Chem 12 U1C1 - Equilibrium
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
open system
allows matter and energy to move in and out
closed system
only allows energy to move in and out
reversible reaction
reactions where the reactants can form products and the products can form reactants
all ______ changes are reversible, whereas only some ______ reactions are reversible
physical, chemical
the reversibility of chemical reactions is dependent on the _______ ______ of both the forward and reverse reactions
activation energies
for a reversible reaction, both the activation energies must be ___ enough that sufficient particles will have enough ______ for a successful collision
low, energy
dynamic equilibrium
when the amount of reactants and products remain constant even though forward and reverse reactions are still occurring
steady state
system has constant properties
conditions for dynamic equilibrium
closed system, reversible reaction
at equilibrium, the
rate of forward and reverse reactions are the same, concentrations and macroscopic properties remain constant
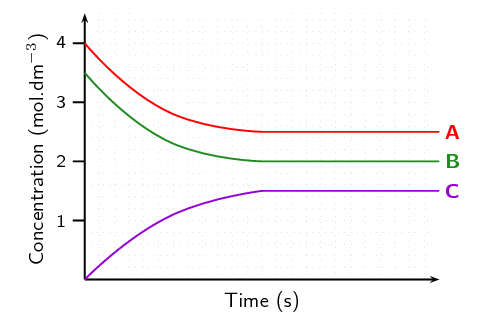
what type of equilibrium graph is this?
concentration vs time
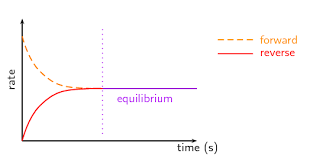
what kind of equilibrium graph is this?
rate vs time
reaction quotient (Q)
same calculation as the equilibrium expression
if Q=K, then
the system is at equilibrium
if Q < K, then
there are less products and more reactants than at equilibrium
If Q > K, then
there are more products and less reactants than at equilibrium
a large value of K =
reaction goes towards completion
small value of K =
reaction occurs to a small extent
value of K close to 1 =
significant concentrations of both products and reactants at equilibrium
yield
how much product can be produced
rate
how quickly that yield is achieved
if the concentration of a reactant is increased,
then the rate of the forward reaction will increase
if the concentration of a product is increased,
then the rate of reverse reaction will increase
if the volume of a system is halved, the pressure, and therefore concentration of all gases would double,
both rates of reaction increase, but the side with more moles will increase more
more volume =
favour side with more moles
less volume =
favour side with less moles
increase in temp increases both, but
increases rate of endothermic more
decrease in temp decreases both, but
decreases endothermic more to favour exothermic
addition of a catalyst
does not affect equilibrium, but increases how quickly it is reached
le chateliers principle states that
if a system at equilibrium is disturbed, the system will act to partially negate the change
activation energy
the energy needed to break the reactants bond in order to form new products
chemical change
a change that produces new substances
chemical system
the chemicals involved in a reaction
collision theory
for a reaction to proceed, the reactant particles must collide with sufficient energy and an appropriate orientation
endothermic reaction
absorbs energy from the surroundings, products have more energy than reactants
enthalpy
the total energy of a substance
equilibrium constant (K)
the value of the ratio between the concentration of products to reactants
equilibrium expression
the ratio of the concentration of products to reactants used to calculate the equilibrium constant
exothermic reaction
releases heat energy to the surroundings, products have less energy than reactants
forward reaction
process of reactants forming products
partial pressure
the pressure exerted by a single gas in a gas mixture
physical change
a change where no new substances are formed