Biological Molecules
1/196
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Food Tests, Enzymes and Enzyme Action
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
197 Terms
What is a polymer?
A long chain made from smaller repeating units called monomers
What is the opposite of hydrolysis?
A condensation reaction
What is a condensation reaction?
The reaction that joins two monomers together. It occurs every time a new-sub unit is added to a polymer
What extra molecule is produced in a condensation reaction?
Water
What is hydrolysis?
When polymers are broken down by the addition of water
What are the monomers that make up carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides
What is the general formula for a monosaccharide?
(CH2O)n
What do you call two bonded monosaccharides?
Disaccharide
What do you call more than two bonded monosaccharides?
Polysaccharide
What is a polysaccharide?
More than two bonded monosaccharides
What is a disaccharide?
Two bonded monosaccharides
What does glucose look like? Alpha and beta
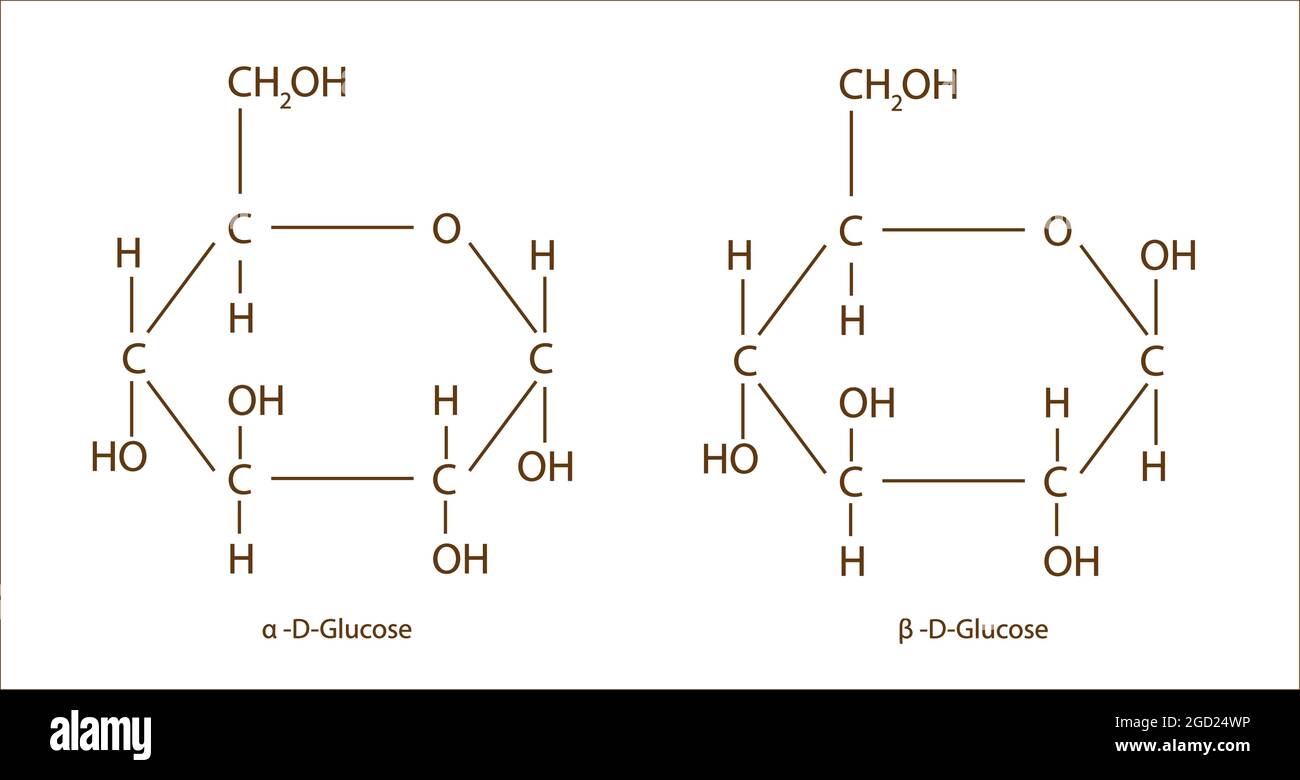
What is the difference between alpha and beta glucose?
In alpha, the OH of carbon 1 is on the bottom, whilst in beta, OH of carbon 1 is on the top
What are 3 monosaccharides?
Alpha glucose
Beta glucose
Beta ribose
What is the bond form between two monosaccharides called?
Glycosidic bond
What does a glycosidic bond look like?
C - O - C
What are 3 disaccharides?
Sucrose
Lactose
Maltose
What monosaccharides make up sucrose?
Glucose and fructose
Where is sucrose produced?
Sugar cane and beet
What do glucose and fructose make?
Sucrose
What do glucose and galactose make?
Lactose
Where is lactose produced?
Mammalian milk
What monosaccharides make up lactose?
Glucose and galactose
What monosaccharides make up maltose?
Alpha glucose and alpha glucose
Where is maltose produced?
Germinating seeds
What do two alpha glucoses make?
Maltose
What are 3 polysaccharides?
Starch
Cellulose
Glycogen
What is starch used for?
Storage of glucose in plants
What are 3 features of starch?
Compact
Insoluble
Large
How does being compact help starch function?
Many glucose molecules can be stored in a small space
How does being insoluble help starch function?
It doesn’t affect the osmotic balance of cells
How does being a large molecule help starch function?
It can’t move out of cells
What two things is starch made of?
Amylose
Amylopectin
What type of glucose molecules is amylopectin made of
Alpha-glucose
What bonds are found in amylopectin?
Alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds
with alpha 1-6 branches
Is amylopectin branched? How does that affect it?
Highly branched
There are more branch ends, which means it has a higher surface area, so can be hydrolysed more quickly
Is starch made mostly of amylopectin or amylose?
Amylopectin
Is amylose branched? How does this affect it?
Unbranched
Few branch ends so it is good for storing glucose
What type of molecule is amylose made of?
Alpha-glucose
What bonds are found in amylose?
Alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds
What is amylose’s structure like? How does this help?
Alpha helix structure
Highly compact so good for storing glucose
What is the function of cellulose?
A structural component in plant cell walls
Is cellulose branched?
Unbranched/Straight
What molecule is cellulose made of?
Beta-glucose
What bonds are in cellulose?
Beta 1-4 glycosidic bonds
What is special about the glucose molecules in cellulose?
Alternate glucose molecules are inverted
What bonds are formed between chains of cellulose molecules?
Hydrogen bonds
What are lots of cellulose chains called?
Microfibrils
What are two features of cellulose?
Very strong
Fully permeable
Why is cellulose strong?
It is made of thousands of chains (and microfibrils) linked together
What does the permeability of cellulose allow?
The movement of substances to and from the membrane
What is the function of glycogen?
Storage of glucose in humans
Is glycogen branched?
Yes, highly branched
What molecules make up starch?
Alpha-glcuose
What bonds are in glycogen?
Alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds
with alpha 1-6 branches
What elements are in lipids?
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
What are the 3 types of lipids?
Triglycerides
Phospholipids
Steroids
What make up steroids?
Four fused rings
What makes up triglycerides?
3 fatty acids
1 glycerol
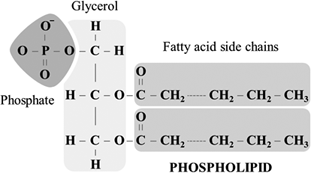
What makes up phospholipids?
2 fatty acids
1 glycerol
1 phosphate group
What are the 3 parts of a fatty acid?
Carboxylic acid group (COOH)
Long hydrocarbon chain
Methyl group (CH3)
Depending on the bonds inside them, what 3 things can fatty acids be?
Saturated (no double bonds between carbons)
Monounsaturated (one double bond between carbons)
Unsaturated (multiple double bonds between carbons)
What state is a saturated fatty acid at room temp?
Solid
What state is an unsaturated fatty acid at room temp?
Liquid
How do fatty acids bond to glycerol? (What reaction)
Condensation reactions
What is the bond between a fatty acid and a glycerol?
Ester bond
What two substances are common forms of triglycerides?
Oil
Fat
What are the 3 uses of triglycerides?
Provide energy
Insulation
Protection for organs
How much energy do triglycerides provide in comparison to carbohydrates/proteins?
Twice as much energy
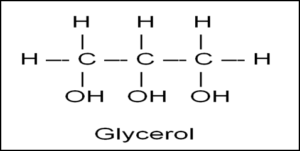
Draw a glycerol molecule
Draw a saturated fatty acid
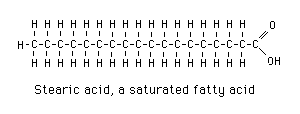
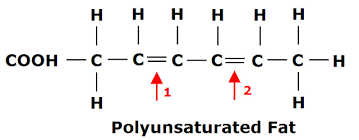
Draw an unsaturated fatty acid
What is produced when a triglyceride is formed?
3 water molecules (from the condensation reactions)
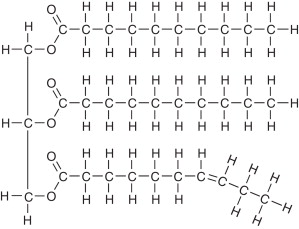
Draw a triglyceride - you can simplify it a bit
What are phospholipids also known as?
Diglycerides
Draw a phospholipid - you can simplify it
What is the most important property of phospholipids?
They are polar
What does polar mean?
The distribution of charge across the molecule is uneven, so one end is slightly positive, while the other is slightly negative
What part of a phospholipid is the head?
The phosphate group
Which part of a phospholipid is the tail?
The fatty acids
Which part of a phospholipid is hydrophilic?
The head / The phosphate group
Which part of a phospholipid is hydrophobic?
The tails / The fatty acids
What is the chemical formula of the phosphate group?
PO4-
What can phospholipids form when in water?
Micelles (these little sphere things)
Phospholipid bilayers
Name 4 features of triglycerides
High ratio of C-H bonds to carbon atoms
Low mass to energy ratio
Insoluble in water
Release energy when oxidised
How does a high ratio of C-H bonds help in trigylcerides?
They store energy, making triglycerides good energy sources
How does a low mass to energy ratio help in triglycerides?
Lots of energy can be stored in small spaces
There is less mass that animals need to carry around
Why are triglycerides insoluble in water? (As in, how does this benefit them?)
So they don’t affect the water potential in cells
What are 3 features of phospholipids?
Polar
Have hydrophilic phosphate ‘heads’
Form glycolipids
What are glycolipids important for?
Cell recognition
What are 6 functions of lipids?
Protection of vital organs
Insulation of the body
Source of energy
Component of cell-surface membranes
Form the myelin sheath
Prevent evaporation in plants and animals
What are the monomers in proteins?
Amino acids
How many different amino acids are there?
20
What are amino acids coded by?
DNA
Draw an amino acid
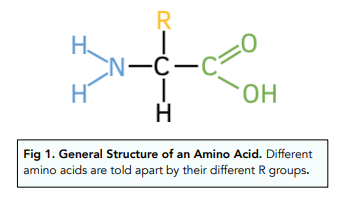
What are the 2 groups all amino acids have?
Amine group
Carboxyl group
What reaction bonds amino acids together?
Condensation reactions
What is the bond formed between amino acids?
Peptide bond
What are two bonded amino acids called?
Dipeptide
What are more than two bonded amino acids called?
Polypeptide