. He reports that he has loss his appetite as well as nausea. He also reports that his stools have been dark and tarry. On a physical exam you mote mid-epigastic tenderness and a coffee ground blood on NG suction. Upper endoscopy is positive for erosive gastritis, let’s say portal hypertension, what is your treatment plan?
PUD, GERD, cancer, biliary tract disease, Viral/bacterial gastroenteritis (stomach bug, food poisoning), Cardiac, aortic aneurysm
Differentials for Gastritis
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
The destruction of the gastric or duodenal mucosa by digestive factors such as acid or pepsin due to impaired/overwhelmed mucosal defense mechanisms
muscularis mucosae, 5mm+
Ulcers extend through the ______________________ and are usually ______ in diameter
duodenum
Peptic ulcers are more commonly (5x) found in the…
NSAID usage, H. Pylori infections (most common)
What causes peptic ulcer disease (90% of ‘em)
reduces the natural protective barrier
What is the mechanism behind H.pylori and PUD?
COX-1 inhibition leads to impaired mucosal defenses
What is the mechanism behind NSAIDs and PUD?
Living with family members with H.plyori, Long-term NSAID usage
PUD risk factors
urea breath test, fecal antigen testing, CBC (Anemia), digital rectal (fecal occult blood), Abdominal Xray
Patient presents to the ER for SEVERE abdominal pain that he describes as gnawing. He said that it has gotten so bad he can’t even sleep, but does get better when he has a midnight snack. You note mid-epigastric tenderness, a rigid abdomen with guarding and positive peritoneal signs. What diagnostics do you want?
Standard triple therapy (PPI, Clarithromycin, Amoxicillin); Preferred is Bismuth Quad
Patient presents to the ER for SEVERE abdominal pain that he describes as gnawing. He said that it has gotten so bad he can’t even sleep, but does get better when he has a midnight snack. You note mid-epigastric tenderness, a rigid abdomen with guarding and positive peritoneal signs. Fecal antigen and urea breath testing are both positive for H. pylori. See CXR. What is your treatment plan?
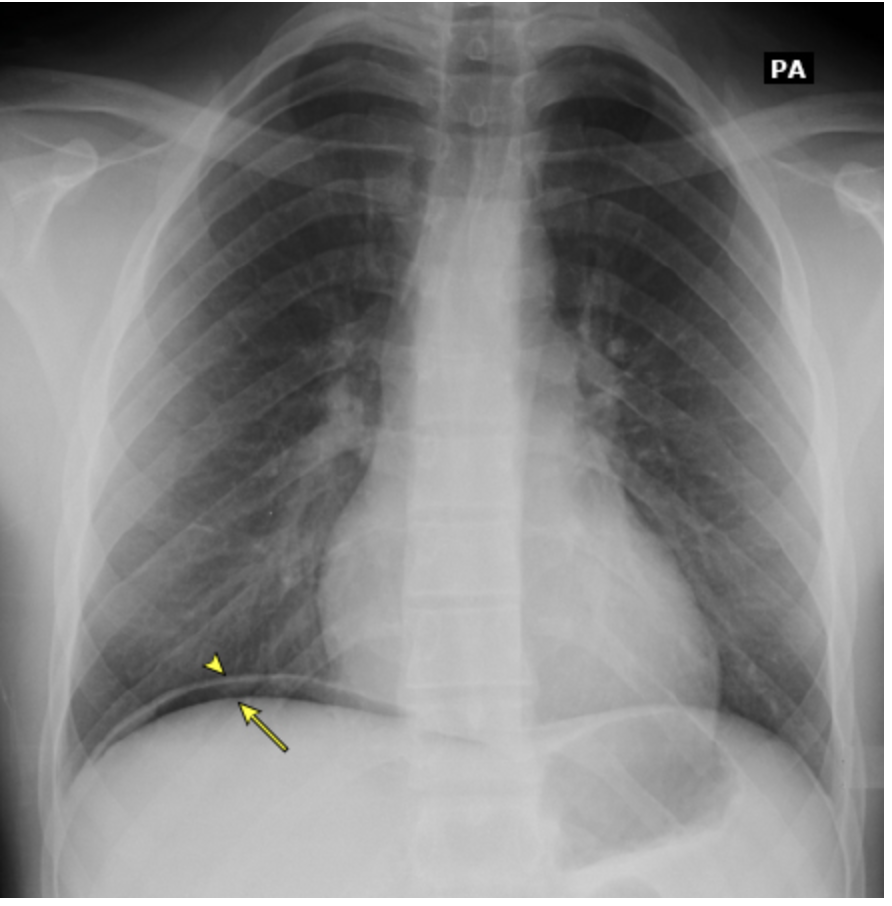
Stop the NSAID, switch to COX-2, Start PPRI for 4-6 weeks, Start broad spectrum abx for the perforation
Patient presents to the ER for SEVERE abdominal pain that he describes as gnawing. He said that it has gotten so bad he can’t even sleep, but does get better when he has a midnight snack. PMHx is positive for back pain for which he is prescribed 800 mg ibuprofen PRN. You note mid-epigastric tenderness, a rigid abdomen with guarding and positive peritoneal signs. Fecal antigen and urea breath testing are both negative for H. pylori. See CXR. What is your treatment plan?
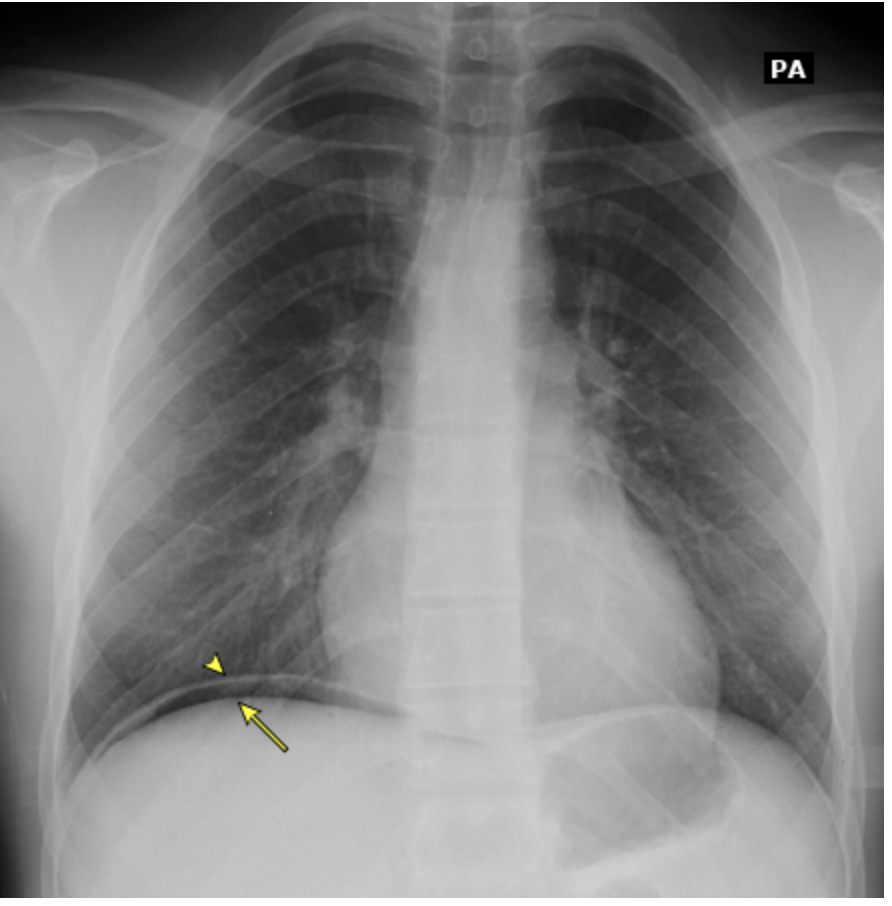
Onset after 50, progressive dysphagia, odynophagia, recurrent vomiting, Sx despite treatment, Postive FOBT, melena, blood in emesis, anemia, Severe abdominal pain, weight loss, FHx of FI cancer in 1st degree
Upper endoscopy is the definitive diagnostic for PUD but is only require IF
gastritis, GERD, Cancer, Billiary tract disease, gastroenteritis
PUD DDx
Pyloric Stenosis
An acquired condition caused by hypertrophy and spasm of the pyloric sphincter resulting in gastric outlet obstruction - occurs in 0.6-0.8% of live birth but can be adult acquired
Male (5x)
Risk factors for Pyloric stenosis, more commonly occur in the first, familial hx, exposure to macrolides
chronic gastritis, Chronic PUD, gastric cancers, Chronic gallbladder disease (Bourveret’s syndrome)
Risk factors for secondary plyoric stenosis
Bouveret’s Syndrome
A rare complication of a bilio-digestive fistula, where a big stone occludes the pyloric-duodenal region
CMP (Cl, bicarb, elevated BUN), Xray, U/S (radiologic test of choice), Barium Swallow study
4 day old baby returns to the ER for failure to thrive. Mother reports the the baby has been projectile vomiting after every feeding and that after the baby eats, “you can see the stomach move”. On a physical exam you note an ability to palpate an olive and dry mucous membranes. What diagnostics you want?

Stabilize (Big IVs, fluids), Surgical pyloromyotomy (definitive), post-op ad lib feeding improves prognosis
4 day old baby returns to the ER for failure to thrive. Mother reports the the baby has been projectile vomiting after every feeding and that after the baby eats, “you can see the stomach move”. On a physical exam you note an ability to palpate an olive and dry mucous membranes. Labs show metabolic alkalosis, hypochloremia, elevated BUN. Xray shows dilated stomach with no gas in the intestines. U/S shows a elongated and thickened pyloris with at target sign. Swallow study shows a string sign. What is your treatment plan
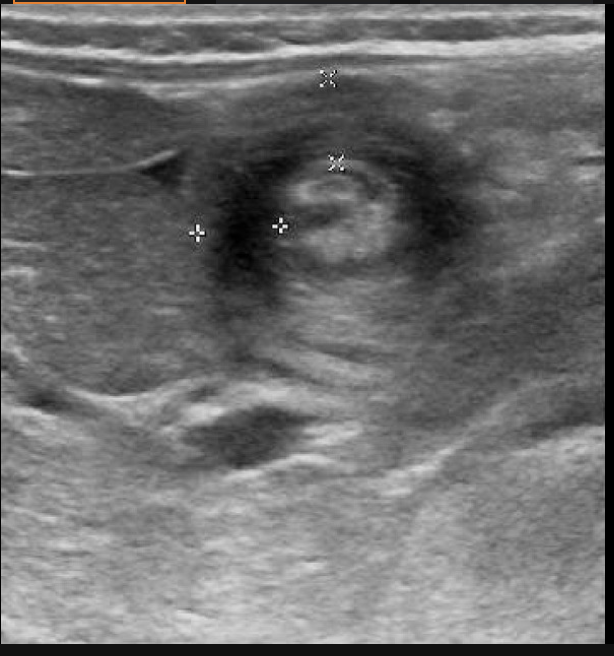
adenocarcinoma, lymphoma, carcinoid tumor
Types of gastric neoplasms
Intestinal (resemble glandular structures), Diffuse (poorly differentiated)
Cellular variants of gastric adenocarcinoma
Chronic H. pylori, Pernicious anemia, smoking, nitrates, salts, low vitamin C, FHx of gastric cancer (consider gastectomy)
Risk factors for Gastric Adenocarcinoma
Upper endoscopy with biopsy, CBC, LFTs, Fecal occult blood
77 y/o male presents to the clinic for heartburn. He also reports symptoms of anorexia and states that “I must not need to eat as much, I get full with like 2 bites.” On physical exam you note midepisgastric tenderness, weightloss, and pallor. What diagnostics?
CT (chest, abdomen, pelvis), Endoscopic U/S
77 y/o male presents to the clinic for heartburn. He also reports symptoms of anorexia and states that “I must not need to eat as much, I get full with like 2 bites.” On physical exam you note midepigastric tenderness, weight loss, and pallor. Initial diagnostics show gastric adenocarcinoma what other test do you want to look at the extension of the cancer?
Surgical resection (laproscopic or open), perioperative chemo, palliative surg/chemo for non curative
Treatment plan for gastric adenocarcinoma
Gastric lymphoma
What is the second most common type of gastric cancer and H. pylori is the largest risk factors?
Upper endoscopy, Fecal occult blood, CBC, LFTs, lymph node biopsy, H. pylori labs
OG Diagnostics for Gastric lymphoma
CT (chest, abdomen, pelvis), bone marrow biopsy
Diagnostics for Gastric lymphoma after the OGs
Treat H. Pylori, radiation and chemo
Treatment plan for gastric lymphoma
Gastric carcinoid tumors
Which is the rarest form of Gastric cancer but most (75%) occur with pernicious anemia?
Skin flushing with hypotension, telangiectasias, diarrhea, bronchospasm
Carcinoid syndrome is characterized by
endoscopy with biopsy
Diagnostic of choice for gastric cancers in general
resection (small, local, single), Radial gastrectomy with regional lymphadenectomy (localized multiple)
Treatment plan for gastric carcinoid tumors
Peptic ulcers, gastritis, GERD, other intra-abdominal tumors, bowel/colon cancers
DDx for gastric neoplasms