Theme 5
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
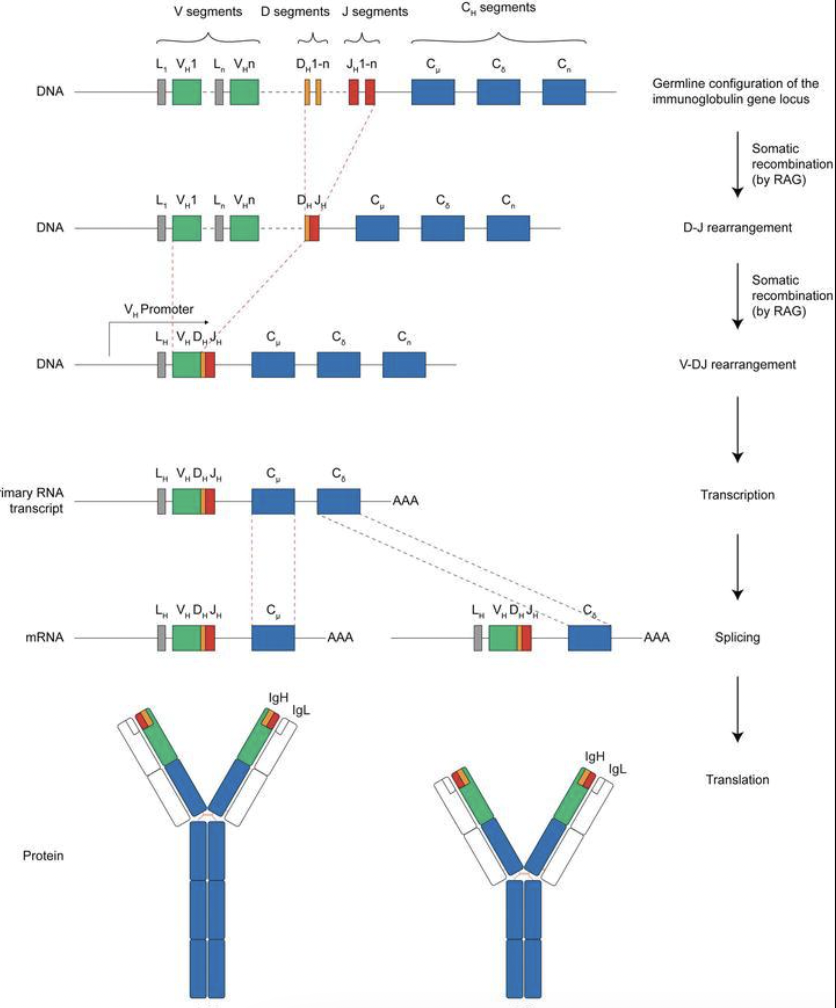
Generation of diversity in immunoglobulin
Antibody repertoire - total number of antibody specificities available to an individual
Germline theory - each antibody is encoded by a separate gene
Somatic diversification - antibodies arise from gene segment rearrangement during B cell development
Mechanisms for generating antibody diversity
V(D)J recombination - genetic shuffling of V, D and J gene segments
Somatic hypermutation - point mutations in activated B cells increase affinity
Class switch recombination - switches the antibody constant region to change its class without altering specificity
V(D)J recombination
One D segment and J segment selected randomly, DNA in between is cut out, DJ join
One V segment is chosen and joined to previously formed DJ, DNA segments are cut using RAG-1 and RAG-2 enzymes
The VDJ sequence is transcribed into mRNA and gets translated into the variable region of the antibody
The variable region is then joined with constant C region
This determines antibody class
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death
Prevents the overaccumulation of lymphocytes
B cells that are not activated undergo apoptosis
Infected cells can self destruct to limit infection spread
Clonal selection
Specific B and T cells are selected and expanded when encountering antigen
Tolerance - immune system avoids self-reactivity
Clonal detection - self reactive cells are removed early in development
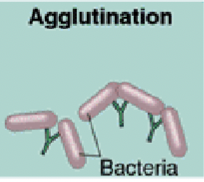
Agglutination
Antibodies cause antigens to clump together
Clumped microbes are easier to trap and remove
Phagocytes can ingest multiple pathogens at once
Example → wrong blood perfusion causes RBC agglutination
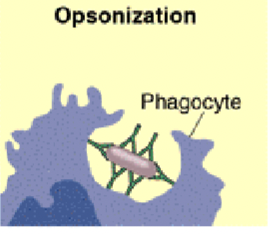
Opsonization
Antibodies coat the surface of a pathogen, Fc region of antibody sticks out
Phagocytic cells (like macrophages and neutrophils) have receptors for the Fc region
When they bind, they are stimulated to engulf and destroy the pathogen
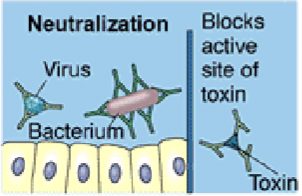
Neutralization
Antibodies bind to viruses, toxins or bacteria and block their ability to bind to host cells
This neutralises toxins by blocking their active site
IgG
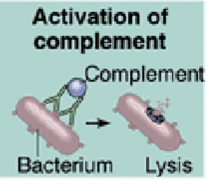
Complement activation
When antibodies bind antigens (especially IgG or IgM), they can activate the complement system → a group of plasma proteins
This complement forms membrane attack complex which punches holes in membranes to cause cell lysis
It can attract immune cells and enhances phagocytosis
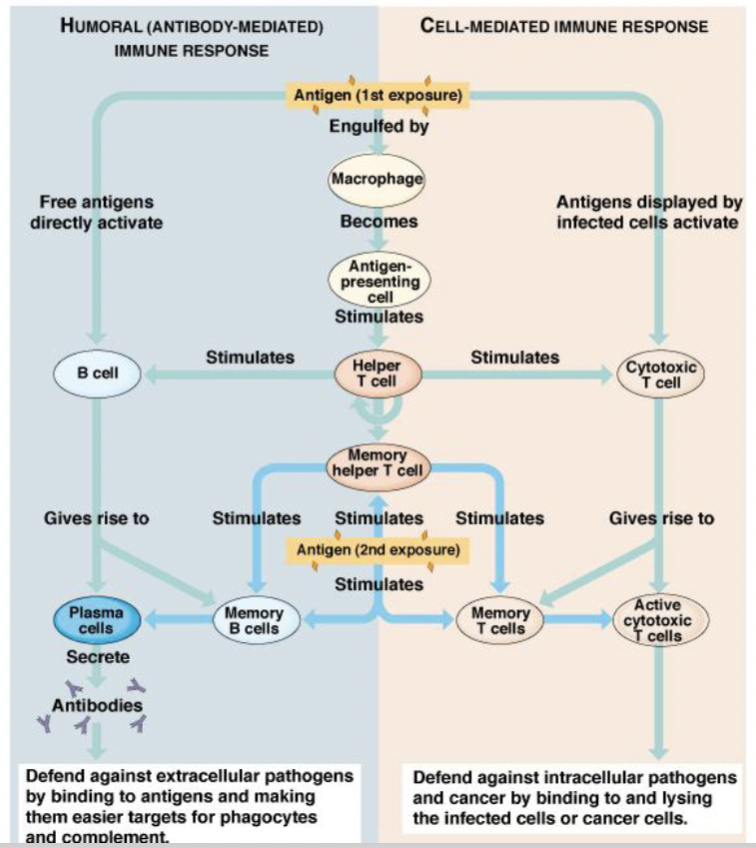
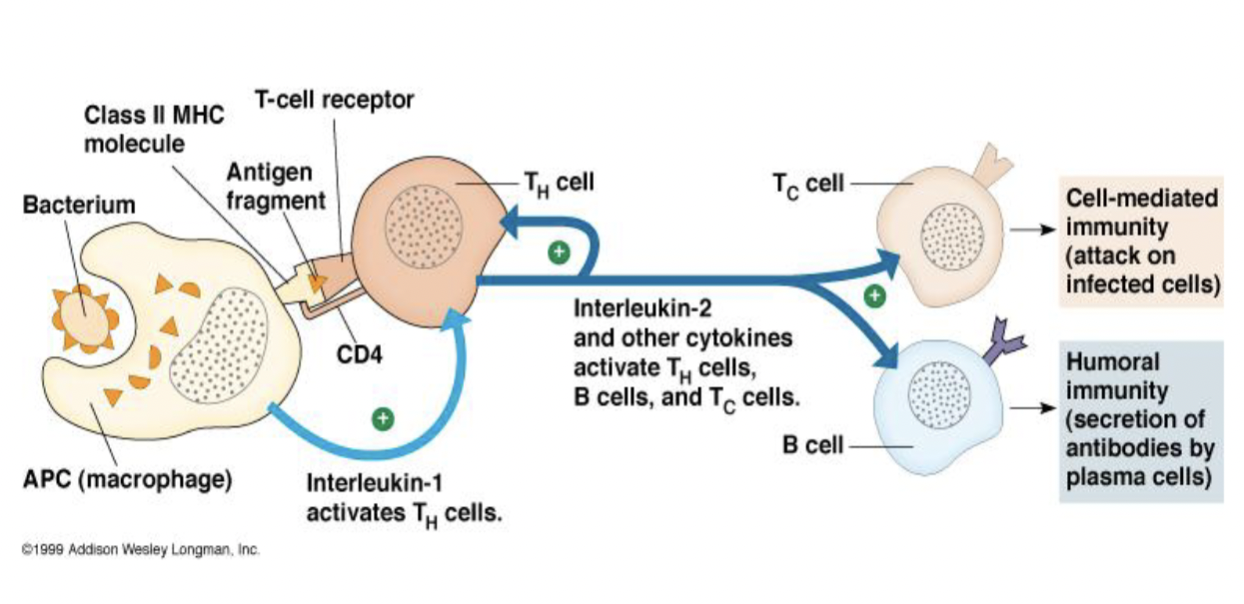
T-cell and cell-mediated immunity
Targets intracellular antigens
Requires antigen presentation MHC
T Helper cells
Most are CD4+
Recognise antigen presented by antigen presenting cells like macrophages
Activates macrophages
Stimulate B cells and cytotoxic T cells
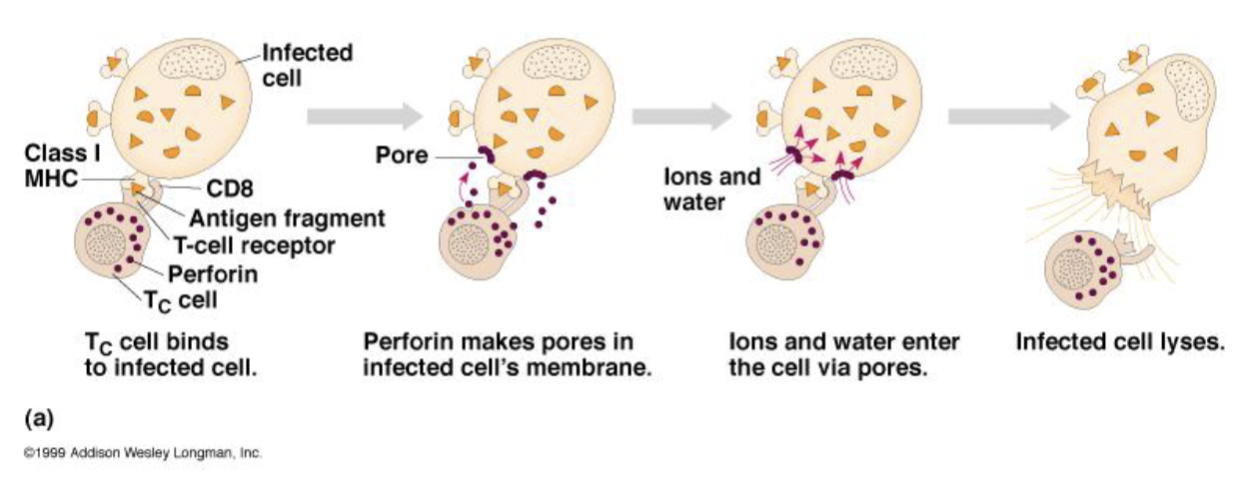
Cytotoxic T cells
Most are CD8+
Kill infected or abnormal host cells (cancer, transplant tissues)
Use perforin to create pores in the target cell → causes lysis
Undergo apoptosis when antigen is cleared
T-dependent vs T-independent antigens
T dependent → require helper T cells, stronger response, antigens are mainly proteins
T independent → do not require T cells, antigens are mostly polysaccharides with repeating subunits, weaker response
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Target cell is covered with antibodies (Fc portion sticks out)
Involves NK cells
Target organism is lysed by substances secreted by attacking cells (cytotoxic granules)
Used to destroy large organisms that cannot be phagocytosed
Overview