reproduction in plants
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
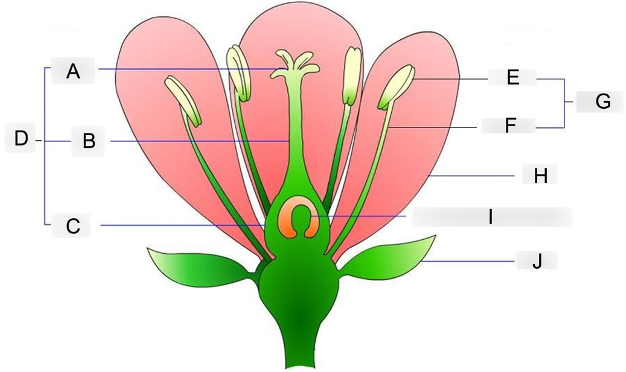
what is A?
stigma
where pollen grains land and germinate
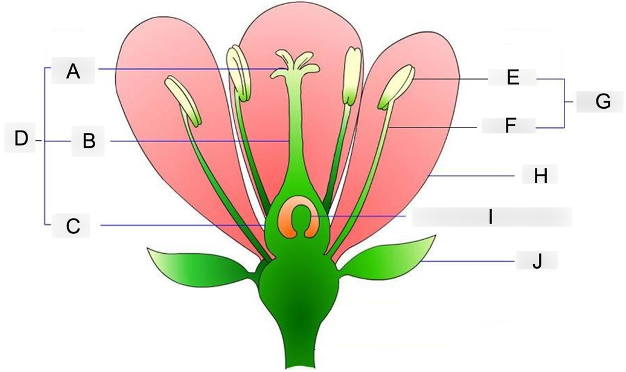
what is B?
style
acts as a tube structure that connects the pollen receiver to the ovary
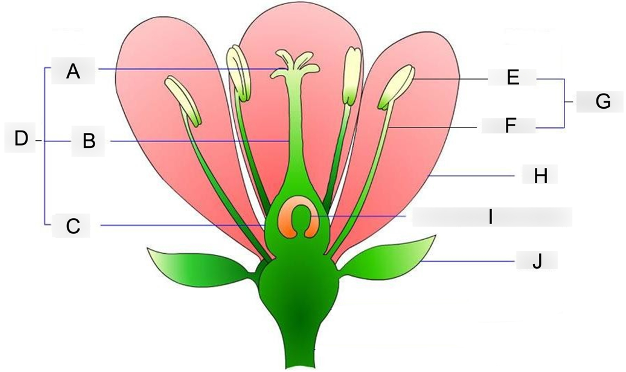
what is C?
ovary
contains the egg cells and prepares for fertilization
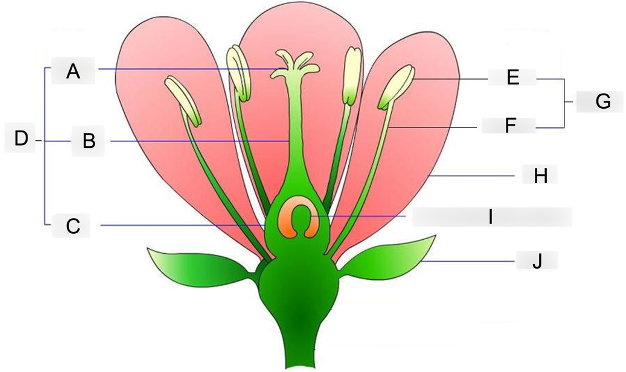
what is D?
carpel
acts as the female reproductive organ
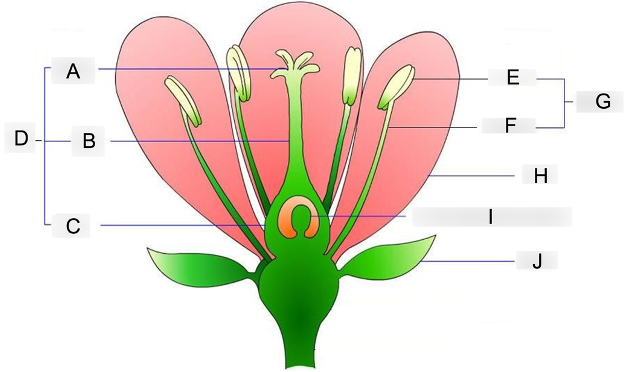
what is E?
anther
holds and protects the pollen grains
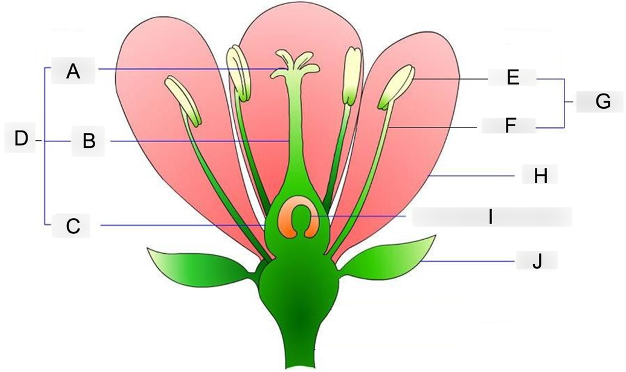
what is F?
filament
supports and holds the anther up
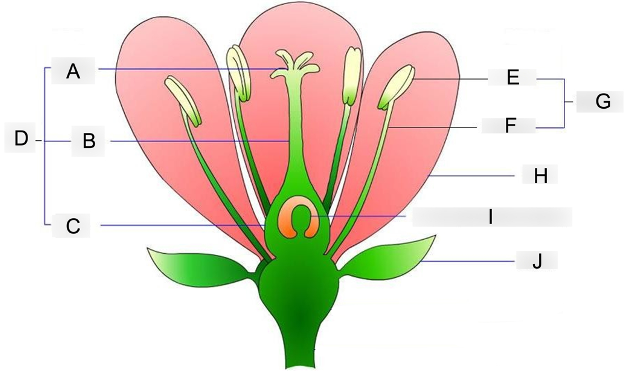
what is G?
stamen
acts as the male reproductive organ
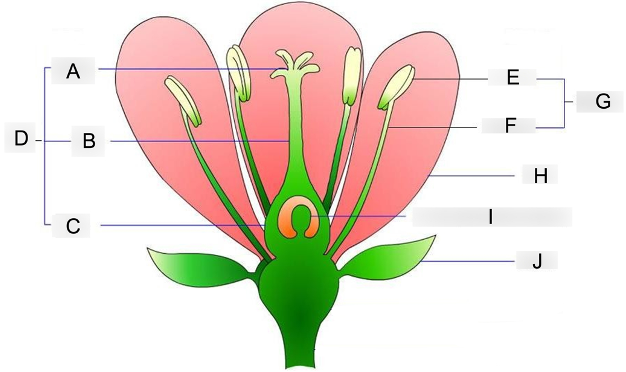
what is H?
petal
contains scent and attractive color that attracts insects to them
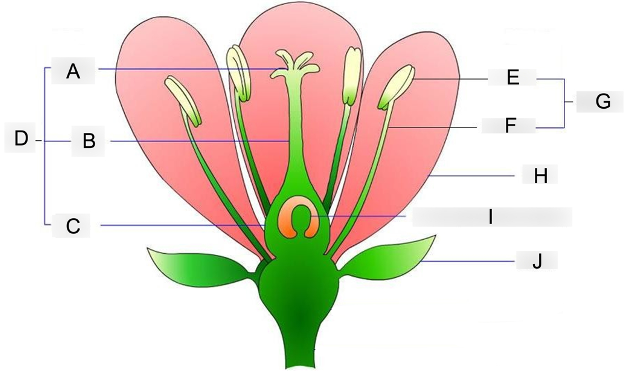
what is I?
embryo sac
where the eggs are stored before fertilization occurs
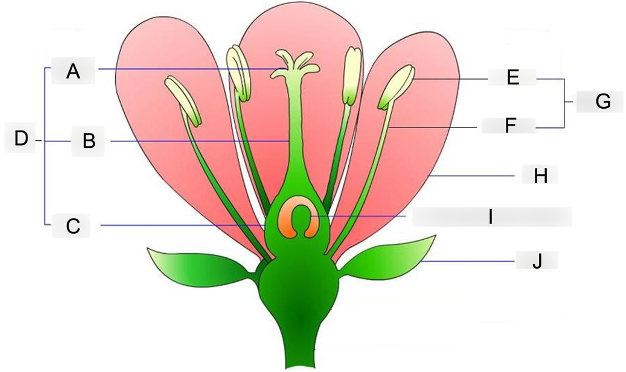
what is J?
sepal
protects the flowering bud from damage until its ready to bloom
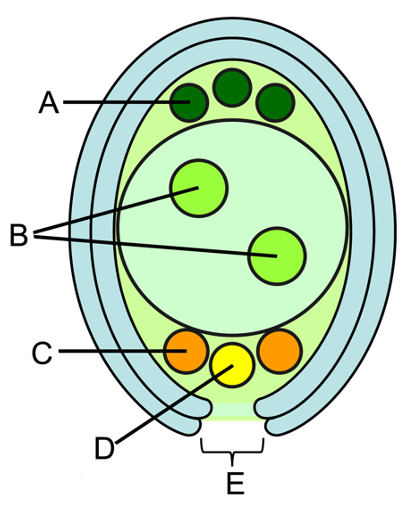
what is A?
antipodals
provides nutrient to the developing embryo
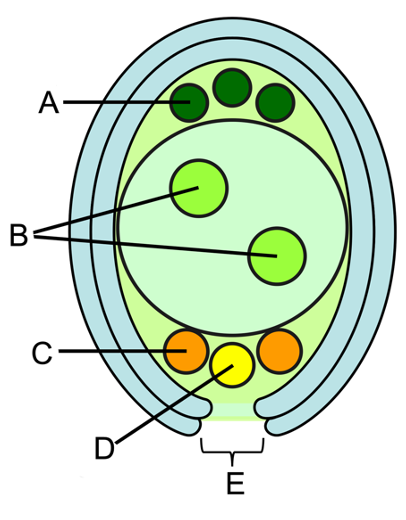
what is B?
polar nuclei (n)
contributes to the formation of the endosperm
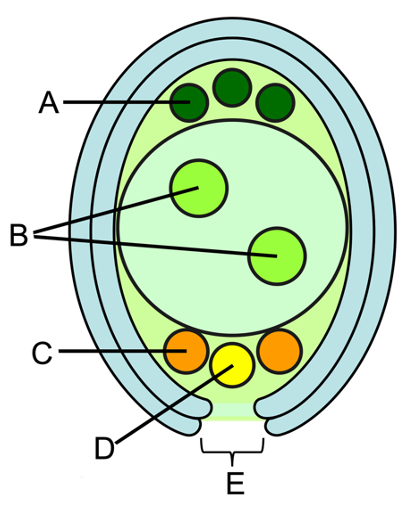
what is C?
synergids
directs the pollen tube towards the egg cell
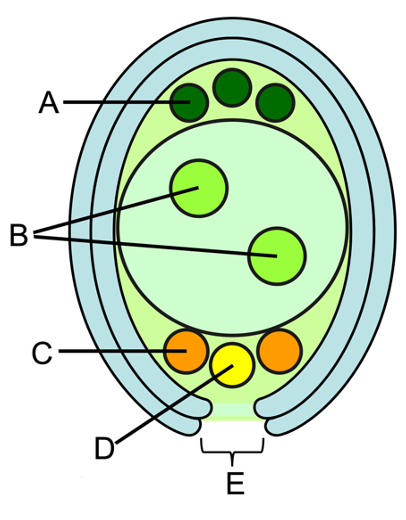
what is D?
egg cell
where it is fertilized with the sperm cells
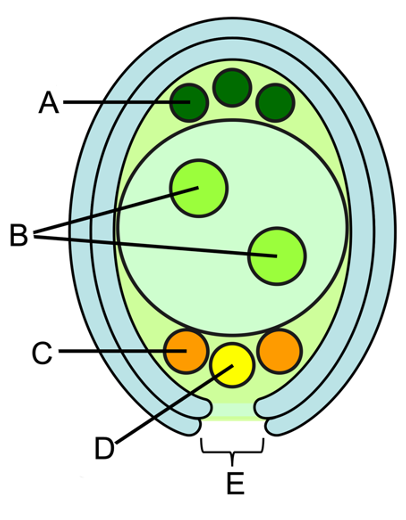
what is E?
micropyle
where pollen tube enters in to deliver the male gamete (sperm) for fertilization
why are pollinators important to plant reproduction and what structures have plants evolved to attract pollinators?
plants have brightly colored petals that pollinators can see in both visible and UV light and flowers have nectaries and pollen grains that are both high in caloric content for pollinators
what is a sporophyte
an adult plant that produces tiny cells called spores through meiosis
what is a gametophytes?
spores grow into new and developed plants called gametophytes and this occurs during mitosis where sperm and eggs cells are produced
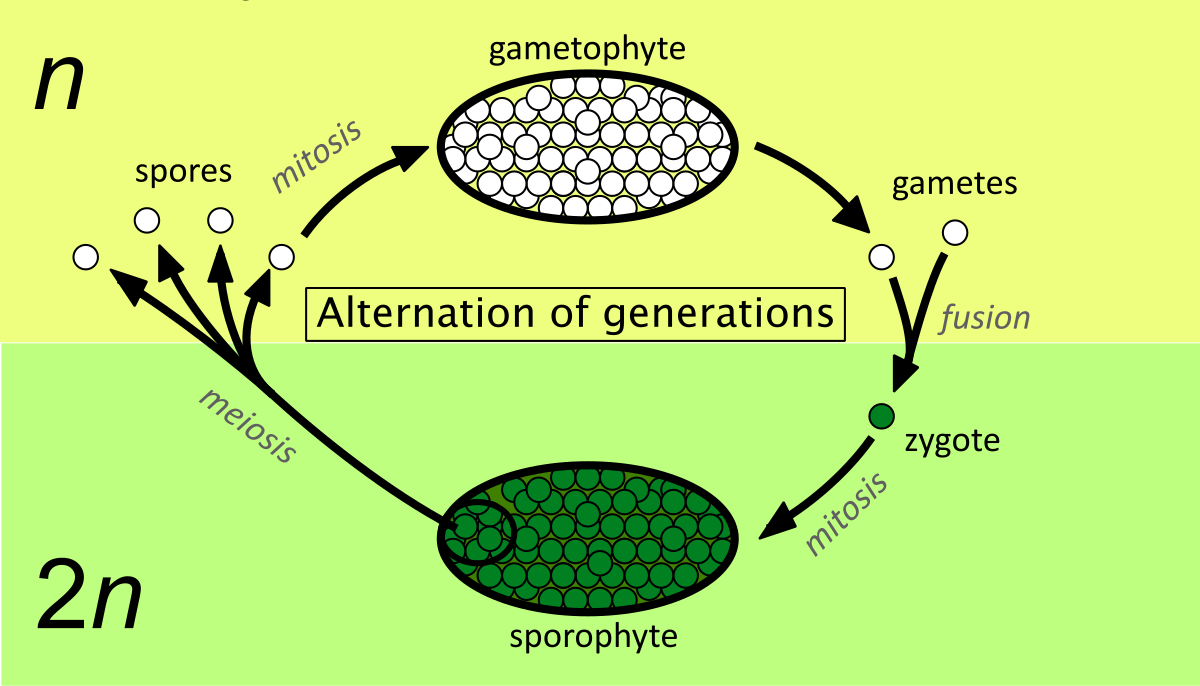
what role does gametophytes and sporophytes play in alteration of generations?
the gametophytes develops from a spore and produces gametes which fuse to form a zygote that grows into a sporophyte continuing the life cycle of plants
what is the plant equivalent of parthenogenesis (in animals)
apomixis
plants make an exact copy of itself through its own seed
how similar are the offspring when produced through apomixis
they are genetically identical
if a hermophoditic plant fertilizes itself, are the offspring identical or different?
the offspring will not be identical, instead it will be different to the variety of different genetic variations that can be passed down to the offspring
what is double fertilization?
two sperm cells from a pollen grain fuse with two different female gametes within the ovule
what cells are fertilized during double fertilization?
the egg cell is fertilized by one sperm cell to form the embryo, while the central cell is fertilized by another sperm cell to form the endosperm
which cell develops into a zygote and then the embryo?
egg cell
what is the endosperm?
tissue that surronds and nourishing the developing embryo inside a seed
how does fruit play a role in seed dispersal
provides a protective casing for seeds, with bright colors and sweetness that attracts animals to eat them
seed germination cycle
step one: resting stage
the seed is dormant (inactive) protected by its seed coat and contains the embryo (baby plant) and stored food
step two: right conditions
when the seed gets water, oxygen and the right temperature it “wakes up” and starts germinating
step three: sprouting (germination)
seeds absorbs water and swells, the seed coat breaks open, the root (radicle) grows down into the soil to absorb water and nutrients, the shoot (plumule) grows upward to reach sunlight
step four: new plant grows
the seedling develops leaves and begins photosynthesis making its own food and growing into a mature plant
what is meristem
consists of undifferentiated cells that are comparable to stem cells that divide when conditions permit