3.1.5 Kinetics
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
when will an ineffective / inelastic collision occur
when particles don't have enough energy for a reaction/ wrong alignment or orientation
activation energy
the minimum energy required for particles to collide to start a reaction
why should the energy distribution of a Maxwell Boltzmann distribution go through the origin
there are no molecules with no energy
whats the Emp of the Maxwell Boltzmann distribution
most probably energy
the peak of the curve
where is the mean usually on the Maxwell Boltzmann distribution
to the right of the Emp
what does the area under the curve of the Maxwell Boltzmann distribution represent?
total number of particles present
why should the curve of the Maxwell Boltzmann distribution never meet the x axis
there is no maximum energy for molecules
x axis of the Maxwell Boltzmann distribution
energy
y axis of the Maxwell Boltzmann distribution
number of molecules
how can a reaction go to completion if few particles have energy greater than Ea?
Particles can gain energy through collisions
as temperature increases, what happens to the Maxwell Boltzmann distribution
it shifts down and right
why does the M-B curve shift down and right when the temp is increased?
more molecules with higher energies (both the Emp and mean energy shift to higher energy values but the number of molecules with those energies decrease because the molecules have a wider range of energies)
Why should the total area under the curve remain constant when the temperature is increased?
bc the total number of particles is constant
rate of reaction
The change in concentration of a substance over time
usual unit of rate of reaction
mol dm-3 s-1
whats the gradient of the curve when a graph of concentration of reactant is plotted vs time
rate of reaction
initial rate
rate at the start of the reaction where it is fastest
how to measure rate of reaction in experiment between sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid
1/time
why can we use 1/time to measure the rate of reaction in the experiment between sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid
bc we can assume the amount o sulfur produced is fixed and constant
concentration
measure of the number of particles per unit volume
effect of increasing concentration/ pressure on rate of reaction
more particles per unit volume
so more particle collisions
so more effective collisions
=faster rate of reaction
If a question mentions doubling of concentration/ rate, what should you mention
double the number of particles per unit volume
double the frequency of effective collisions
effect on M-B curve when concentration/ pressure is increased
shape of curve stays the same
curve will be higher (bc more particles per unit volume)
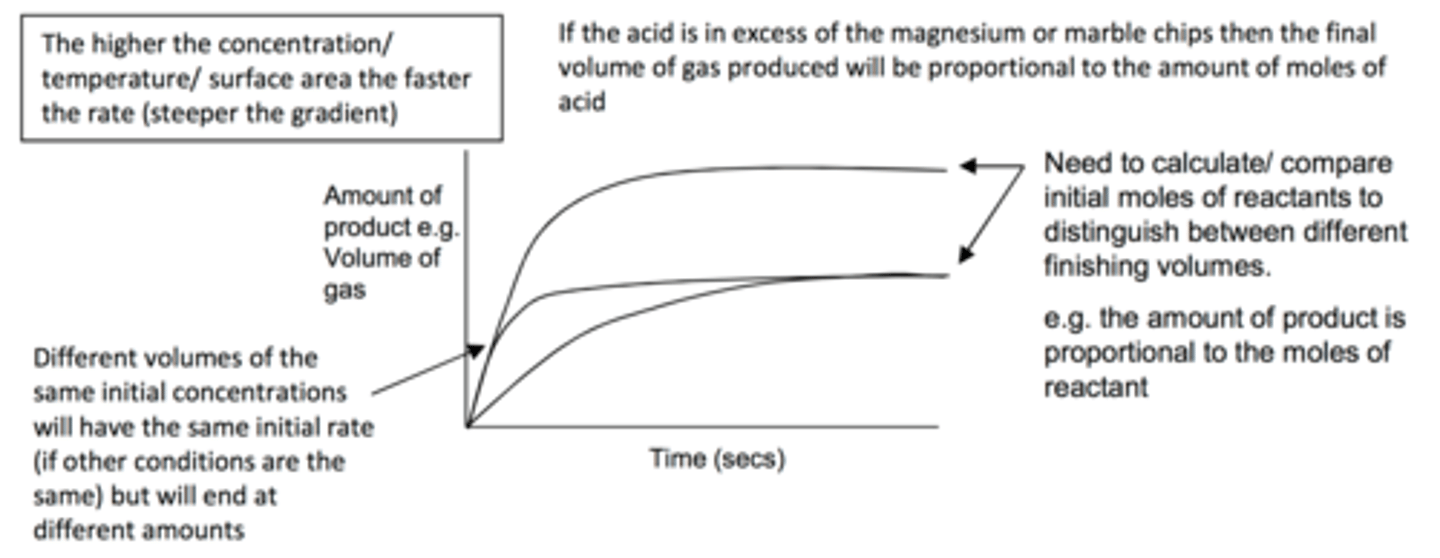
Comparing rate curves
catalyst definition
increase rates of reaction without getting used up
catalysts explanation
they provide an alternative route or mechanism with a lower activation energy
effect of catalyst on M-B curve
Ea lowers (so more particles have the activation energy, so higher frequency of effective collisions)
how does the enthalpy change for a catalysed reaction change?
it doesn't