Pulmonary Pathology, Pt.II
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
True or False: Most upper respiratory tract infections are minor & transient
True
True or False: Upper respiratory tract infections are common in the western world
True
True or False: Most lower respiratory tract infections are minor & transient
False ==> significant caused of morbidity & mortality
Any infection of the lung is known as _________________.
pneumonia
Which infections cause pneumonia?
-viruses
-bacteria
-fungi
-parasites
What are the old classifications of acute bacterial infections?
-bronchopneumonia
-lobar pneumonia
When the pathogen that causes pulmonary infection cannot be identified, how are pulmonary infections classified?
classified by clinical setting
Which types of pneumonia are classified by clinical setting?
-community-acquired acute pneumonia
-community-acquired atypical pneumonia
-nosocomial pneumonia
-aspiration pneumonia
-chronic pneumonia
-necrotizing pneumonia & lung abscess
-pneumonia in immunocompromised hosts
*pathogen can't be identified in all of these, so we go by setting
what is the most common cause of community-acquired acute pneumonia?
Streptoccus pneumoniae
What type of infection is community-acquired acute pneumonia usually?
bacterial
All of the following bacteria usually cause which type of pneumonia?
-Streptoccocus pneumoniae
-haemophilus influenzae
-moraxella catarrhalis
-staphyloccocus aureus
-legionella pneumophila
-klebsiella pneumonia
community-acquired acute pneumonia
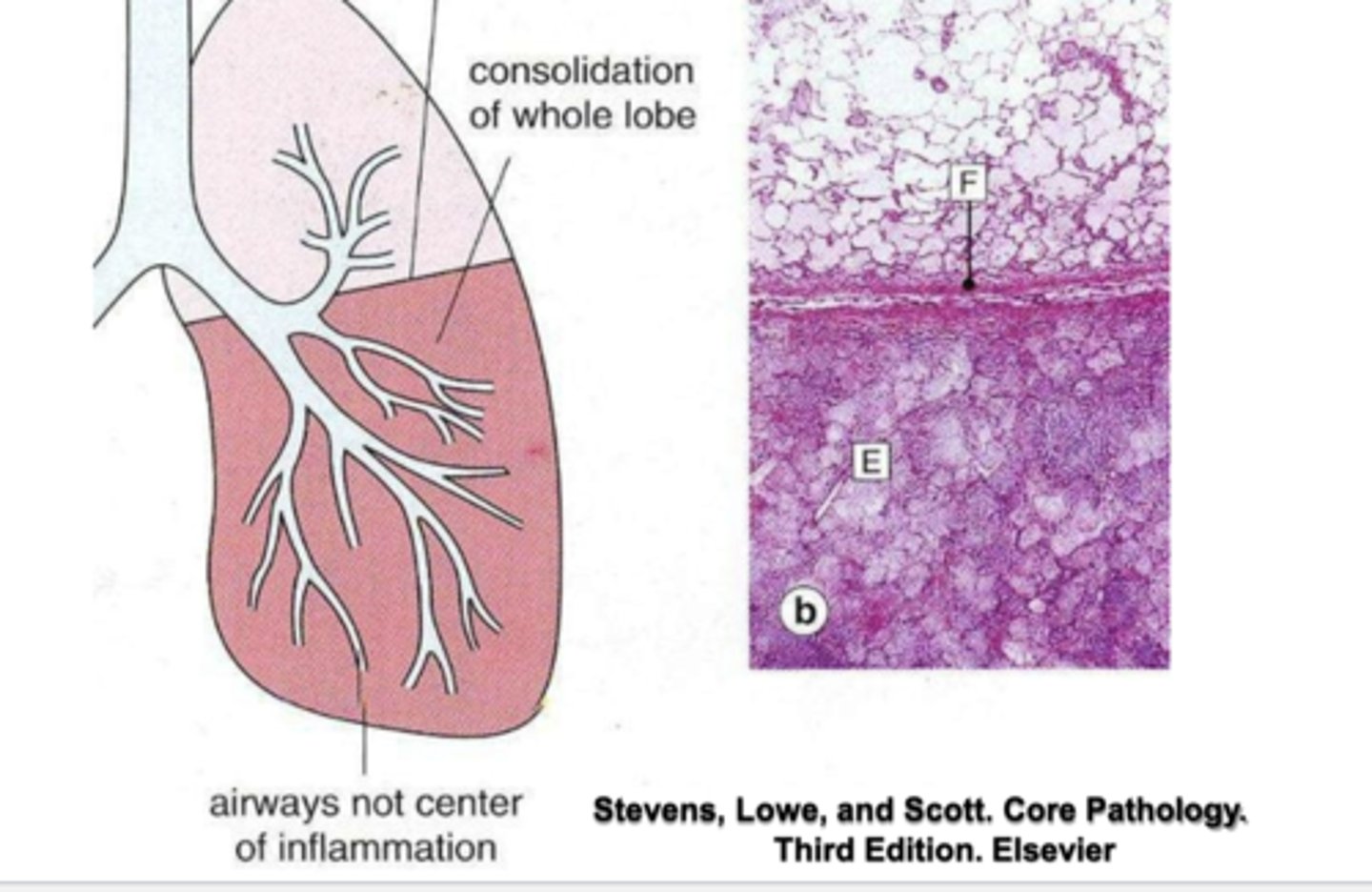
How does consolidation appear in the lung due to community-acquired acute pneumonia?
-consolidation of the entire lobe below the pulmonary fissure
-airways not center of inflammation
What is the most common cause of community acquired atypical pneumonia?
mycoplasma
Community-acquired atypical pneumonia can be caused by which infections?
-mycoplasma
-rhinovirus
-influenza types A & B
-parainfluenza
-respiratory syncytial virus
-human metapneumovirus
-adenovirus
Which type of pneumonia is acquired during hospital stays?
nosocomial pneumonia
Nosocomial pneumonia is common in which type of patients?
-severe underlying disease
-immunosuppression
-H/O prolonged antibiotic regimens
which kind of bacteria usually cause nosomial pneumonia?
gram-negative rods
True or False: S. pneumoniae is a common pathogen that causes nosomial pneumonia
False ==> S. pneumoniae not a common pathogen that causes nosocomial pneumonaie
The following are signs/symptoms of which pneumonia?
-abnormal gag & swallowing reflexes facilitate aspiration
-infection partly chemical & partly bacterial
-abscess formation common survivors
aspiration pneumonia
When is chronic pneumonia most often localized?
when in otherwise healthy patients
when is chronic pneumonia most often disseminated?
when in immunocompromised patients
which type of pneumonia presents with granulomatous inflammation due to bacteria or fungi?
chronic pneumonia
What percent of deaths does TB cause worldwide?
6%
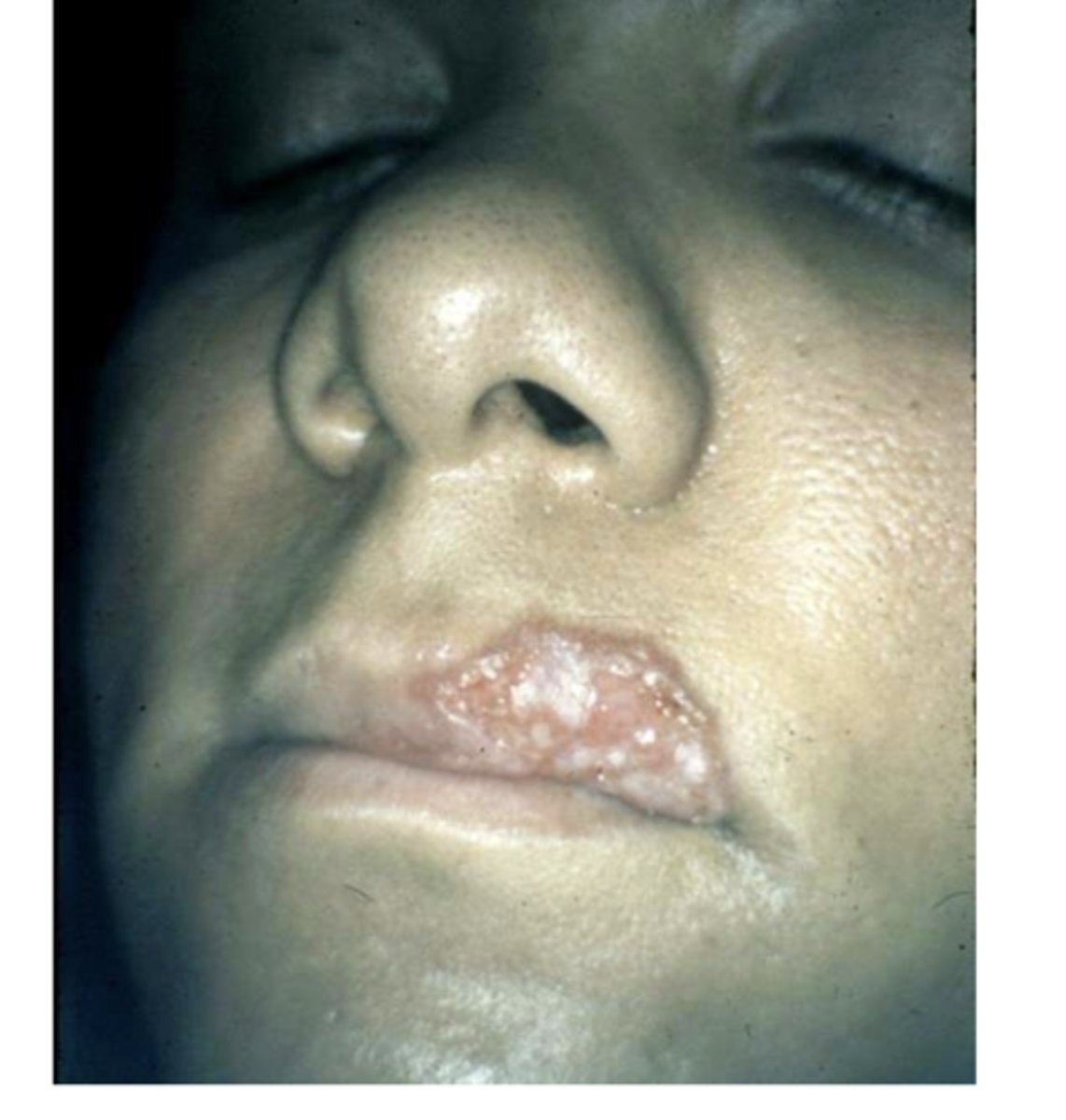
What are the clinical features of tuberculosis?
-rare oral lesions --> typically painless ulcers
-0.5 - 5% of infected patients have clinically evident lesions
-most cases represent secondary infection
-rare primary cases
-bone involvement may be seen
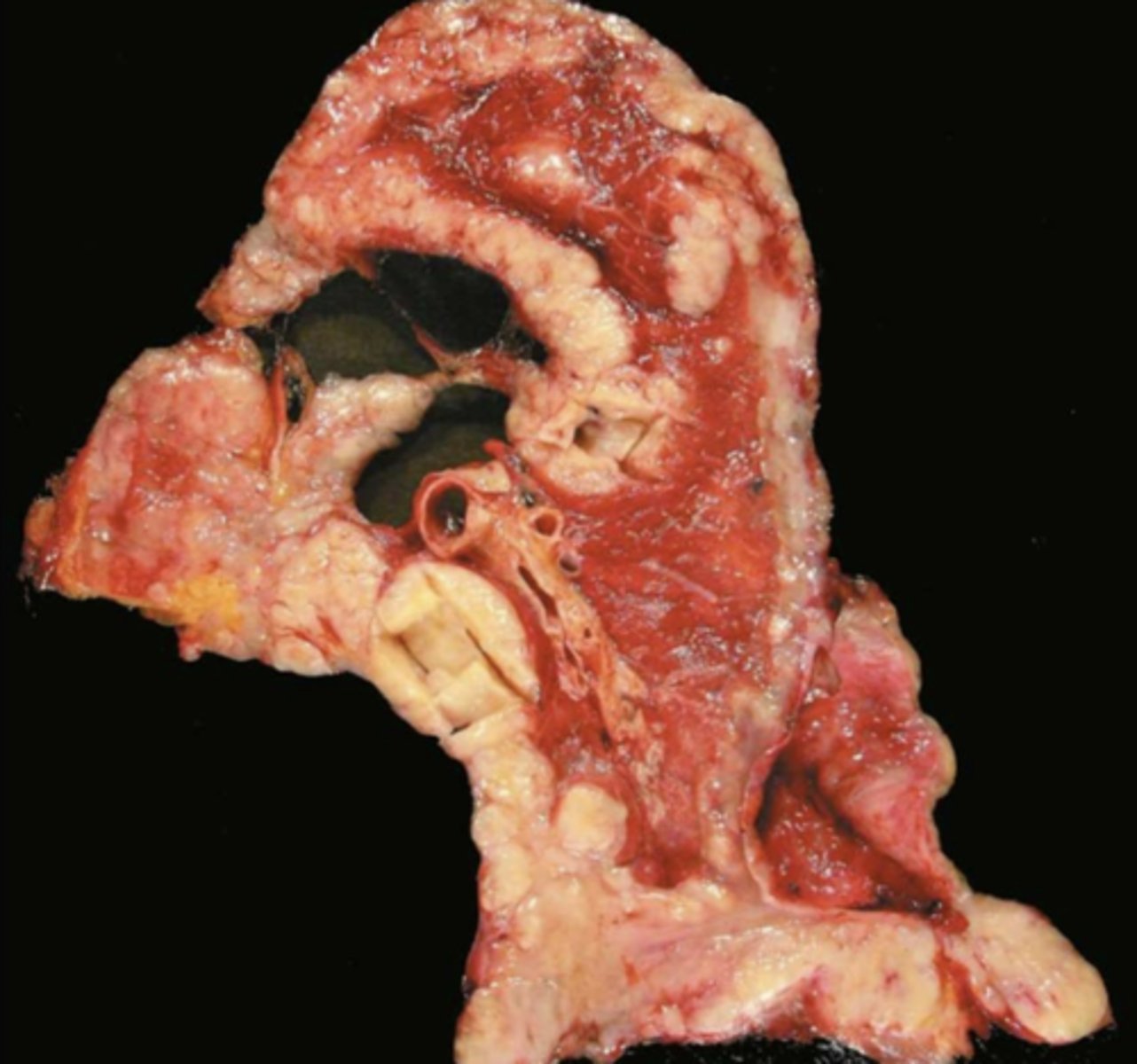
Oral mucosa ulcer due to TB
tongue ulcer due to TB
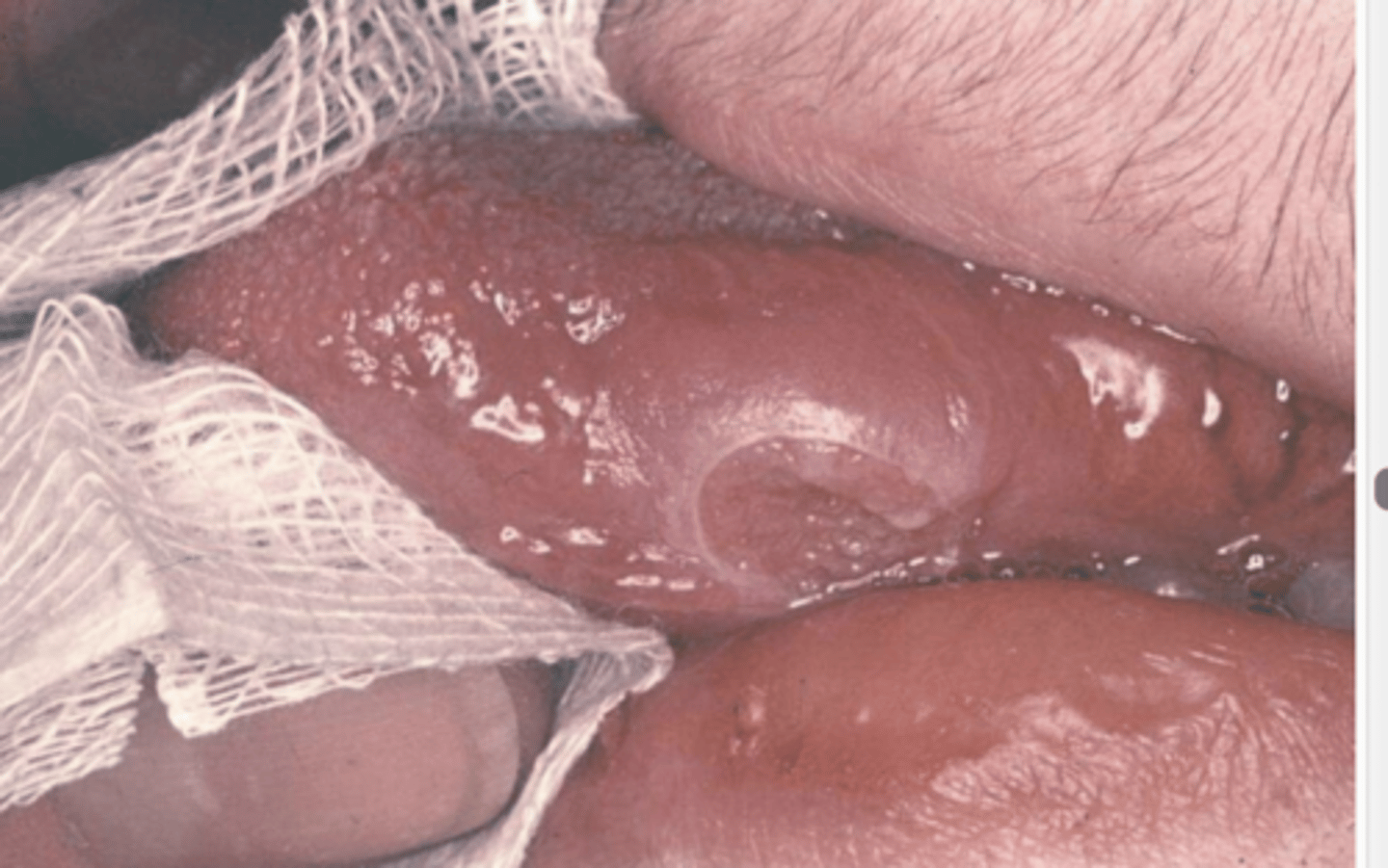
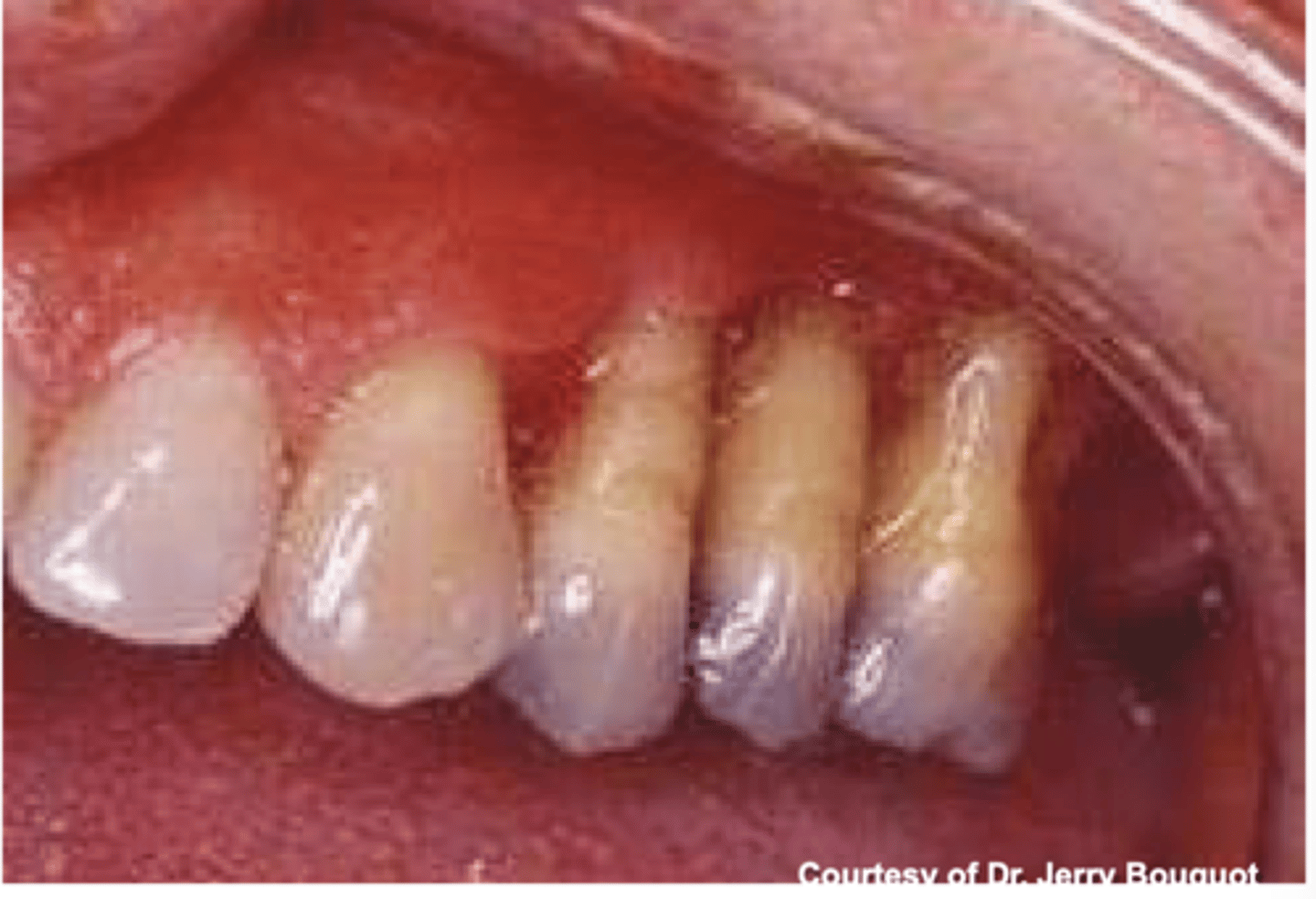
gum recession due to TB
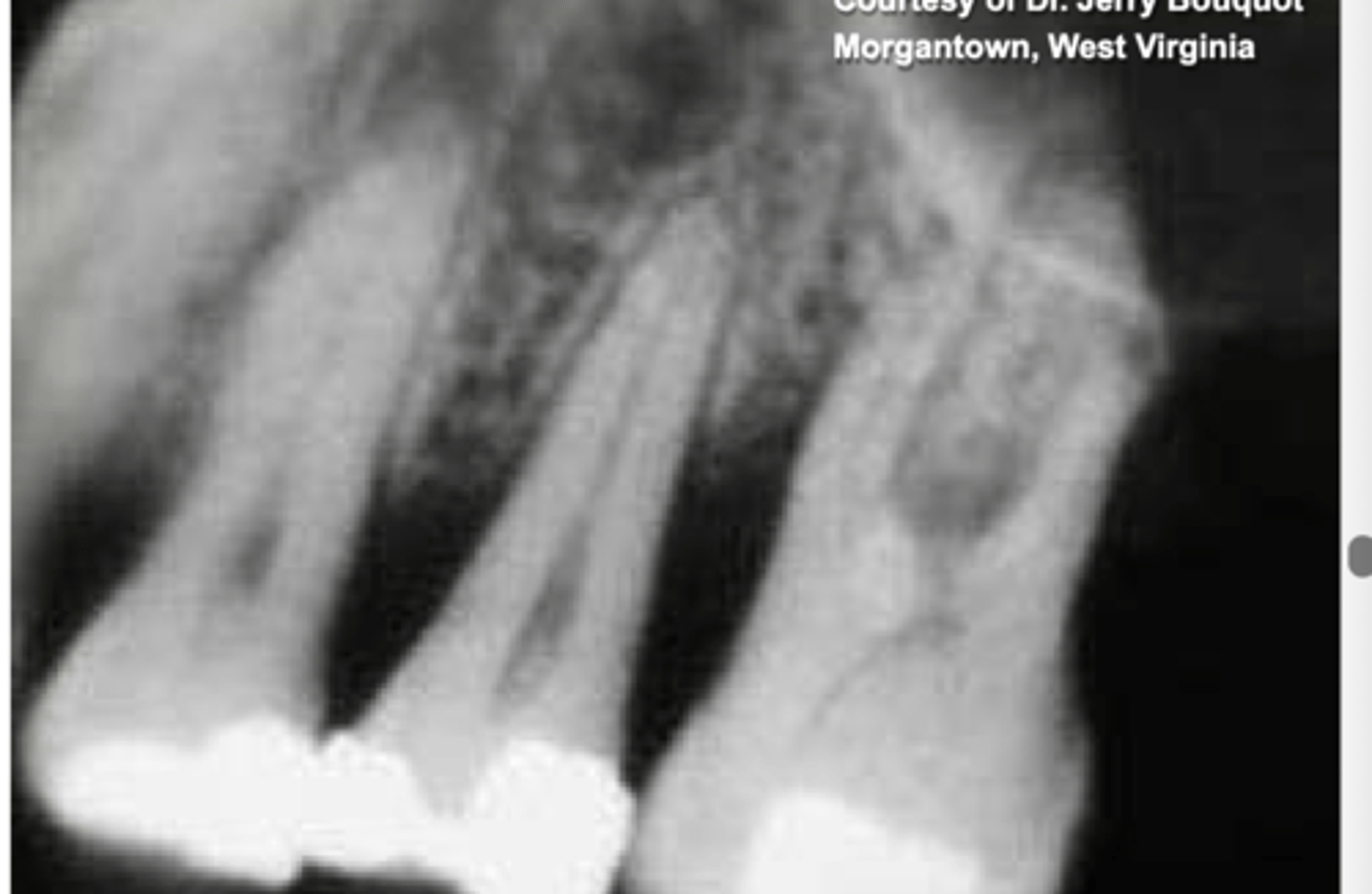
bone loss due to TB
True or False: The organisms that cause fungal pneumonia often have a typical geographic distribution
True
Histoplasma capsulatum, fungi that causes fungal pneumonia, is often found at what geographic locations?
-ohio
-mississippi river valley
coccidioides immitis, fungi that causes fungal pneumonia, is often found at what geographic location?
southwestern USA
what are the characteristics of fungal pneumonia?
-acute pulmonary infection
-chronic granulomatous pulmonary infection
-disseminated miliary disease
which type of pneumonia does the following describe?
-multiple small areas of cavitation
-lung abscess that = localized area of suppurative necrosis w/in pulmonary parenchyma
necrotizing pneumonia
When necrotizing pneumonia is due to aspiration of infective material?
necrotizing pneumonia
What occurs in 10-15% of patients with bronchogenic carcinoma?
necrotizing pneumonia
What are the opportunistic bacterial pathogens that tend to cause pneumonia in immunocompromised patients?
-mycobacterium
-pseudomonas aeruginosa
What are the opportunistic viruses that tend to cause pneumonia in immunocompromised patients?
cytomegalovirus
What are the opportunistic fungi that tend to cause pneumonia in immunocompromised patients?
-mucormycosis --> often seen w/ hematologic malignancy or diabetes
-pneumocystis jiroveci
-candida
-aspergillus
-cryptococcus neoformans
-zygomycetes
which opportunistic fungal infection often causes pneumonia in patients with hematologic malignancy or diabetes?
mucormycosis
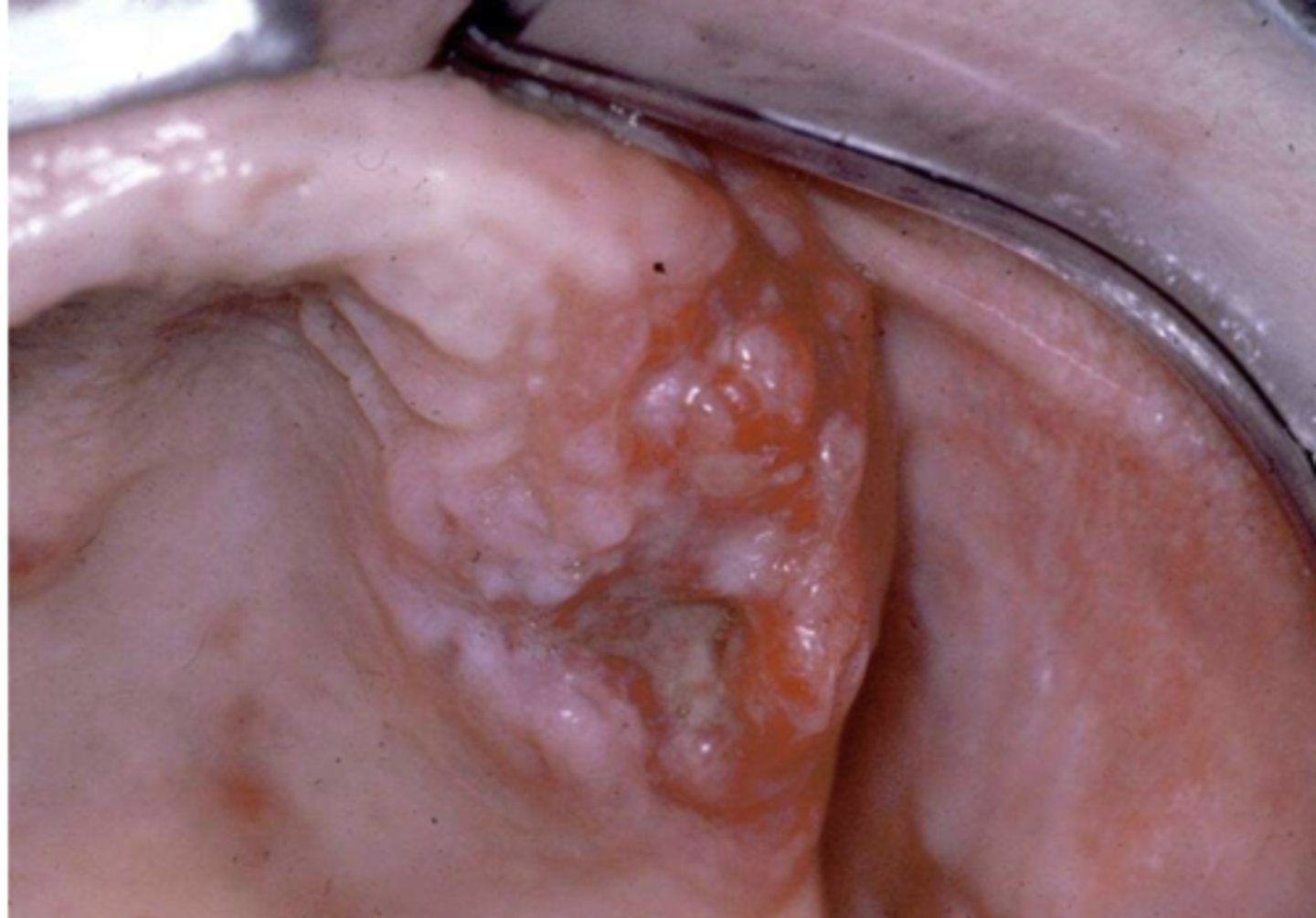
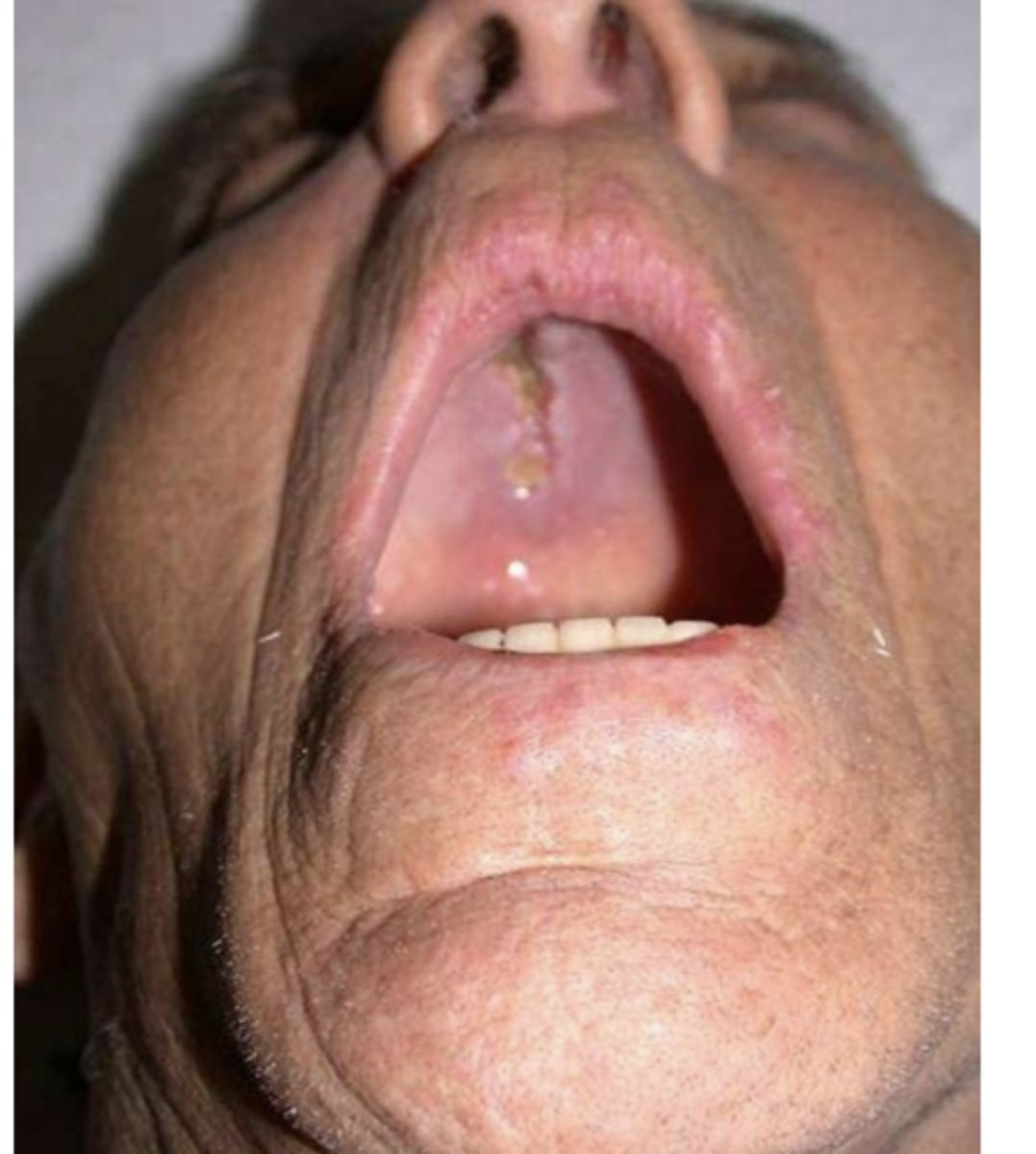
True or False: Fungal pneumonia in immunocompromised patients often presents with lesions on oral mucosa of hard palate
True
oral lesion due to fungal pneumonia
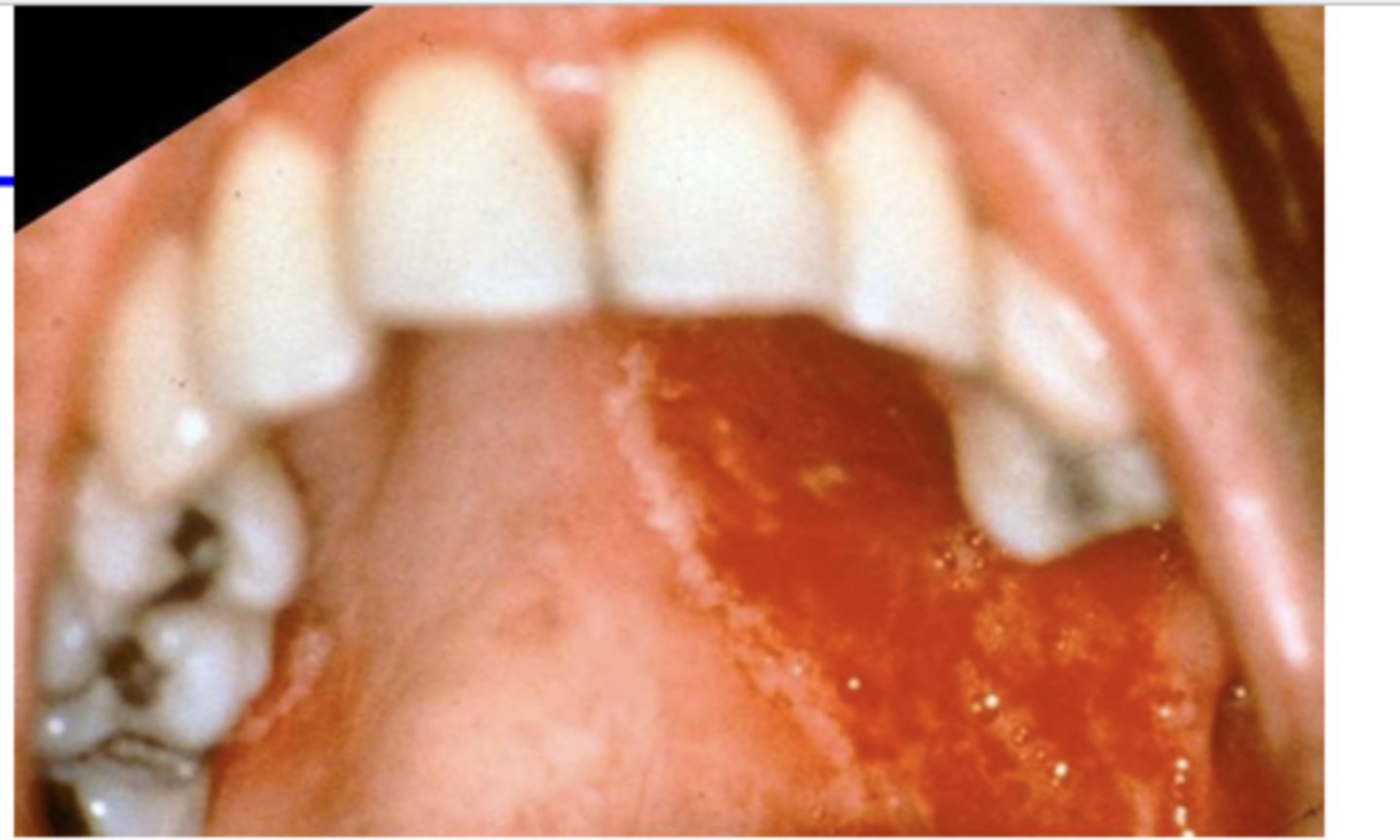
oral lesion due to fungal pneumonia (2)
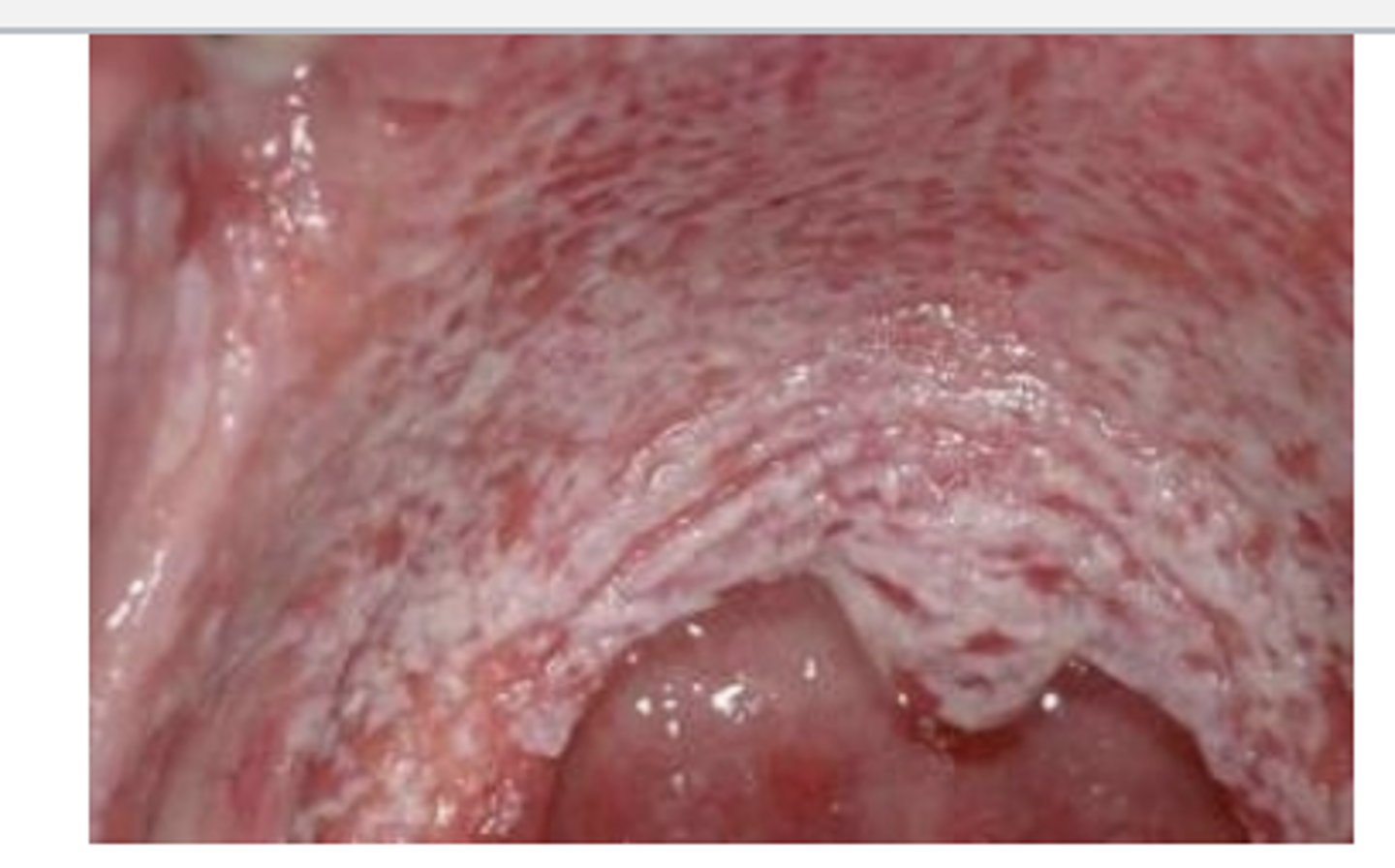
oral lesion due to fungal pneumonia (3)
what are 95% of the neoplastic diseases of the lungs?
bronchogenic carcinomas
what makes up 13% of all cancers in the USA?
neoplastic disease of the lungs
how many people were diagnosed with neoplastic disease of the lungs in the USA in 2019?
228,150
how many deaths are due to neoplastic disease of the lungs annually in the USA?
142,670
what is the 5 yr survival rate of neoplastic disease of the lungs?
16%
what percent of neoplastic disease of the lungs are benign tumors of other malignancies?
5%
What is associated with increased lung cancer incidence in developing countries?
increased smoking in developing countries
True or False: Smoking cessation for 10 years will reduce the risk for lung cancers back to control risk level
False ==> will reduce risk level but never back to control level (control = risk level for non-smoker)
What's the risk of a passive smoker developing lung cancer?
2x
what is associated with the following carcinomas in these areas?
-oral cavity
-pharynx
-larynx
-esophagus
-pancreas
-uterine cervix
-kidney & urinary bladder
smoking
When did the incidence of bronchogenic carcinoma begin to decline for men?
1980s
when did the incidence of bronchogenic carcinoma begin to decline for women?
mid-2000s
What is the incidence of bronchogenic carcinoma directly related to?
cigarette smoking & environmental factors
Which environmental factors are directly related to the incidence of bronchogenic carcinoma?
-radioactive material/natural radioactive material (ex: radon)
-asbestos
-nickel
-chromium
-iron oxides
-coal gas plants
what are the 4 main histopathologic types of bronchogenic carcinoma?
-adenocarcinoma (38%)
-squamous cell carcinoma (20%)
-small cell anaplastic carcinoma (14%)
-large cell anaplastic carcinoma (3%)
*also have mixed types (25%)
what is the main histopathologic type of bronchogenic carcinoma?
adenocarcinoma (38%)
what is the most common type of bronchogenic carcinoma in women?
adenocarcinoma
Does adenocarcinoma of the lungs have a predilection for men or men?
neither ==> equal gender incidence, but it's the most common type in women
True or False: Adenocarcinoma of the lungs is not as closely linked to cigarette smoking as the other types of bronchiogenic carcinoma
True
Where does adenocarcinoma of the lung usually develop?
peripherially
The following are all patterns of which bronchogenic carcinoma of the lungs?
-acinar
-papillary
-solid
-mucinous (formerly bronchoalveolar carcinoma)
adenocarcinoma
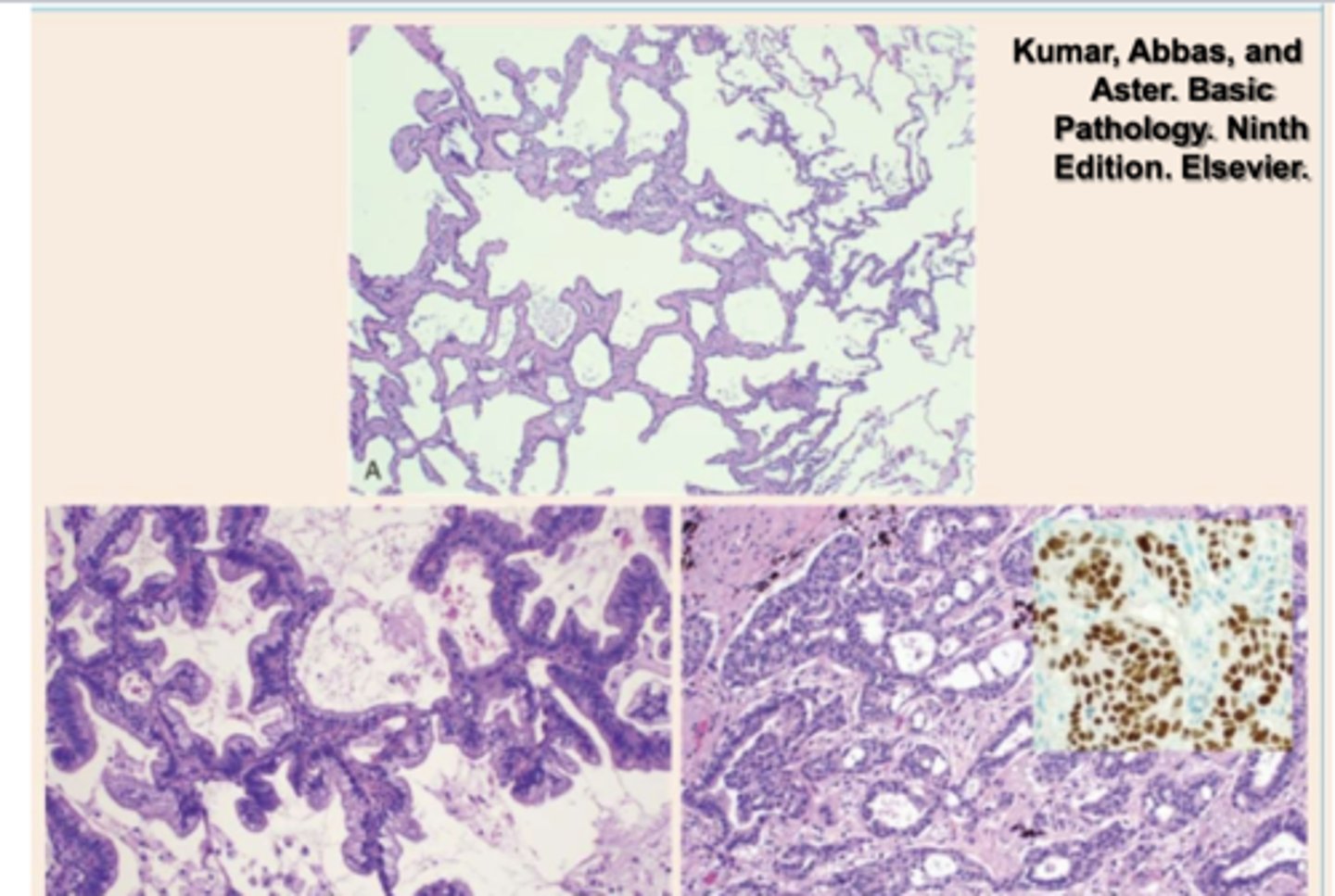
does squamous cell carcinoma of the lung have a male or female predilection?
male
True or False: squamous cell carcinoma of the lung is closely correlated with smoking history
True
where in the lung does squamous cell carcinoma arise?
arises centrally in major bronchi
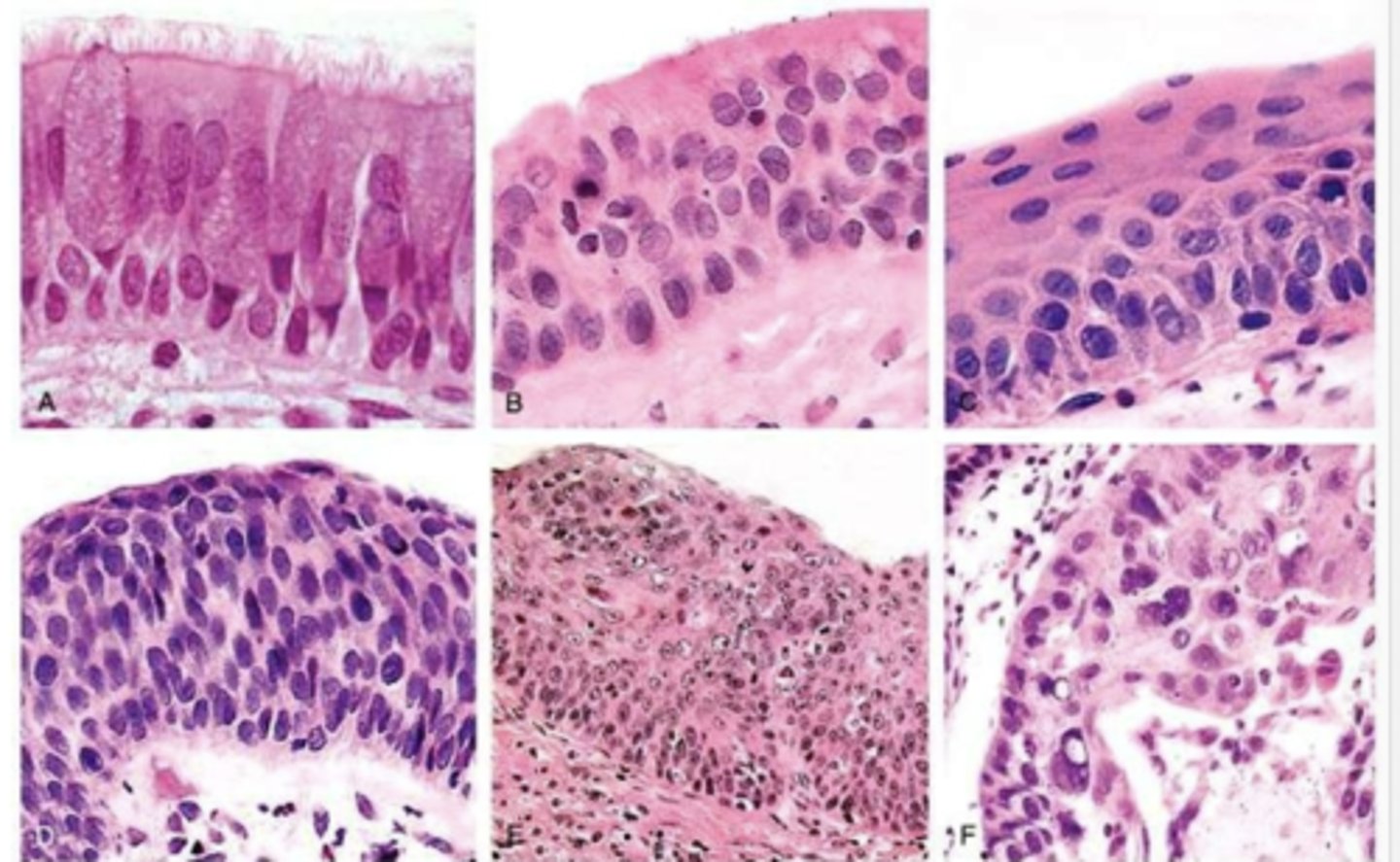
squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
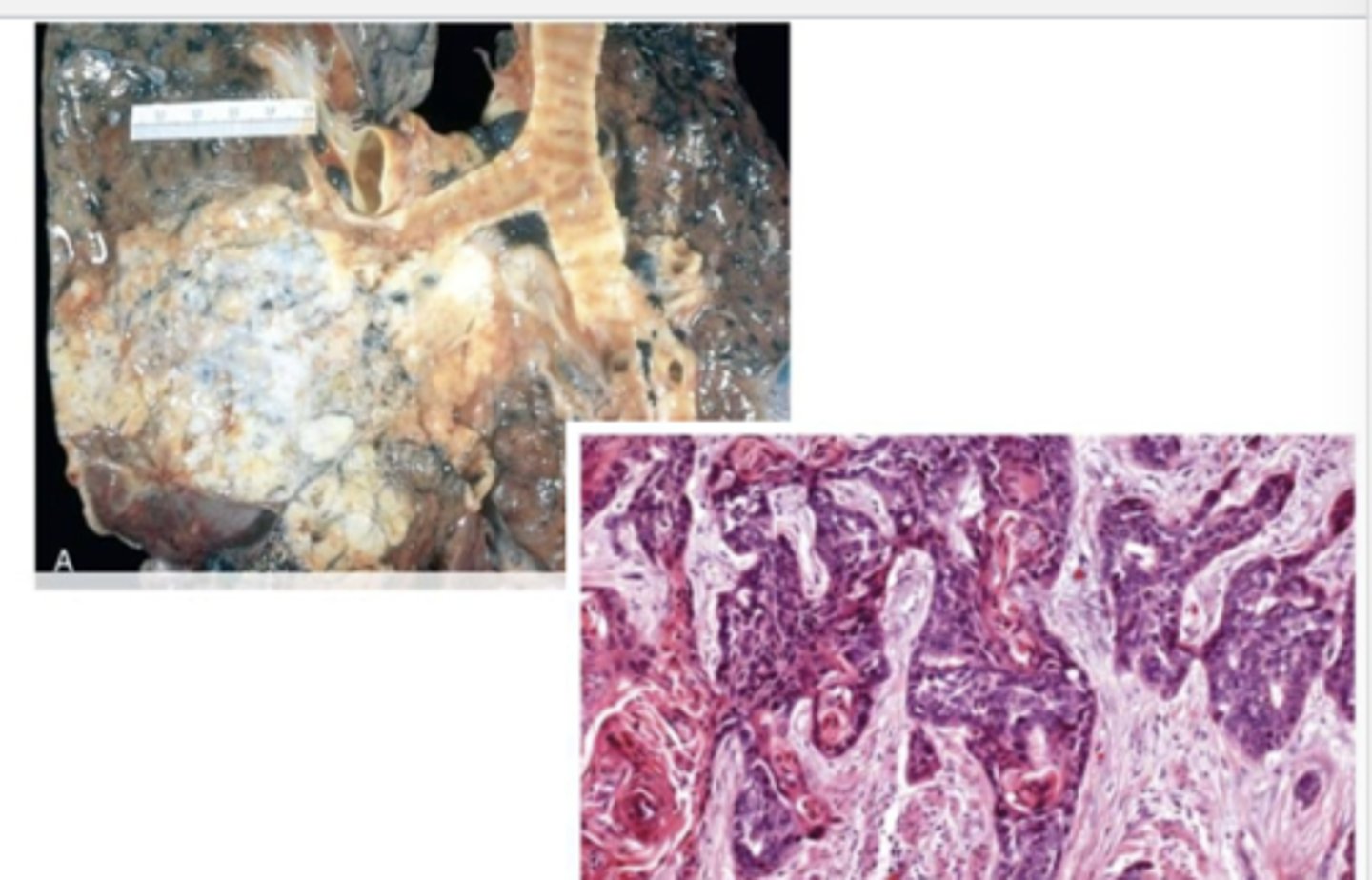
what is the most aggressive lung cancer?
small cell lung carcinoma
*metastasis usually present at diagnosis
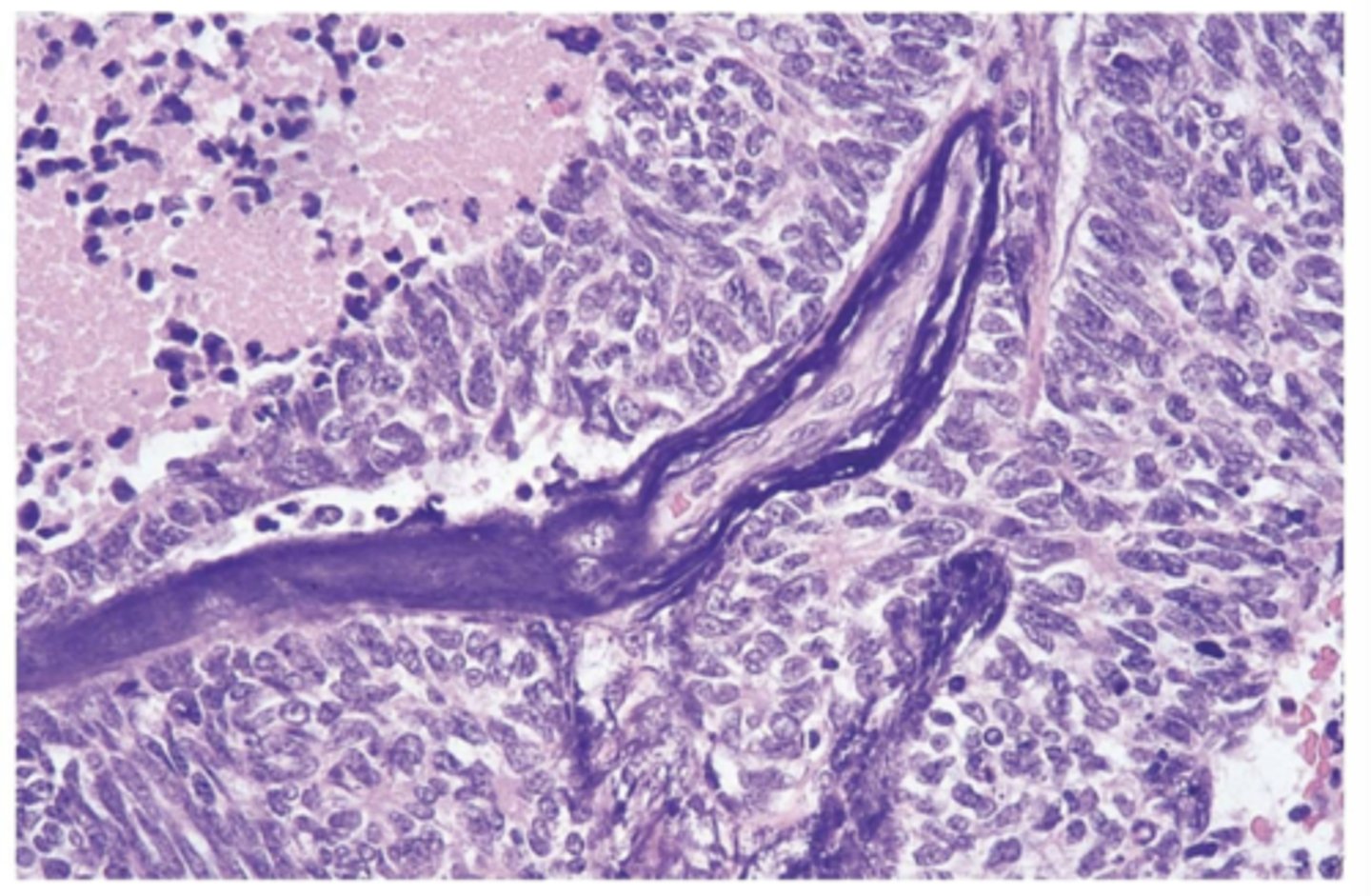
which lung cancer is most often associated with ectopic hormone production?
small cell lung carcinoma
where is small cell lung carcinoma located in the lung?
centrally located
what percent of small cell lung carcinoma arises in non-smokers?
1%
which bronchiogenic carcinoma has undifferentiated tumors that lack glandular, squamous, or endocrine features?
large cell carcinoma
where is large cell carcinoma of the lung typically located in the lung?
central or peripheral location
why does large cell carcinoma of the lung have a poor prognosis?
frequently widely disseminated at time of diagnosis
what are the local symptoms of neoplastic disease of the lungs?
-cough
-dyspnea
-chest pain
what are the systemic symptoms of neoplastic disease of the lungs?
-weight loss
-anorexia
-malaise
what is a presenting feature in 70% of lung cancer?
lung cancer metastasis
How are neoplasms of the lungs diagnosed?
-clinical features
-imaging
-histopathology
What types of histopathology are used in the diagnosis of neoplastic disease of the lungs?
-sputum cytology
-cytology of pleural effusion
-percutaneous needle aspiration
-bronchoscopy & biopsy
what are the paraneoplastic syndromes present in 3-10% of lung cancer patients?
-hypercalcemia --> esp w/ squamous cell carcinoma
-cushing syndrome
-inappropriate secretion of ADH
-neuromuscular syndrome
-clubbing fingers
-coagulopathy --> usually seen in adenocarcinoma
what paraneoplastic syndrome is typically seen in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung?
hypercalcemia
What paraneoplastic syndrome is typically seen in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung?
coagulopathy
paraneoplastic syndromes are usually seen in what percent of lung cancer patients?
3- 10%
paraneoplastic syndromes are most commonly seen in patients with which type of lung cancer?
small cell carcinomas
what is the 5 year survival rate of patients with lung cancer?
16%
what is the 5 year survival rate of patients with lung cancer that's a localized disease?
45%
What are KRAS mutations in patients with lung cancer associated with?
worsened prognosis
*noted in 30% of patients
True or False: Non-small cell carcinoma of the lung has a slightly better prognosis than small cell carcinoma of the lung
True
What is a common benign neoplasm of the lung?
lung hamartomas
What's the usual diameter of lung hamartomas?
greater than 3-4cm in diameter
What are lung hamartomas mostly made out of?
cartilage w/ fat & muscle
How are lung hamartomas usually discovered?
discovered as incidental findings on chest radiograph as rounded radio-opacities = coin lesions
what is the most common cause of pleural effusions?
congestive heart failure
what are the different pleural fluid types?
-transudate
-exudate
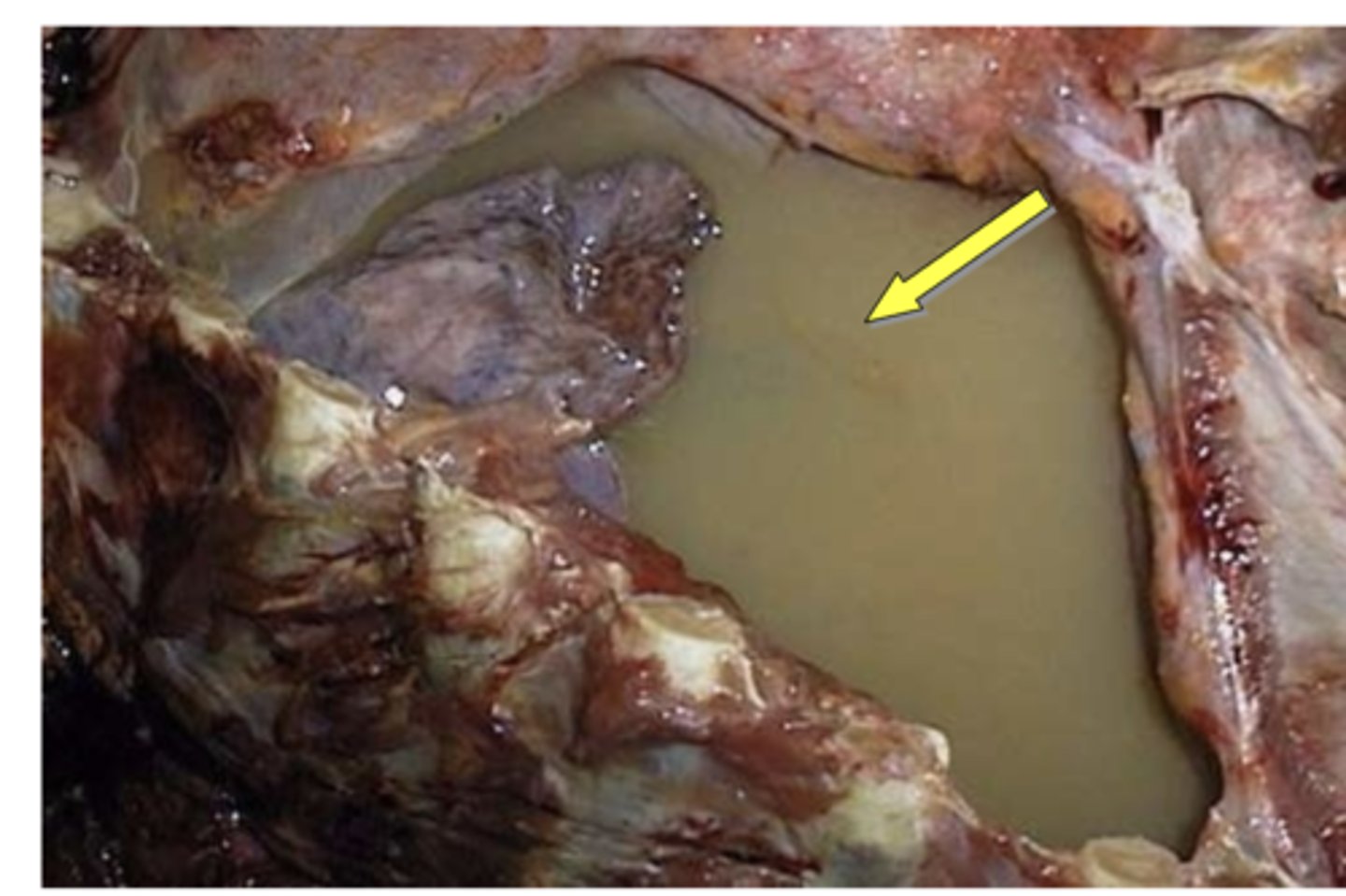
what typically causes transduate pleural effusion?
congestive heart failure
what typically causes exudate pleural effusion?
-infection
-cancer
-pulmonary infarction
what are the most common neoplasms of the pleura?
metastatic tumors, esp from the lung & breast
what is metastasis to the pleura usually associated with?
pleural effusion
what is the most common primary neoplasm of the pleura?
mesothelioma
*rare but strongly associated w/ asbestos exposure--> long latent period up to 40 yrs