L9_Helicopter Performance, Weight and Balance
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
power output
lift production
A helicopter’s performance is dependent on the _____ of the engine and the _____ of the rotors, whether it is the main rotor(s) or tail rotor.
predict
A pilot’s ability to _____ the performance of a helicopter is extremely important.
It helps to determine how much weight the helicopter can carry before takeoff, if the helicopter can safely hover at a specific altitude and temperature, the distance required to climb above obstacles, and what the maximum climb rate will be.
density altitude
weight
wind
A helicopter’s performance is dependent on the power output of the engine and the lift produced by the rotors, whether it is the main rotor(s) or tail rotor. Any factor that affects engine and rotor efficiency affects performance.
The three major factors that affect performance are (3).
Density Altitude
altitude in the standard atmosphere corresponding to particular value of air density.
high
lower
A decrease in density means a_____-density altitude, and an increase in air density means a _____ density altitude.
Excessive weight
reduces the flight performance, manufacturers attempt to make an aircraft as light as possible without sacrificing strength or safety.
performance
Most _____ charts include weight as one of the variables.
antitorque thrust
At higher gross weights, the increased power required to hover produces more torque, which means more _____ is required.
Wind direction and velocity
also affect hovering, takeoff, and climb performance.
Headwinds
are the most desirable as they contribute to the greatest increase in performance.
Strong crosswinds and tailwinds
may require the use of more tail rotor thrust to maintain directional control.
tail rotor thrust
This increased _____ absorbs power from the engine, which means there is less power available to the main rotor for the production of lift.
Performance Charts
depicting the aircraft performance that can be expected under specified conditions.
include parameters that can be quantified, such as range, endurance, maximum and minimum speeds, takeoff and landing distances, time to altitude, ceiling, and engine capability.
autorotational performance charts
state that autorotational descent performance is a function of airspeed and is essentially unaffected by density altitude and gross weight.
flare and touchdown
downward momentum
collective pitch angle
Potential energy expended during the autorotation is converted into kinetic energy for the _____ and _____ phase of the maneuver.
It is at that point that increased density altitudes and heavier gross weights have a great impact on the successful completion of the autorotation. The rotor disk must be able to overcome the _____ of the helicopter and provide enough lift to cushion the landing.
With increased density altitudes and gross weights, the lift potential is reduced and a higher _____ (angle of incidence) is required.
hovered
Helicopter performance revolves around whether or not the helicopter can be _____.
translational lift
More power is required during the hover than in any other flight regime.
Obstructions aside, if a hover can be maintained, a takeoff can be made, especially with the additional benefit of _____.
IGE hover ceiling
is usually higher than the OGE hover ceiling because of the added lift benefit produced by ground effect.
density altitude
As _____ increases, more power is required to hover.
At some point, the power required is equal to the power available. This establishes the hovering ceiling under the existing conditions.
hovering ceiling
Any adjustment to the gross weight by varying fuel, payload, or both, affects the _____.
decreased
increases
The heavier the gross weight, the lower the hovering ceiling.
As gross weight is ____, the hover ceiling _____.
climb performance
Most of the factors affecting hover and takeoff performance also affect _____.
best rate-of-climb speed (VY)
A helicopter flown at the ____ obtains the greatest gain in altitude over a given period of time.
best rate-of-climb speed (VY)
this speed is normally used during the climb after all obstacles have been cleared and is usually maintained until reaching cruise altitude.
Angle of climb
is a function of altitude gained over a given distance.
VY
results in the highest climb rate, but not the steepest climb angle, and may not be sufficient to clear obstructions.
best angle of climb speed (VX)
depends upon the power available.
VX
If there is a surplus of power available, the helicopter can climb vertically, so _____ is zero.
weight and balance
It is vital to comply with _____ and _____ limits established for helicopters.
weight limitation
Operating above the maximum _____ compromises the structural integrity of the helicopter and adversely affects performance.
Balance
is also critical because, on some fully loaded helicopters, center of gravity (CG) deviations as small as three inches can dramatically change a helicopter’s handling characteristics.
unsafe
Operating a helicopter that is not within the weight and balance limitations is _____.
allowable
OGE hovers
When determining if a helicopter is within the weight limits, consider the weight of the basic helicopter, crew, passengers, cargo, and fuel.
It is critical to understand that the maximum _____ weight may change during the flight.
When operations include _____ and confined areas, planning must be done to ensure that the helicopter is capable of lifting the weight during all phases of flight.
basic empty weight
The starting point for weight computations is the _____, which is the weight of the standard helicopter, optional equipment, unusable fuel, and all operating fluids including engine and transmission oil, and hydraulic fluid for those aircraft so equipped.
external maximum weight
Most helicopters have an internal maximum gross weight, which refers to the weight within the helicopter structure and an external maximum gross weight, which refers to the weight of the helicopter with an external load.
The _____ may vary depending on where it is attached to the helicopter. Some large cargo helicopters may have several attachment points for sling load or winch operations.
These helicopters can carry a tremendous amount of weight when the attachment point is directly under the CG of the aircraft.
Weight limitations
are necessary to guarantee the structural integrity of the helicopter and enable pilots to predict helicopter performance accurately.
handling
Operating below a minimum weight could adversely affect the _____ characteristics of the helicopter.
structural deformation or failure
failure
Operating above a maximum weight could result in _____ or _____ during flight, if encountering excessive load factors, strong wind gusts, or turbulence.
position
Helicopter performance is not only affected by gross weight, but also by the _____ of that weight.
CG range
It is essential to load the aircraft within the allowable _____ specified in the RFM’s weight and balance limitations.
Center of Gravity
defined as the theoretical point where all of the aircraft’s weight is considered to be concentrated.
point at which the body is balanced.
Total moment / total weight is concentrated

nose-low attitude
The helicopter has a _____ that will need an excessive rearward displacement of the cyclic control needed to maintain a hover in a no-wind condition.
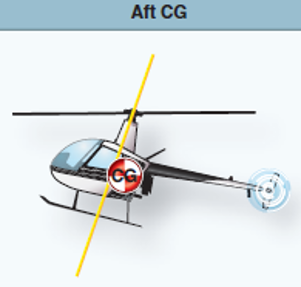
tail-low attitude
The helicopter will have a _____, and will need excessive forward displacement of cyclic control to maintain a hover in a no-wind condition.
gross weight
CG range
When determining whether a helicopter is properly loaded, two questions must be answered:
Is the gross weight less than or equal to the maximum allowable _____?
Is the CG within the allowable _____, and will it stay within the allowable range throughout the duration of flight including all loading configurations that may be encountered.
Balance
is determined by the location of the CG, which is usually described as a given number of inches from the reference datum.
horizontal reference datum
imaginary vertical plane or point, arbitrarily fixed somewhere along the longitudinal axis of the helicopter, from which all horizontal distances are measured for weight and balance purposes.
horizontal reference datum
there is no fixed rule for its location.
may be located at the rotor mast, the nose of the helicopter, or even at a point in space ahead of the helicopter.
Arm / Moment Arm
distance of the load from the datum.
can be Positive or Negative.
Moment
combination of weight and position of a load.
density altitude
weight
wind
Major factors that affect performance: (3)
CG
Moving the ____ can affect the performance of a helicopter.
weight and balance
Always compute for the _____ and _____ of a helicopter before each flight to ensure that it is within standards.