Pure Maths
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Transformation y = |f(x)|
Negative values of y are reflected in x-axis
Transformation y = f(x) + a
+a in y-axis
Transformation y = f(x + a)
-a in x-axis
Transformation y = af(x)
All y-coordinates ×a
Transformation y = f(ax)
All x-coordinates ÷a
Transformation y = -f(x)
Reflection in x-axis
Transformation y = f(-x)
Reflection in y-axis
When is a binomial expansion valid (yr13)?
For (a + bx)n, valid when | bx/a | < 1
or |x| < a/b
x = an as a log?
n = logax
loga (xk) rearranged
klogax
log(xy)
log(x) + log(y)
log(x/y)
log(x) - log(y)
Order of transformations
x: reflect, stretch, translate | y: translate, stretch, reflect , modulus
π Radians in degrees
180
Condition for increasing function?
dy/dx ≥ 0
Condition for decreasing function?
dy/dx ≤ 0
Condition for local minimum?
d2y/dx2 > 0
Condition for local maximum?
d2y/dx2 < 0
Condition for concave function?
d²y/dx² ≤ 0
Condition for convex function?
d²y/dx² ≥ 0
Percentage Change
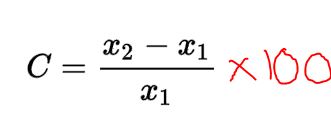
Area of circle segment
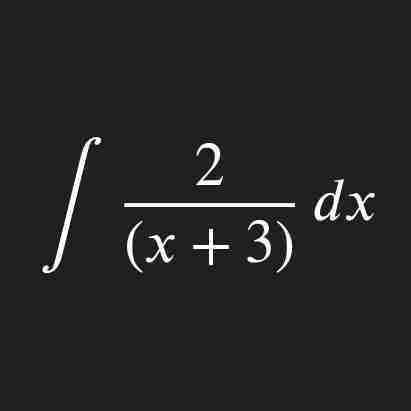
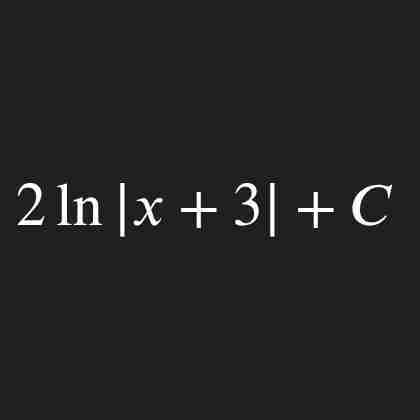
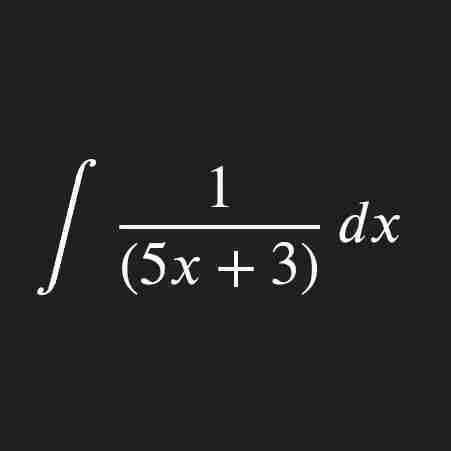
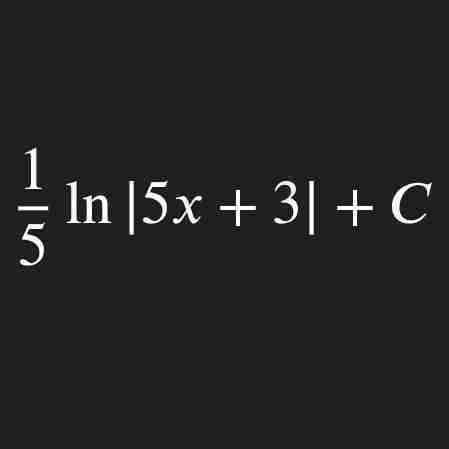
How to integrate a parametric function?
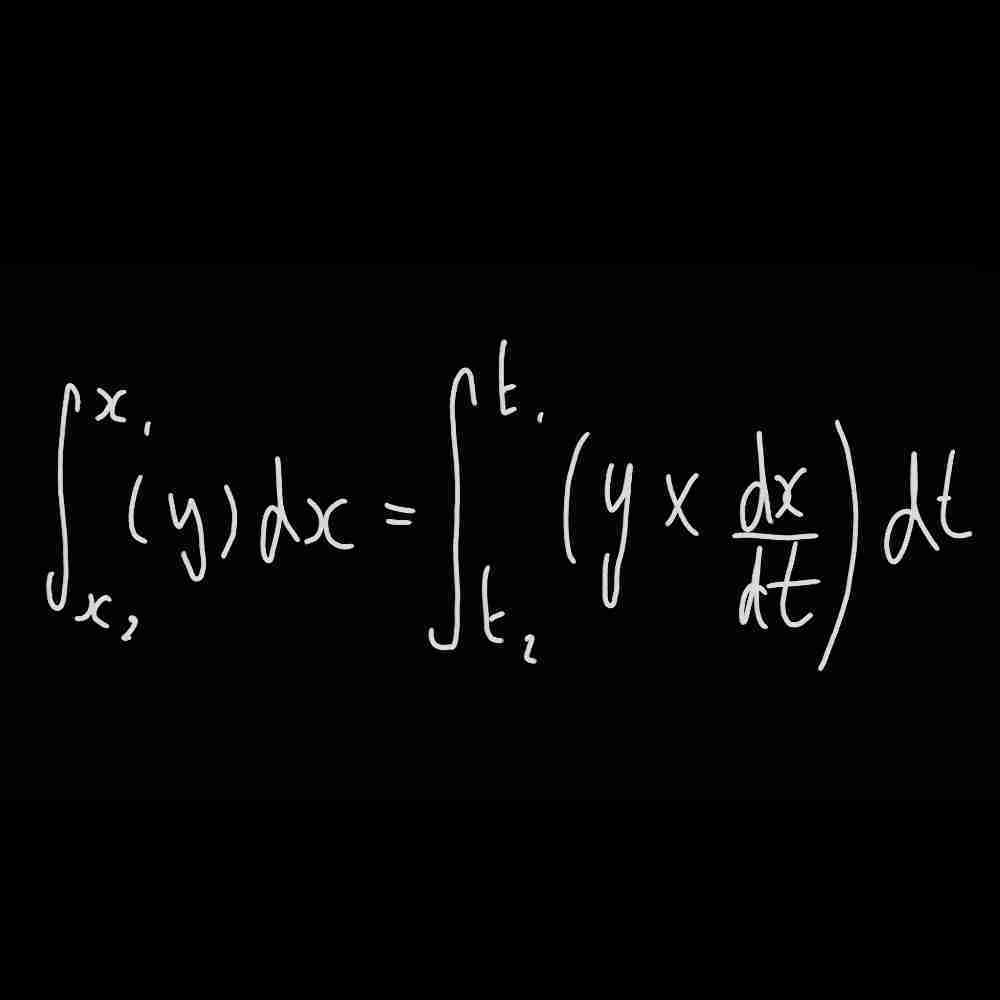
Differentiate
y = ln(5x)
dy/dx = 1/x
Graph of sec x
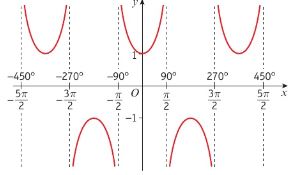
Graph of cosec x
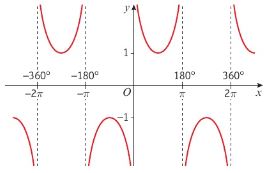
Graph of cot x
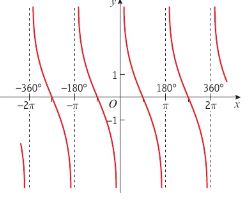
Domain and range of sec x
Domain: x ∈ R, x ≠ any odd multiple of 90
Range: between -1 and 1
Domain and range of cosec x
Domain: x ∈ R, x ≠ any multiple of 180
Range: between -1 and 1
Domain and range of cot x
Domain: x ∈ R, x ≠ any multiple of 180
Range: y ∈ R
Differentiate y = akx
dy/dx = akx k ln(a)
nth term of a geometric sequence
arn-1
Equation for length of a line
[ (x2 - x1)² + ( y2 - y1)² ]1/2
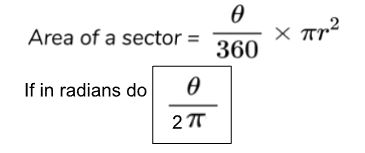
Arc Length equation
arc length = 2πr × (θ/360)
if in radians then (θ/2π)
What is ‘n’ for trapezium rule?
Number of rectangles
If for trapezium rule 5 ordinates are used to approximate area, what would n be?
n = 4
Area of a triangle (not 1/2bh)
½(a)(b)(sinC)
cos rule for triangles
a² = b² + c² - 2(b)(c)(cosA)
Integral of f’(x) × f(x)^n
f(x)^(n+1)
÷ n+1
What makes a function a function?
If it is one-to-one or many-to-one
ie NOT one/many - many
When sketching two ranges e.g f(x) = 5 - 2x for x < 1 and = x² + 3 for x>=1, how do you represent these inequalities?
Draw both graphs up to limits
Use a coloured in circle for =
Use a not coloured in circle for < or >
Join the circles with a straight line
Limitations of change in sign method
There can be a change in sign but not root if the graph is not continuous e.g 1/x
There can be no change in sign but a repeated root if it touches the axis
There can be no change in sign because the points are too spread apart so there are e.g two roots between them
Graph of y = ln x
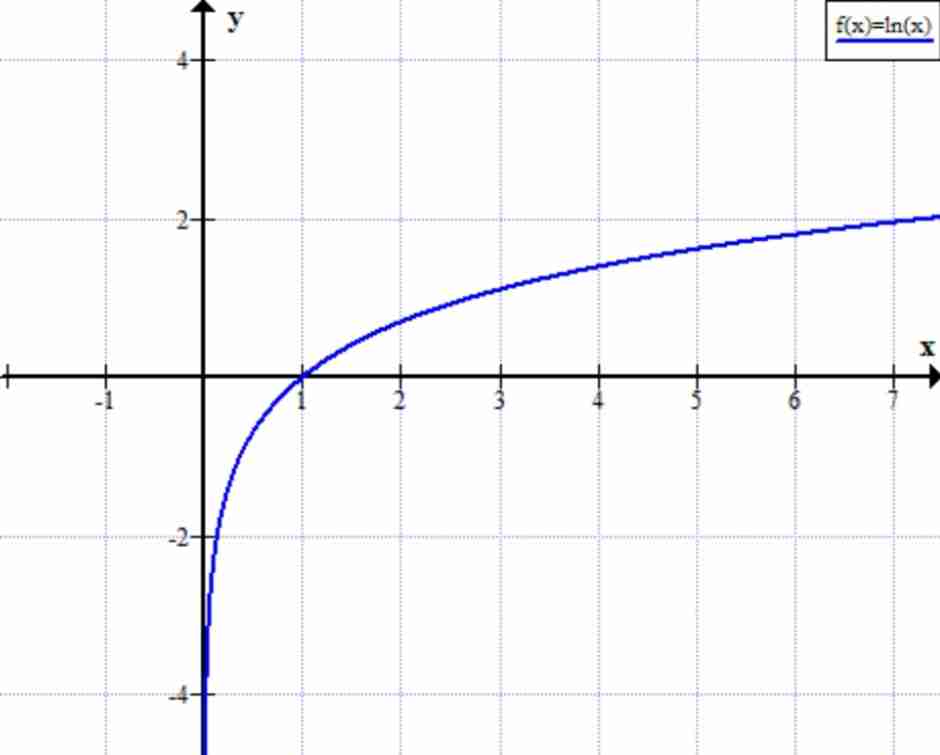
When does Newton-Raphson fail?
If f’(x) gives zero it means x0 (first number being inputted) is a stationary point so the gradient is zero, therefore the tangent at x0 is a horizontal line and won't cross the x-axis so no x1 is produced
Iterations are diverging
Iterations converge to another root
When does a function have an inverse?
When the function is one-to-one
Volume of a cone
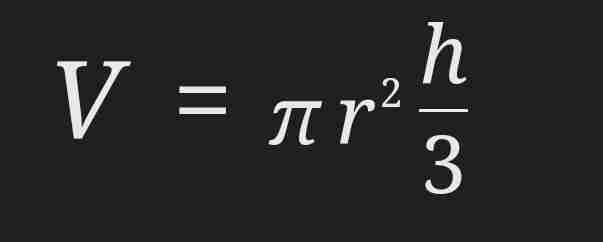
Volume of a cylinder
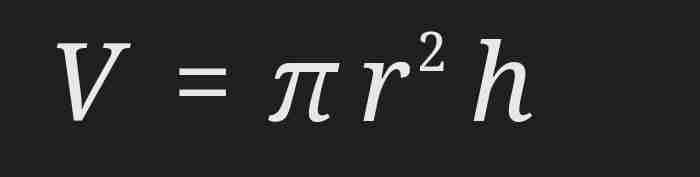
Volume of a sphere
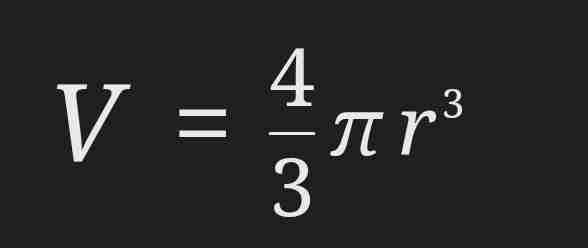
Surface area of a sphere
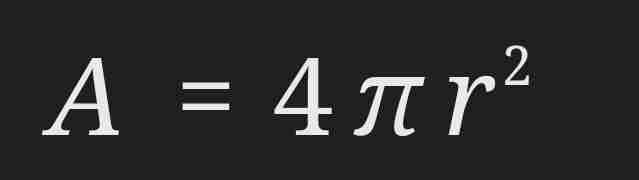
Types of triangle
Equilateral - all sides equal
Isosceles - two equal sides
Scalene - all sides are different
Acute triangle - all angles > 90°
Obtuse triangle - one angle < 90°