IGCSE Chemistry
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
markscheme answers and keywords
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
characteristics of compounds in a homologous series
same general formula
same functional group
trend/gradual change in physical habits
similar chemical properties
neighbouring members differ by same stated increments
exothermic
= a reaction which releases thermal energy to surroundings
condenser in distillation
M1: condenser cools ethanol vapour
M2: ethanol vapour condenses into a liquid
alkaline metal + water
effervescence
floats
moves
white trail
gets smaller
phenolphthalein
colourless in acidic/neutral
pink in alkalis because OH-/ hydroxide ions are present
reason for cleaning wire before flame test
prevent impurities that will affect results
so they don’t interfere with flame colour
percentage of nitrogen in atmosphere
78%
environmental effects of acid rain
acidifies lakes
kills fish
test for ammonium
M1: add sodium hydroxide and heat
M2: test gas with red litmus paper
M3: red litmus turns blue
isomers
M1: compounds with the same molecular formula
M2: but different structural/displayed formula
methods for disposing polymers
burying them in landfill sites
inert/unreactive/do not biodegrade
burning them to release heat energy
produce toxic fumes/greenhouse gases when burned
carbon monoxide effect
poisonous
toxic
limits capacity to carry oxygen in blood
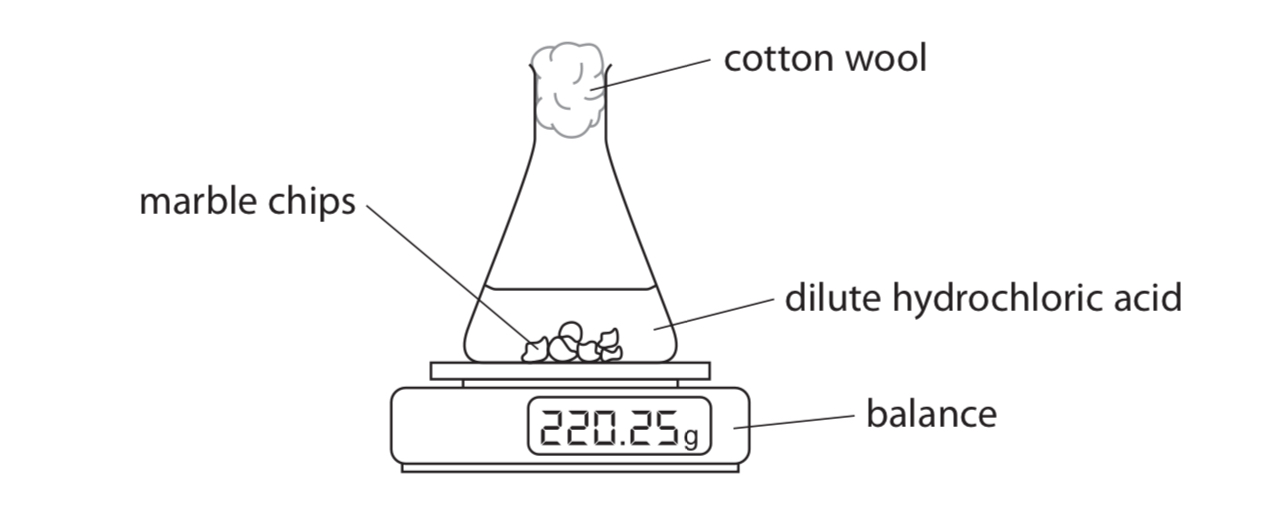
purpose of cotton wool
to prevent acid spray from leaving flask
percentage yield
(actual yield/ theoretical yield) * 100
silver ion
Ag+
copper ion
Cu2+
iron ion
Fe2+ and Fe3+
lead
Pb2+
zinc
Zn2+
hydroxide
OH-
hydrogen
H+
ammonium
NH4+
carbonate
CO32-
nitrate
NO3-
sulfate
SO42-
covalent bond
= electrostatic attraction between atoms by the sharing of a pair of electrons
solubility rules
common sodium, potassium and ammonium compounds are soluble
all nitrates are soluble
common chlorides are soluble - except silver and lead(II)
common sulfates are soluble - except barium, calcium and lead(II)
common carbonates are insoluble - except sodium, potassium and ammonium
common hydroxides are insoluble - except sodium, potassium and calcium (slight soluble)
acid
proton donor
base
proton acceptor
catalyst
lower the activation energy by providing an alternative pathway
properties of alkanes
shorter alkanes are more volatile & more flammable
the longer the chain the higher the boiling point
describe how crude oil is separated into fractions in the fractionating column [4 marks]
M1: crude oil is heated from liquid to gas/vapourized
M2: column is hotter at the bottom and cooler at the top
M3: vapours/gases rise up the column
M4: vapours condense at their boiling point
bitumen uses
road tar
surfacing roads
cracking
= process of breaking down long-chain hydrocarbons to form shorter chains of alkanes/alkenes/hydrocarbons
unsaturated hydrocarbons
double bond between carbon atoms
contains only hydrogen and carbon atoms
explain why metals are malleable
layers of metal cations
can slide over each other
negative elctrode
place of reduction (gain of electrons)
negatively charged so it attracts cations
why sodium metal doesn’t form in the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of sodium chloride
= sodium is more reactive than hydrogen
dynamic equilibrium
forwards and reverse reactions occur at the same rate
concentrations of reactants and products remain constant
titration
rinse burette with named alkali
fill burette with named alkali
make sure that jet contains liquid
add a few drops of indicator to conical flask
add named alkali from the burette until indicator changes colour permanently
swirl the conical flask
near the end-point add dropwise
record the final and initial volume on burette
repeat until concordant results
exothermic reaction reasoning
energy released from bond formation is greater than energy absorbed for bond breaking
bond formation is exothermic/ bond breaking is endothermic
faraday
= a unit of electric charge; amount of electric charge needed to supply one mole of electrons.
equivalent to 96 500C (Coulombs)
sulfur dioxide + water
sulfurous acid
pollutants thar form acid rain
nitrogen oxide
sulfur dioxide
problems caused by acid rain
corrodes limestone
causes iron to rust
harms aquatic life
what happens to temperature change when the volume of the solvent is increased
change in temperature is less
because a larger volume has to be heated