Modern Physics Lecture 2 - Atoms and their Structure
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Give a brief history of the atom:
Democritus 400BC - matter is composed of “atoms”
Dalton - 1800 - Matter is composed of limited number of types of atoms - called elements - which differ in mass. Evidence - mass ratios in chemical reactions
1869 - Periodic table of elements developed by Mendeleyev. No notion of internal atomic structure.
Thomson - “cathode rays” - a stream of electrons coming from the cathode in a vacuum tube. Cathode rays are deflected by an electric field. Consistent with negatively charged particles with a specific mass to charge ratio.
Atoms are neutral but can release negative elcectrons.
Rutherford “planetry model”
Describe the stability of matter for the planetry model
Orbiting electrond must be accelerating towards nucleus
Electromagnetic theory predicts that accelerating charges generate electromagnetic radiation
Electrons should therefore lose energy as they rdiate and will spiral into the nucleus
What is the formula to account for the spectrum of hydrogen (balmer series)?
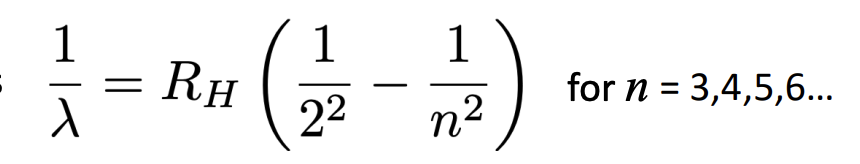
Why does the rutherford model fail to explain the Rydberg formula?
According to classical electromagnetism, orbiting electrons should absorb and emit radiation at all frequencies, spiralling in and out in their orbits as they do so.
Describe the Bohr atom for hydrogen
Single electron has a circular orbit. Orbits are quantised.
What did Davisson and germer see when they scattered an electron beam from a single crystal of nickel?
What they saw has teh same pattern as diffraction pattern from a grating. The distance between peaks was consistent with the supposed de Broglie wavelength of the electrons
What is needed for two-slit interference effects to be seen?
Slit separartion must be approximately the same size as the wavelength.
Define the angular momentum in terms of an equation
L = pr = mvr = hbar*n
What is the bohr radius?
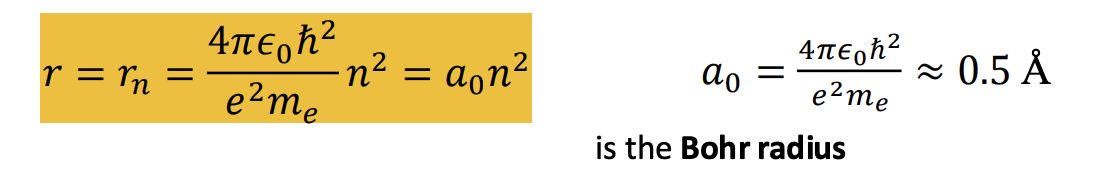
Give formula for quantised energies in the Bohr model
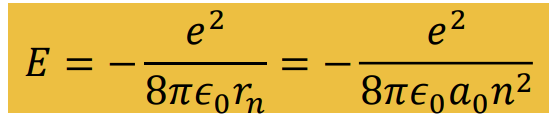
Give the successes of the Bohr model
Atoms are stable by assumption
The Rydberg formula for spectral lines can be derived
Bohr radius gives us a size scale for atoms
Bohr model gives us intuition about atomic structure
Give failiures of the bohr model
Quantisation condition is completely unexplained
Based on classical mechanics
Suggest minimum angular momentum of electron in hydrogen is hbar. Experiments say it is 0.
What happens if you heat bucky balls
They glow like a black body
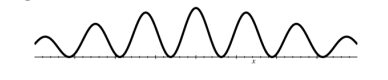
Give the pattern produced when cold bucky balls are fired through a double slit one by one.
Give the pattern produced when hot bucky balls are fired through a double slit one by one
With hot bucky balls the double slit interference pattern disappears
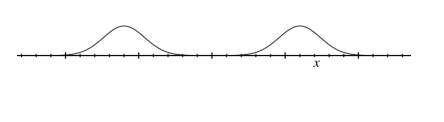
Why does this happen with hot buckyballs?
They emit light so we can see which slit they travelled through.
The interference pattern is then destroyed.
Measuring the path of a particle forces it to choose a slit
Describe the wavefunction for a particle
The quantum mechanical representation of the particles position. It is a function of position and time and can be both positive and negative (or even complex)
What is the Born rule and what does it tell us?
Tells us the probabiity of findinf the particle in a region of space

What conditions are necesary for wavefunctions to satisfy?
Must be continuous (first derivative is finite)
Must be continuous in their first derivatives (ensures second derivative is finite)