Chapter 13 Anatomy and Physiology (McGraw Hill)
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Cranial Nerves
12 pairs of nerves from the neck, up
Spinal nerves
31 pairs of nerves from the neck, down
What are the functions of the spinal cord?
conduction, neural integration, locomotion, reflexes
Where is the spinal cord in the vertebral canal?
In the upper two thirds
Where does the inferior margin of the spinal cord end?
At L1 (or slightly beyond)
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
31 pairs, 62 total (8, 12, 5, 5, 1)
Cauda Equina
"horse's tail", a fan of nerve fibers below the spinal cord
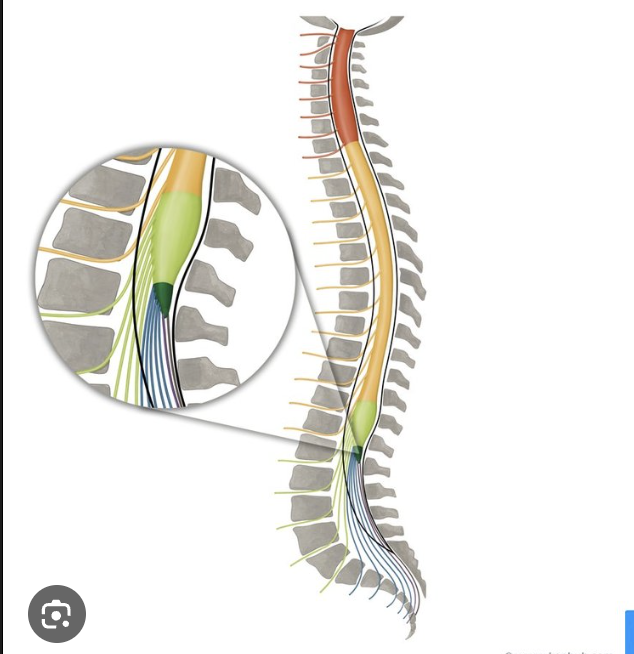
Medullary cone
shape at the end of the spinal cord with nerves that continue coming off
What are the meninges?
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
Where is the lateral horn found in the spinal cord?
Only from T2-L1
Where is cerebrospinal fluid found?
subarachnoid space
What is the posterior median sulcus?
a groove on the dorsal surface of the spinal cord
What is the anterior median fissure?
a deep, wide groove on the anterior (front) side of the spinal cord.
spina bifida
birth defect in which one or more vertebrae fail to form a complete vertebral arch for enclosure of the spinal cord (most serious form: spina bifida cystica)
What reduces the risk of spina bifida?
folic acid before conception
where is white and gray matter found in the brain?
Gray matter is superficial to white matter
where is white and gray matter found in the spinal cord?
white matter is superficial to gray matter
what makes up gray matter?
neuron cell bodies with little myelin
what makes up white matter?
myelinated axons
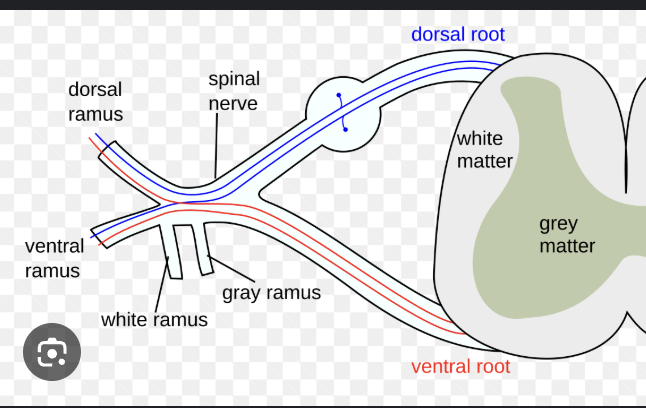
posterior (dorsal) root of the spinal cord carries only what?
sensory information
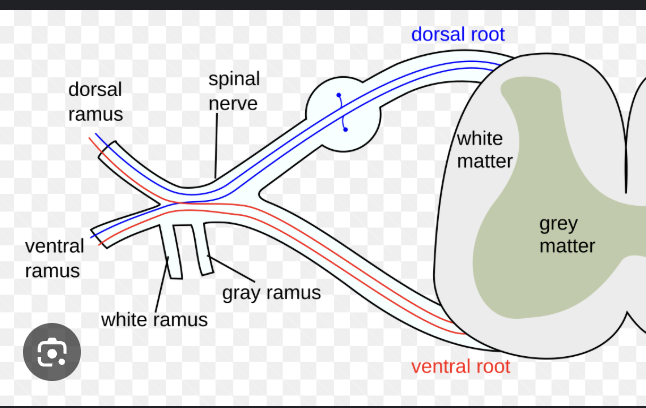
anterior (ventral) root of the spinal cord carries only what?
motor information
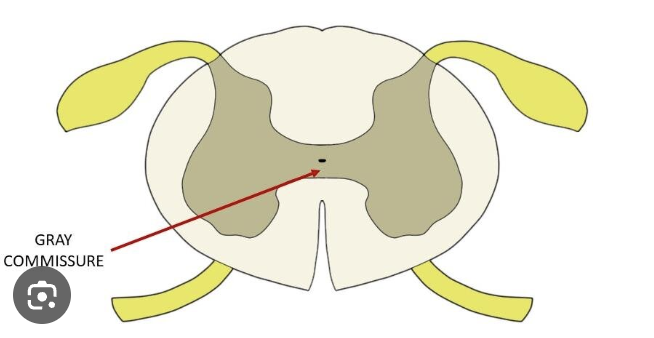
gray commissure
connects the right and left sides of the gray matter in the spinal cord
what does the lateral horn do?
connects neurons of sympathetic nervous system
What is gray matter called?
Horns (ventral, lateral and dorsal)
What is white matter called?
columns or funiculi (ventral, lateral and dorsal)
Where are spinal tracts found?
in the CNS
where are spinal nerves found?
in the PNS
What do ascending tracts do?
carry sensory information up
What do descending tracts do?
carry motor information down
decussation
The anatomical crossing over of neurons from left to right (right brain controls left side of body)
contralateral
when the origin and destination of a tract are on opposite sides of the body
ipsilateral
when the origin and destination of a tract are on the same side of the body
sensory signals travel across how many neurons from origin to destination in the sensory areas of the brain?
3
What are first order neurons?
detect stimulus and transmit signal to spinal cord or brainstem
what are second order neurons?
continues to the thalamus at the upper end of the brain
what are third order neurons?
carries the signal the rest of the way to the sensory region of the cerebral cortex
Descending tracts involve how many motor neurons?
2
upper motor neuron
originates in cerebral cortex or brainstem and terminates on a lower motor neuron
lower motor neuron
soma is in brainstem or spinal cord
schwann cells
form neurilemma and myelin sheath around the axon
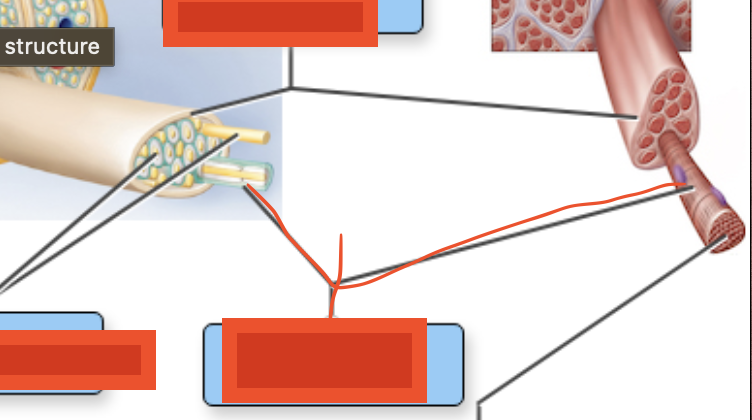
endoneurium
loose connective tissue external to neurilemma
perineurium
layers of overlapping squamous cells that wrap fascicles: bundles of nerve fibers
Epineurium
dense irregular connective tissue that wraps entire nerve
what penetrates connective tissue coverings?
blood vessels
Poliomyelitis and ALS causes
both diseases cause destruction of motor neurons leading to skeletal muscle atrophy from lack of innervation
poliomyelitis
caused by poliovirus
Amyotropic Lateral Sclerosis (Lou Gehrig's Disease)
damage to motor neurons - muscles stop working but brain is still fine
ganglion
A cluster of nerve cell bodies, often of similar function, located in the PNS.
Sensory (affarent) nerves
carry signals from sensory receptors to the CNS
Motor (efferent) nerves
carry signals from CNS to muscles and glands
mixed nerves
contain both sensory and motor fibers
somatic or visceral senses
things we aren't aware of (blood pressure, heart rate, body temperature)
general senses
temperature, pain, touch, stretch, and pressure
special senses
vision, hearing, taste, smell, equilibrium
spinal nerves are _________________, roots are ________________
mixed; not
which is larger, the ventral or dorsal ramus?
Ventral
What does the cervical plexus -C3, C4 And C5 do?
Keep the diaphram alive
What does the brachial plexus innervate?
Entire upper limb
What is under the brachial plexus?
intercostal nerves with NO thoracic plexus
axillary nerve innervates
deltoid
radial nerve innervates
Extensors
Ulnar nerve innervates
flexor carpi ulnaris
median nerve innervates
pronator
lumbar plexus supplies
quads and adductors
the sacral and coccygeal plexuses supply
hamstrings (sciatic nerve)and reproductive activity (pudendal nerve)
Radial nerve injury
Passes through axilla, crutch paralysis, wrist drop
Sciatic nerve injury
Sciatica: sharp pain that travels from gluteal region along the posterior side of the thigh and leg to ankle
90% of cases result from herniated intervertebral disc or osteoporosis of lower spine
dermatome
a specific area of skin that conveys sensory input to a spinal nerve
Shingles
herpes zoster, caused by varicella-zoster virus (chicken pox)traveling down the sensory nerves when immuse system is compromised
reflexes
quick, involuntary, stereotyped reactions of glands or muscle to stimulation
reflexes include:
glandular secretion and contraction of all three types of muscle
Pathway of a somatic reflex arc
1. somatic receptors
2. afferent nerve fibers
3. integrating center
4. efferent nerve fibers
5. effectors
Patellar tendon reflex steps
Stimulation
Information Sent
Decision Make
Information Out
Something Happens
flexor reflex
the quick contraction of flexor muscles resulting in the withdrawal of a limb from an injurious stimulus
crossed extension reflex
contraction of extensor muscles in the opposite limb from the one being withdrawn - maintains balance by extending other leg
flexor relex uses an _______________ reflex arc, whereas crossed extension reflex uses a ____________________ reflex arc
ipslipateral; contralateral
intersegmental reflex
one in which the input and output occur at different levels (segments) of the spinal cord (pain in foot causes contraction of abdominal muscles)
propioceptors
monitor the position and movement of body parts (know where your body and all parts of it are is in three dimensional space)
muscle spindle
stretch receptors embedded in skeletal muscles (helps you keep upright when standing on a boat)
Stretch (myotatic) reflex
when a muscle is stretched, it "fights back" and contracts (helps maintain equilibrium and posture)
paraplegia
paralysis of both lower limbs
quadriplegia
paralysis of all four limbs
hemiplegia
paralysis of one side of the body
paresis
partial paralysis or weakness of the limbs
in the spinal cord, what is the space within the gray commissure that contains CSF?
central canal
somatic nerve fibers innervate:
skin, skeletal muscles, bones and joints
All spinal nerves except C1 pass through which structure to emerge from the vertebral column?
Intervertebral Foramen
layer of loose connective tissue that surrounds a nerve fiber
endoneurium
In an adult, the spinal cord ends at which vertebra?
L1
Within a nerve, each fascicle is wrapped in a layer called a ________
perineurium
the __________________ ramus of the spinal cord innervates the muscles, joints, and skin of the back
posterior