Microeconomics: Definitions and Diagrams (copy)
1/75
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
law of demand
A law stating that as the price of a good falls, the quantity demanded will increase over a certain period of time, ceteris paribus.
market demand
The sum of the individual demand curves for a product of all the consumers in a market.
law of diminishing marginal utility
The idea that as an individual consumes additional units of a good, the additional satisfaction enjoyed decreases.
law of supply
A law stating that as the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied will rise over a certain period of time, ceteris paribus.
market supply
The sum of the individual supply curves for a product of all the producers in a market.
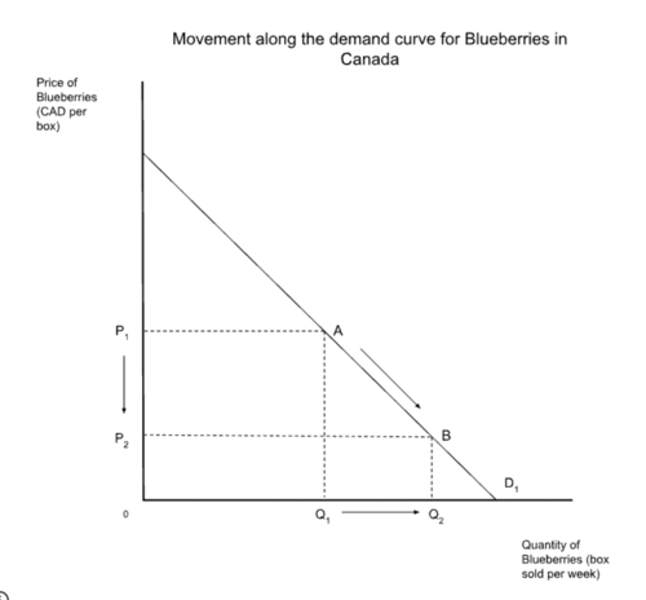
change in quantity demanded
Downward movement along the demand curve
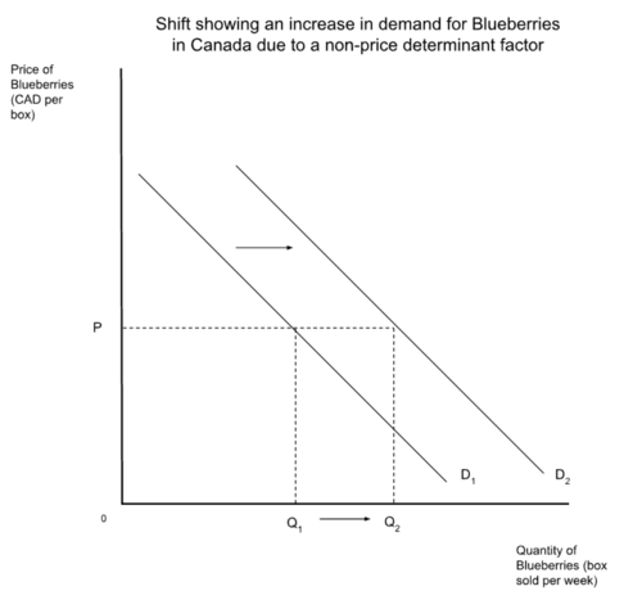
change in demand
Rightward shift in demand
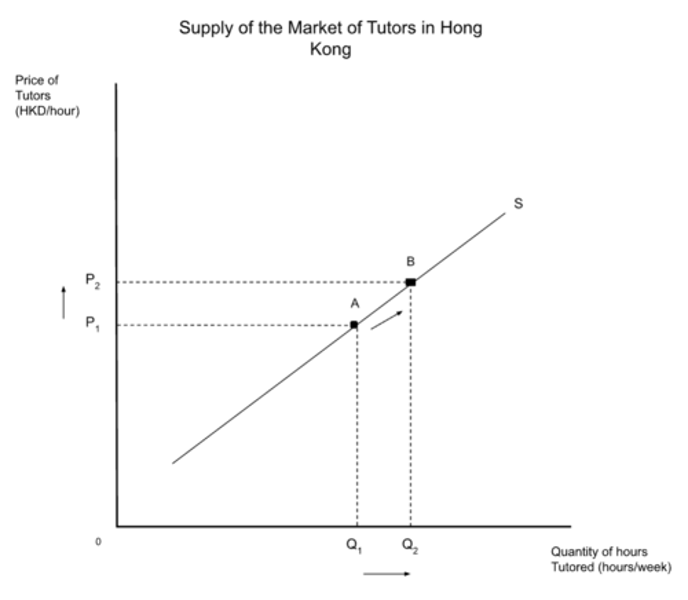
change in quantity supplied
Upward movement along the supply curve
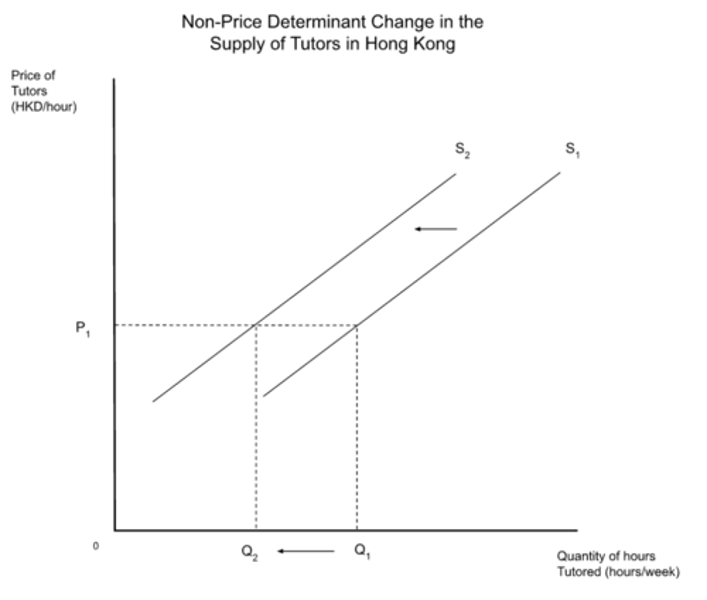
change in supply
Leftward shift in supply
surplus
An excess of something over something else. It occurs when quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded at a particular price
shortage
Arises when the quantity demanded of a good or services is more than the quantity supplied at some particular price.
market equilibrium
In a market this occurs at the price where the quantity of a product demanded is equal to the quantity supplied. This is the market clearing price since there is no excess demand or excess supply.
price mechanism
The system where the forces of demand and supply determine the prices of products. Also known as the market mechanism.
signal (price as signal)
The ability of prices, and changes in prices, to communicate information to consumers and producers about the existence of excess demand or excess supply, on the basis of which they make economic decisions, which together with prices as incentives lead to an efficient allocation of resources (assuming no market failures)
incentives (price as incentives)
Prices provide producers and consumers the incentive to respond to price changes. Given a price change, producers have the incentive to change the quantity supplied in accordance with the law of supply, while consumers have the incentive to change the quantity demanded based on the law of demand.
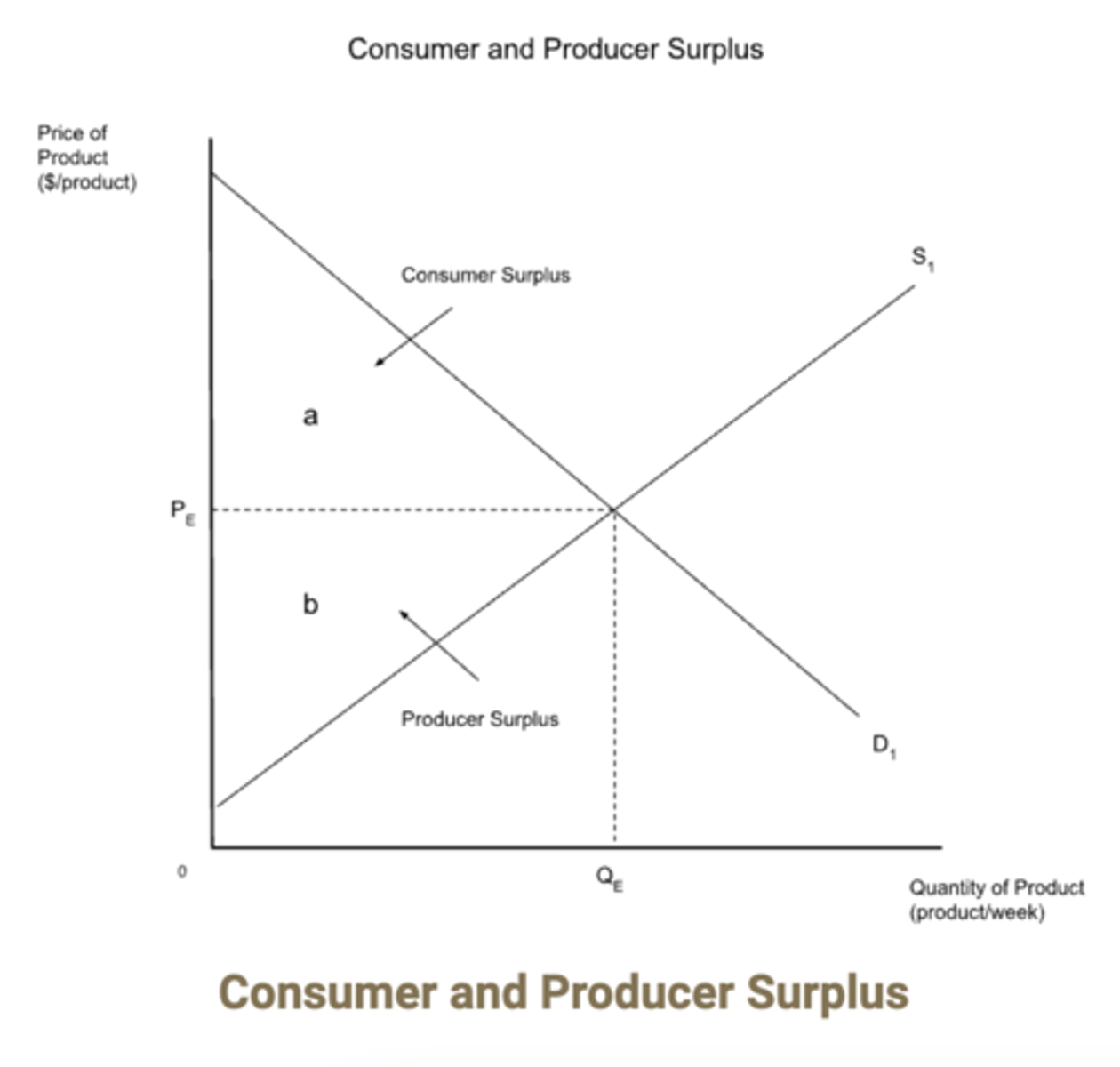
consumer surplus
The difference between how much a consumer is at most willing to pay for a good and how much they actually pay.
producer surplus
The benefit enjoyed by producers by receiving a price that is higher than the price they were willing to receive.
marginal benefit
The extra or additional benefit enjoyed by consumers that arises from consuming one more unit of output.
marginal cost
The extra or additional costs of producing one more unit of output.
rational consumer choice
Occurs when consumers make choices based on the following assumptions: they have consistent tastes and preferences, they have perfect information and they arrange their purchases so as to make their utility as great as possible (maximize it). It is assumed in standard microeconomic theory.
behavioural economics
A subdiscipline of economics that relies on elements of cognitive psychology to better understand decision-making by economic agents. It challenges the assumption that economic agents (consumers or firms) will always make rational choices with the aim of maximizing with respect to some objective.
nudge theory
Nudges (prompts, hints) are used to influence the choices made by consumers in order to improve the well-being of people and society.
choice architecture
The design of environments based on the idea that the layout, sequencing, and range of choices available affect the decisions made by consumers.
profit maximisation
A possible objective of firms that involves producing the level of output where profits are greatest: where total revenue minus total cost is greatest or where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
rationing
a method used to divide or appropriate goods and services or resources among the various interested parties
includes: price rationing
price elasticity of demand (PED)
A measure of the responsiveness of the percentage quantity demanded of a good or service to a percentage change in its price.
income elasticity of demand
The responsiveness of the percentage of quantity demanded for a good or service to a percentage change in income.
price elasticity of supply
A measure of the responsiveness of the percentage quantity supplied of a good or service to a percentage change in its price.
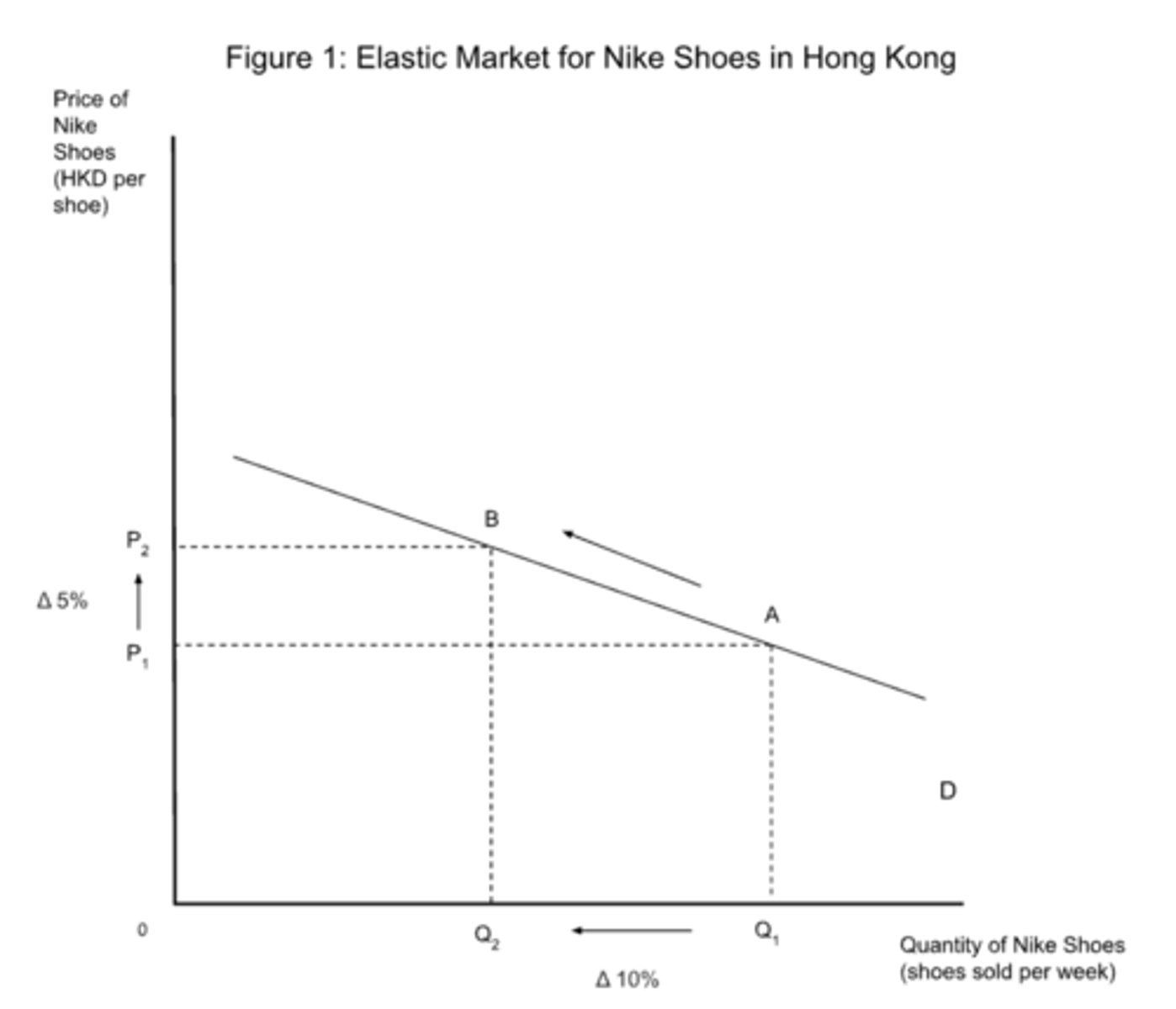
elastic PED
- PED > 1
- percentage change in quantity is greater than the percentage change in price
- luxury goods
- in the long-run, PED of goods can become more inelastic
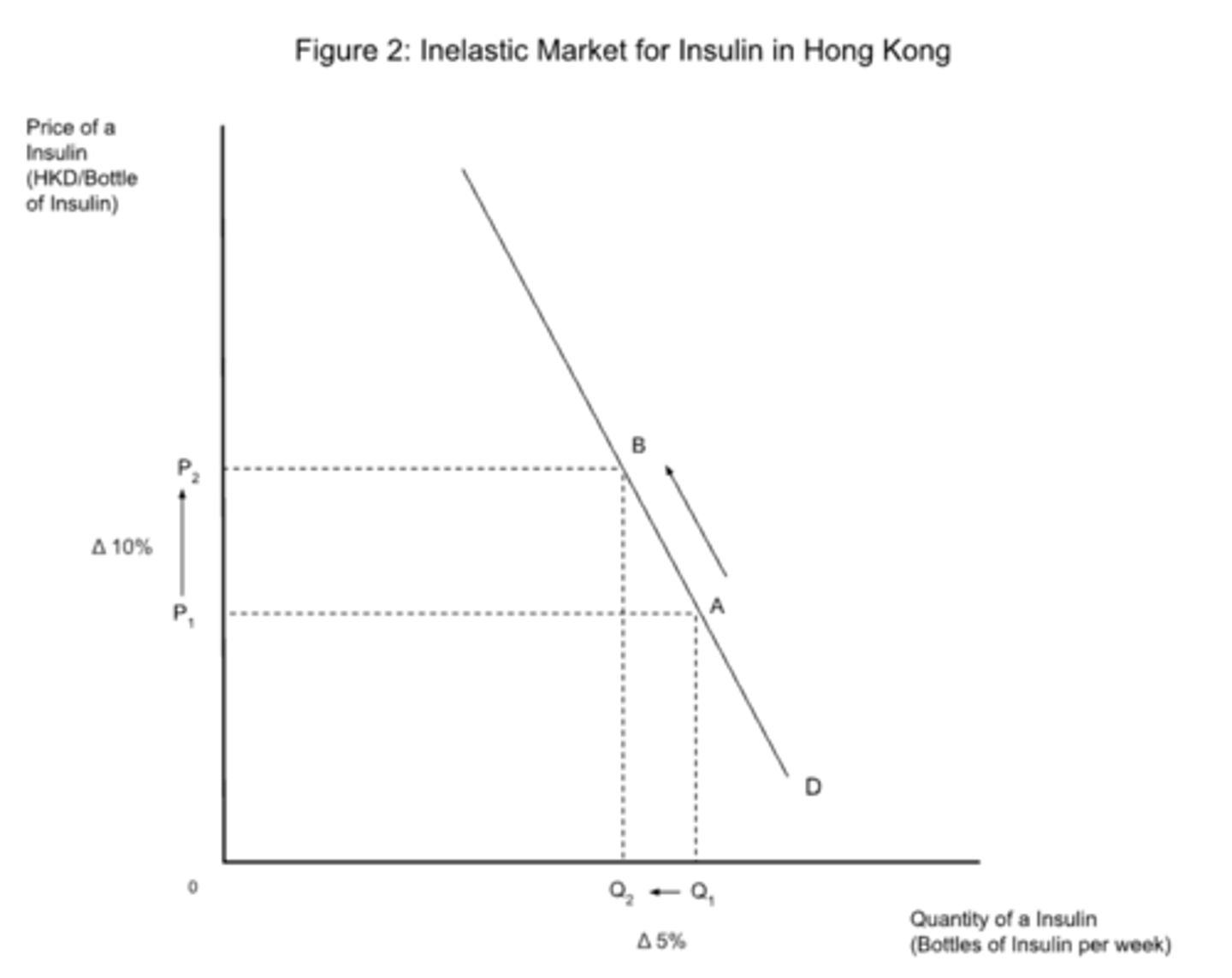
inelastic PED
- PED < 1
- the percentage change in quantity is less than the percentage change in price
- necessary goods are inelastic
- in the short-run, PED of goods are inelastic
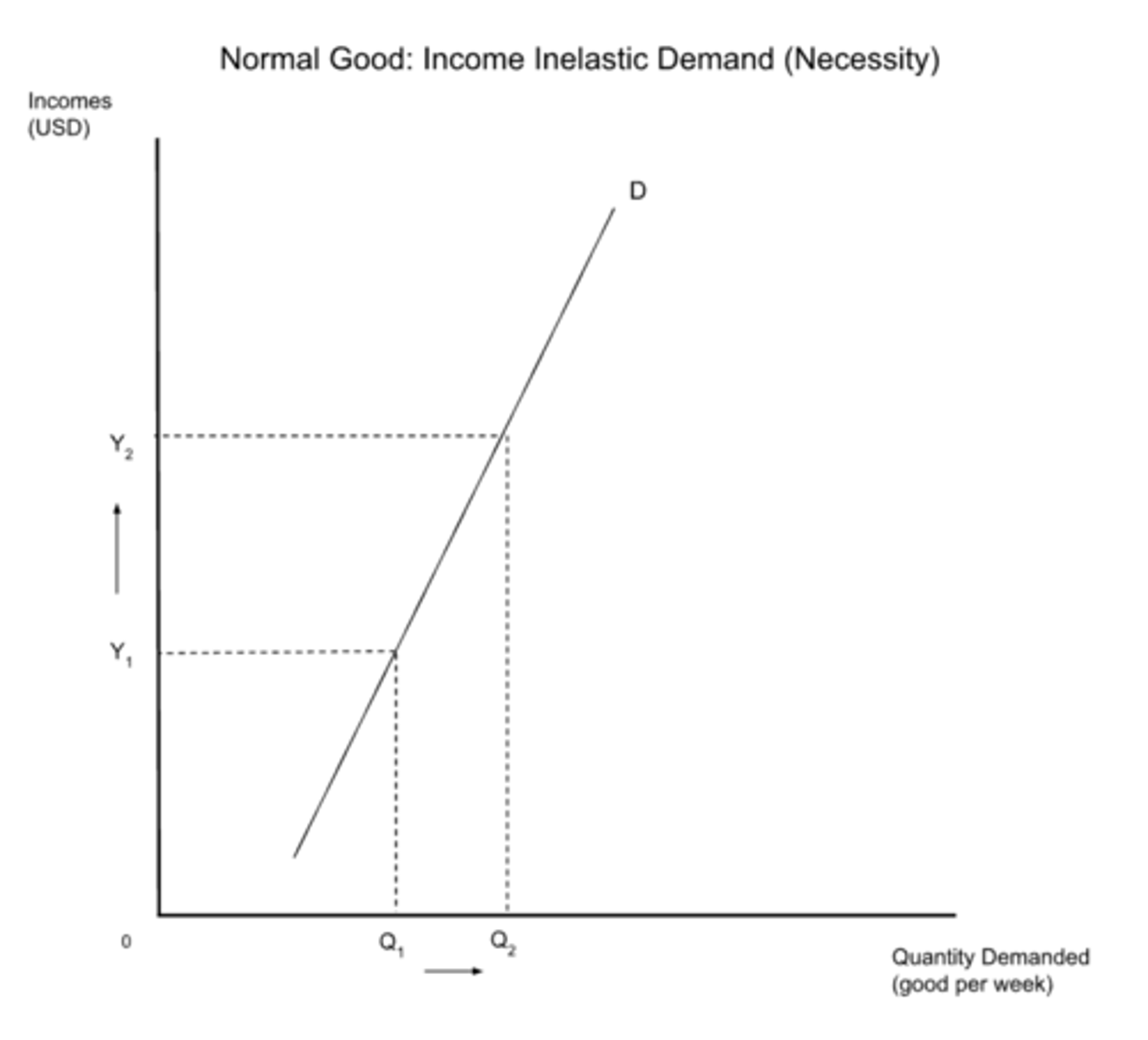
inelastic YED
0 < YED < 1
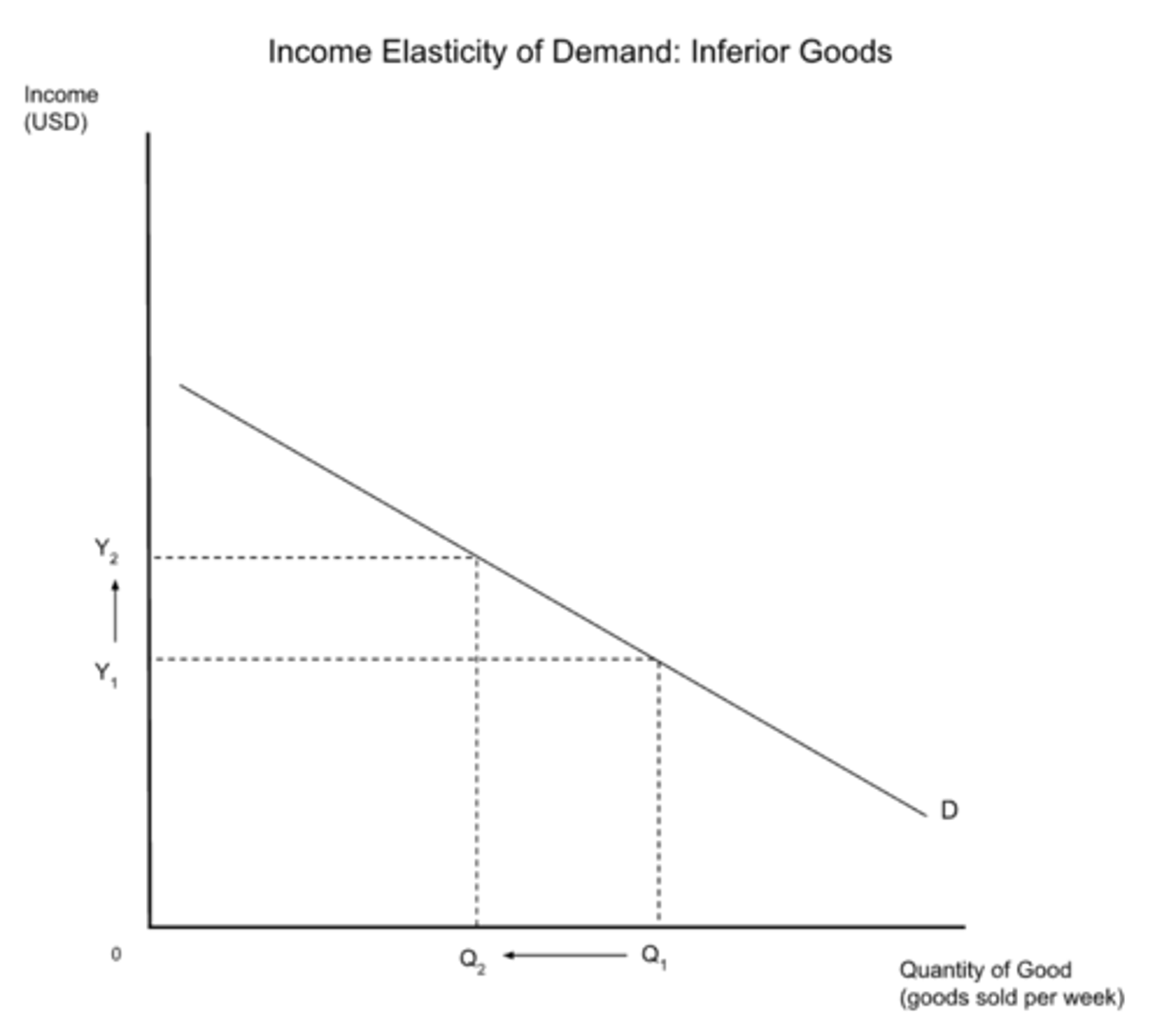
negative elasticity of YED
YED < 0
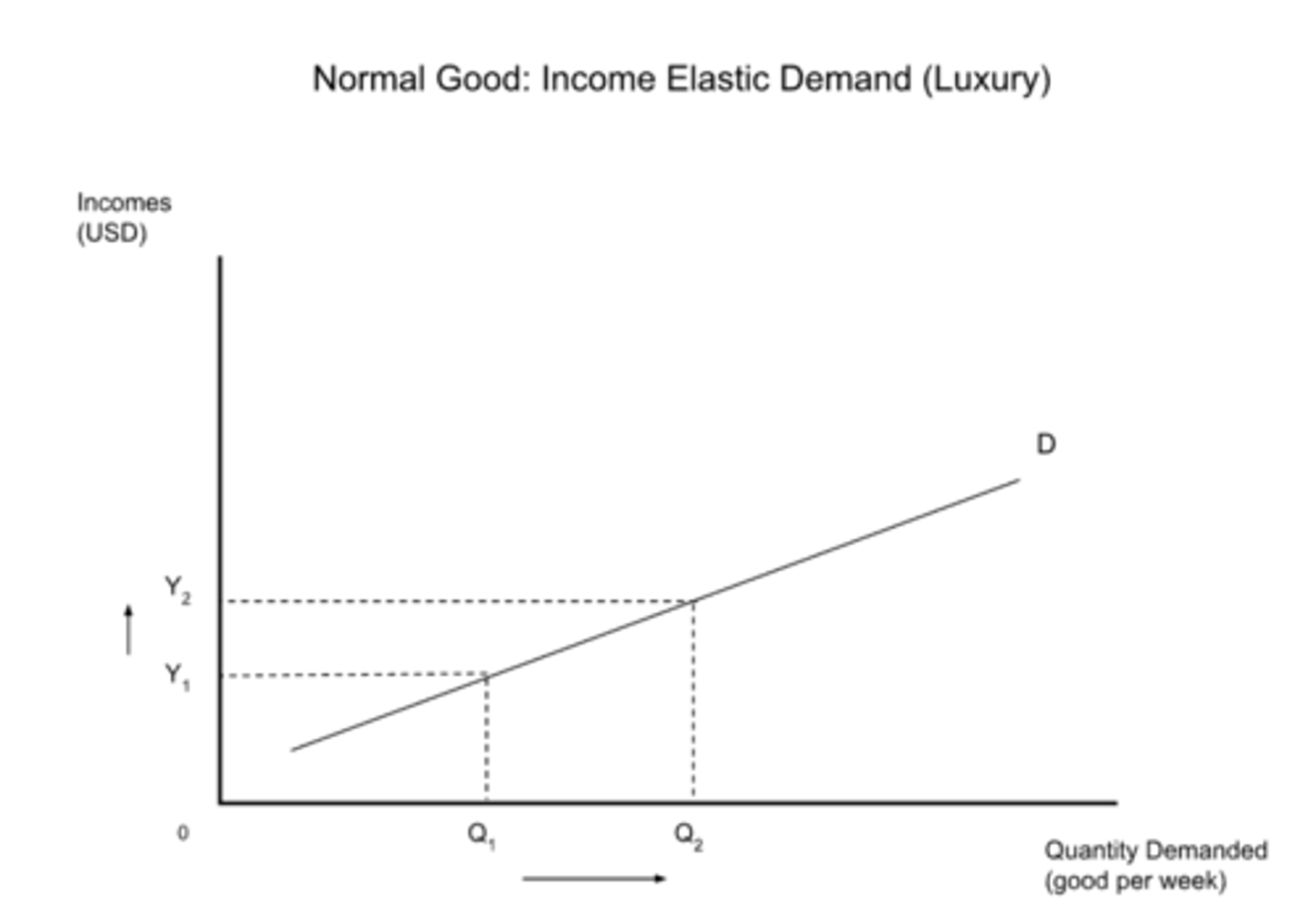
elastic YED
YED > 1
determinants of PED (SPLAT)
1. Number and Closeness of Substitutes
2. Proportion (income spend on a good)
3. Luxury or Necessity:
4. Addictive goods
5. Time
Determinants of PES (TUMAR)
"these are the reasons why (insert good) are inelastic"
1) Time (length)
2) Unused Capacity (Spare)
3) Mobility (Flexibility) and Cost of f.o.p
4) Ability to Store Stock (Inventory)
5) Rate at Which Costs Increase
welfare loss
Loss of total welfare or the social surplus (consumer plus producer surplus) due to reasons like taxes or subsidies, price ceilings or floors, externalities and monopoly pricing.
indirect tax
Taxes on expenditure to buy goods and services.
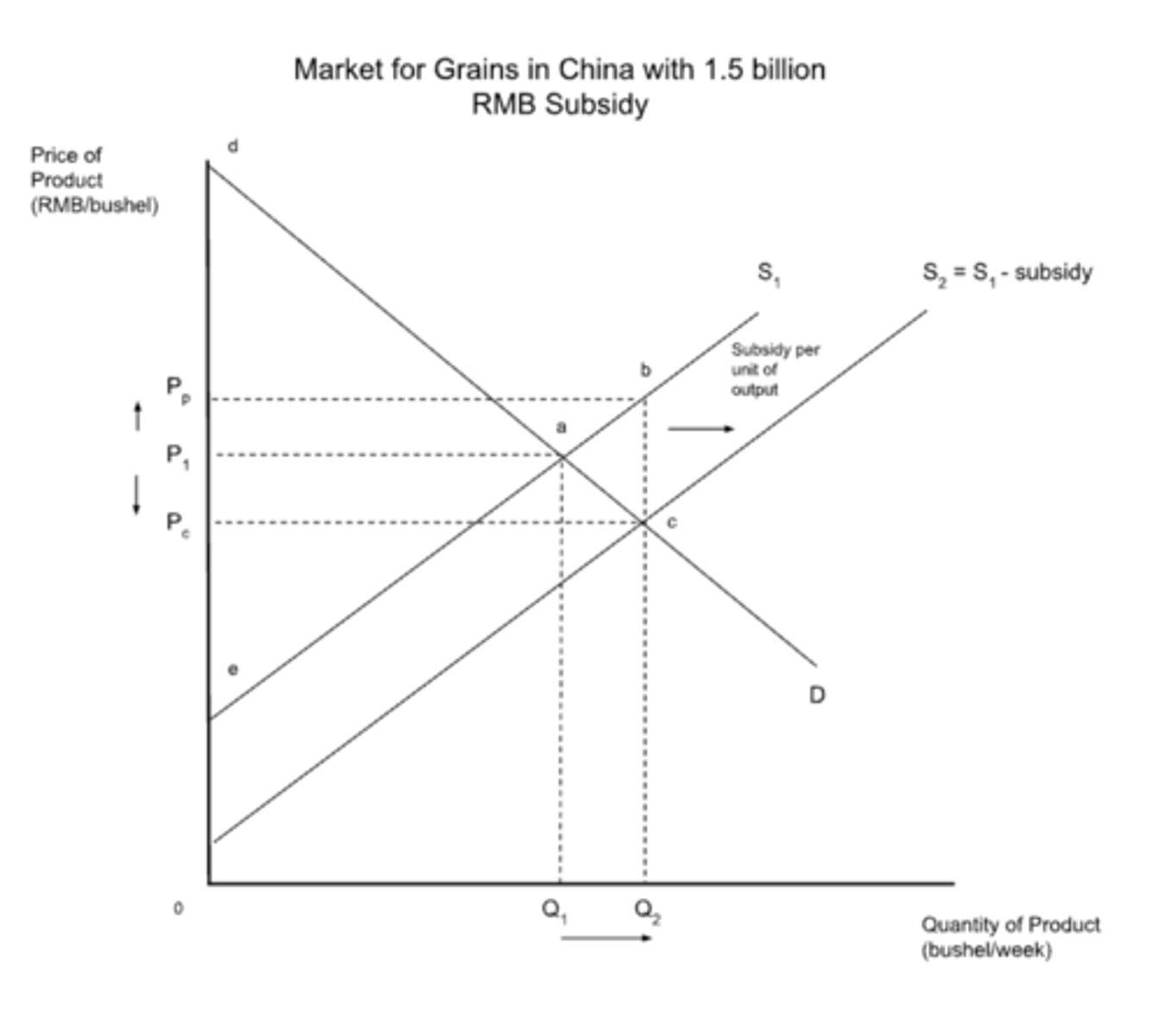
subsidies
An amount of money paid by the government to a firm, per unit of output, to encourage production and lower the price to consumers.
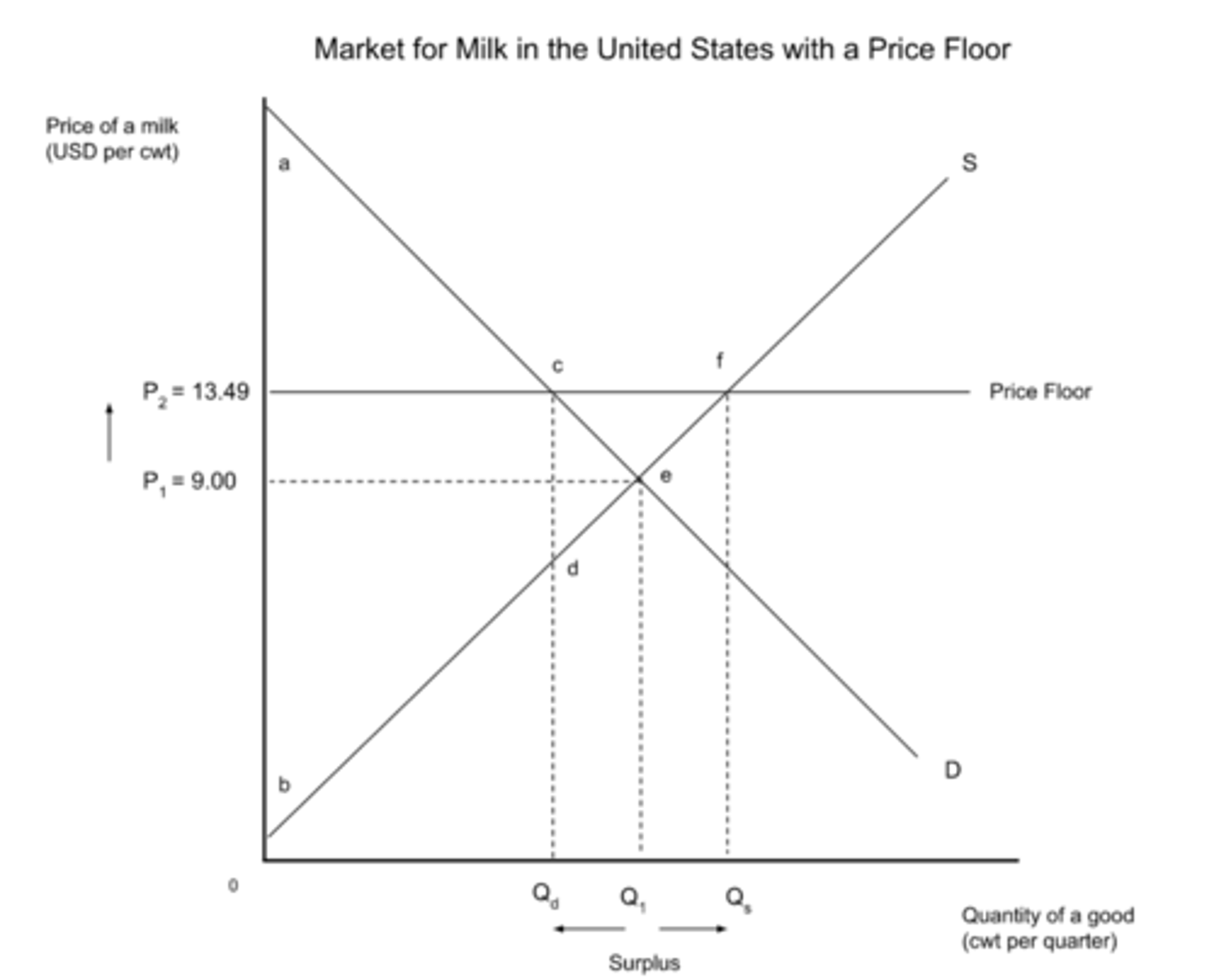
price floor
A price imposed by an authority and set above the market price. Prices cannot fall below this price.
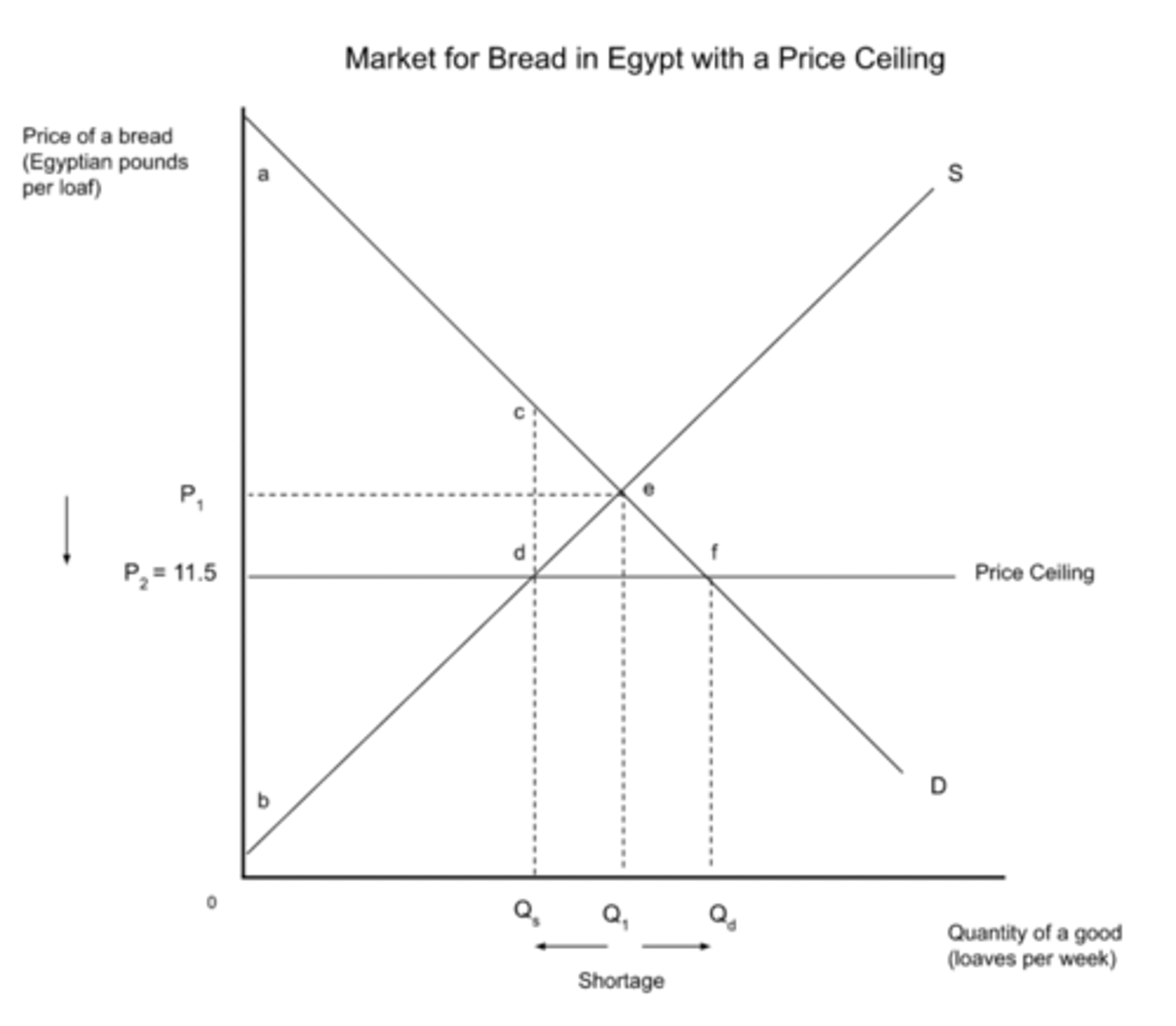
price ceiling
A price imposed by an authority and set below the equilibrium price. Prices cannot rise above this price.
subsidy (diagram)
price ceiling (diagram)
reasons for government intervention
1. earn government revenue
2. support firms
3. support households on low incomes
4. influence level of production
5. influence the level of consumption
6. correct market failure
7. promote equity
price floor (diagram)
externalities
External costs or benefits to third parties when a good or service is produced or consumed. An externality arises when an economic activity imposes costs or creates benefits on third parties for which they are not compensated or do not pay for respectively.
third parties
An individual or group that is involved in a transaction that is primarily between two other entities. In the case of externalities the third party is not part of the transaction between the two primary parties but is either positively or negatively effected by the transaction.
spillover
Is the costs associated with a transaction borne upon a party/parties that are non participants in the transaction (third parties).
common pool/access resources
A diverse group of natural resources that are non-excludable, but their use is rivalrous, for example, fisheries.
non-excludable
A characteristic of a good, service or resource where it is impossible to prevent a person, or persons, from using it.
rivalrous
Goods and services are considered to be rivalrous when the consumption by one person, or group of people, reduces the amount available for others.
Non-rivalrous
A characteristic of some goods such that their
consumption by one individual does not reduce
the ability of others to consume them. It is a
characteristic of public goods.
merit goods
Goods or services considered to be beneficial for people that are under-provided by the market and so under-consumed, mainly due to positive consumption externalities.
demerit goods
Goods or services that not only harm the individuals who consume these but also society at large, and that tend to be overconsumed. Usually they are due to negative consumption externalities.
negative externalities of consumption (NEC)
Negative effects suffered by a third party whose interests are not considered when a good or service is consumed, so the third party are therefore not compensated.
negative externalities of production (NEP)
Negative effects suffered by a third party whose interests are not considered when a good or service is produced, so the third party are therefore not compensated.
positive externalities of consumption (PEC)
The beneficial effects that are enjoyed by third parties whose interests are not accounted for when a good or service is consumed, therefore they do not pay for the benefits they receive.
PEP
The beneficial effects that are enjoyed by third parties whose interests are not accounted for when a good or service is produced, therefore they do not pay for the benefits they receive.
normal goods
A good where the demand for it increases as
income increases.
asymmetric information
A type of market failure where one party in an economic transaction has access to more or better information than the other party.
adverse selection
A type of market failure involving asymmetric information, where the party with the incomplete information is induced to withdraw from the market. The buyer, for example, in the used car market, may hesitate to buy without knowing about the quality of the vehicle. The seller, for example of health insurance, may hesitate to sell a policy without knowing the health of the buyer.
moral hazard
A type of market failure involving asymmetric information where a party takes risks but does not face their full costs by changing behaviour after a transaction has taken place. It is very common in insurance markets.
signalling
In asymmetric information, the participant with more information sending a signal revealing relevant information about a transaction to the participant with less information, to reduce adverse selection.
screening
In asymmetric information, the use of a screening process by the participant with less information to gain more information regarding a transaction, and so reduce adverse selection.
perfect competition
A market structure where there is a very large number of small firms, producing identical products, with no barriers to entry or exit, and perfect information. All the firms are thus price takers.
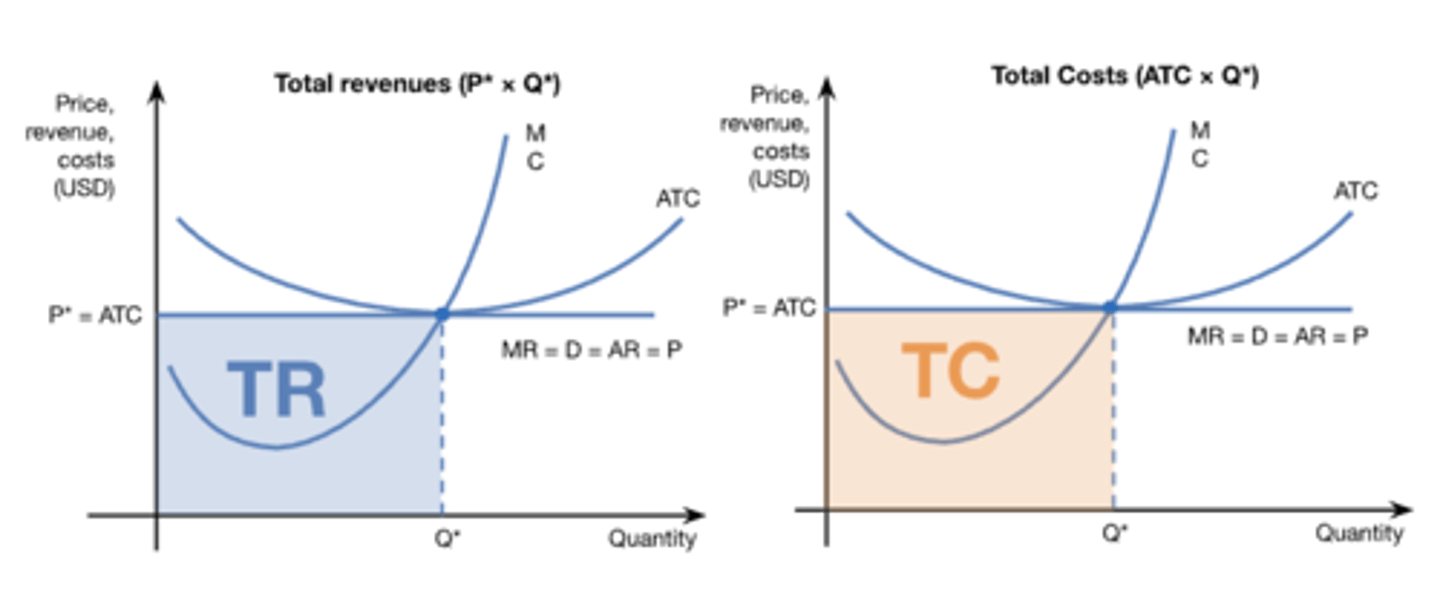
perfect competition normal profit (diagram)
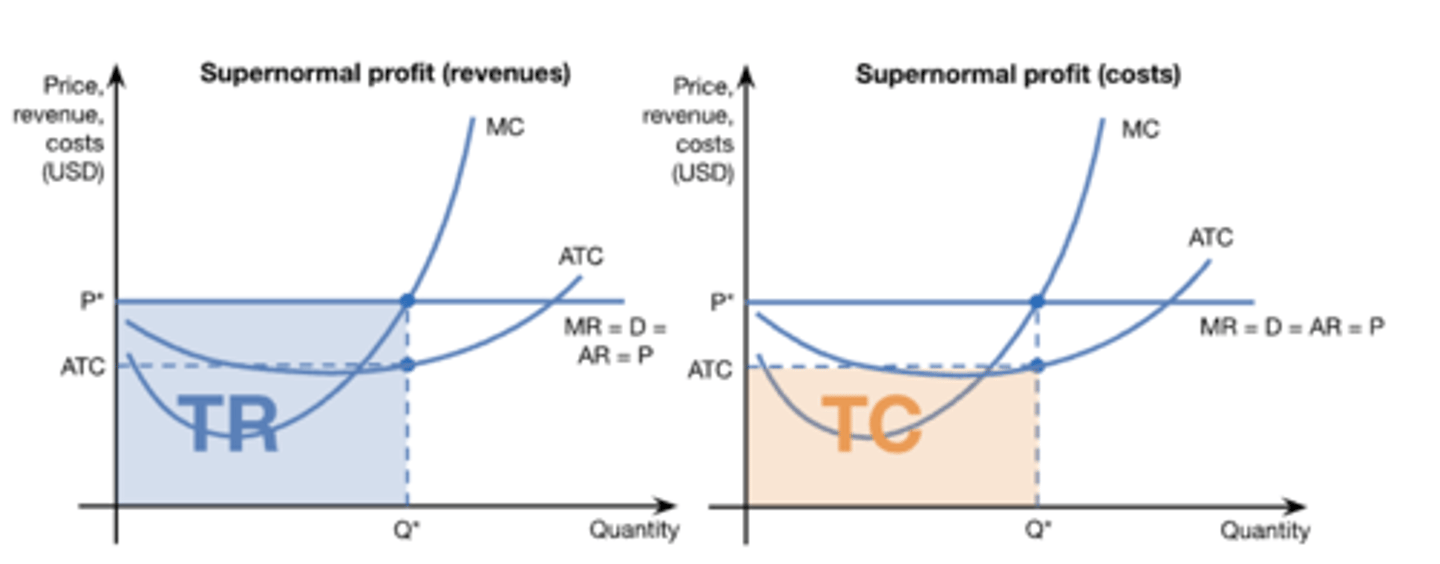
perfect competition short-run profit (diagram)
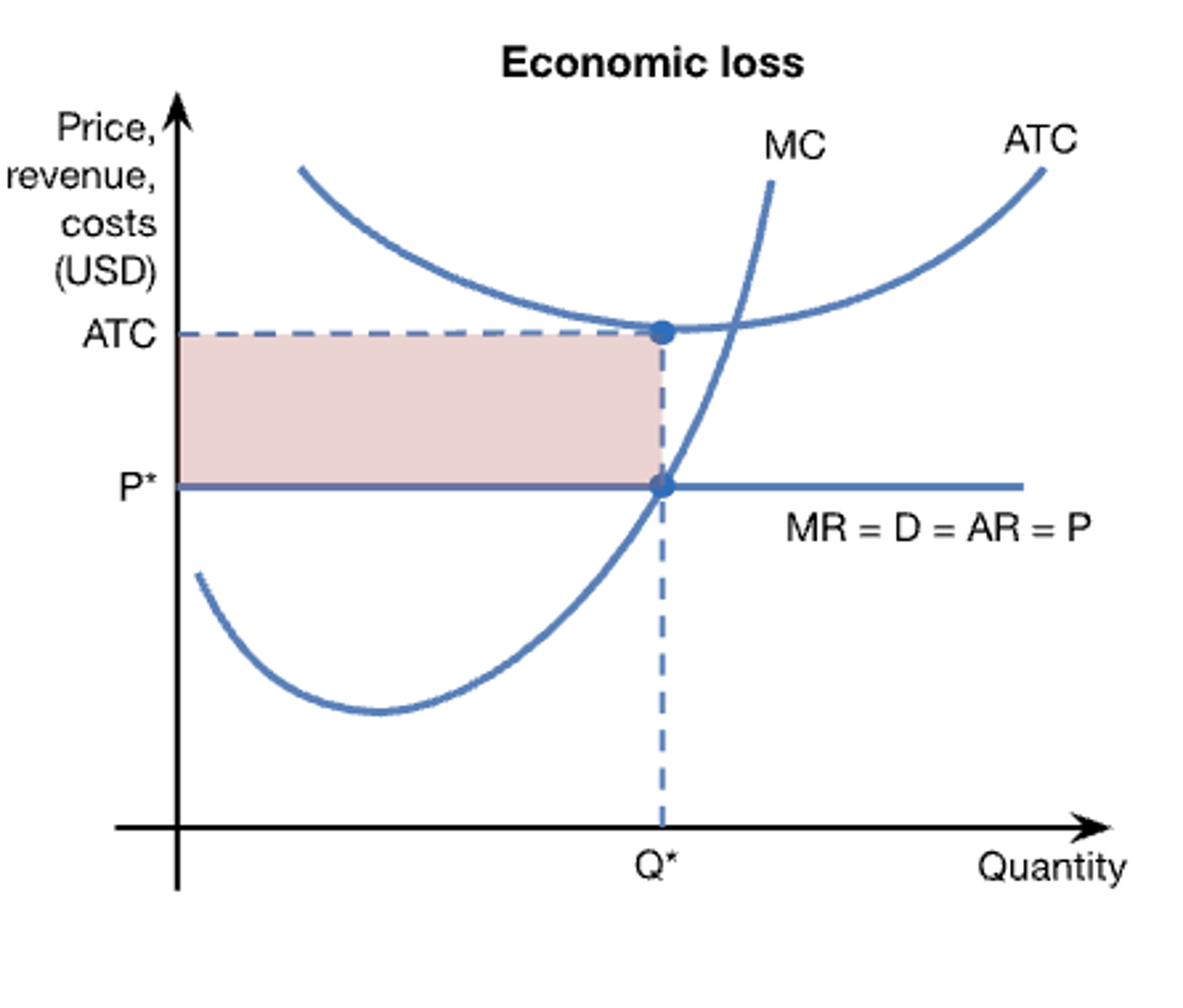
perfect competition short-run loss (diagram)
monopoly
A market structure where there is only one firm in the industry, so the firm is the industry. There are high barriers to entry.
monopoly normal profit (diagram)
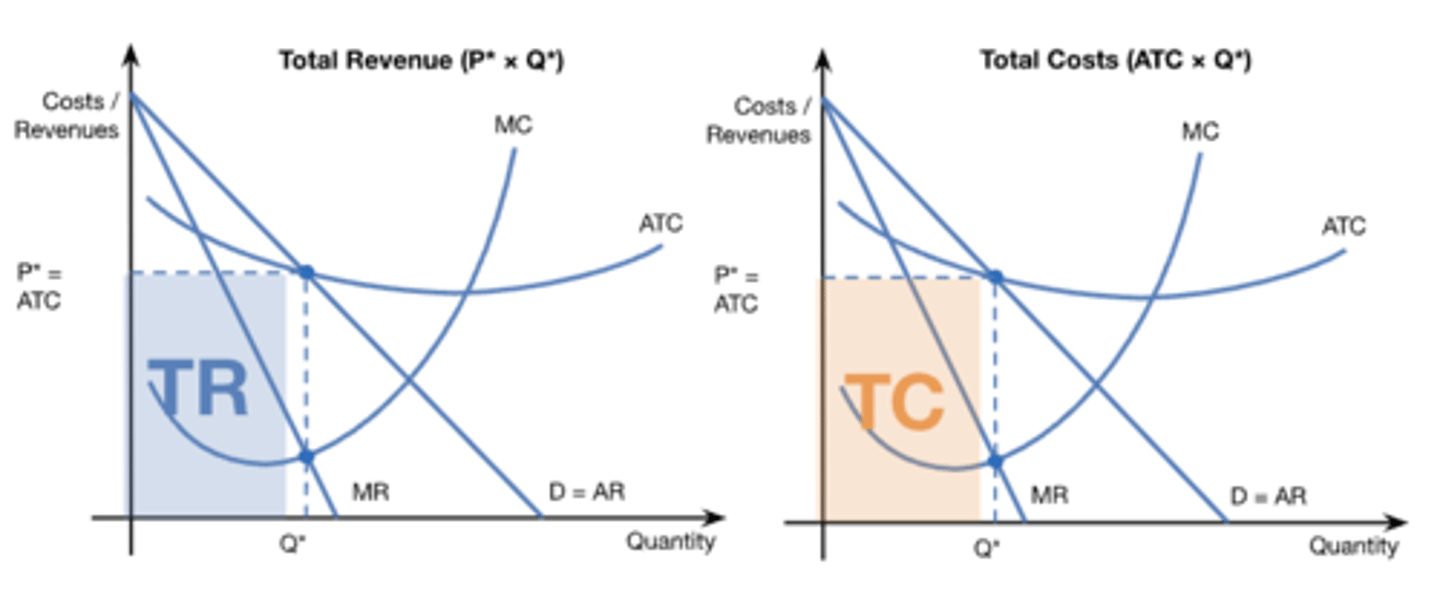
monopoly profit (diagram)
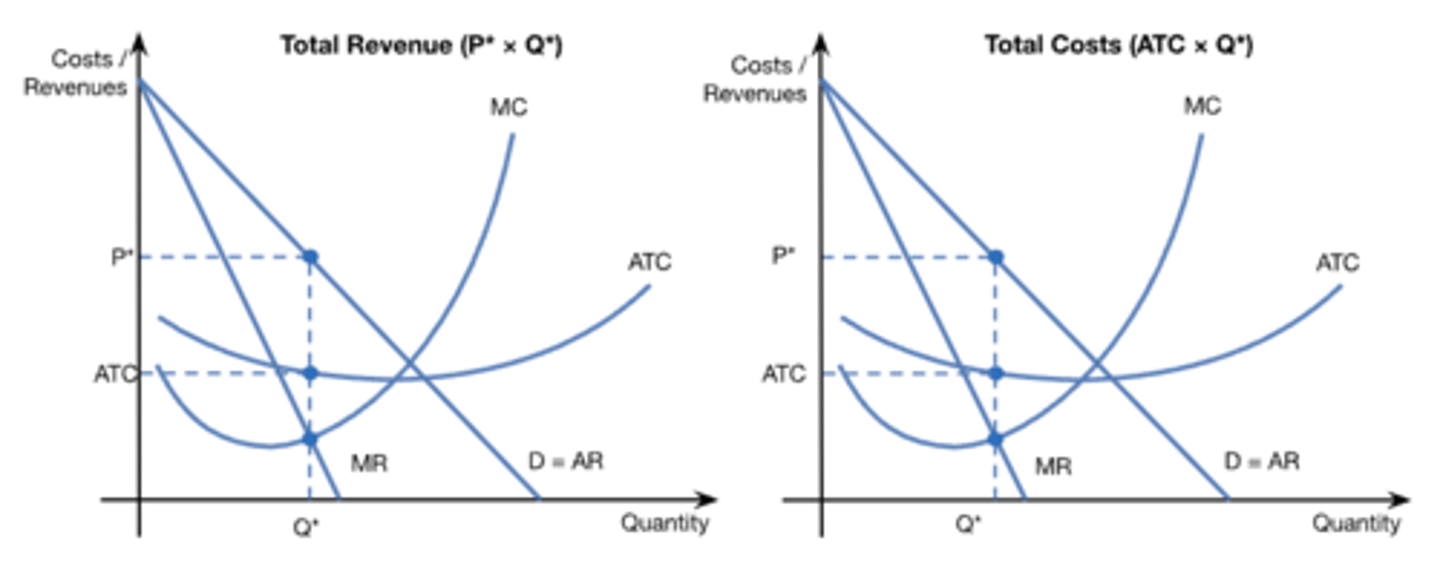
monopoly loss (diagram)
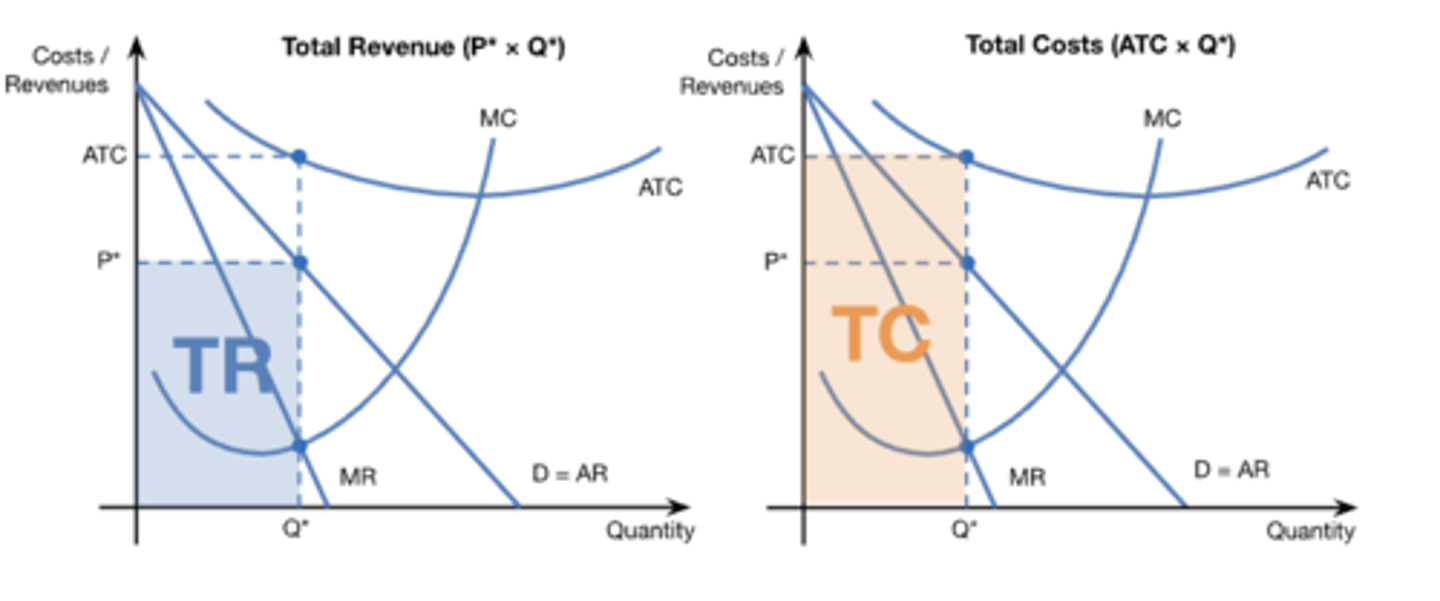
natural monopoly
** do diagrams
monopolistic competition
A market structure where there are many sellers, producing differentiated products, with no barriers to entry.
monopolistic competition normal profit (diagram)
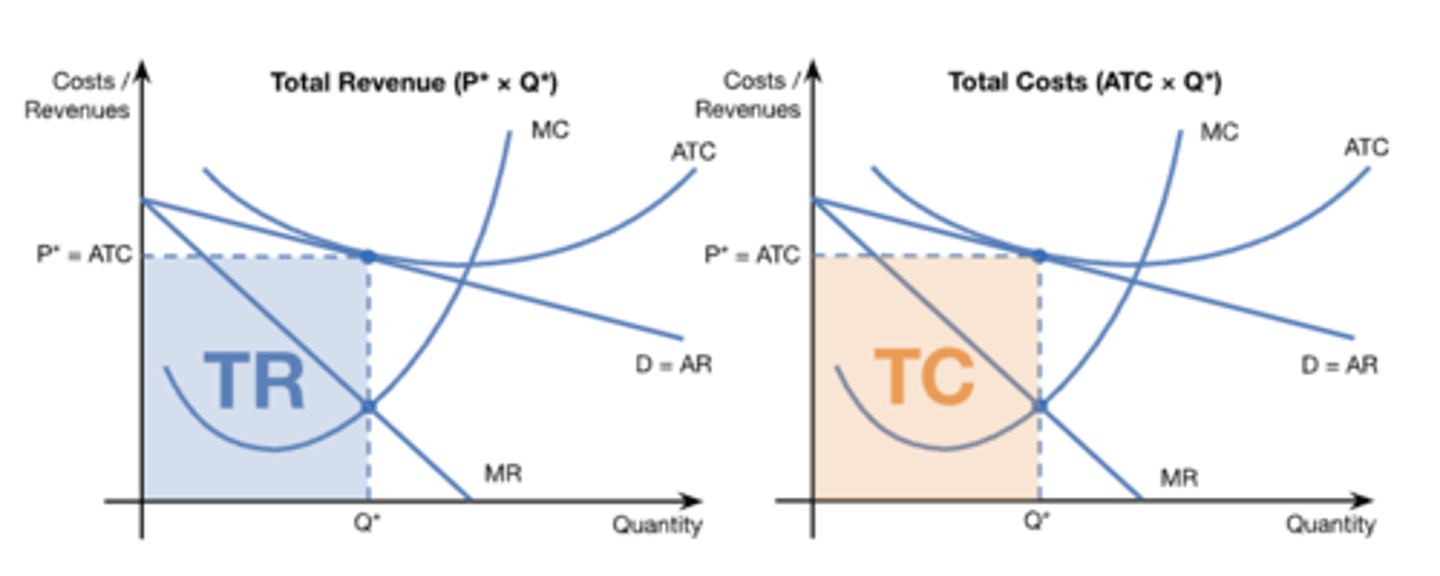
oligopoly
A market structure where there are a few large firms that dominate the market, with high barriers to entry
collusive oligopoly
A market where firms agree to fix price and/or to engage in other anticompetitive behaviour.