Reagants/Mechanisms
1/282
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Final
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
283 Terms
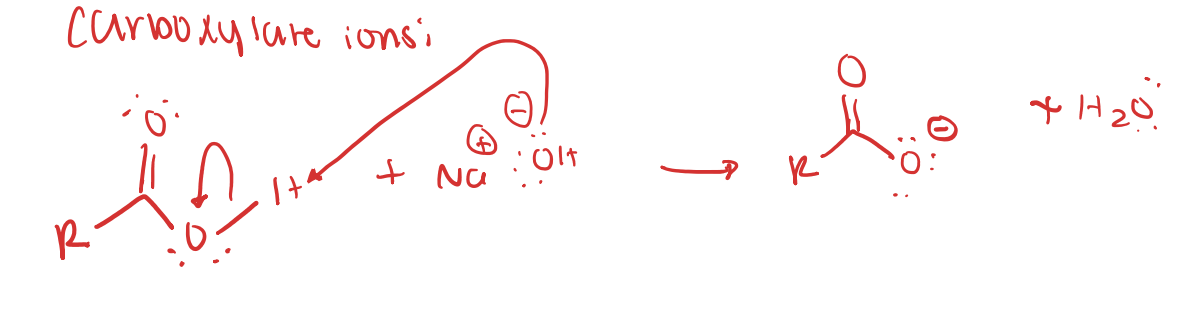
Carboxylate ions
Oxidation of Primary OH to COOH
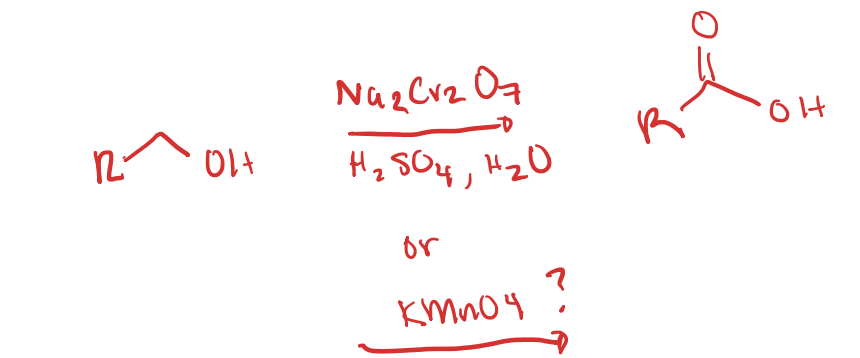
Oxidative Cleavage of Alkynes
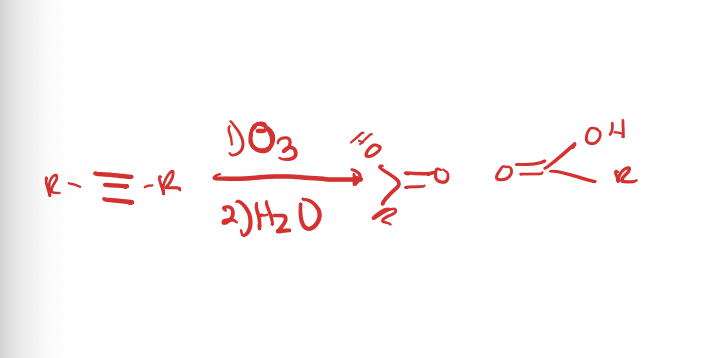
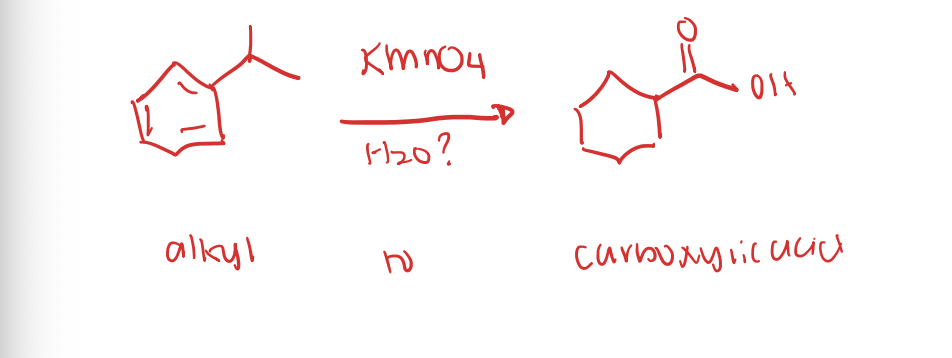
Oxidation of Alkyl Benzenes
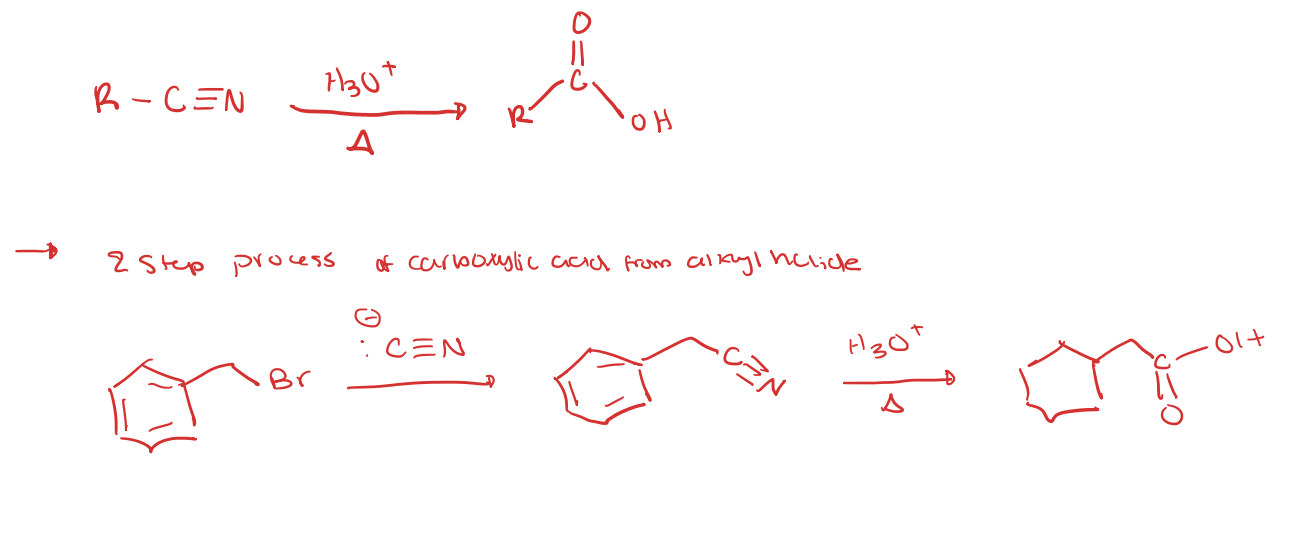
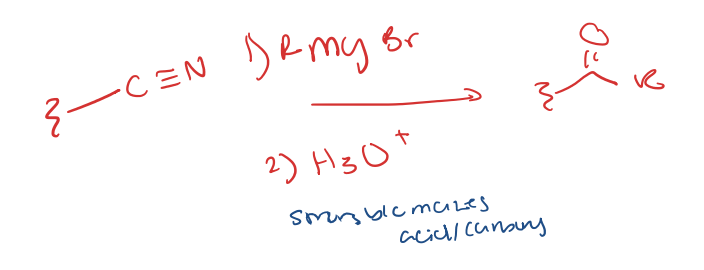
Hydrolysis of Nitriles
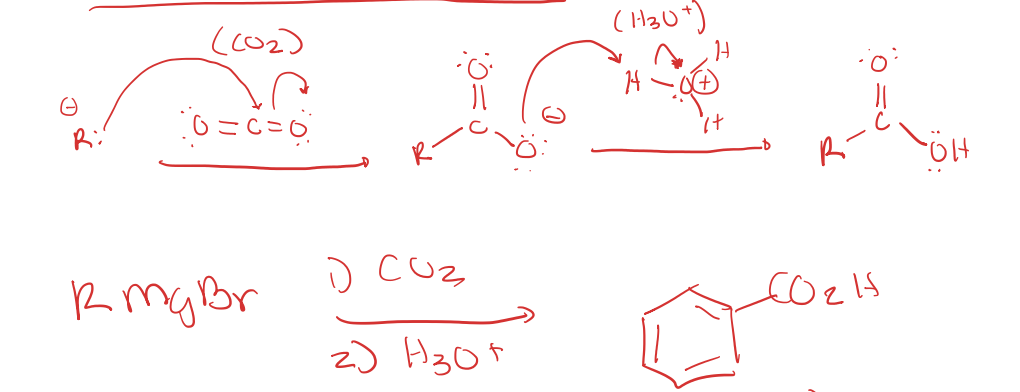
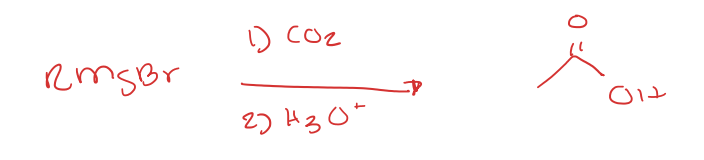
Carboxylation of Grignard Reagents
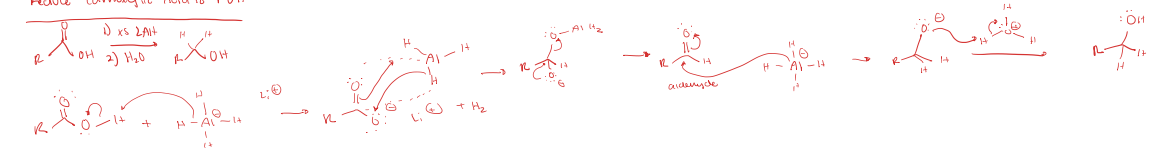
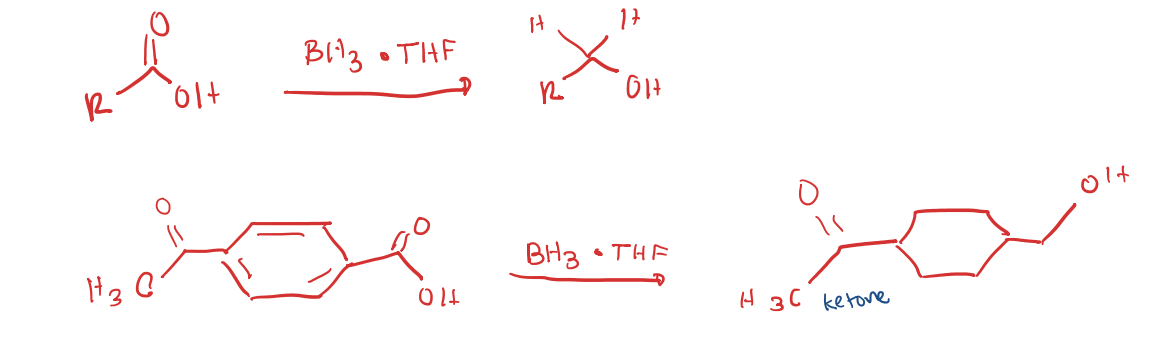
Reduces Carboxylic Acid to Primary OH
Chemoselective for Reducing a Carboxylic acid
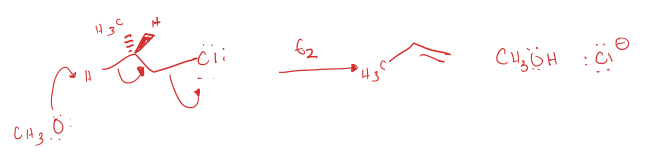
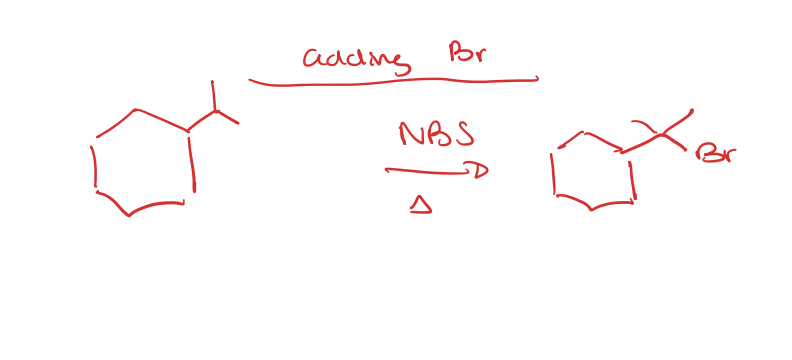
Adding Tertiary Br
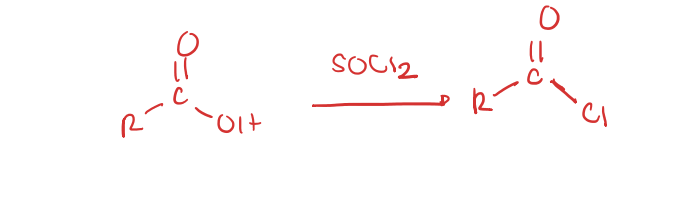
carboxylic acid to acid chloride
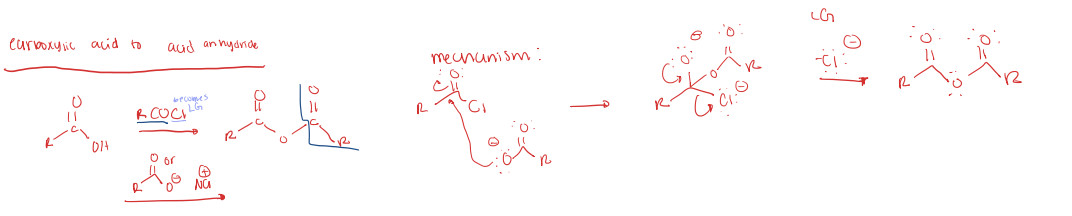
carboxylic acid to acid anhydride
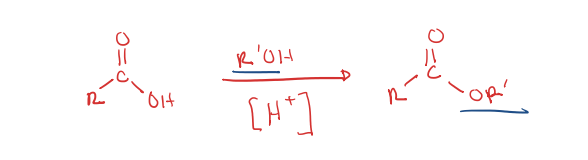
carboxylic acid to ester
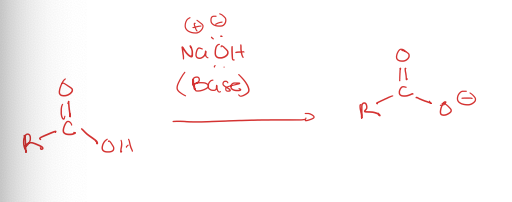
carboxylic acid to carboxylic ion
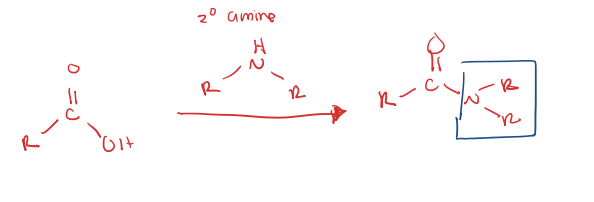
carboxylic acid to amide
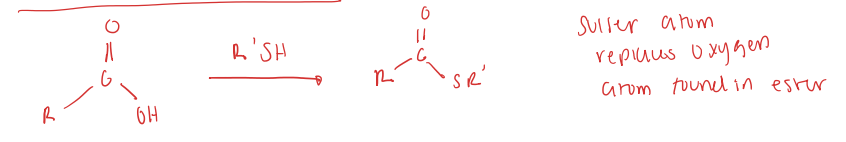
carboxylic acid to thioester
nucleophilic acyl substitution to carboxylic acid derivatives
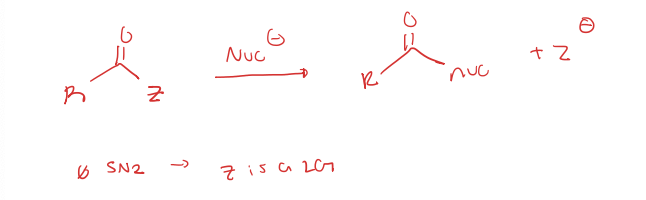
acid chloride to primary amide

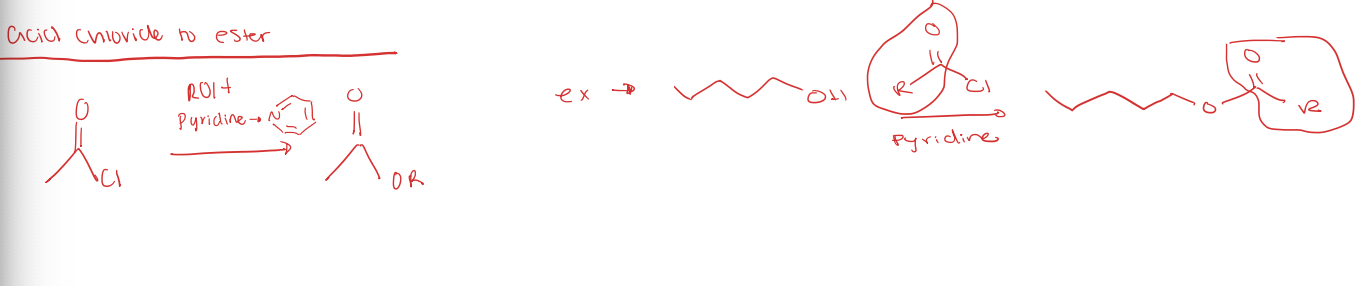
acid chloride to ester
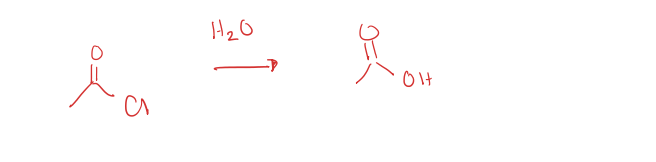
acid chloride to carboxylic acid
acid chloride to R group attached

acid chloride to primary alcohol
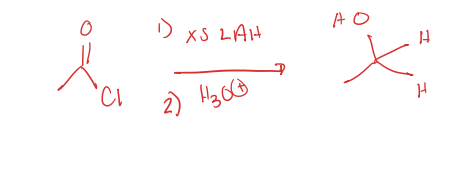
acid chloride to aldehyde
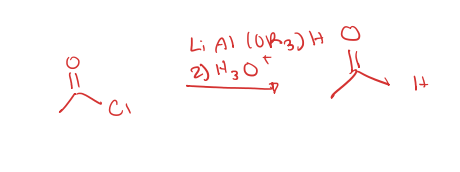
acid chloride to tertiary alcohol
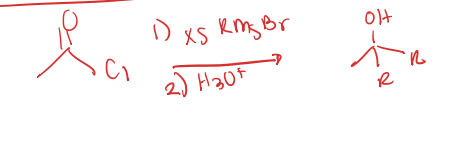
acid anhydride to ester with R group
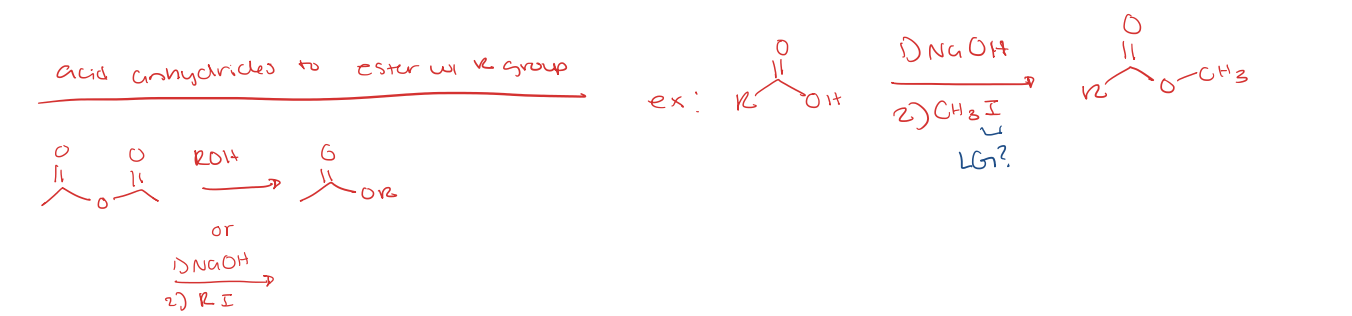
acid anhyride to primary amide
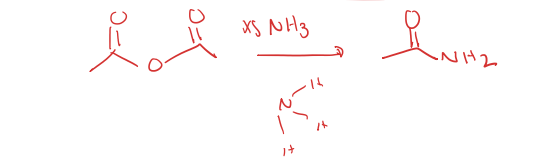
acid anhydride to secondary amide
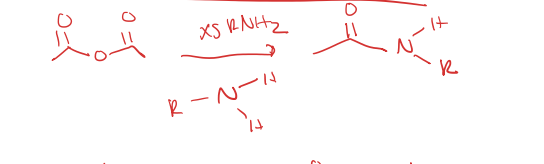
acid anhydride to tertiary amide
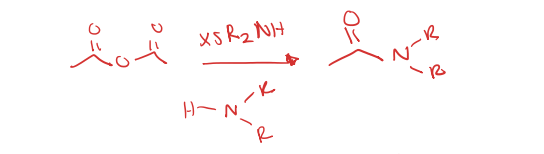
acid anhydride to primary alcohol
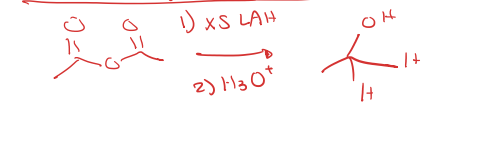
acid anhydride to aldehyde
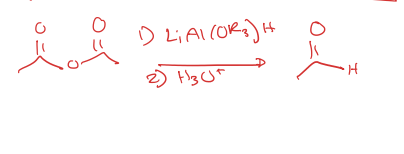
acid anhydride to tertiary alcohol

acid anhydride to R group attached (ketone)

anhydride to carboxylic acid

carboxylic acid to anhydride
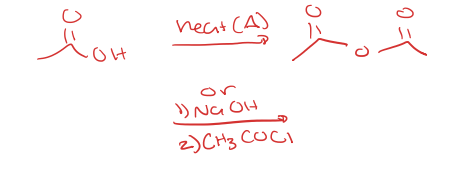
fischer esterification
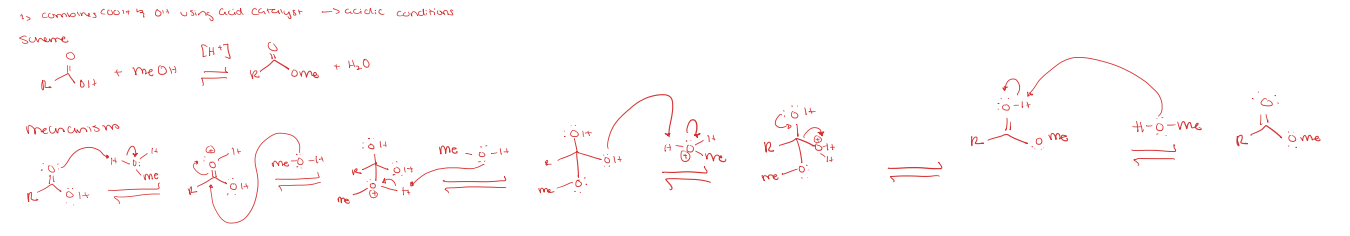
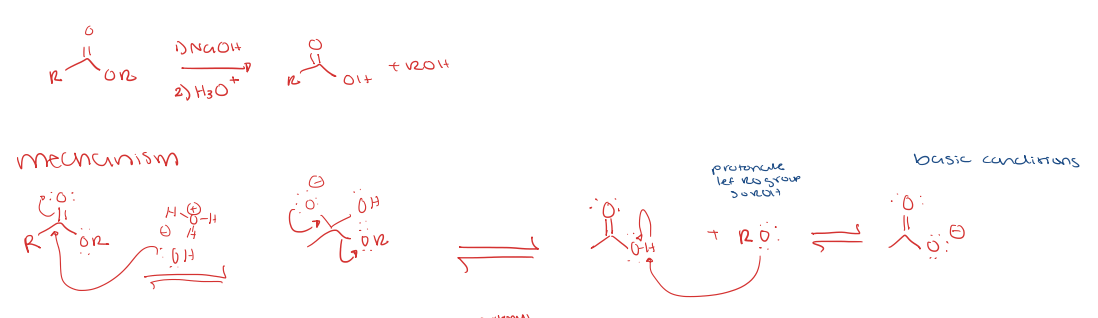
saponification under basic conditions (hydrolysis)
ester to carboxylic acid
makes an enolate
saponification under acidic conditions (reverse of fischer esterification)
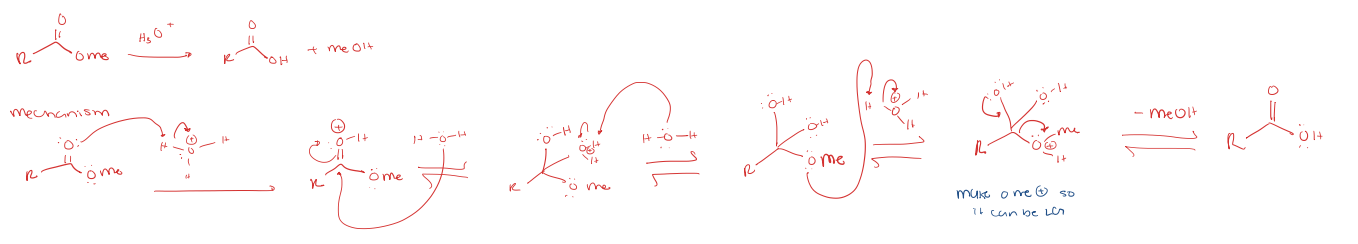
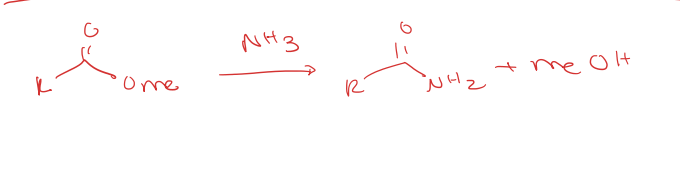
aminolysis (ester OMe to primary amide)
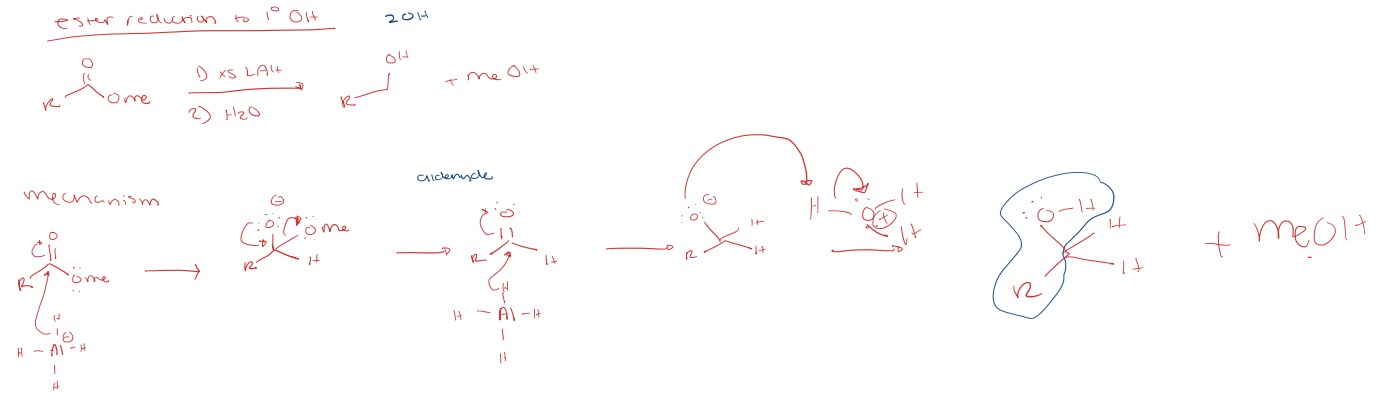
ester reduction to a primary alcohol
ester to tertiary alcohol using a grignard reagent

stopping ester reduction to an aldehyde
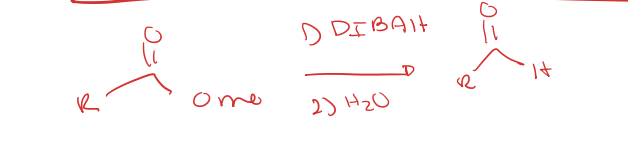
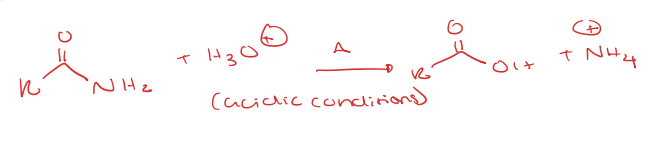
primary amide to carboxylic acid under acidic conditions
primary amide to carboxylic acid under basic conditions
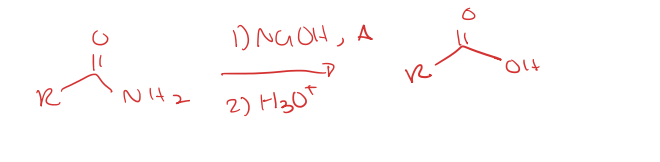
amide reduction to primary amine (NH2)
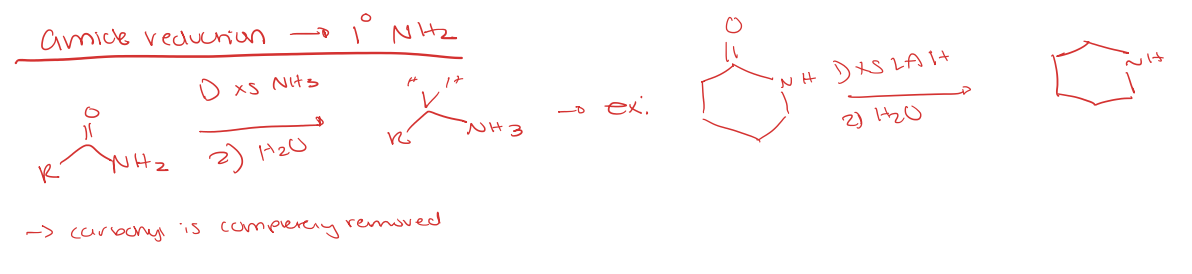
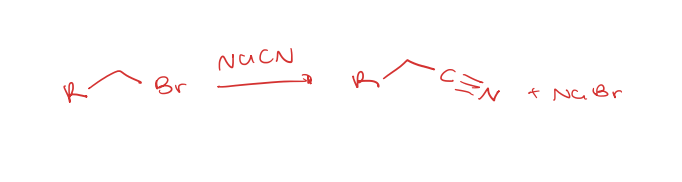
primary or secondary alkyl halide to nitriles
primary amide to nitrile
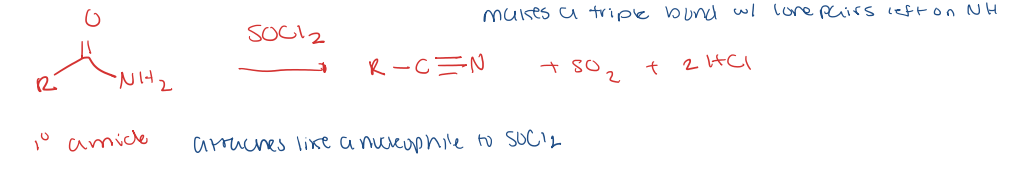
nitrile to carboxylic acid under basic conditions
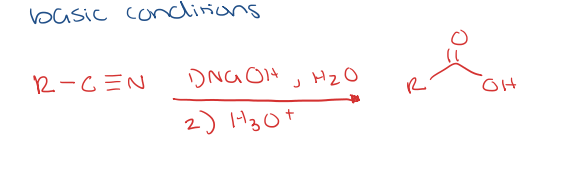
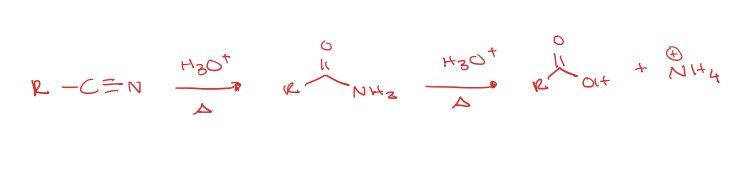
nitrile to carboxylic acid under acidic conditions
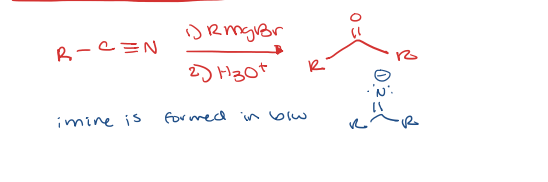
nitriles to ketone
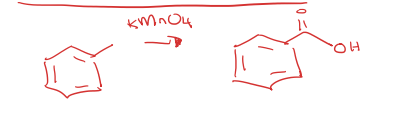
methyl attached to benzene (toluene) to carboxylic acid
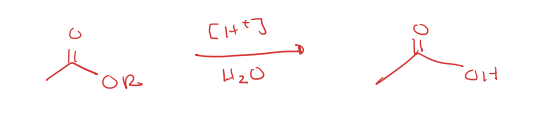
ester to carboxylic acid under acidic conditions
primary alkyl halide to carboxylic acid
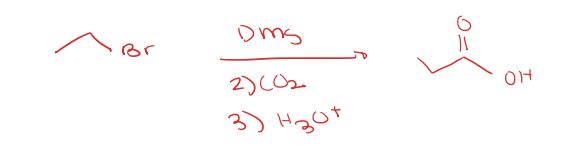
methyl group added
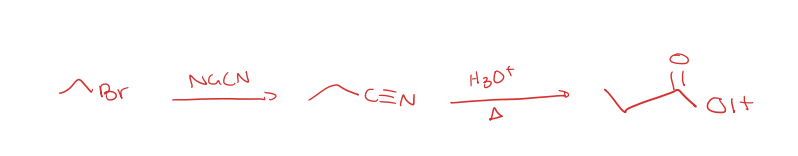
primary alkyl halide to nitrile to carboxylic acid
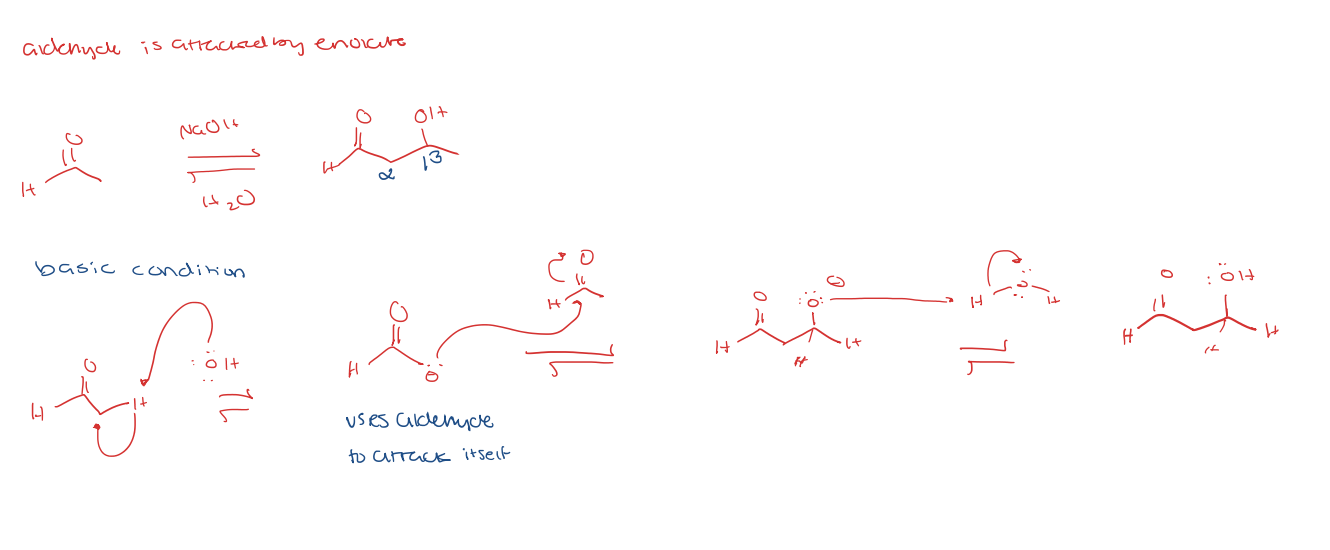
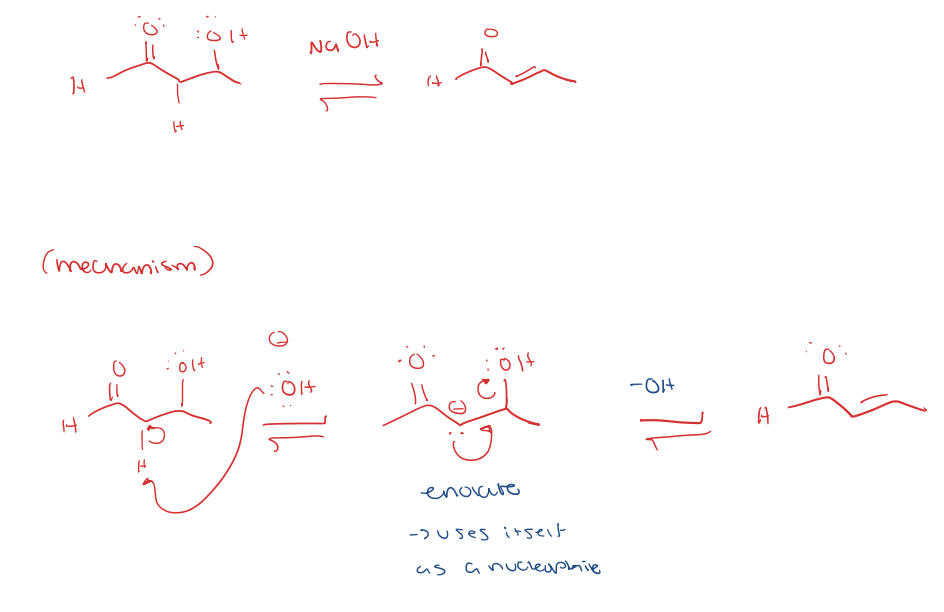
aldehyde to enolate
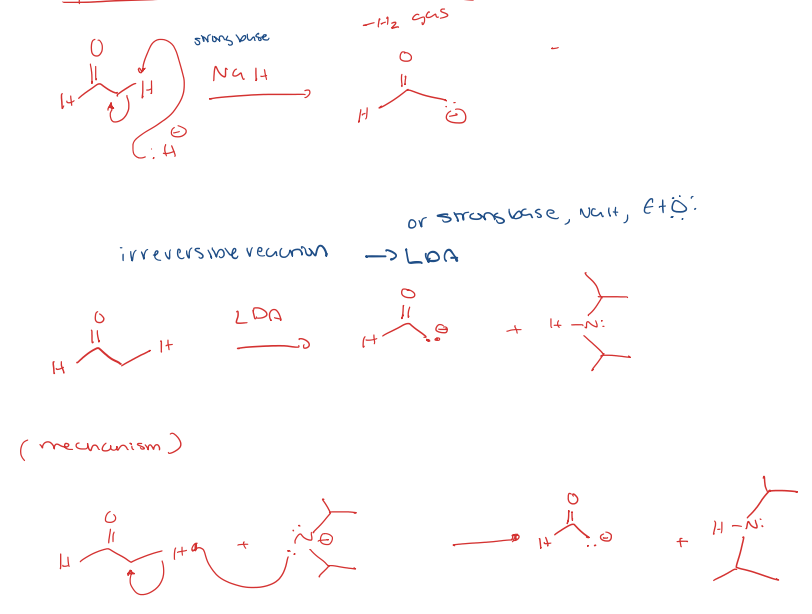
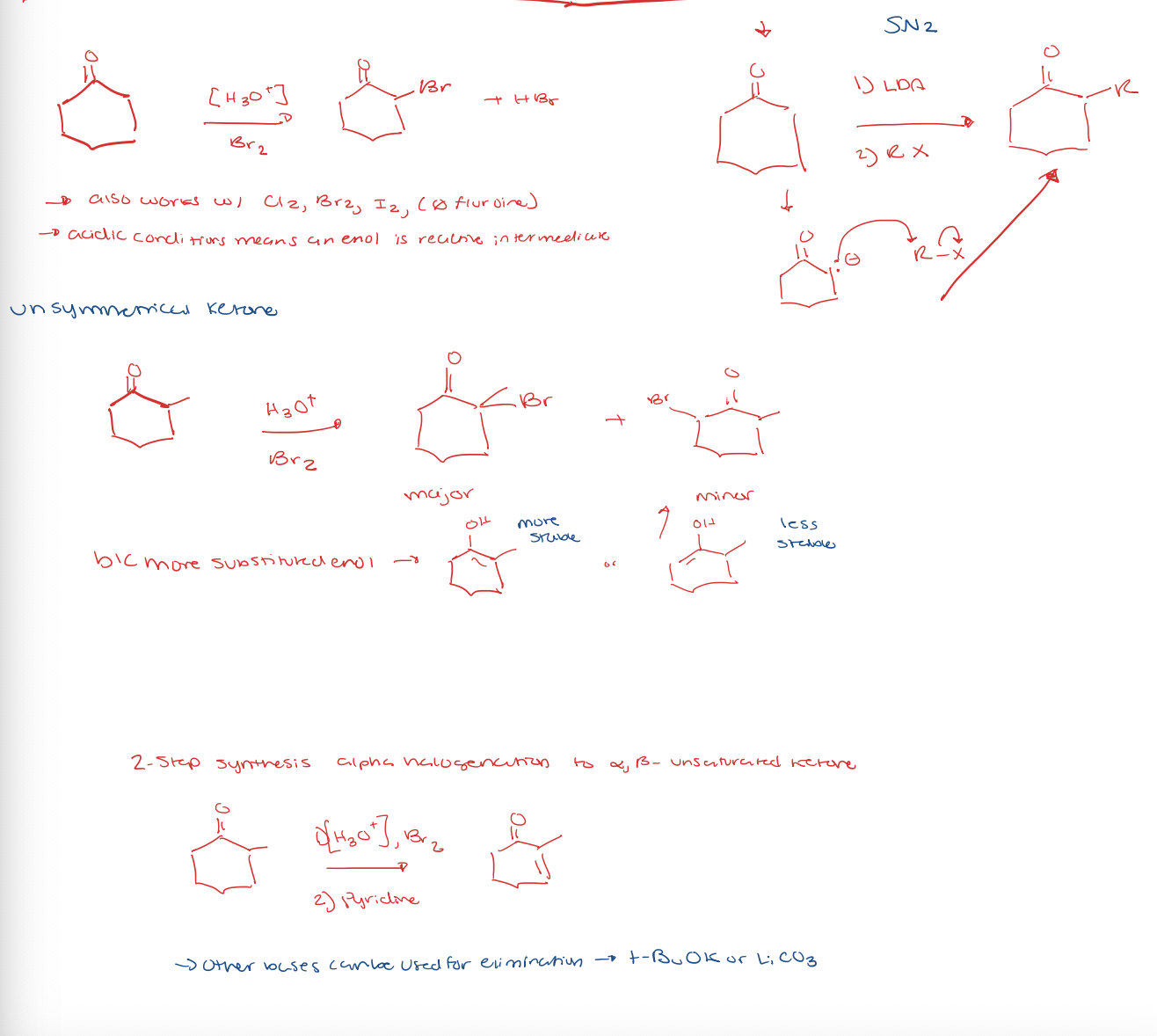
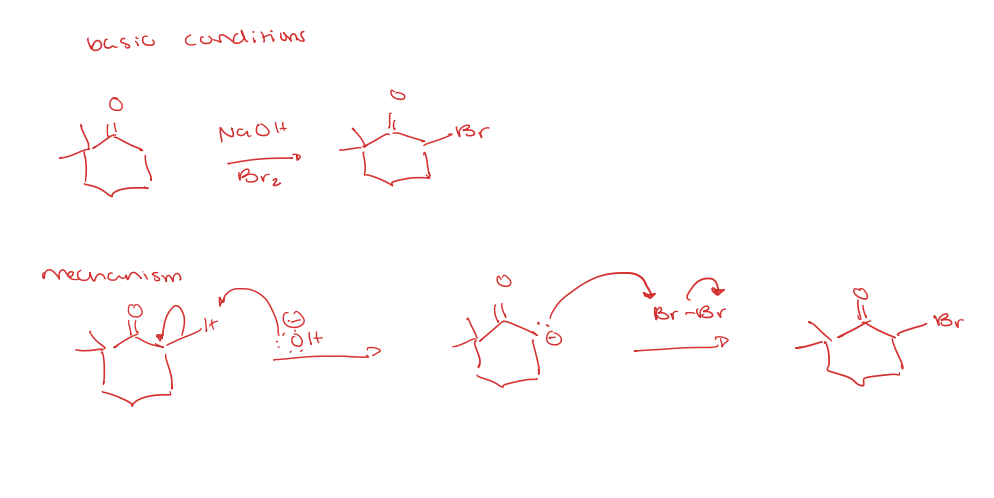
ketone/aldehyde to alpha halogenation/alkylation of the alpha position
enolate intermediate under basic condition
aldol addition under basic condition
combined aldehyde and primary alcohol
aldol condensation
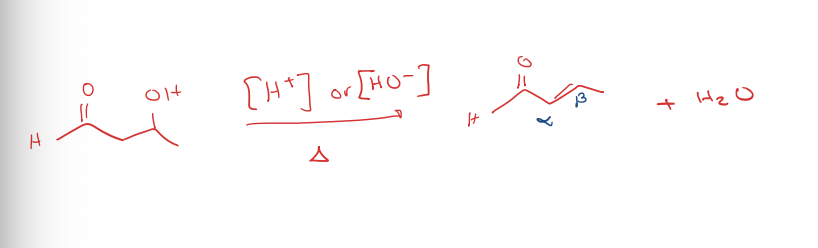
aldehyde and alkene with H2O, alpha, beta hydroxycarbonyl
aldehyde to aldol condensation
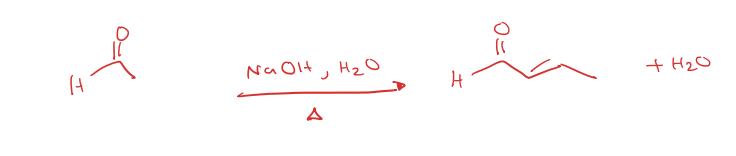
aldol addition to aldol condensation
crossed aldol reactions
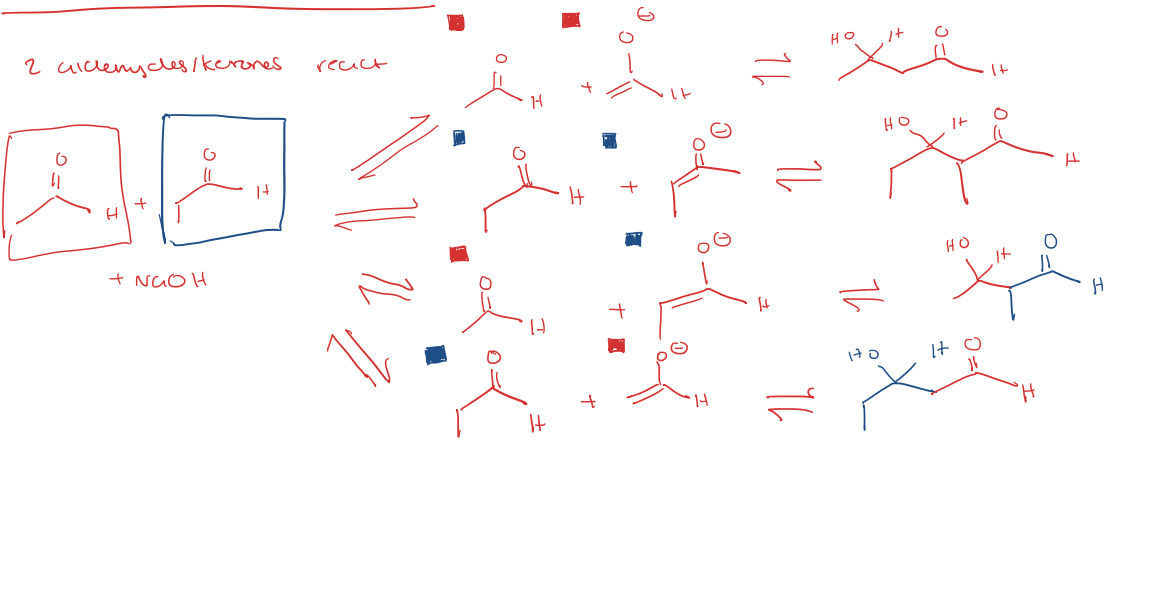
2 aldehydes/ketones react
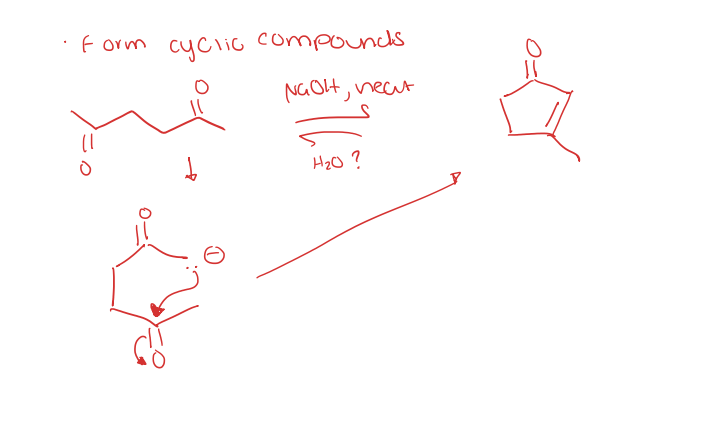
intramolecular aldol reactions
claisen condensations (ester to beta-keto ester)
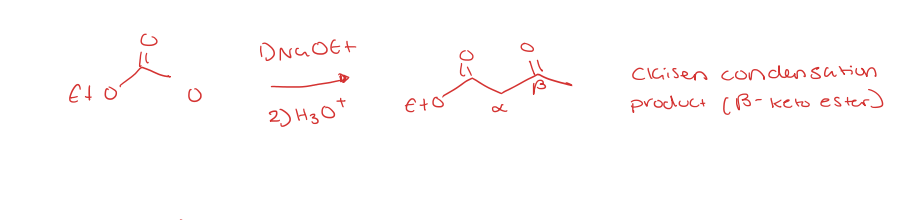
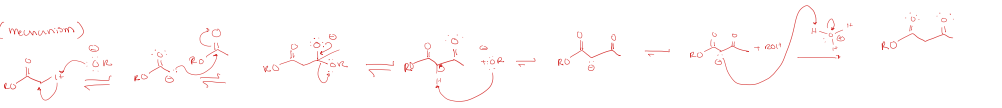
2 alpha carbons at least
hydroxide (OH-) cannot be used b/c hydrolysis will occur
dieckmann cyclization

kinetic alkylation of the alpha position
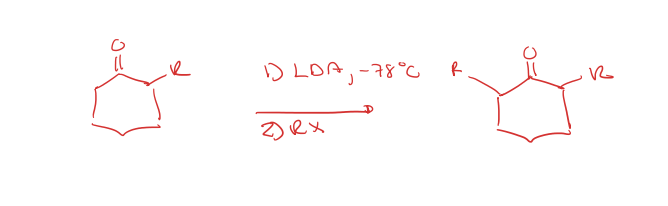
thermodynamic alkylation of the alpha position
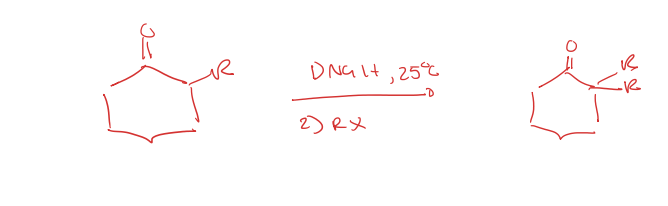
most substituted
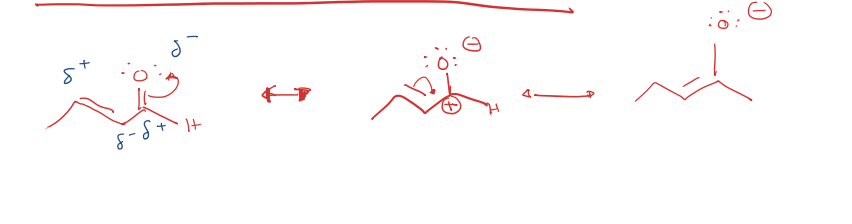
resonance of alpha, beta unsaturated carbonyls
organometallic reagent using a grignard reagent
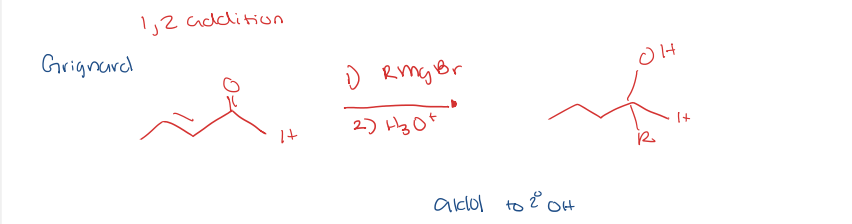
aldol condensation to secondary alcohol
1,2 addition
organometallic reagent with gilman reagent
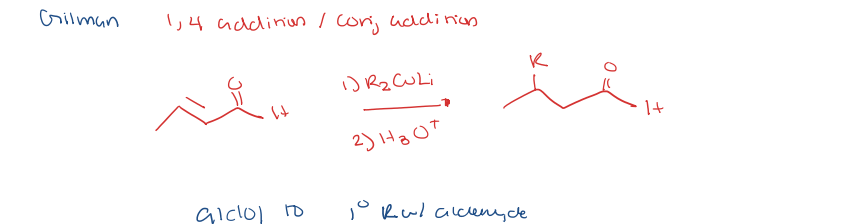
aldol condensation to 1,4 addition
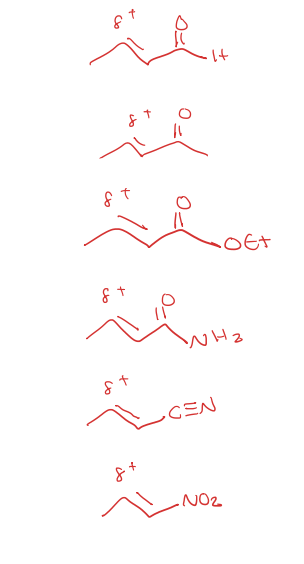
michael donors
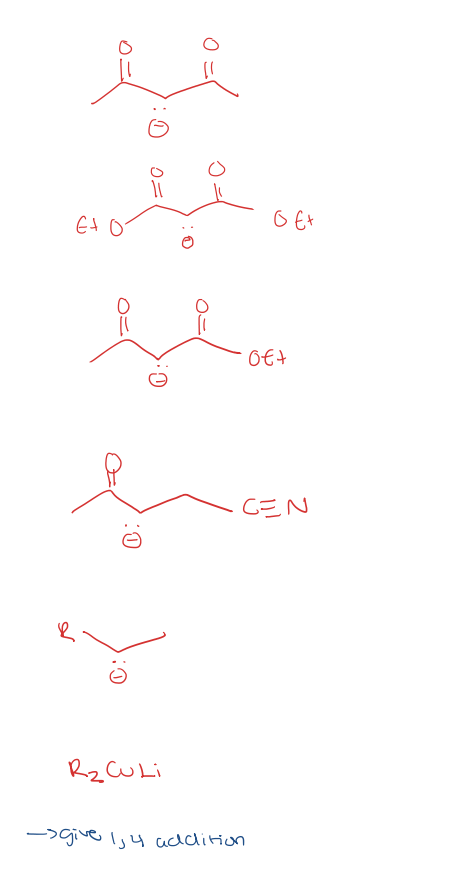
michael acceptors
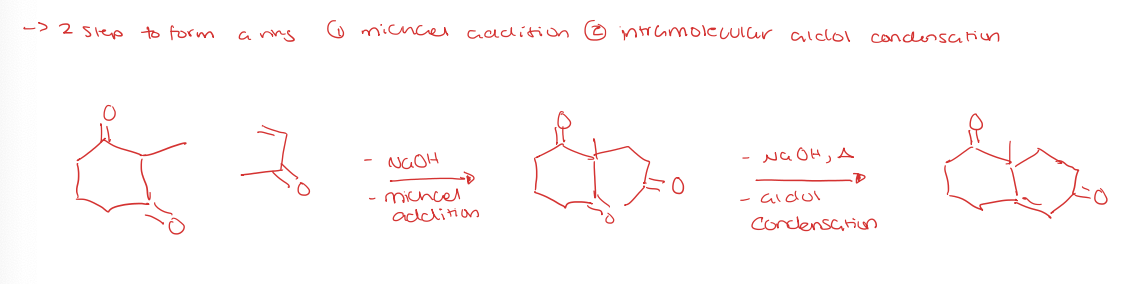
robinson annulation
1)alpha position of an enolate attacks an alkyl halide 2) michael donor attacks the beta position of a michael acceptor to alkylation
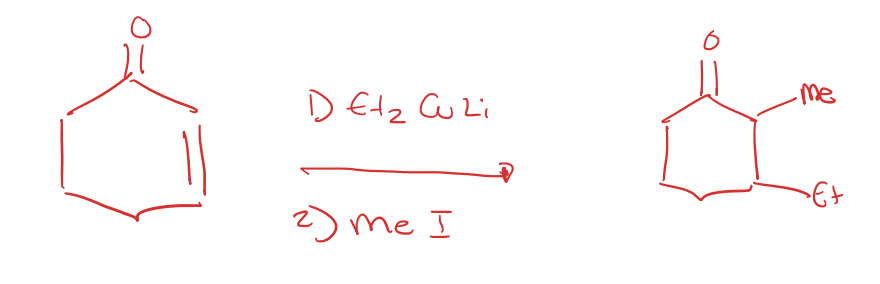
michael reaction
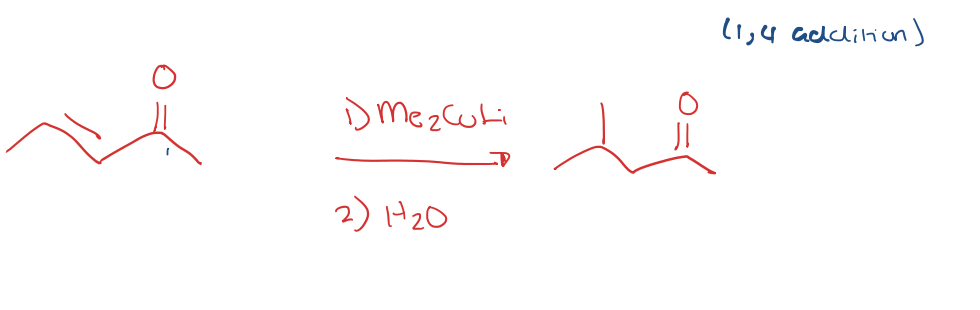
organolithium origin
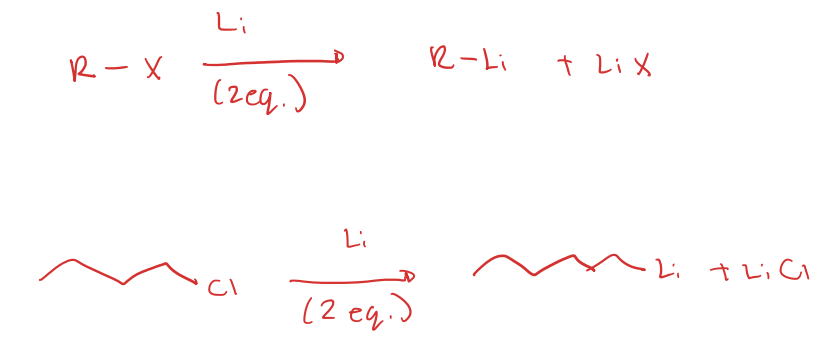
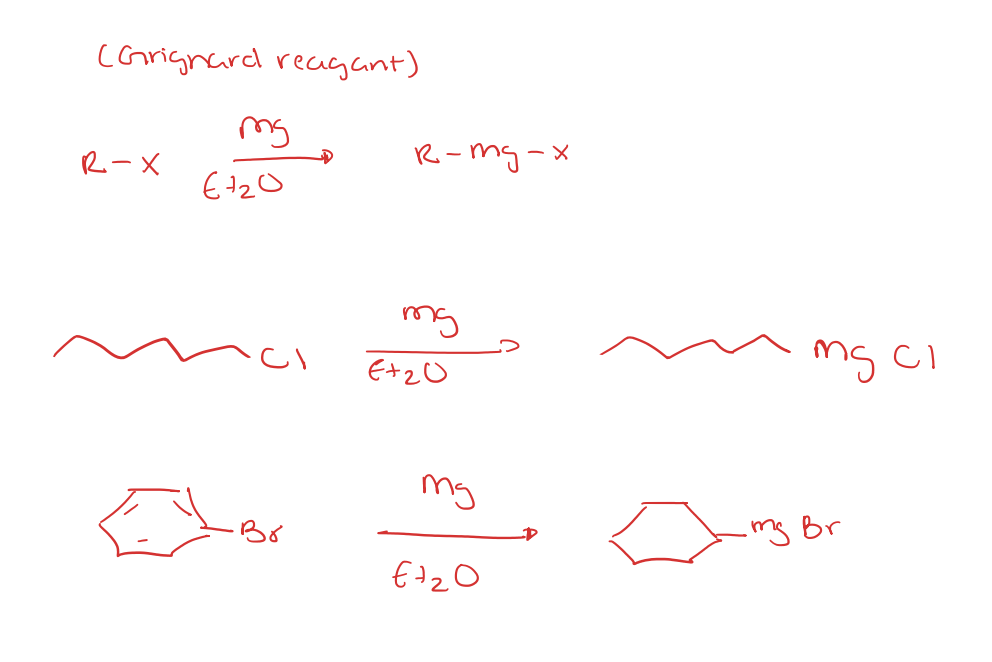
organomagnesiums origin/review
ketone/aldehydes to teritary alcohol
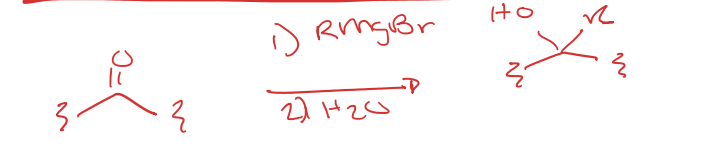
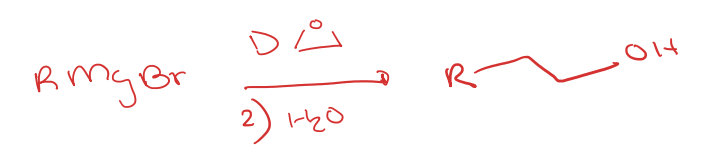
grignard reagent to primary alcohol using an epoxide
grignard reagent to carboxylic acid
nitrile to carbonyl with R group (ketone)
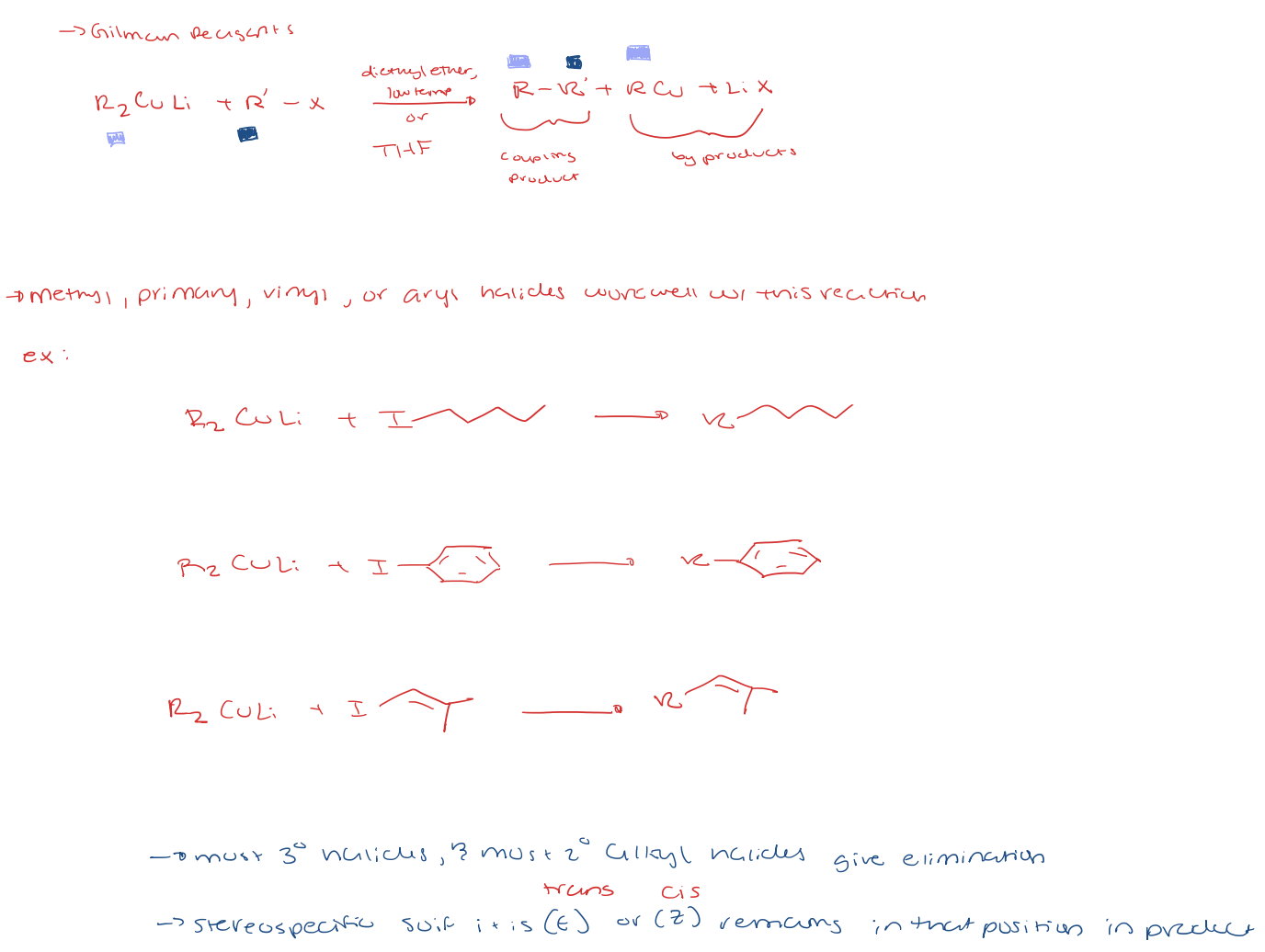
preparation for gilman reagents (Li Dialkyl Cuprate)
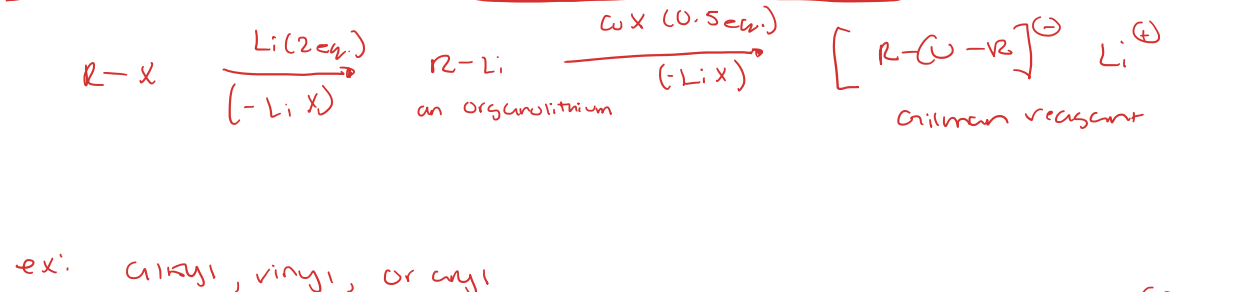
alpha,beta unsaturated ketone to 1,4 addition with Li Dialkyl cuprates
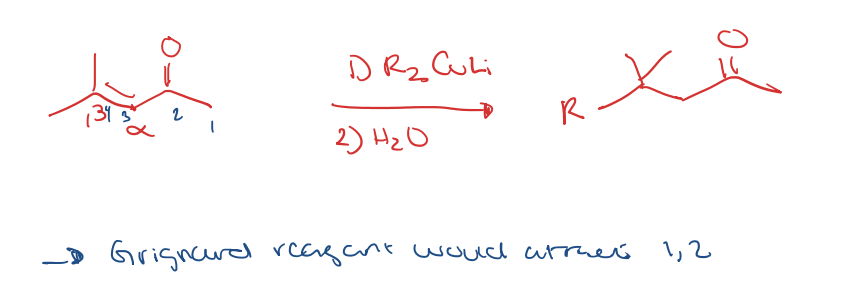
corey-posner/whitesides-house reaction
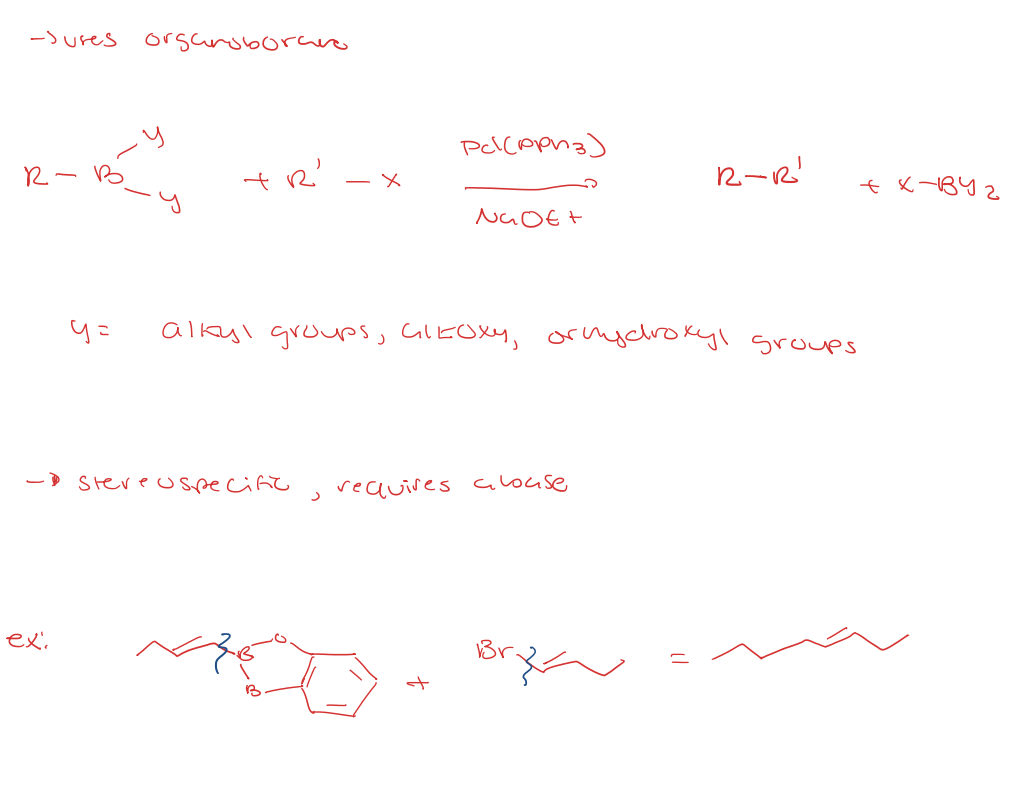
suzuki coupling
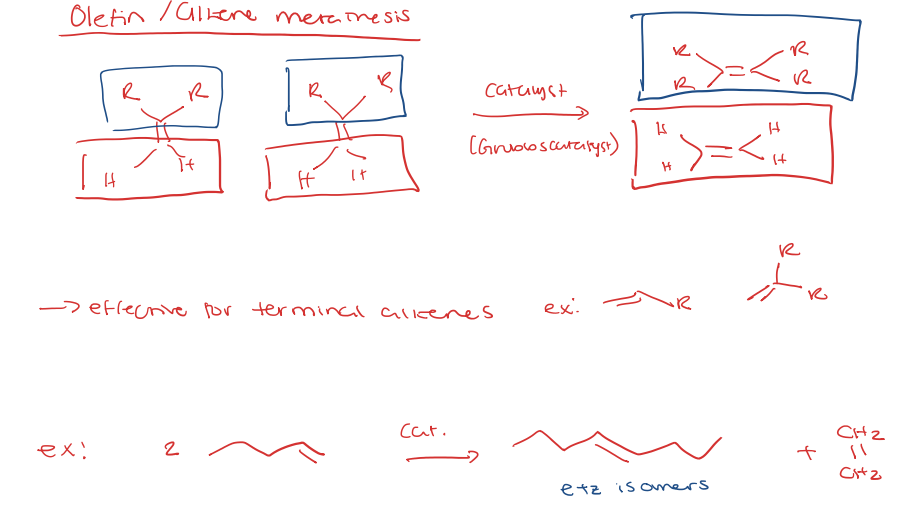
olefin/alkene metathesis
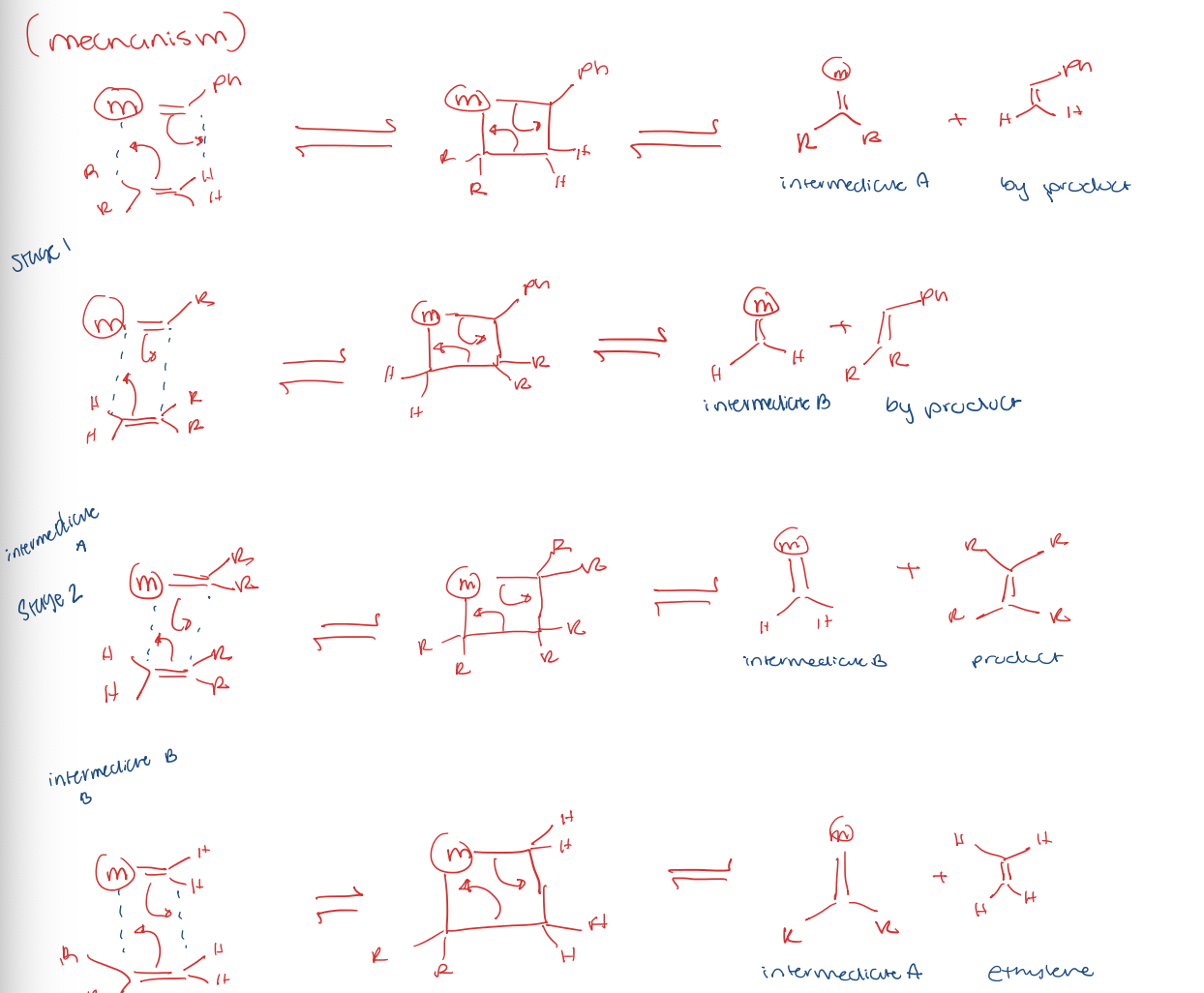
alkene metathesis for ring closing (RCM)
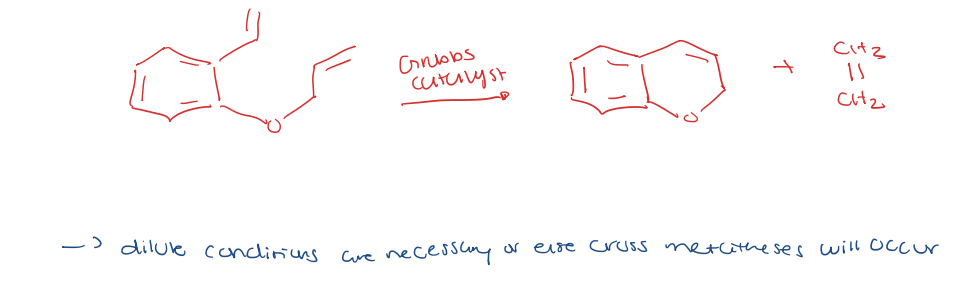
alkene metathesis for ring opening

chemoselectivity to reduce carboxylic acid to primary alcohol
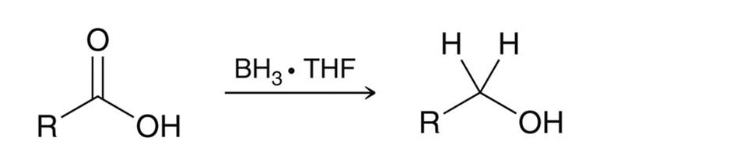
also bh3 and h30+
only reduces COOH exclusively

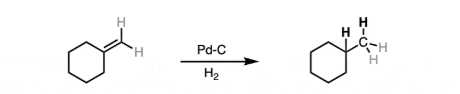
reducing agent H2, Pd-c
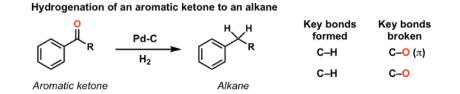
reduces carbonyl derivatives and COOH to primary alcohol, alkenes to alkanes, N3 to primary amines
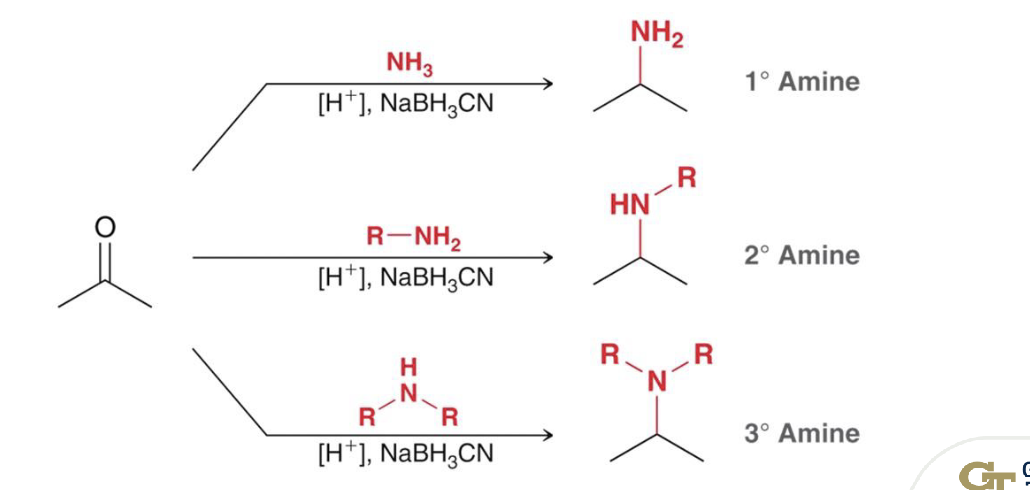
NaBH3CN and H3O+
reductive amination: converts aldehydes/ketones, then to an imine then into primary or secondary amines
selective
NaBH4 and H3O+
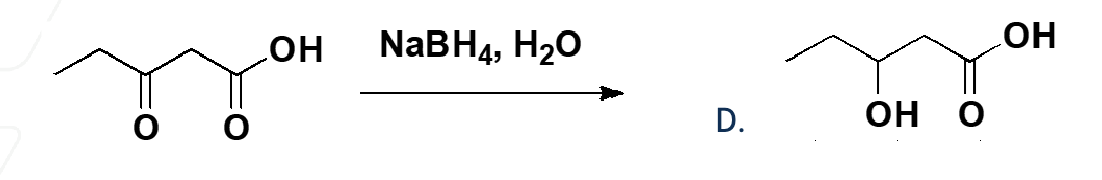
reduces ketones and aldehydes to primary OH not carboxylic acid
Wittig Reaction to make a double bond
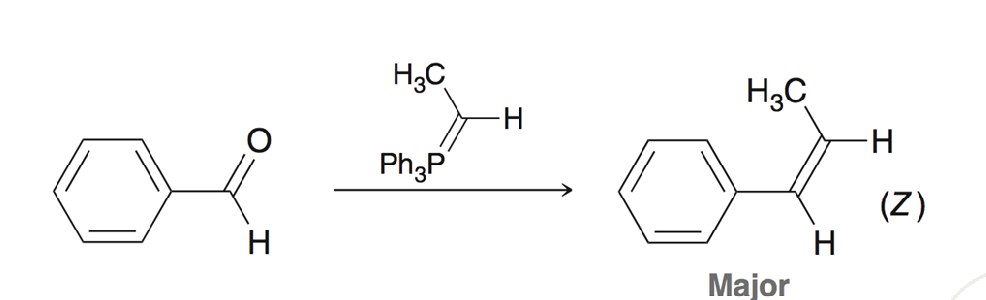
Z alkene is favored, stereoselective
H2 reducing agent
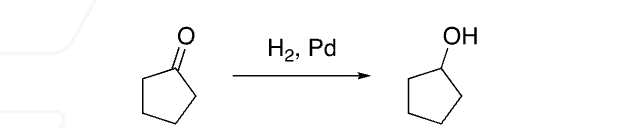
cleaves double bonds to make alkanes, carbonyl derivatives to primary OH
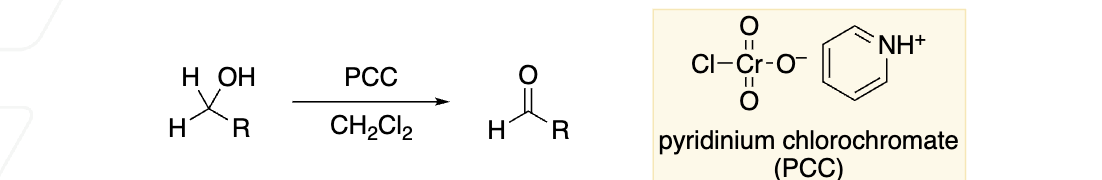
primary alcohol to aldehydes
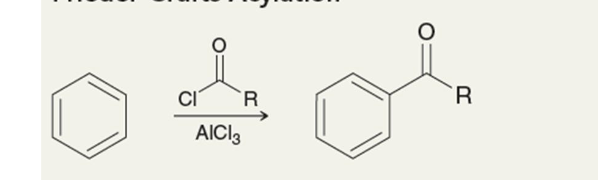
friedel-crafts acylation
reduction using LAH and H2O/H3O+
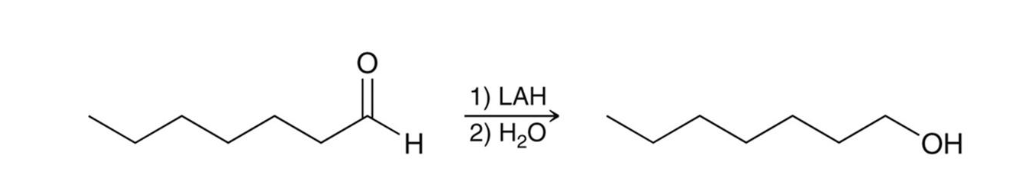
reduces carbonyl compounds, usually to primary OH
enol vs enolate
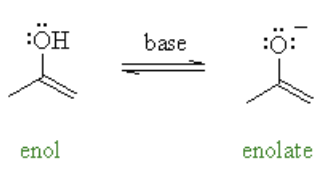
enol = oh attached
enolate = o(-) attached
electrophile association
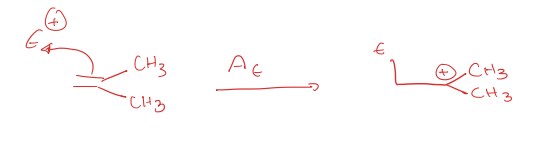
1,2 rearrangement (1,2R)
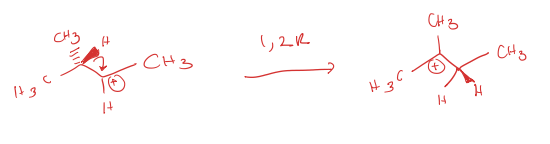
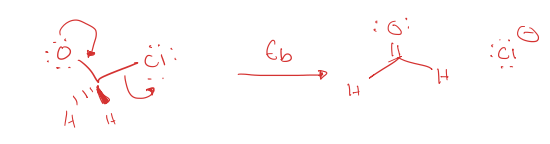
beta-elimination (Eb)
biomolecular elimination (E2)