Glycolysis
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is glycolysis?
A metabolic process that breaks down glucose through a series of reactions to pyruvate and releases energy for the body in the form of ATP
Where does glycolysis occur?
In the cytoplasm of the cell
Is glycolysis aerobic or anaerobic?
Anaerobic. Glycolysis is the first step in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration
What is the overall reaction of glycolysis?
Glucose + 2NAD+ + 2ADP + 2Pi → 2 Pyruvate + 2NADH + 2H+ + 2ATP + 2H2O
How many enzymes catalyze the glycolytic pathway?
10
What are the main products of glycolysis?
2 pyruvate molecules, 2 NADH, and a net gain of 2 ATP
How many ATP molecules are used during glycolysis?
2 ATP are used
How many ATP molecules are produced during glycolysis?
4 ATP are produced
What is the net ATP yield of glycolysis?
Net gain of 2 ATP per glucose molecule
What happens in the phosphorylation step of glycolysis?
Glucose (6C) is phosphorylated by 2 ATP to form fructose bisphosphate (6C)
What occurs in the lysis step of glycolysis?
Fructose bisphosphate (6C) splits into two molecules of triose phosphate (3C)
What happens in the oxidation step of glycolysis?
Hydrogen is removed from triose phosphate and transferred to NAD+ to form NADH
What is the final product of glycolysis?
Pyruvate
What can happen to pyruvate after glycolysis?
It can enter the next stage of respiration (Krebs Cycle/Citric Acid Cycle)
List the intermediates involved in glycolysis
Girls Get Fine Food; Gentlemen Dine Girls; Boys Prefer to Pick up Pepperoni Pizza
Girls Get Fine Food:
Glucose
Glucose-6-phosphate
Fructose-6-phosphate
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
Gentlemen Dine Girls:
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Boys Prefer to Pick up Pepperoni Pizza:
1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate,
3-Phosphoglycerate,
2-Phosphoglycerate,
Phosphoenolpyruvate,
Pyruvate
List the enzymes in glycolysis
Hungry Peter Pan in the growling Pink Panther eat pies
Hexokinase
Phosphoglucose isomerase,
Phosphofructokinase, etc.
(aldolase)
Isomerase
Triose Phosphate Dehydrogenase
Phosphoglycerokinase
Phosphoglyceromutase
Enolase
Pyruvate Kinase
What happens in the oxidation of glucose?
Oygen is reduced
Carbon in glucose is oxidised
Glucose is the reducing agent as it gives electrons
Oxygen is the oxidising agent as it accepts electrons
Give an overview of glycolysis
2 ATP are used to convert glucose to glucose phosphate then to fructose bisphosphate.
This is then converted to 2 glycerate-3-phosphates (3C)
NAD+ is then converted to NADH and a H+ to turn glucerate-3- phosphate into pyruvate (3C)
This is done with each glycerate-3-phosphate resulting in the production of 4 ATP and a net production of 2 ATP during glycolysis
What is the link reaction
Pyruvate is actively transported to the matrix of the mitochondria where it is converted to Acetyl-CoA with the production of CO2 and NADH
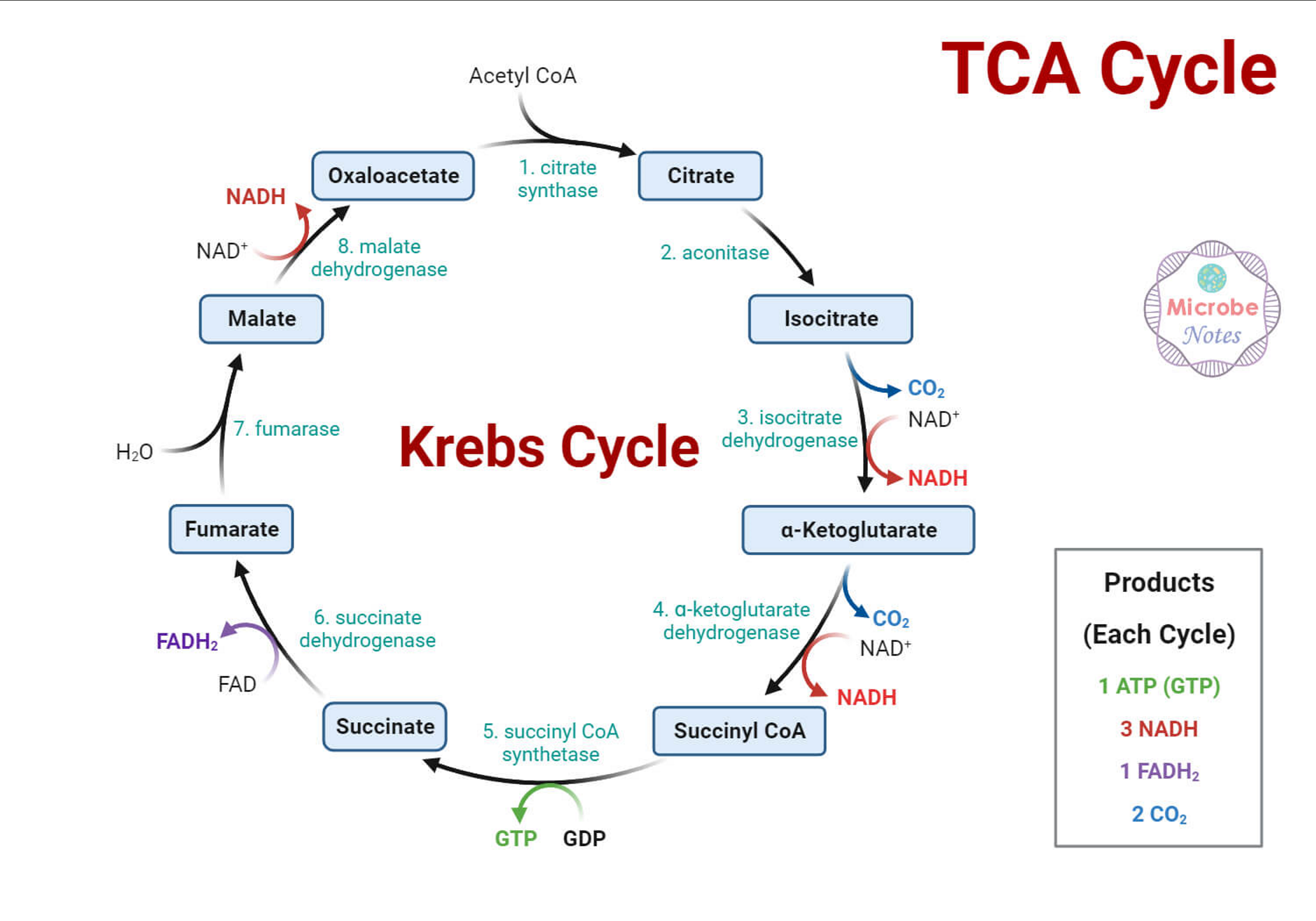
Give an overview of the Kreb cycle
Acetyl-CoA converts oxaloacetate to citrate.
Citrate is converted to isocitrate which is converted to a-ketoglutarate with the production of one NADH.
a-ketoglutarate is converted to succinyl-CoA with the production of one NADH.
Succinyl-CoA is converted to succinate with the production of one ATP.
Succinate is converted to fumarate with the production of one FADH2.
Fumarate is converted to malate which is converted to oxaloacetate with the production of one NADH.
The net result is three NADH, one FADH2, one ATP/GTP, and each glucose provides two acetyl-CoA so double this net result
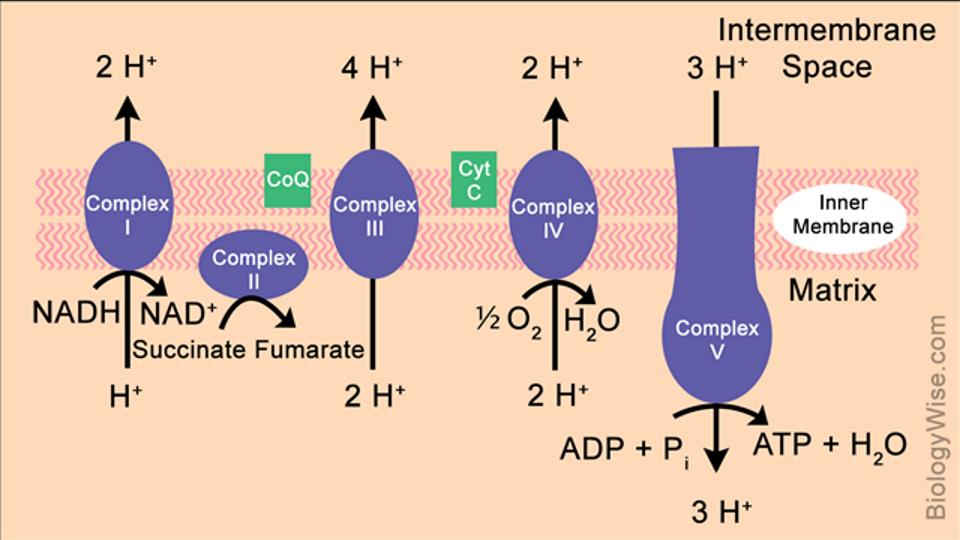
Describe the electron transport chain/oxidative phosphorylation
Electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 are passed to oxygen through a series of enzymes that each release a small amount of energy.
The complexes 1-IV are capable of receiving electrons through their clusters of iron, sulphate and copper and use that energy to pump protons from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space.
These protons then flow down their electrochemical gradient into the matrix, with the energy being use to generate ATP.
ATP synthesis occurs in complex V (ATP synthase) which is the final enzyme in the oxidative phosphorylation pathway.
As protons pass through complex V, the coupled ATP synthase causes a conformation change in the complex resulting in a inorganic phosphate being added to ADP forming ATP.
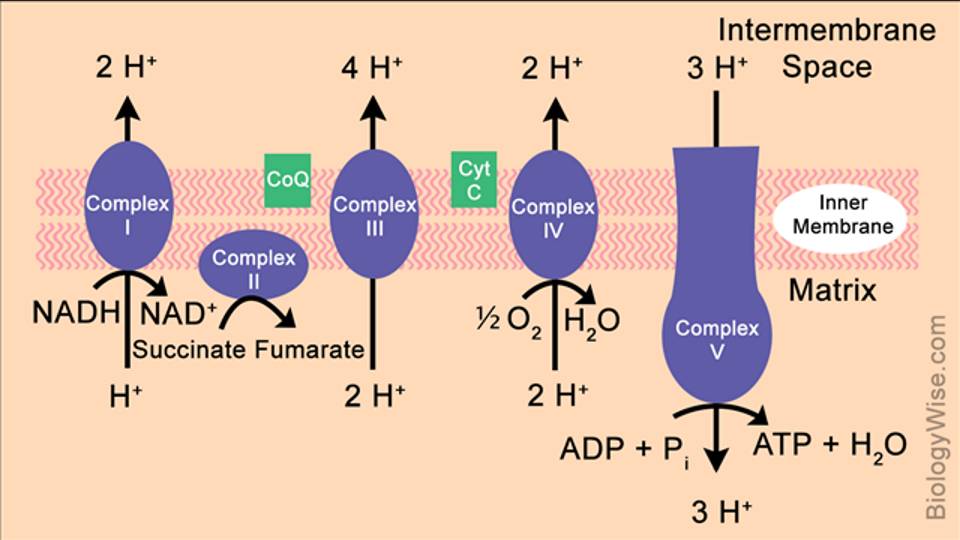
Describe the impact of the inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation
Inhibiting just 1 enzyme will shut it all down which is fatal quickly. Cyanide and hydrogen sulphide are the best known, they bind more strongly to the Fe-Cu centre in cytochrome C oxidase (complex IV) preventing the reduction of oxygen. CO can also bind to Fe-Cu in cytochrome c oxidase causing hypoxia and direct CO-mediated damage at cellular level.