Histology, Tissue Types, and Cell Junctions: Key Concepts for Biology Students
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is histology?
The study of tissues, their structure, and how they are organized to perform specific functions.
How are cells held together to form tissues?
By intercellular junctions, which connect and communicate between neighboring cells.
What are tight junctions?
Membranes of adjacent cells fuse and merge, closing the space around the cells; for example, they form sheet-like layers around the lining of the small intestine.
What are desmosomes?
Mechanical links or rivets that fasten cells together and reinforce the structure; for example, they bind cells of the outer skin (epidermis).
What are gap junctions?
Tubular channels that link cells and allow for the exchange of ions and small molecules; for example, they are found in muscle cells of the heart and digestive tract.
What is the blood-brain barrier (BBB)?
A vast network of capillaries in the brain whose cells are held together by overlapping tight junctions, preventing many substances from passing into the brain.
What substances can cross the blood-brain barrier?
Small molecules soluble in fat, such as alcohol, caffeine, nicotine, and antidepressants.
What are the four major tissue types?
Epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
What is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
To cover body surfaces, line organs, and compose glands.
What are the general characteristics of epithelial tissue?
Has a free (apical) surface, a thin basement membrane, is avascular, and readily divides for rapid healing.
What distinguishes simple epithelium from stratified epithelium?
Simple epithelium has a single layer of cells, while stratified epithelium has two or more layers.
What are the shapes of epithelial cells?
Squamous (thin, flattened), cuboidal (cube-like), columnar (elongated), and transitional (changes shape based on need).
What is keratinization?
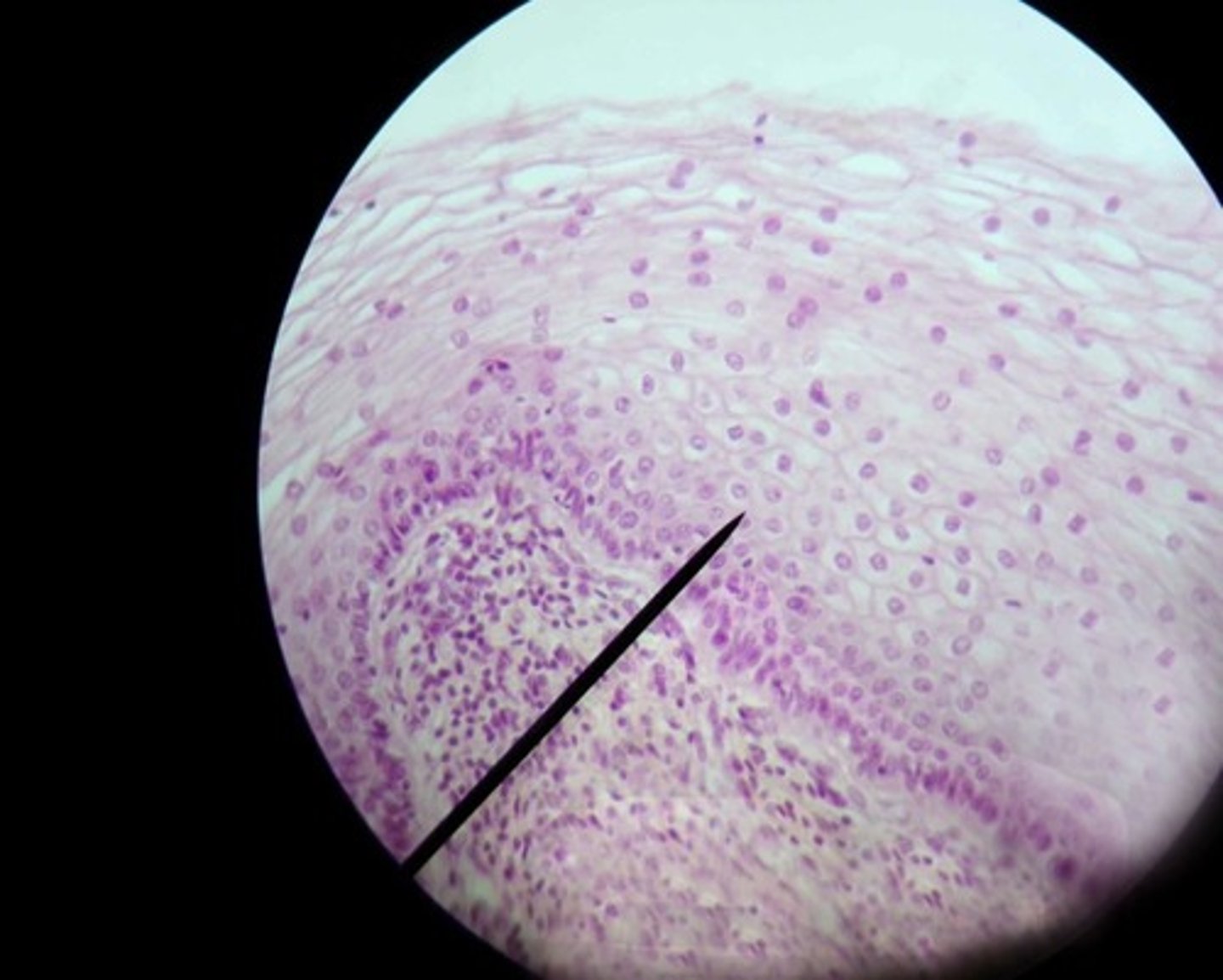
The process where keratin accumulates in tissues, providing extra protection in areas under friction, found in stratified squamous epithelium.
What is glandular epithelium?
Specialized cells that produce and secrete substances; can be unicellular or multicellular.
What is the difference between exocrine and endocrine glands?
Exocrine glands secrete products into ducts that open onto surfaces, while endocrine glands have no ducts and empty secretions into the bloodstream.
What is the most common disease associated with epithelial tissue?
Cancer (carcinomas), as most cancers arise in epithelial tissues.
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissue.
What characterizes skeletal muscle tissue?
It is striated, under voluntary control, and constitutes 40% of a human's body weight.
What distinguishes smooth muscle tissue?
It lacks striations, is involuntary, and makes up the walls of hollow organs.
What is unique about cardiac muscle tissue?
It is found only in the heart, is striated and branched, and is controlled involuntarily.
What are intercalated disks?
Structures that join cardiac muscle cells end to end, containing gap junctions for communication.
What are the three main parts of a neuron?
Cell body, axons, and dendrites.
What is the primary function of neurons?
To communicate with each other and other tissues by sending electrical signals called action potentials.
What are neuroglia?
Support cells of the nervous system that nourish, protect, and insulate neurons.
What is the most abundant tissue by volume in the body?
Connective tissue.
List three structures made of connective tissue.
Bone, cartilage, and blood.
What are the main functions of connective tissue?
Provide support, store fat, produce blood cells, connect tissues, protect against infection, cushion and insulate, and provide transport.
What is the extracellular matrix (ECM) composed of?
Protein fibers and ground substance (fluid, gel-like, or solid).
What are the three types of protein fibers found in connective tissue?
Elastic fibers, collagenous fibers, and reticular fibers.
What is the role of elastic fibers?
To provide elasticity; they can be stretched and return to their original shape.
What is the function of collagenous fibers?
To provide strength and flexibility; they are important in ligaments and tendons.
What are fixed cells in connective tissue?
Cells that reside in the tissue for an extended period, such as fibroblasts and mast cells.
What do mast cells do?
Release chemicals that promote inflammation and prevent blood clotting.
What are wandering cells in connective tissue?
Cells that move through and appear in tissues temporarily, usually in response to injury or infection.
What is the primary role of macrophages?
To ingest foreign particles and act as scavenger cells for defense against infection.
What are the two methods of tissue repair?
Regeneration and replacement.
What is inflammation?
The body's response to injury or stress, characterized by redness, heat, edema, pain, and disruption of function.
What mediators are released during inflammation?
Histamines, kinins, prostaglandins, and leukocytes.
What is the role of neutrophils in tissue repair?
They are phagocytic white blood cells that ingest bacteria and debris at the injury site.
What happens if the edges of a wound are close together?
A clot forms, and epithelial cells regenerate under the scab, leading to normal healing.
What is granulation tissue?
A tissue formed during healing that consists of collagenous fibers, blood vessels, and fibroblasts.
What is wound contracture?
The contraction of granulation tissue that pulls the edges of a wound closed, which can lead to scarring.
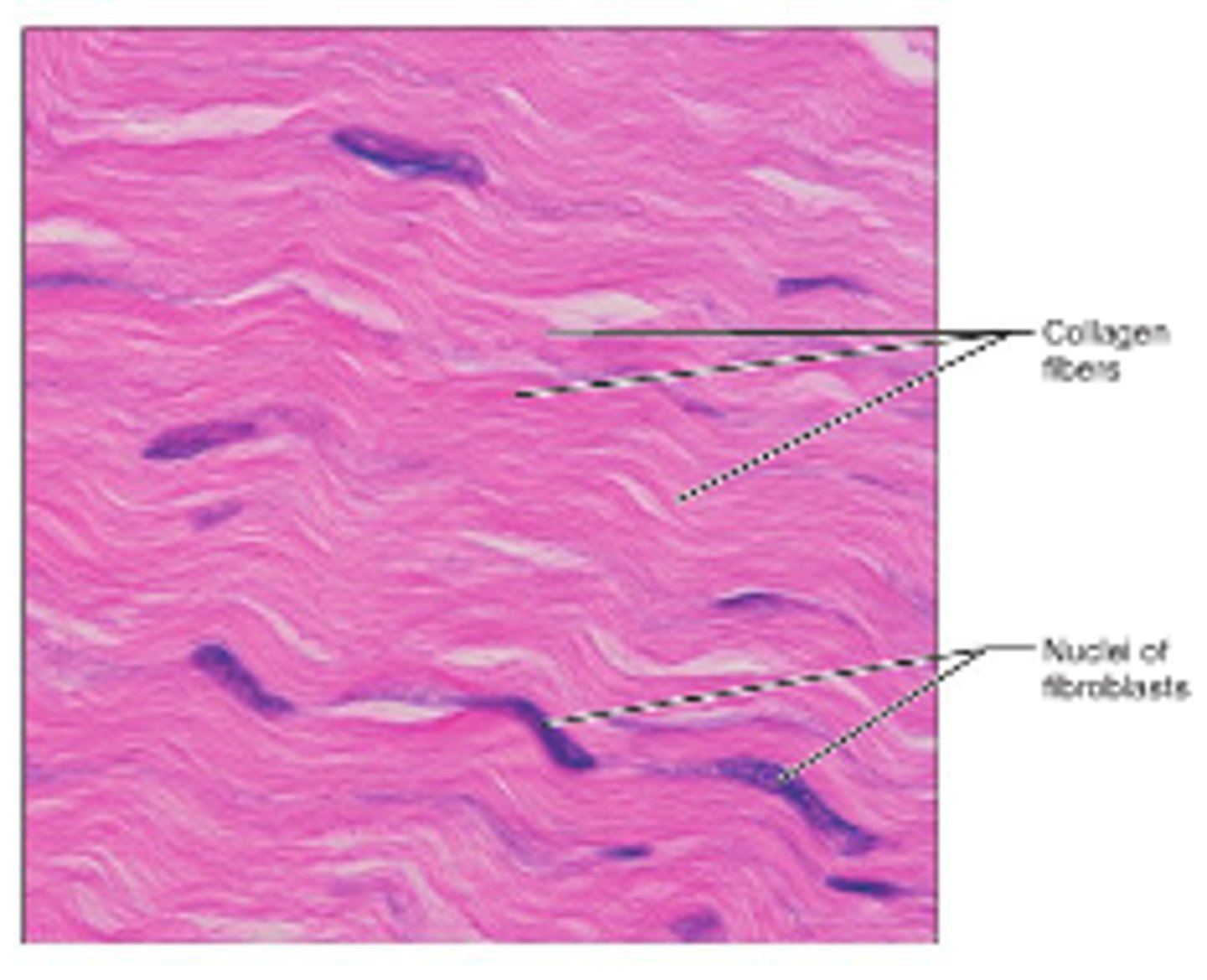
dense regular ct
elastic cartalige
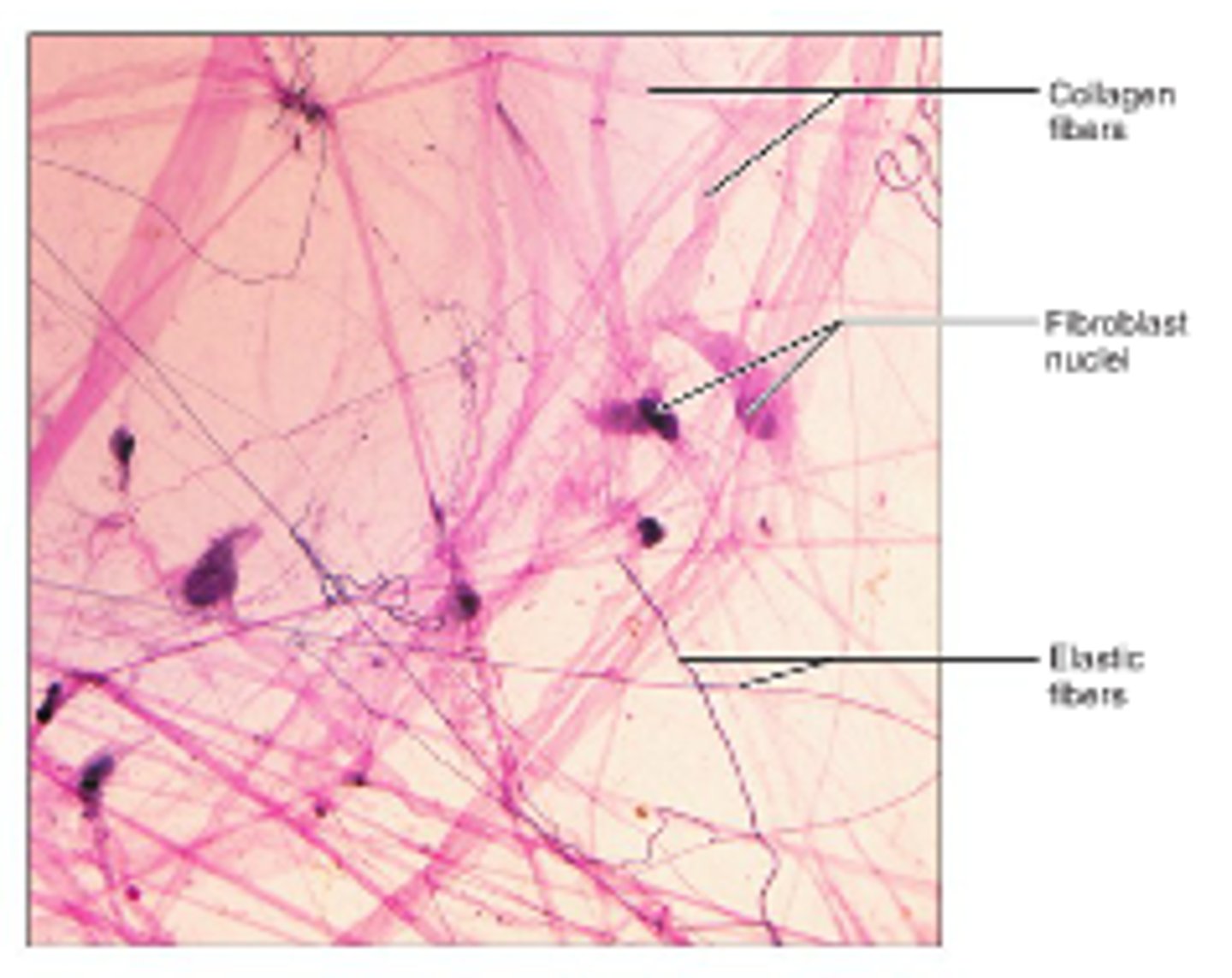
Areolar CT
adipose ct
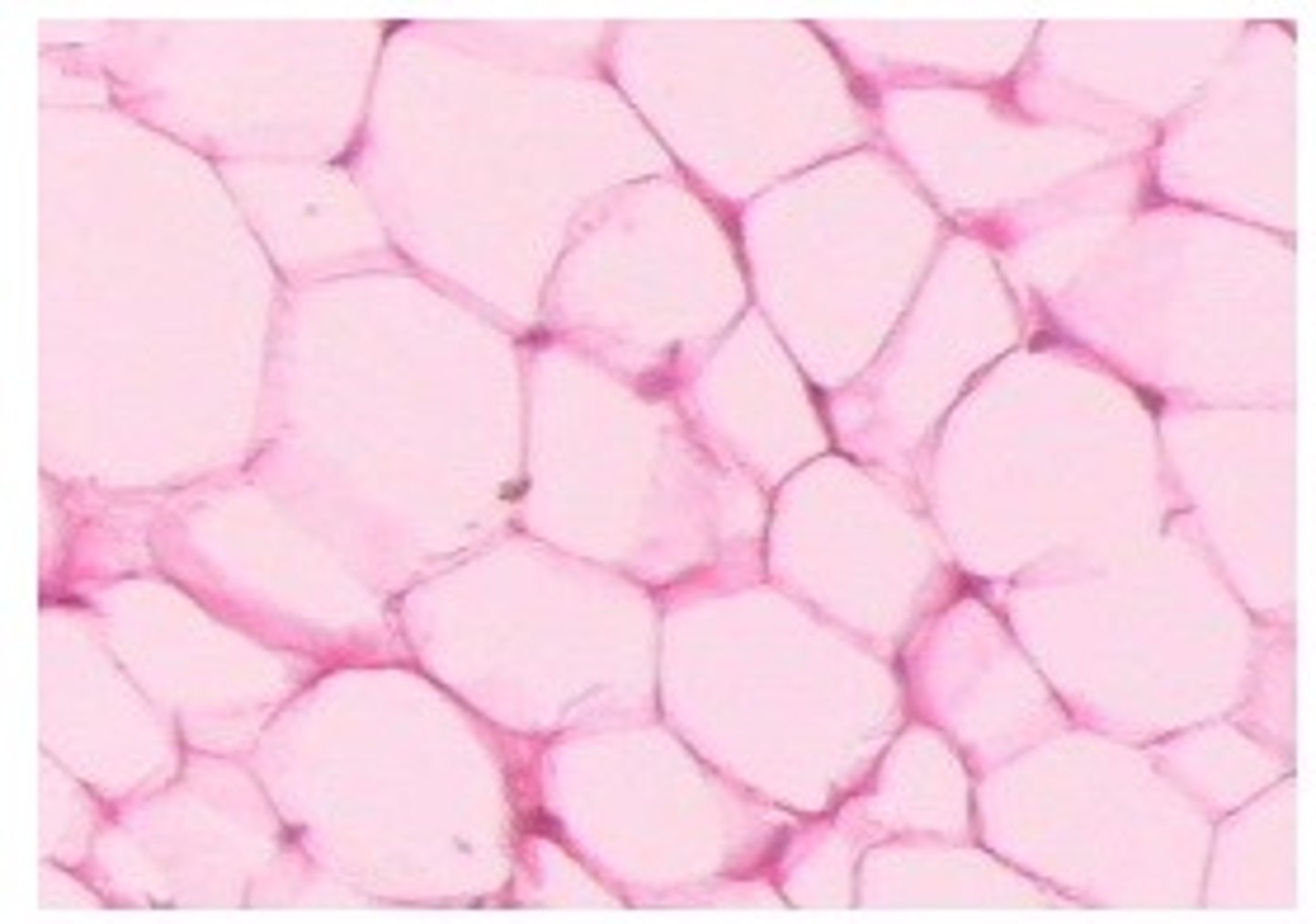
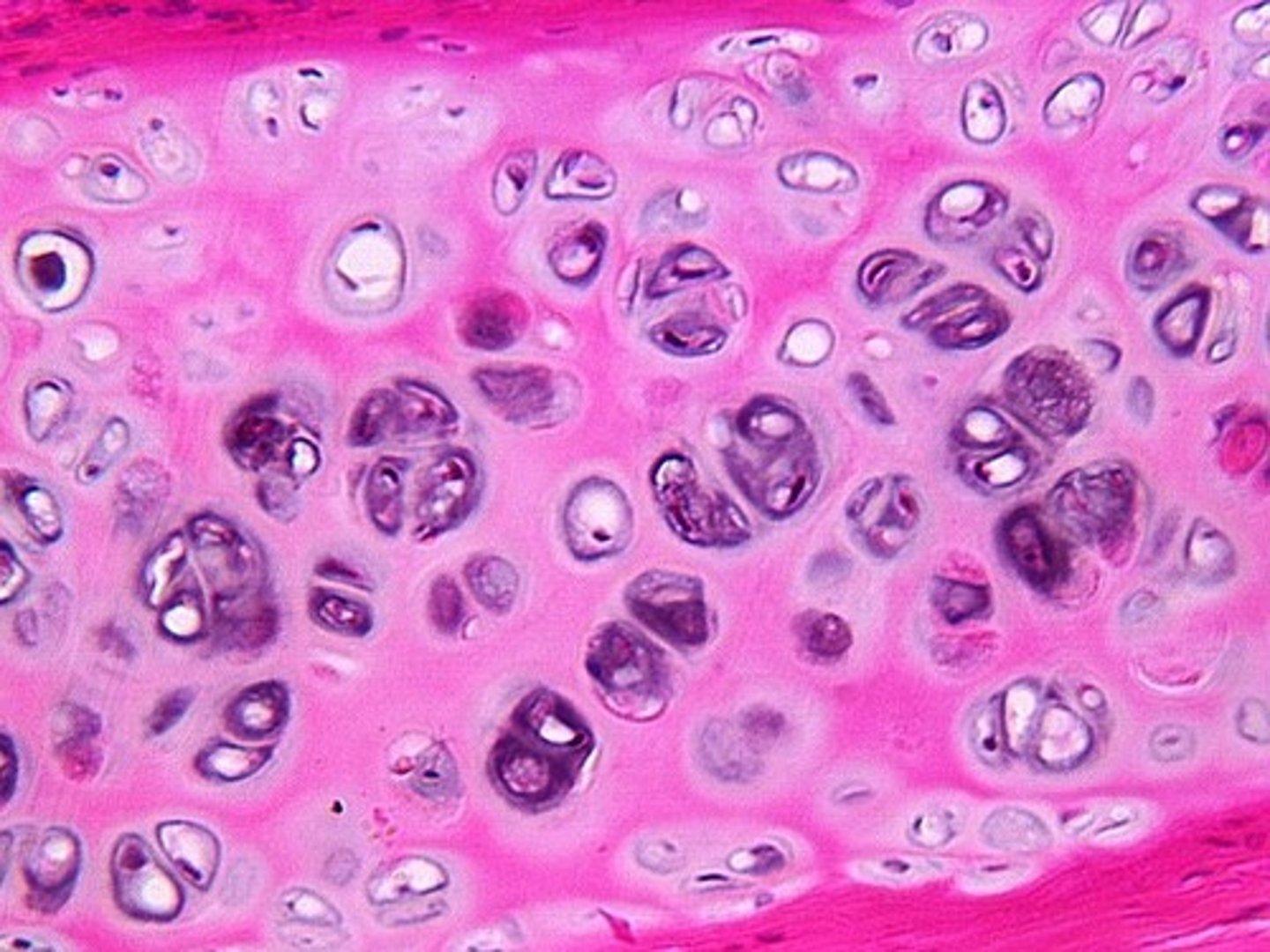
hyaline cartalige
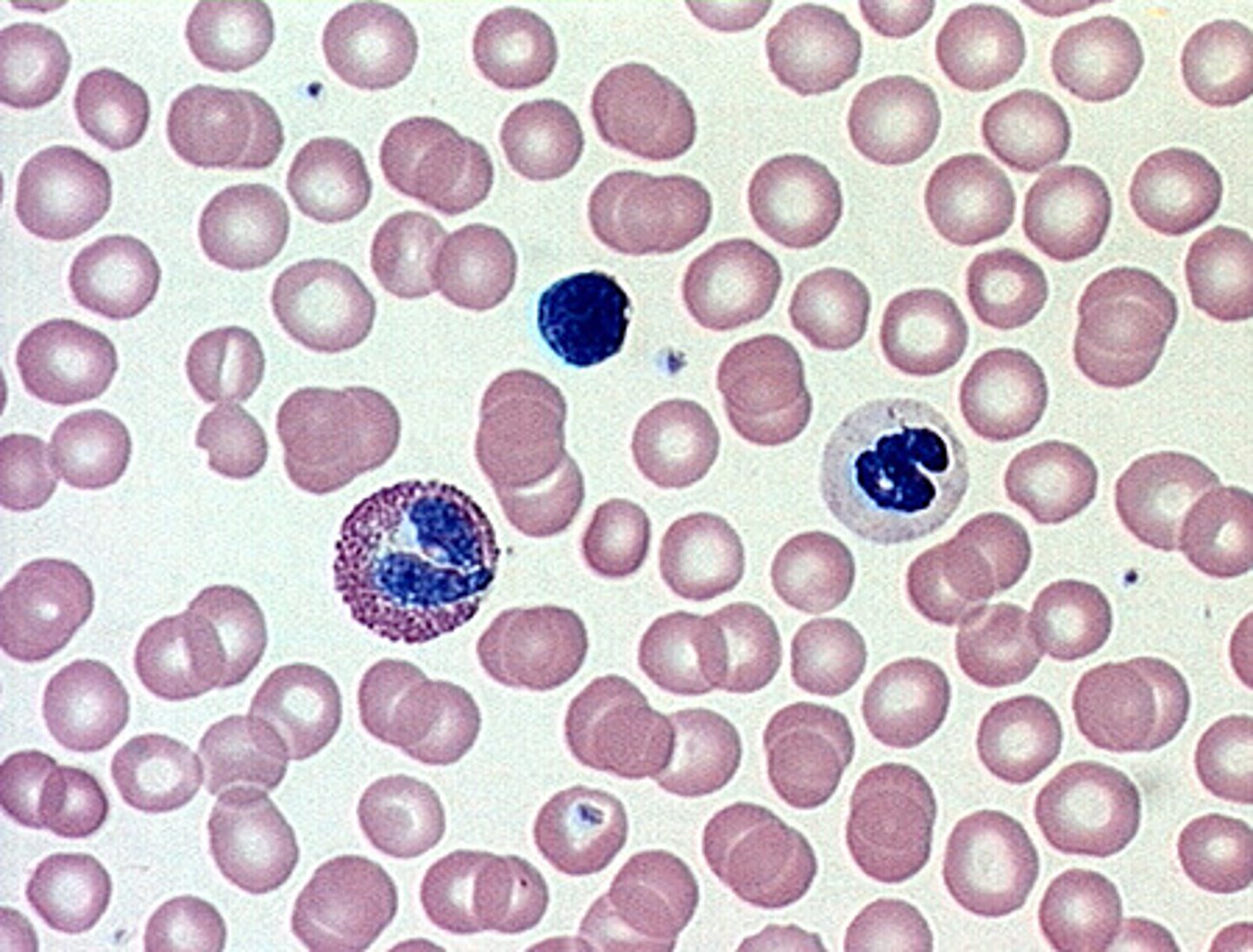
blood
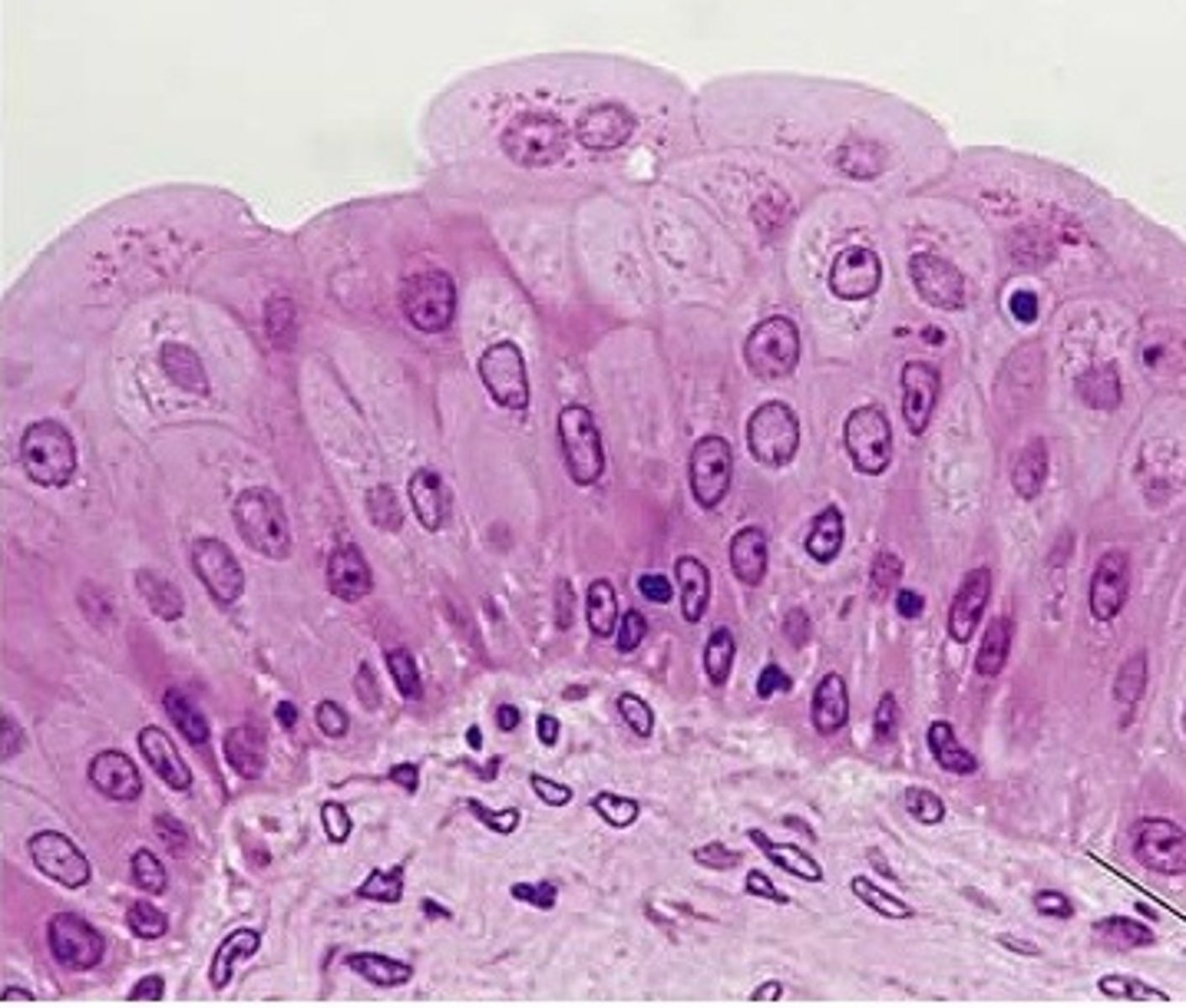
transitional et
simple squamous et
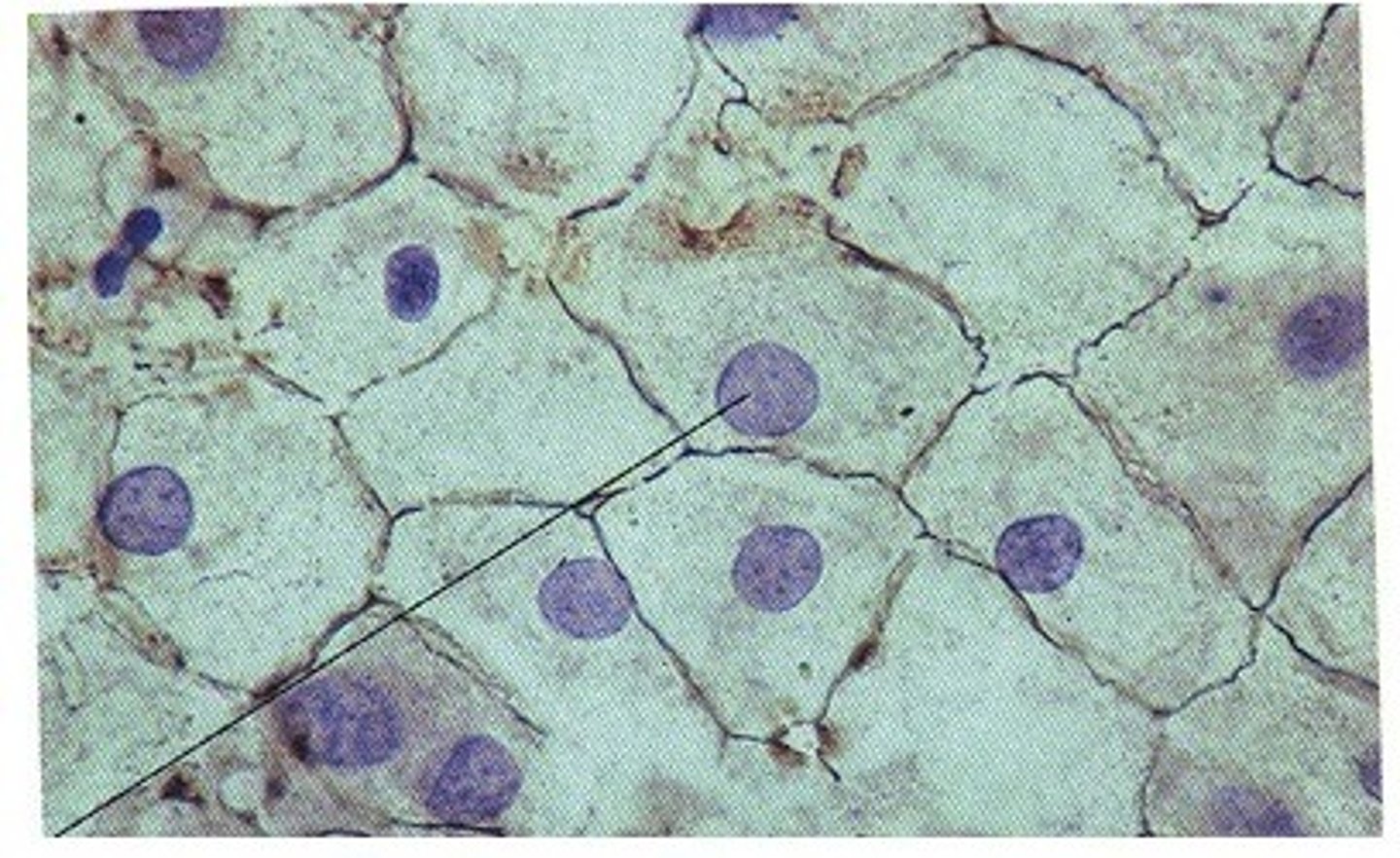
simple cuboidal et
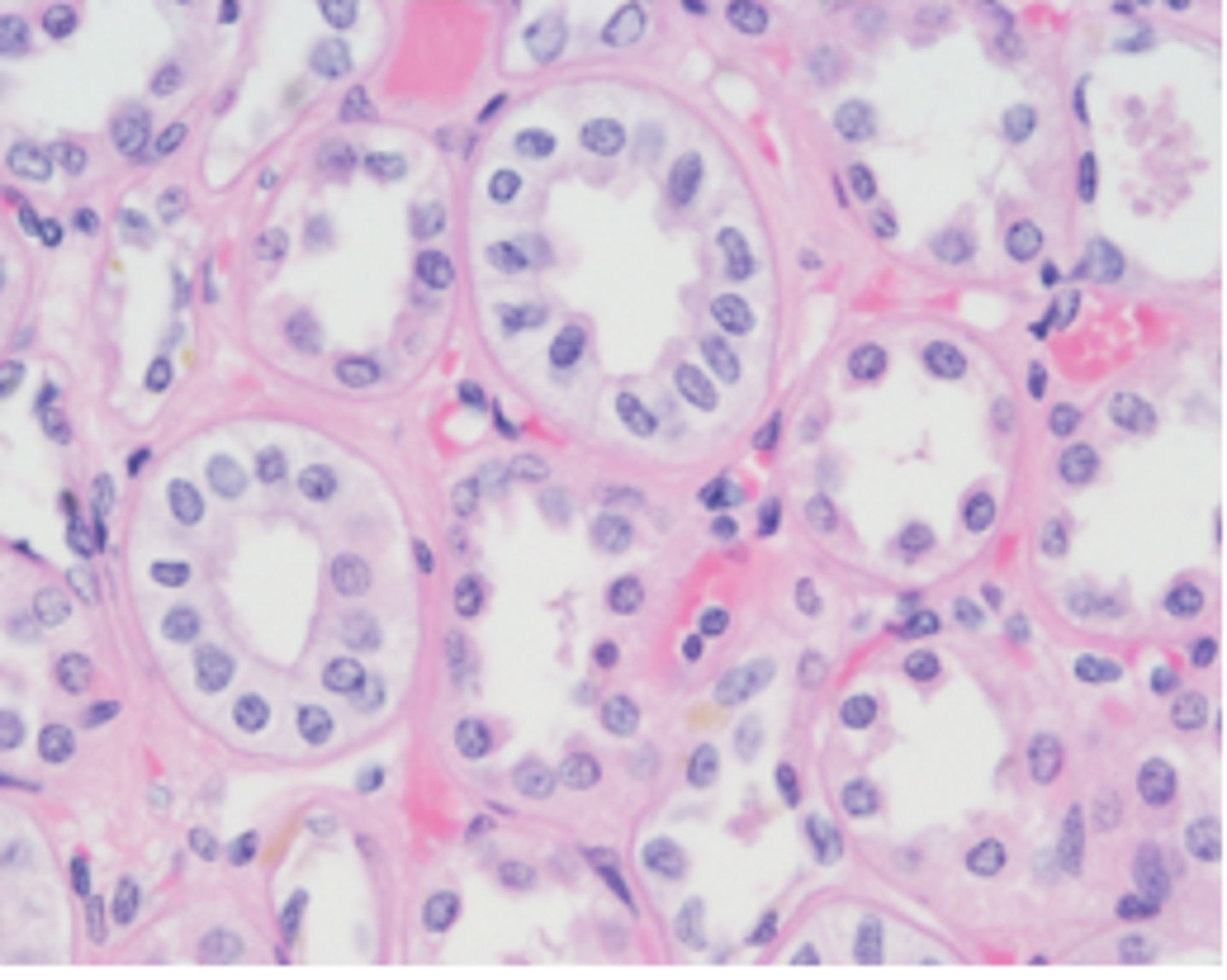
simple columnar et
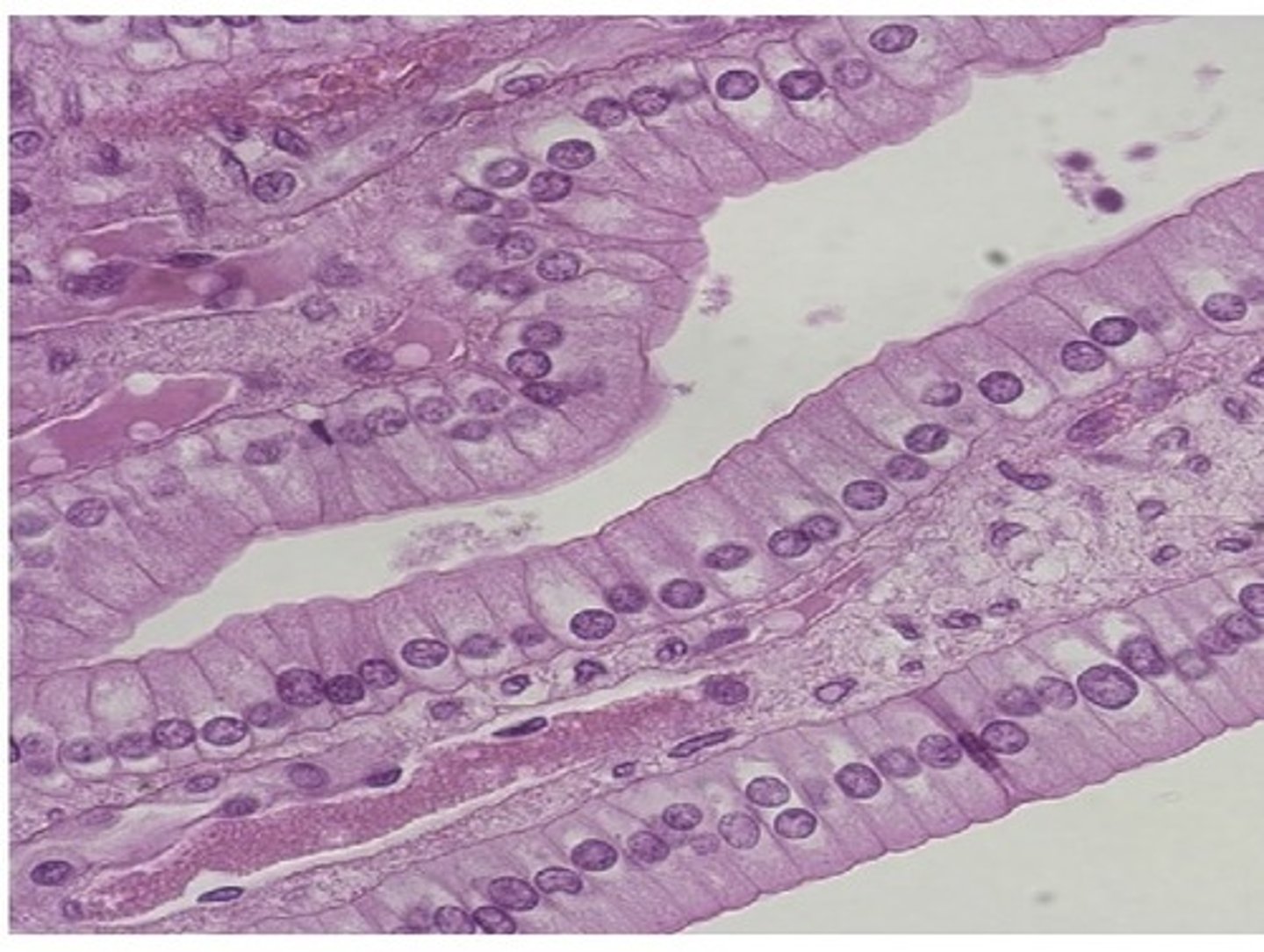
psuedostratified columnar et
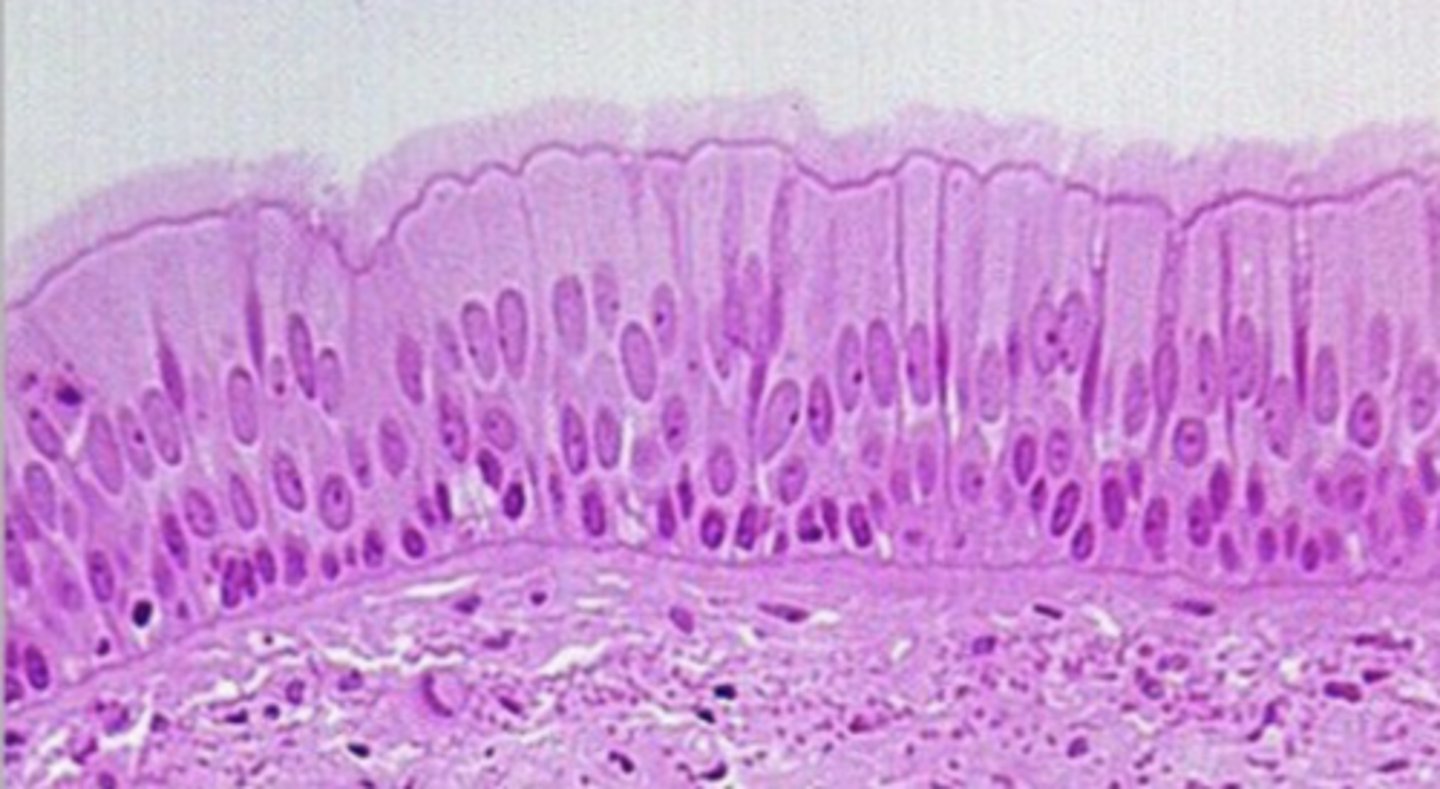
stratified squamous nonkeritanized
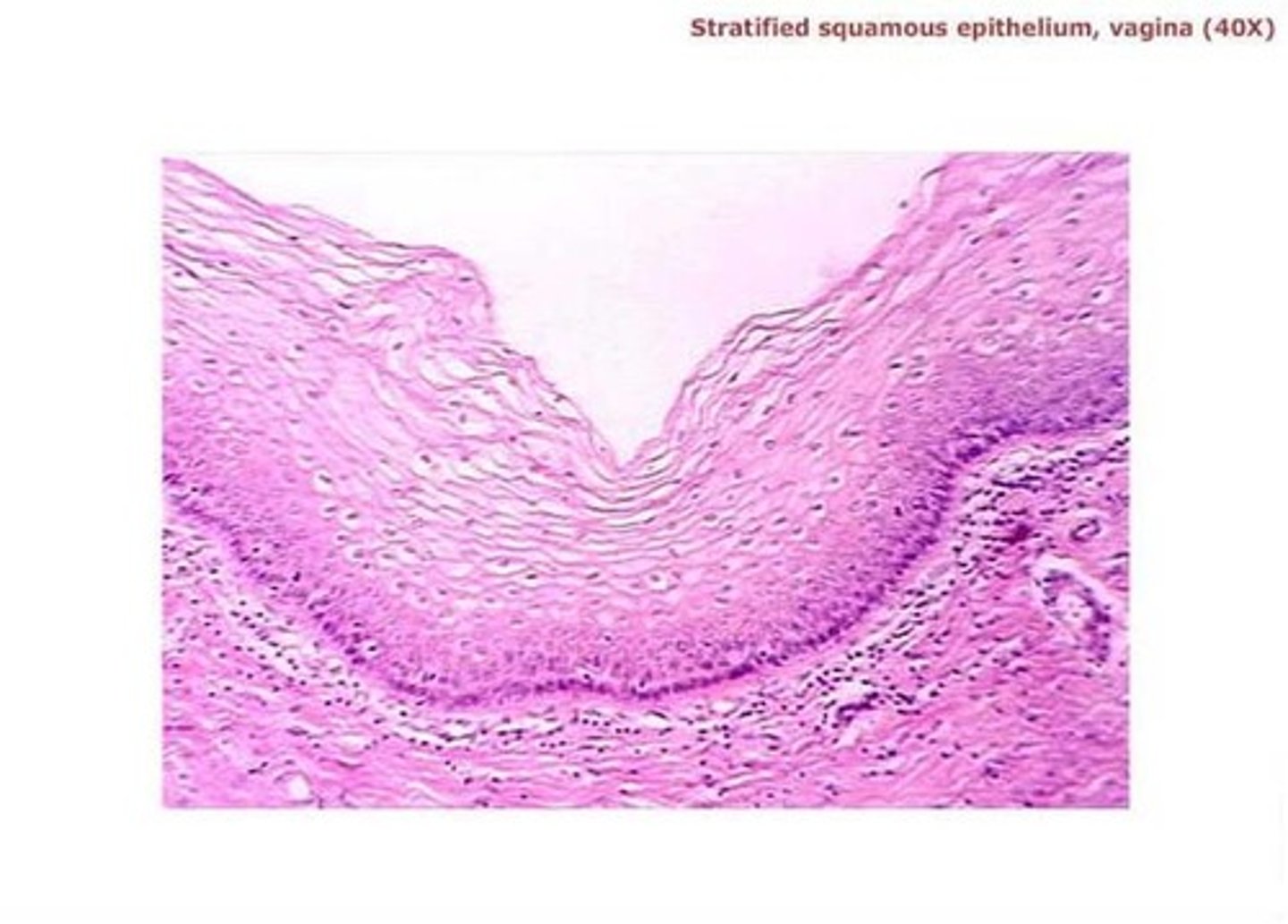
stratified squamous keritanized