Lecture 9: Portfolio risk & return, diversification, expected value, variance, standard deviation
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
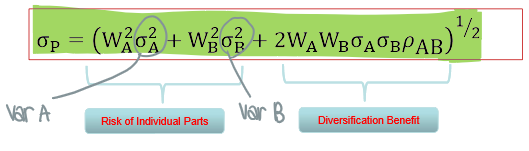
What is the formula to measure portfolio risk?
What is covariance?
Capture how much 2 securities move together
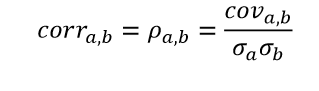
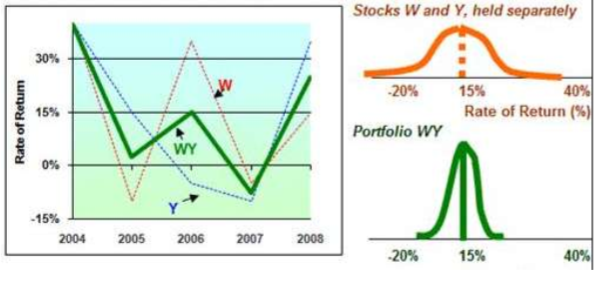
What is the extreme case where correlation = -1?
Securities a and b move in opposite directions
1 moves up, other moves down proportionally
risk reduction
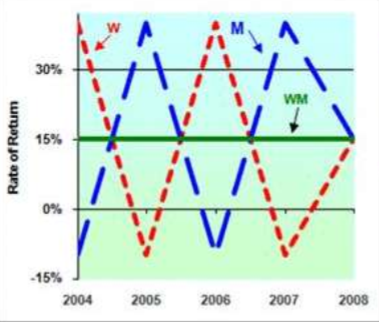
What is the extreme case where correlation = 1?
The 2 securities move in sync
1 moves up, other moves up
no diversification/risk reduction benefit
What is the normal case where the correlation = 0.35?
Buy 2 random stocks → some co-movement
a little diversification
some risk reduction, not a lot (don’t put all eggs in 1 basket)
What is the modern portfolio theory of the efficient frontier?
Minimize standard deviation for a given expected return
by changing portfolio weights & finding the respective E[R] → gives you the curve
any point on the curve is better than a single point off the curve (better reward for same level of risk)
![<p>Minimize standard deviation for a given expected return</p><ul><li><p>by changing portfolio weights & finding the respective E[R] → gives you the curve</p></li><li><p>any point on the curve is better than a single point off the curve (better reward for same level of risk)</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/35094d2b-d94a-495e-a242-087816ec6904.png)
What are the limits of diversification?
Systematic (market) risk: more securities you get, more co-variances you get → can’t get rid of co-variances
Unsystematic risk: risk specific to each firm which can be eliminated through diversification
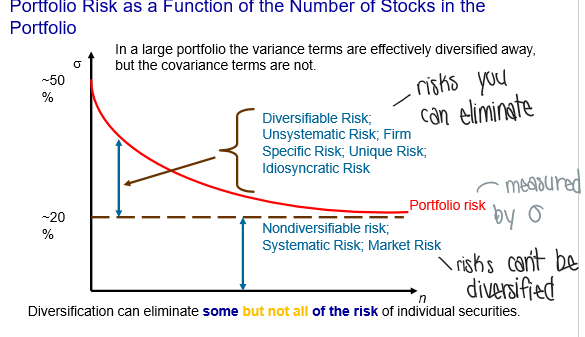
What is international diversification?
There are more benefits to investing outside of Canada → more diversification, higher E[R], lower risk
What are the benefits of combining a risky portfolio and a risk-free asset?
Ability to invest in risk-free asset will ensure a positive return, which will give you leverage to start at A and eventually invest more towards B
M is efficient → highest E[R] relative to risk
points on graph depends on your risk preference
![<p>Ability to invest in risk-free asset will ensure a positive return, which will give you leverage to start at A and eventually invest more towards B</p><ul><li><p>M is efficient → highest E[R] relative to risk</p></li><li><p>points on graph depends on your risk preference</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d9a6593a-ff8b-4fcf-8a19-2aa0c4b6dae8.png)
What is Beta?
A systematic risk measure → need for market portfolio
standard deviation is still a good measure of risk, but Beta is good for a single security

What is the portfolio beta?
Diversification reduces unique risk, but not market risk
Calculates the beta of a portfolio as the weighted average of securities individual betas
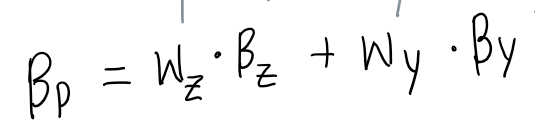
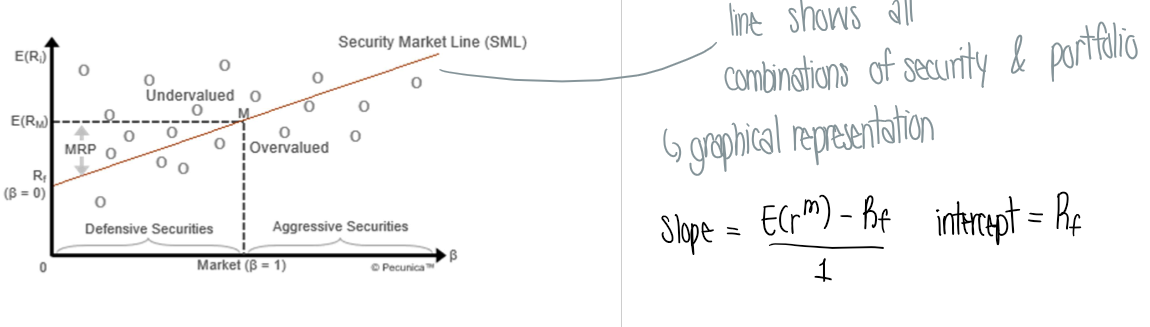
What is the security market line?
Line that shows all combinations of security & portfolio
line is an equilibrium → the securities adjust
What is the capital asset pricing model?
Forecasts the expected returns of individual stocks

What does it mean when the expected result using the capital asset pricing model is less than the risk free rate?
This means when the market goes down, this company goes up
Hedge → a company booms when everyone else suffers (acts as insurance)
cost of this insurance is getting less than risk free rate
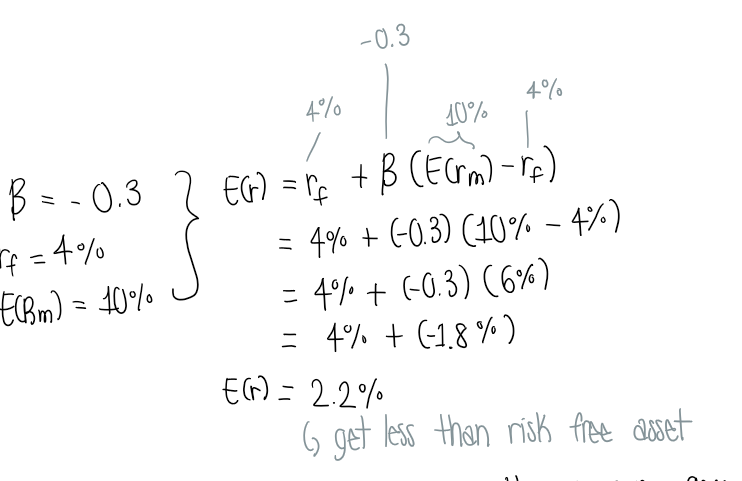
What are some concerns of the capital asset pricing model?
Real estate & human capital is not included
Momentum → strategy where assume stocks that performed well previously will perform will in the future