Chemistry - Kinetics
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I cannot get the same mark i got on energetics please bro
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
define a rate of reaction
the speed at which reactants are converted into products
how is the rate of reaction expressed? (think units)
rate of a reaction is usually expressed in terms of a change in concentrations of one of the participants per unit time
Rate of reaction = Δ[Reactant]/Δt
_____ show the greatest rate of increase at the beginning and the _______ show the greatest rate of decrease at the beginning of the reaction
products, reactants
What is the instantaneous rate
slope of the tangent to the curve at any point in a measure of the reaction at that point
what is the average rate
the slop of the secant line allows a measure of the average rate of the reaction during the time period
Name ¾ techniques that can be used to measure concentration (depending on reaction and available apparatus)
1) titrations (for reactions in solutions)
2) changes in colour can be indications of concentration change and can be measured in a spectrometer
3) density and electrical conductivity may vary with concentration
4) for gases, a pressure change may tend to indicate a concentration change
True or False: the main feature of a rate is that it must be able to be measured physically
True
What two factors does the rate of reaction depend on?
1) number of collisions per unit time between the reacting species
2) the fraction of these collisions that are successful in producing a new molecule
What does collision geometry state?
if two or more molecules collide, but are not oriented correctly, then no reaction will take place
What two things must be right in order for a chemical reaction to occur?
1) sufficient energy (to overcome repulsion forces)
2) proper orientation
What does the Maxwell-Botzmann Distribution show?
It represents all molecules at a specific temperature from low kinetic energy to high kinetic energy (some are moving faster and some are moving slower, even though in the same temperature)
Name the four factors that affect reaction rates and chemical kinetics
1) Chemical Nature of Reactants
2) Concentration of Reactants and surface area
3) Temperature Changes
4) Catalysts
Explain how the chemical nature of reactants affects reaction rates
if molecules have weaker bonds, they have a smaller activation energy (means more molecules have reacted at a lower kinetic energy)
the less complicated the reactant, the better collision geometry (orientation of the molecule is less precise)
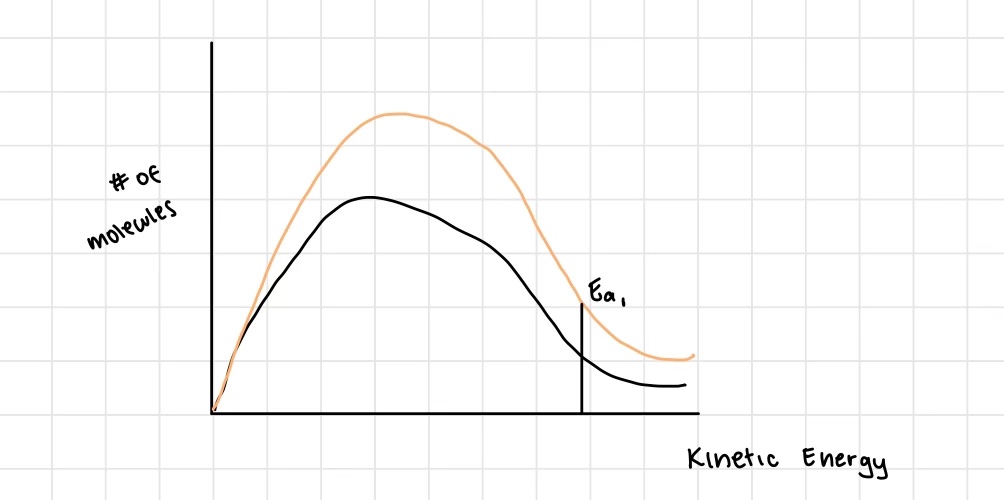
Explain how the concentration of reactants and surface area affects reaction rates
if the initial concentration of a reactant is increased, then the reaction rate generally increases
increased number of reactant molecules per volume are more likely to collide, increasing rate
As surface area increases, the rate of reaction should also increase.
For ex: dust and grain silo explosions
Mostly important in heterogenous reactions
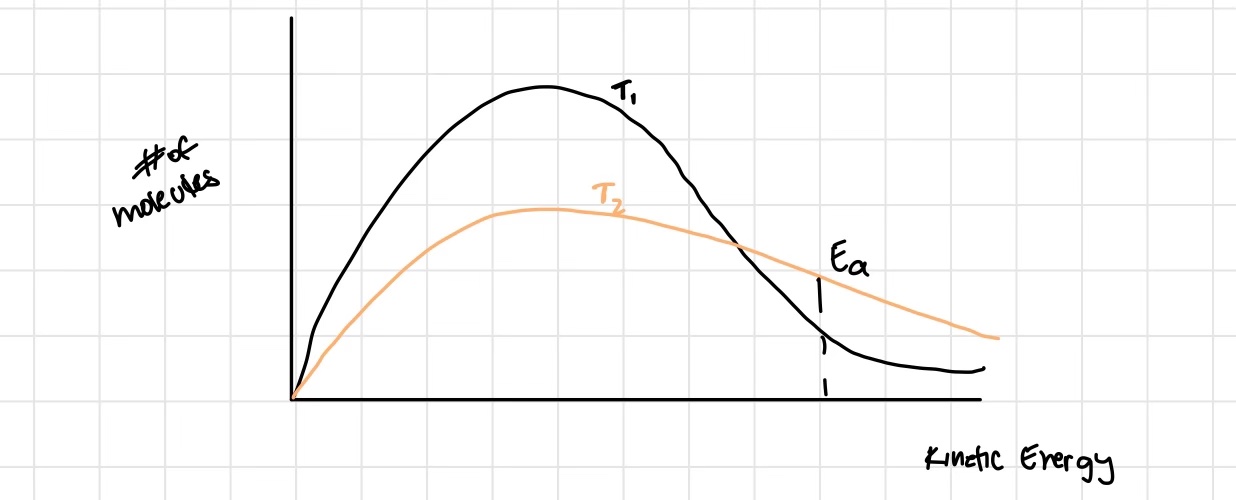
Explain how temperature changes affect reaction rates
if temperature increases, rate of reaction generally increases
Increasing temperature causes molecules to collide both more often, and with greater kinetic energy on average, making any individual collusion more likely to be effective
(remember, just because they hit at the right orientation, does not mean there is enough energy or vice versa)
Define catalysts
a substance which affects the reaction rate without being consumed by the overall reaction
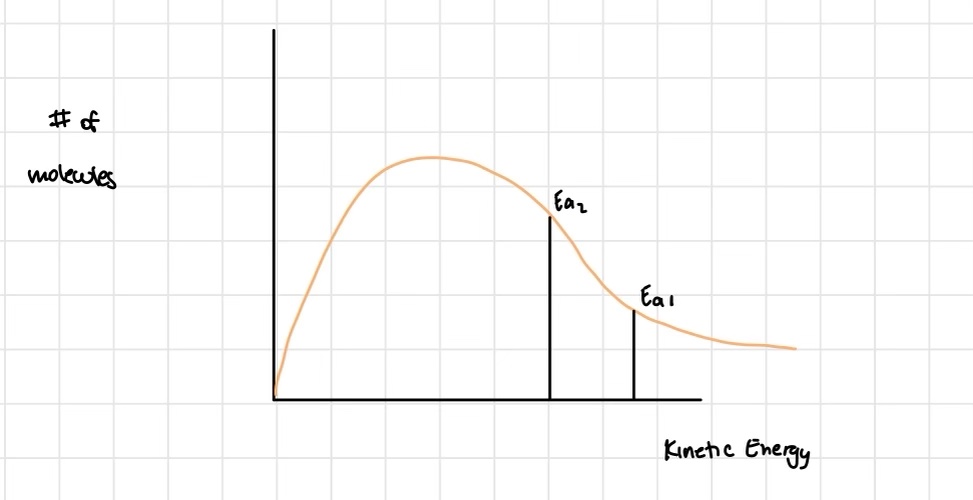
Explain how catalysts affect rate of reaction
catalysts are able to lower the energy required for the reaction to occur by finding a different pathway for the reaction to take place
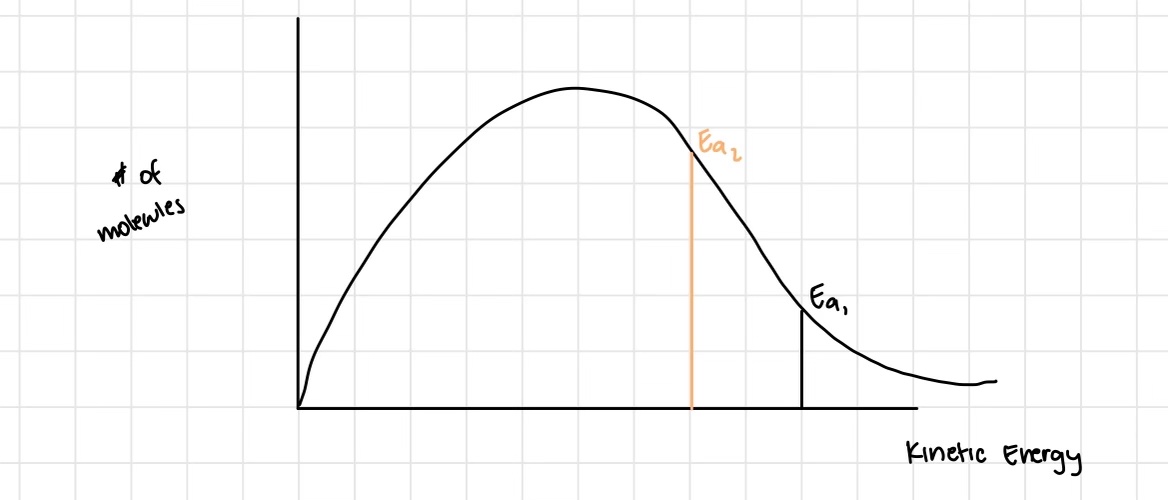
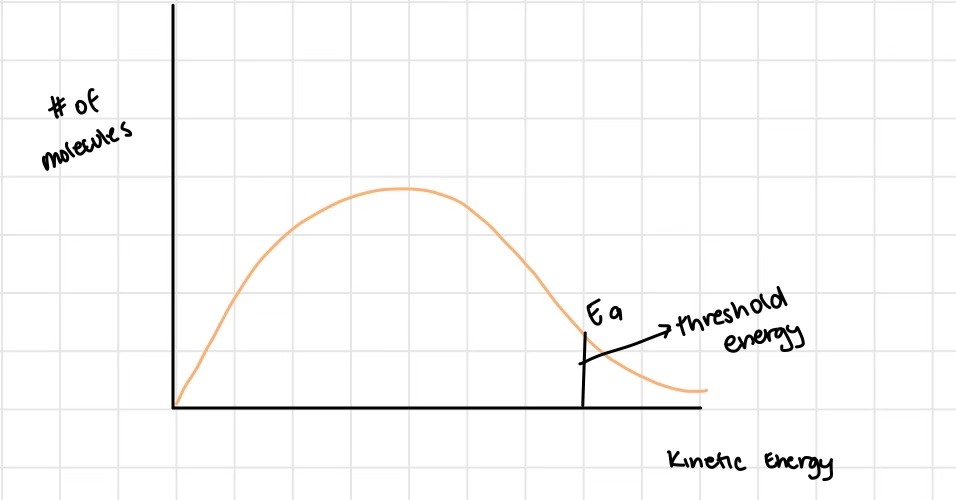
define activation energy
the energy that must be reached by two colliding molecules before a reaction can take place
How does activation energy affect the rate of reaction
the greater the activation energy, the less reactions will occur (harder to get past it)
what two things happen as a bimolecular reaction (reaction of two molecules) occurs ?
there is angle bending
for ex: an initially pyramidal molecule will become planar
there is bond making and breaking
What is an activated complex / transition state?
the point of highest potential energy
An activated complex can only be formed if what?
If they initially have sufficient kinetic energy to turn into the potential energy of the activated complex
true or false: an activated complex can be isolated
False
What two points on an energy profile can we pinpoint?
the difference between the average energy of the products and the average energy of the reactions (ΔH)
the activation energy (obtained experimentally)
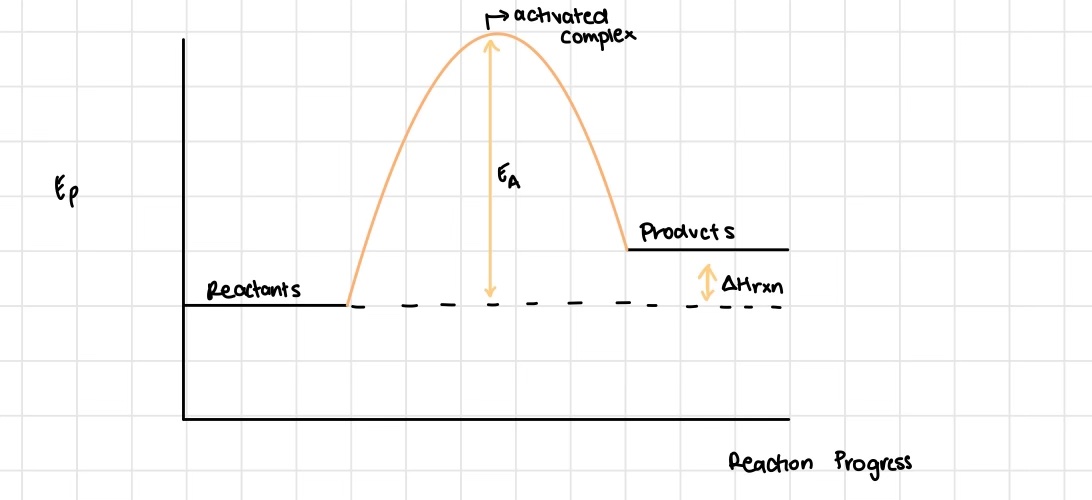
True or False: there is only one way for the reactants to interact and so pass to the products
False - there are multiple ways!
Which energy pathway is most favoured by reactants to become products?
the minimum energy pathway
In which type of reaction does the activation energy NOT include ΔH
Exothermic!
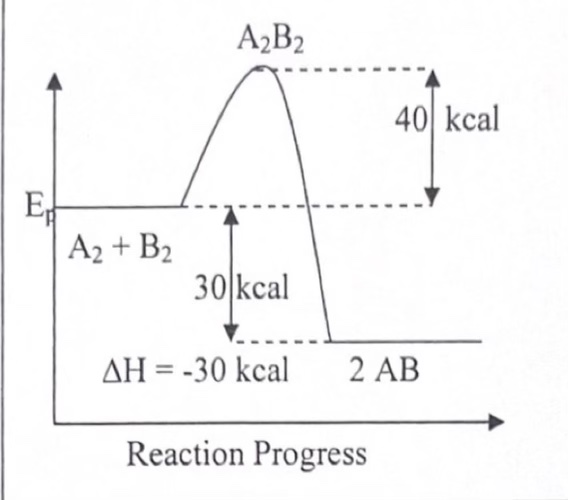
In which type of reaction does the activation energy include ΔH?
Endothermic
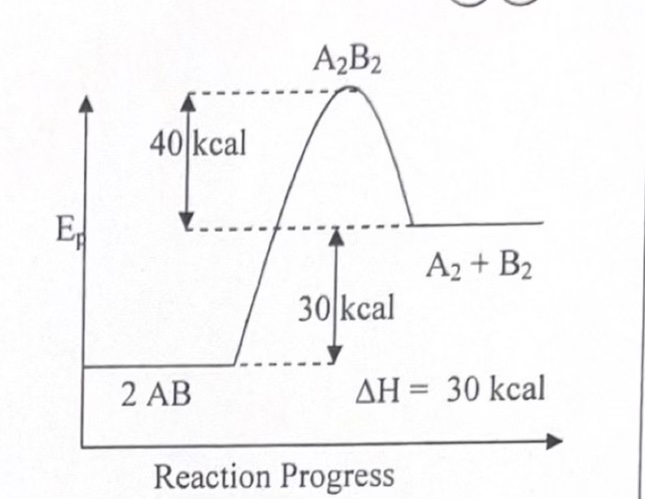
_____ reactions have high activation energies. _____ reactions have low activation energies. (think speeds)
Slow, fast
An ______ reaction always has a greater activation energy and a slower rate than the opposing _____ reaction. (exo / endo)
endothermic, exothermic
True or False: An increase in temperature affects the rate of the endothermic reaction more than that of the exothermic reaction
True
what is a reaction mechanism?
A step by step sequence of elementary processes by which overall chemical reaction occurs
what is an elementary process?
a one step process in which the product particles are in most cases the direct result of only two reactant particles
3 particle collisions are considered _____ and 4 particle collisions are considered ____
rare, improbable
why are 4 particle collisions considered improbable?
they occur outside a rate of reaction that we consider possible (if they occur, they don’t occur in the span of a human life)
what determines how fast or slow a reaction takes place?
the activation energy (lower activation energy, faster it occurs; higher activation energy, slower it occurs)
What are reaction intermediates?
Molecules that are formed in the steps in the reaction mechanism, but are not part of the overall reaction
what are free radicals?
Bonus - why are they so detrimental in our bodies?
free floating atoms
bonus - they can break double bonds in our DNA which most of the time can be killed by our bodies immune system, however, sometimes it is repaired incorrectly and survives, creating cancerous cells
what does the law of mass action state?
the rate of a chemical reaction is proportional to the product of the concentration of the reactants
what is the rate law expression
Rate = k[A]^m[B]^n
what is k affected/not affected by?
not affected by concentration changes
varies with temperature change
in what situation are m and n the stoichiometric numbers from the balanced equation?
when the equation is a one step reaction
what must be done with the other reactants in order to find the relationship of one reactant
the other reactants must be kept constant
what does the predicted rate law use?
the coefficients of stoichiometric relations
ex: 2A + 3B —> 2C + 4D
rate = k[A]²[B]³
what are intermediates and their properties?
molecules formed then consumed in a following step
exist for short time
potential energy minimums (relative to activated complex)
higher potential energy than reactants and products
what are activated complexes and what are their properties?
potential energy maximums
exist for a very short time
exist in the middle of each step
define half life
the time it takes for a reactant to decrease to ½ of its present value
properties of first order reactions in terms of half life
t1/2 is constant
independent of rate
properties of second order reactions in terms of half life
t1/2 is double the preceding
t1/2 is inversely proportional to the rate
properties of zeroth order in terms of half life
t1/2 is half the preceding
t1/2 is proportional to the rate
What does rate law take into account?
concentration, the rate constant (k), the effect of temperature, nature of reactants, and catalysts described by the Arrhenius Equation
what is Arrhenius equation?
k = Ae^(-Ea/RT)
what does e^(-Ea/RT) count?
the fraction of molecules which have energies equal to or in excess of activation energy
what is A in Arrhenius’ equation?
the frequency of collisions and orientation
does not change with small changes in temp
what is the equation of the line when lnK and T(-1) are being graphed against each other?
lnK=(-Ea/R)(1/T)+ lnA
How much will the rate of reaction increase approximately with a 10 degree increase at room temp?
double
Give the reaction mechanism for the formation of ozone (O3)
1) O2 —> 2 O*
the ozone is formed when the double bond in the oxygen is broken by very short wavelength in UV-C light
2) O2 + O* —> O3
An oxygen free radical is formed and reacts with another oxygen atom to form ozone gas, O3.
Give the reaction mechanism for the depletion of ozone (O3)
When O3 absorbs longer wave length UV-B light, it is broken down into a double bonded O2 molecule and a oxygen free radical. This is because the two pi bonding electrons are shared between the entire structure and therefore has weaker bonds compared to O2.
1) O3 —> O2 + O*
The oxygen free radicals react with another resonance structure to form O2.
2) O* + O3 —> O2
What are the two main ozone depleting pollutants and what are their sources?
1) CFC (chlorofluorocarbons)
mainly found in hairspray or deodorant cans as propellant, old refrigerators, etc.
2) oxides of nitrogen (NOx)
formed from high temperature reactions in N2 and O2 in supersonic aircraft engines and lightning
Give the reaction mechanism that occurs as CFCs float up towards unfiltered UV light
As they float up to the unfiltered UV light, the H-Cl bond can break and then produce a highly reactive Cl free radical
1) CCl2F2 + UV light —> *CClF2 + Cl*
2) Cl* + O3 —> ClO* + O2
3) ClO + O* —> O2 + Cl*
Steps 2 and three will continue to break apart O3 molecules, allows more UV-B wavelengths to reach the earth.
Give the reaction that occurs as NOx molecules float up towards unfiltered UV light.
1) NO + O3 —> NO2 + O2
2) NO2 + O* —> NO + O2
more UV light will reach the earth increasing the chances for skin cancer, sun burns, damage to animals and vegetation, and even genetic mutations
what is a heterogeneous catalyst?
a substance that increases the rate of reaction and is in a different phase than the reactants