Specialised digestive systems
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
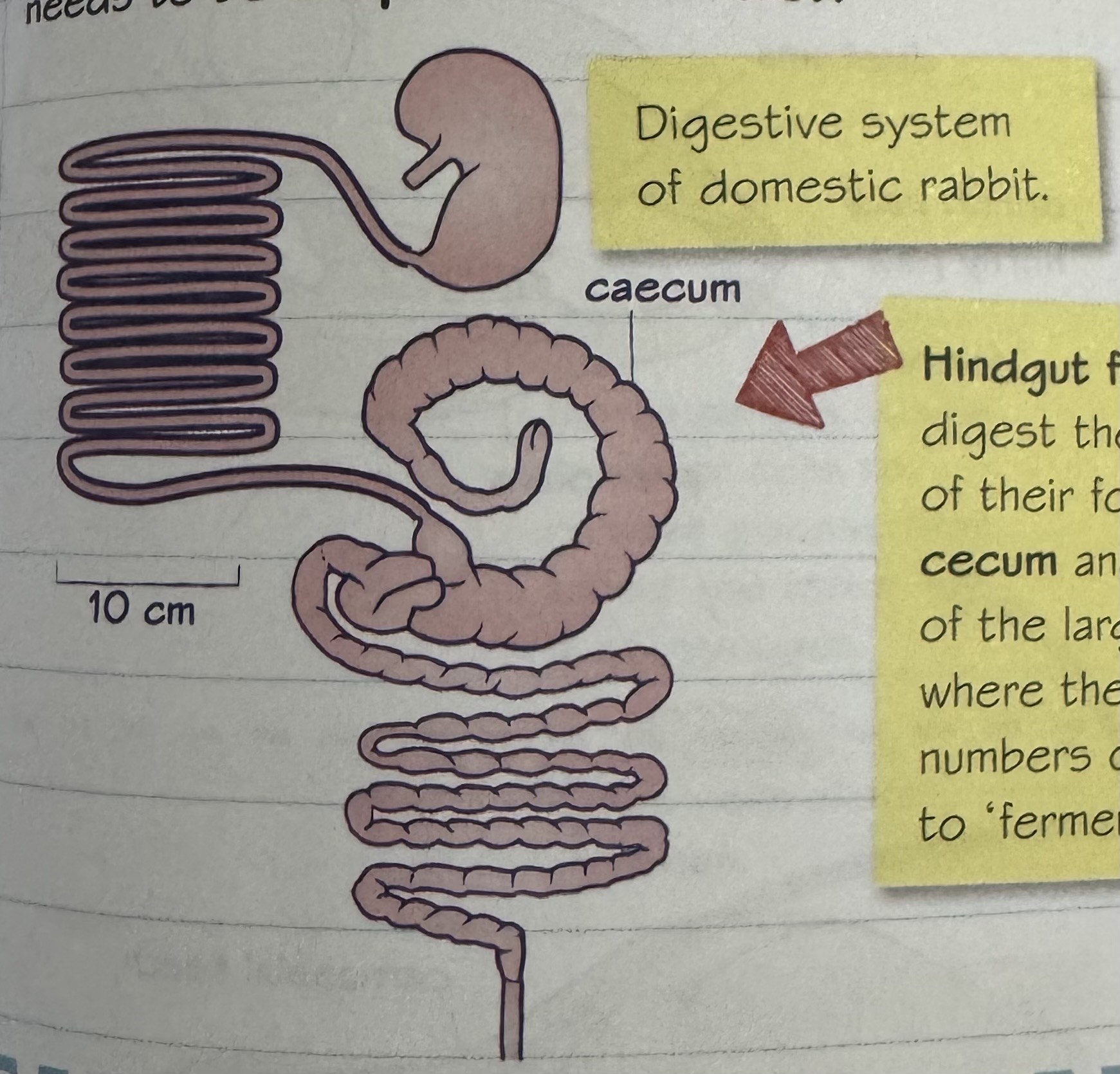
hindgut fermenters
herbivores that eat mostly high fibre plant material
have adapted digestive systems as fibre is hard to digest
how are hindgut fermenter digestive systems adapted?
digest most food in cecum and at the start of the large intestine - where there are large numbers of microbes to ‘ferment’ the food
domestic rabbit digestive system diagram
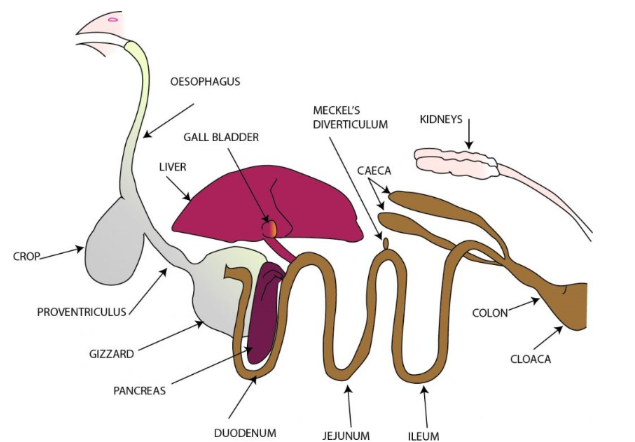
bird digestion
Use their tongue to move food to the back of their mouth where it is swallowed (do not chew)
food moves from oesophagus to the crop (temporary storage area)
food passes to the proventriculus where digestive enzymes and HCl are added
food moves to ventriculus (gizzard) where it is mechanically digested
where the small and large intestines join, there are two ceca (pouches) where some water is reabsorbed and the food is fermented
the cloaca, at the end of the digestive system, mixes digestive and urinary waste and expels them as one substance
do birds chew?
no
how do birds swallow food?
use tongue to move food to back of mouth
crop function
temporary storage area
what happens in the proventriculus?
digestive enzymes and HCl is added
another name for the ventriculus
gizzard
ventriculus function
mechanically digests food
what happens at the ceca in bird digestion?
some water is reabsorbed and food is fermented
function of cloaca
mixes digestive and urinary waste and expels them as one substance
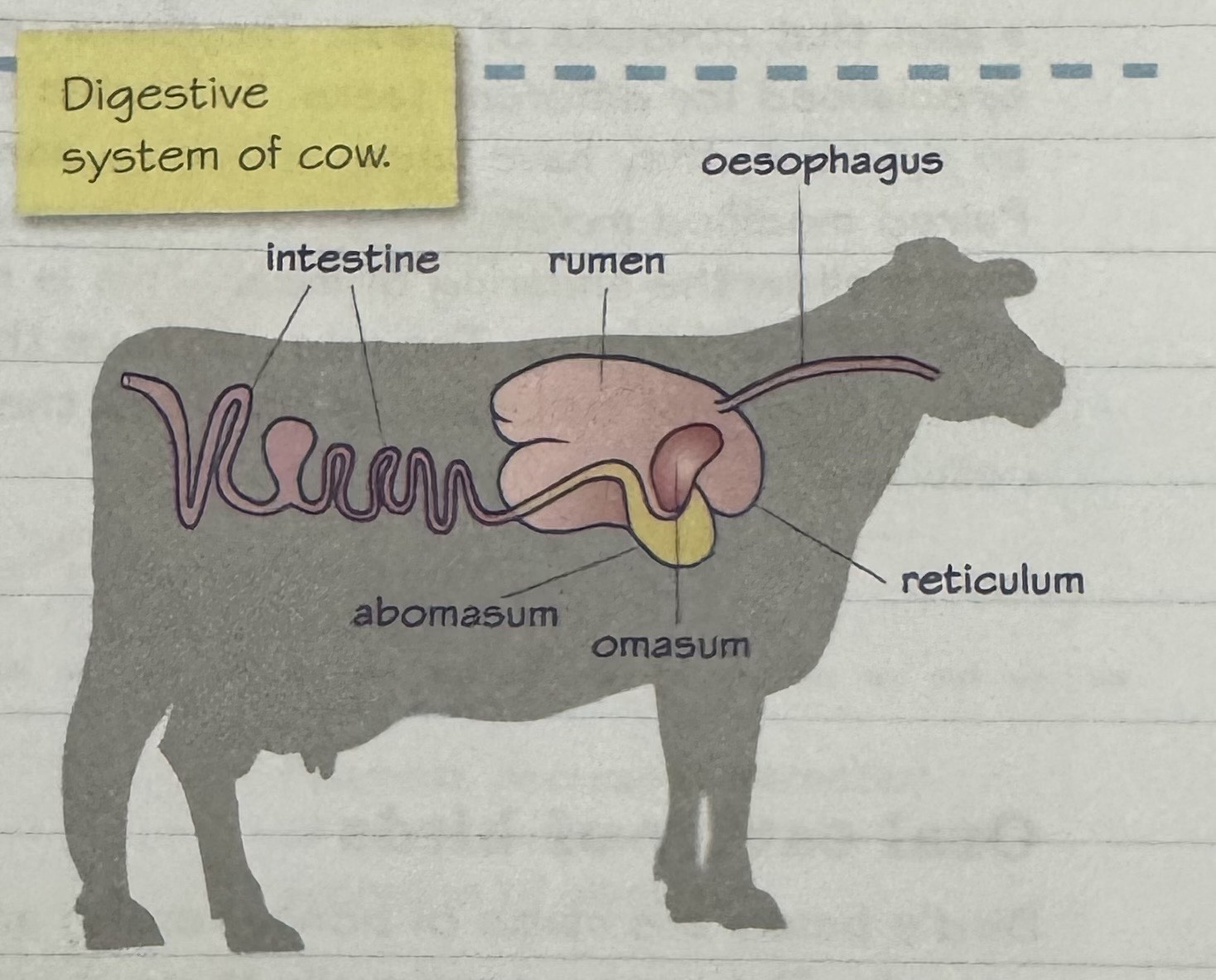
ruminants
specialised foregut fermenters - stomach consists of four chambers
parts of a ruminant stomach
rumen, omasum, abomasum, reticulum
ruminant digestion process
Rumen - fermentation occurs here in an anaerobic environment where microbes secrete enzymes e.g. cellulase to breakdown cellulose. Saliva helps ensure there is a suitable environment for micro-flora (bacteria) to survive. Reticulum aids the rumen and helps form undigested feed into cud. Retro (reverse) peristalsis allows feed to be brought back up to allow it to be mechanically broken down by chewing and then swallowed, allowing further digestion
Reticulum - filters food in rumen, allowing only sufficiently broken down parts to move onto the omasum
Omasum - some water and salts are absorbed, then remaining matter is passed to abomasum
Abomasum - aka true stomach, digestive enzymes and acid are added
what happens in the rumen in ruminant digestion?
fermentation
micro-flora
bacteria
reticulum function in ruminant digestion
filters food in rumen
omasum function in ruminant digestion
some water and salts are absorbed
abomasum function in ruminant digestion
digestive enzymes and acid are added
which stomach compartment in ruminants is also known as the true stomach?
abomasum
cow digestion diagram
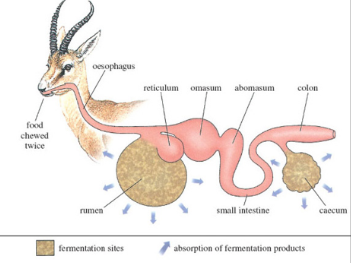
examples of ruminant animals
buffalo, cattle, goat, sheep, bison, yaks, water buffalo, antelope, deer, camels, giraffes, alpacas, llamas, kangaroos and other Australian marsupials
antelope digestive system diagram
horse digestive system diagram
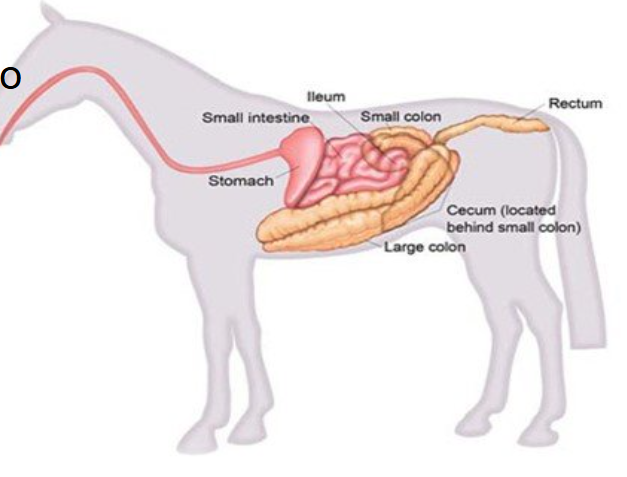
examples of hindgut fermenters
rabbits, guinea pigs, hares, rodents, horses, rhino
coprophagy
consumption of faeces, seen in animals like rabbits. It allows them to re-indigest nutrients and vitamins produced by gut microbes, enhancing nutrient absorption. This is essential to obtain maximum nutrition from their diet. Preventing this can lead to nutrient deficiencies and digestive issues, as these animals rely on this process to maintain their health
bird digestion diagram
enzyme
groups of molecules that help speed up chemical reactions
what is amylase produced by?
salivary glands and pancreas
structure of enzymes
subunits of amino acids
active site to take in substrate and break down
hepatocytes
liver cells