Cell Membrane Parts
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are the 5 functions of the cell membrane?
Regulates what leaves and enters the cell
Communicates with other organelles
Gather information
Repair
Removes waste
Structure of the cell membrane:
Bilayer (2 layers of lipids), proteins create CHANNELS and pumps materials in and out of the cell.
Other names for the cell membrane:
Lipid bilayer, plasma membrane
What must a cell maintain in order to function properly?
Homeostasis- the state of equilibrium, and this state is controlled by the cell membrane.
What goes IN the cell membrane?
Water, gases, nutrients
What goes OUT the cell membrane?
Wastes
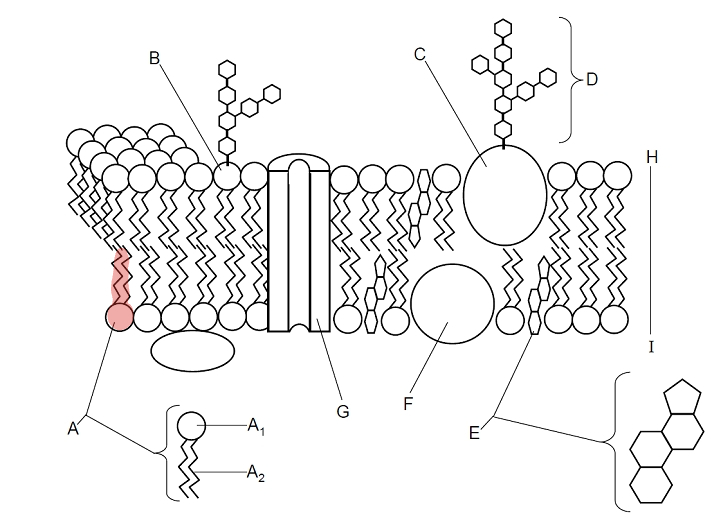
Which part is A?
Phospholipid
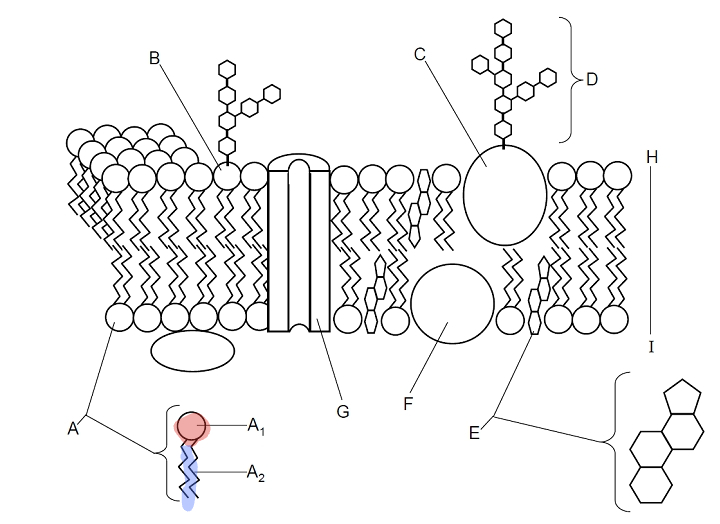
Which parts are A1 and A2?
A1 = Hydrophilic head, A2 = Hydrophobic fatty acid tail
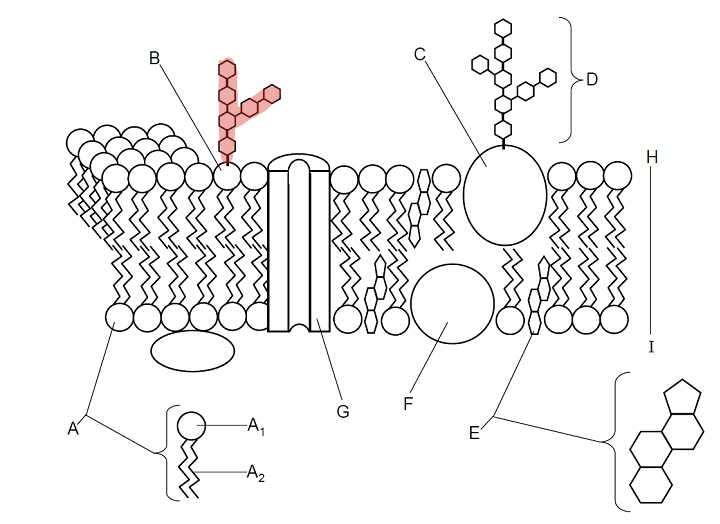
Which part is B?
Glycolipid
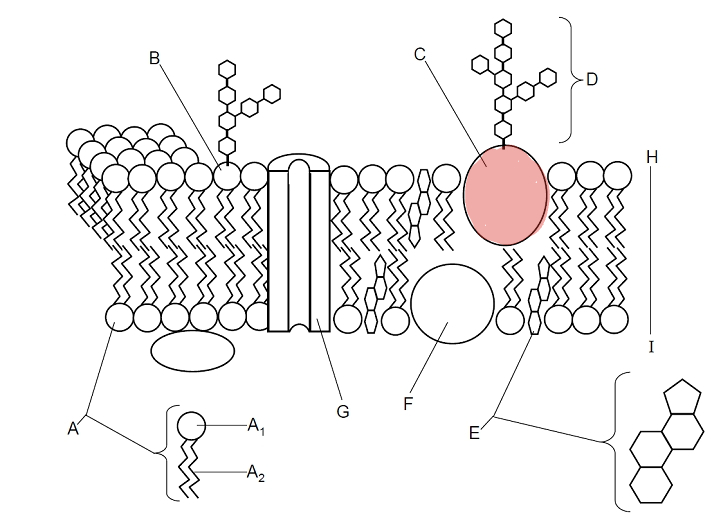
Which part is C?
Glycoprotein
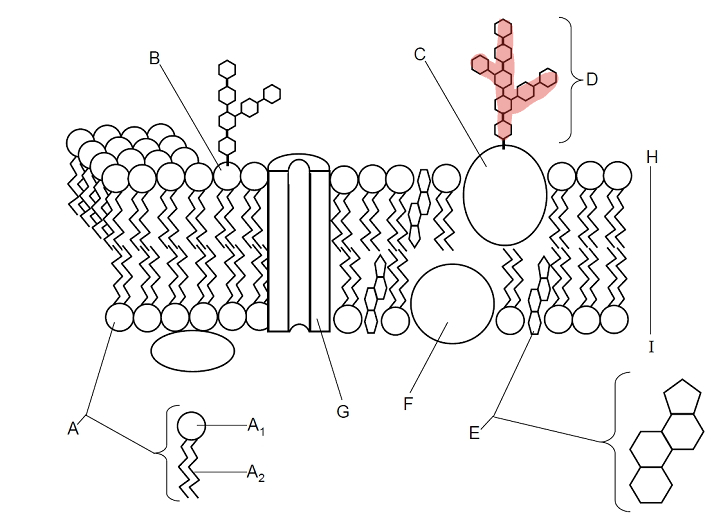
Which part is D?
Carbohydrate Chain
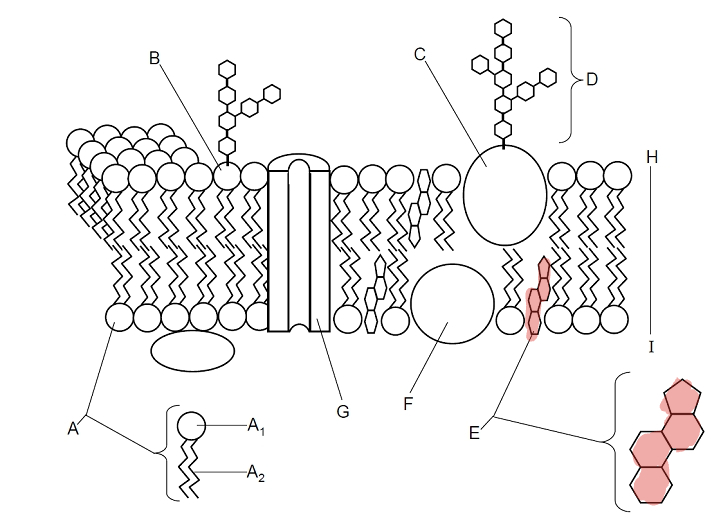
Which part is E?
Cholestrol
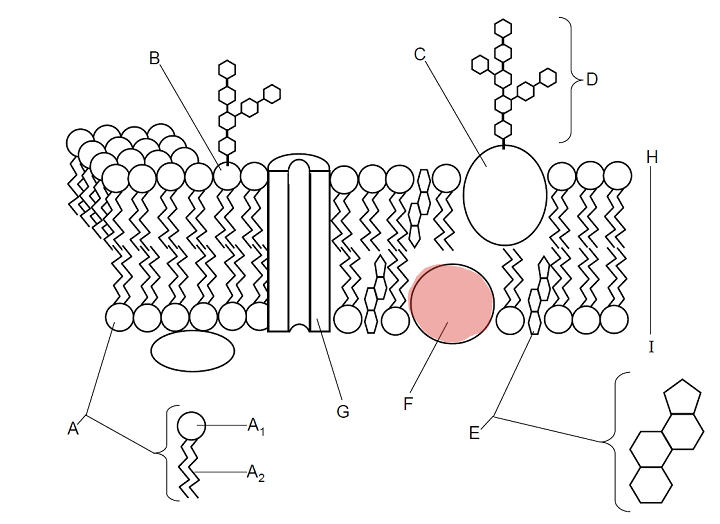
Which part is F?
Protein
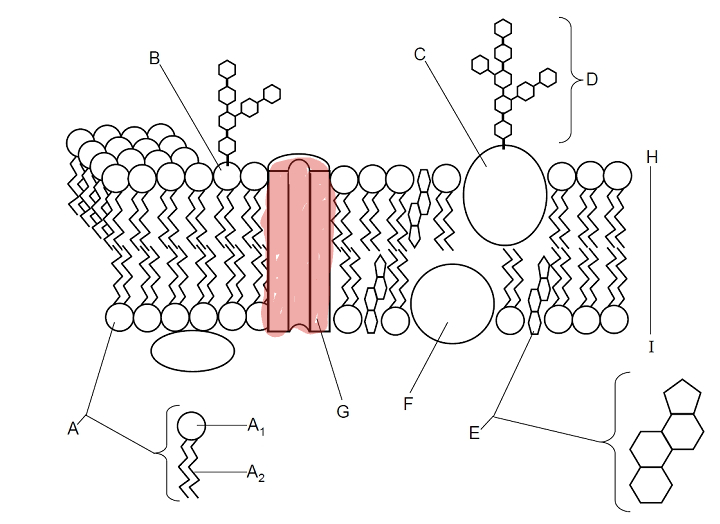
Which part is G?
Protein Channel
What 3 parts make up the hydrophilic head?
Polar group
Phosphate
Glycerol
What does it mean when the phospholipid is hydrophilic and hydrophobic?
The head is hydrophilic and soluble in water while the tail is hydrophobic and insoluble in water. The phospholipid is polar.
Why is the cell membrane described as a Fluid Mosaic Model?
“Fluid” = the cell membrane is very flexible and moves around easily
“Mosaic” = made up of many parts
“Model“ = represents the cell membrane
What acts as doors with channels on the cell membrane?
Membrane proteins
What do receptors do?
Help identify the cell
Cell signaling
Recognize and bond to carbohydrates such as sugars or starches
Cell signaling
When the receptor interacts with itself/others to receive/transmit chemical signals to carry out functions
What does the cholestrol do?
Helps “pack in” the phospholipids, giving it structure and making it more fluid at colder temperatures
Adds stability at warmer temperatures
Separates the phospholipid tails so they don’t stick together
What does glycoprotein do?
Involved with cell recognition and the immune response, also act as receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters. Also helps stabilize membrane structure.
What does the glycolipid do?
Like the glycoprotein, it can act as surface receptors and help stabilize the membrane. The difference is that it is attached to a hydrophilic head.
Channel protein
Have pores filled with water which act as channels for water-soluble ions to pass through the membrane by FACILITATED DIFFUSION.
Carrier protein
Can change their shape to move certain substances which are too large to move by facilitated diffusion. They are specific to the substance they transport, due to shape.