Core exam 3 blue blueprint
1/370
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
371 Terms
Nurses observe and trust their instincts, even when nothing is obviously wrong. Instinct is just another word for
nursing judgement. We prefer to catch the issue when it is small and fixable, not when it is big and deadly
The Brain is the most sensitive to decreased oxygen because
it uses that largest percentage of oxygenated blood
what organ will tell you first if the patient is getting low O2
the brain
early stages of hypoxia
- tachypena
- tachycardia
- restlessness, anxious, agitated
- elevated BP
- Accessory muscles
late stages of hypoxia
- Decreased LOC such as stupor
- Cyanosis
- Bradypnea
- Bradycardia
- Hypotension
- Cardiac dysrhythmias
change in mental status can be a sign of
oxygenation issues
Comfort and oxygenation
poor oxygenation can cause pain and decrease level of comfort
Ischemia
decreased level of oxygenation that can cause pain in affected tissues
Inferior lobes of lungs are the largest and most important to auscultate because
fluid settles in lower lobes
Alveoli interface with pulmonary capillaries at end of bronchioles to
facilitate gas exchange, workhorses of respiratory system
Alveoli that deflate or filled with fluid are called, Number one respiratory complication after surgery
atelectasis
ventilation
movement of air in and out of the lungs, breathing
inspiration
- inhalation
- movement of muscles inn thorax bringing air into the lungs
- active phase
expiration
- exhalation
- breathing out, movement of air out of the lungs
- passive phase
Diffusion
movement of O2 and CO2 between alveoli and blood in the capillaries
- as pressure of oxygen increases it facilitates movement of O2 from alveoli to capillaries
Perfusion
the process by which oxygenated capillary blood passes through body tissues
Eupnea
normal respirations
adults 12-20 BMP
Older adults 12-24 BMP
hypercarbia/hypercapnia is
high CO2 in the blood
Too much CO2 in the blood can
raise the blood PH
chemoreceptors sites
carotid arteries and aorta
when chemoreceptors are triggered to high CO2 it tells the body to
increase respiratory rate
COPD patients are used to function on lower levels of oxygen
- their breathing is regulated by hypoxic drive
- we breathe because of ↑ CO2. People with lung disease (that retain CO2) breathe because of ↓ O2. We can make them stop breathing by giving them even slightly too high levels of supplemental oxygen
Ventilation, diffusion, perfusion
all three are required for adequate oxygenation
Tachypena
more than 20 breaths per minute
Bradypnea
less than 12 breaths per minute
apnea
absence of breathing
dyspnea
difficult or labored breathing
orthopnea
difficulty breathing when lying down
subjective data
what the patient says
"I smoke a pack a day"
objective data
what the nurse can see or measure with her senses/assessments
- cyanosis noted in fingertips
lifestyle behaviors to increase oxygenation
- quit smoking
- ROM exercises
- light cardio
- incentive spirometer
- receive flu and pneumonia vaccine
Respiratory nursing assessment Observe for
- chest symmetry (should have equal movement on both sides, COPD patients have barreled chest)
- respiratory effort/ use of accessory muscles
- oxygenation status (pulse ox on warm finger to gauge oxygen sat)
Respiratory nursing assessment auscultate for
- normal/ expected breathing sounds ( clear bilaterally)
- adventitious breathing sounds ( not clear sounds, wheezing, crackles, ect.)
Lung Auscultation expected sounds
bronchial, bronchovesicular, vesicular
Lung Auscultation unexpected sounds
- crackles or rales
- wheezes
- rhonchi
- pleural friction rub
- absence of breath sounds
- stridor
bronchial breath sounds
loud, high-pitched, hollow sounds normally heard over the trachea and the large bronchi
bronchovesicular sounds
normal breath sounds heard over the upper anterior chest and intercostal area
Vesicular breath sounds
soft, fine, breezy, low-pitched sounds heard over peripheral lung tissue
rales or crackles
- bubbly sound of fluid expanding and falling in alveoli
- air moving through fluid (not good).
- does not clear with coughing
wheezes
- air moving through a narrowed airway (narrowed by bronchoconstriction on the outside of the airway or swelling of the lining of the airway on the inside)
- louder on expiration
Rhonchi
- Rattling noise of mucous in the lungs
- loud, course, low pitched
- can be cleared with coughing
Pleural friction rub
continuous, dry grating sound caused by inflammation of pleural surfaces and loss of lubricating pleural fluid, sounds like sandpaper
Stridor
A high pitched sound generated from partially obstructed air flow in the upper airway
- squeaky toy
best time to take sputum sample
first thing in the morning
- cough it up or endotracheal suction it out
Hemoglobin carries oxygen in blood, it can tell us
how much oxygen is available in blood
arterial blood gasses ( ABGs)
- monitor patients acid base balance
- retrieved from artery not vein
- pH
- carbon dioxide(PaCO2)
- bicarbonate( HCO3)
- PaO2
- SPO2
- most accurate and most invasive measurement of client's oxygen status
Pulse Oximetry (SpO2)
- measures percent of Hemoglobin that bound with O2
- expected is 95-100% ( some Pts vary)
- chronic lung disease 85-89% but with oxygen 88-92%
Respiratory issues diagnostic tests
- chest x ray
- Ct scan (detailed internal image of body)
- MRI (strong magnetic fields generate images)
- bronchoscopy (scope the lungs)
Alterations to oxygenation assessment
- fatigue( can not fully expand chest)
- irritable
- discomfort
- changes in LOC
severe alterations
- hypoxemia
- hypoxia
Chronic hypoxia
- cyanosis is late sign of hypoxemia
- clubbed fingers, commonly seen in COPD
respiratory Independent nursing interventions
- raise HOB at least 30 degrees
- encourage turning, coughing, and deep breathing
- pursed lip breathing for COPD
- positioning
- encourage smoking cessation
- encourage fluid intake to thin secretions
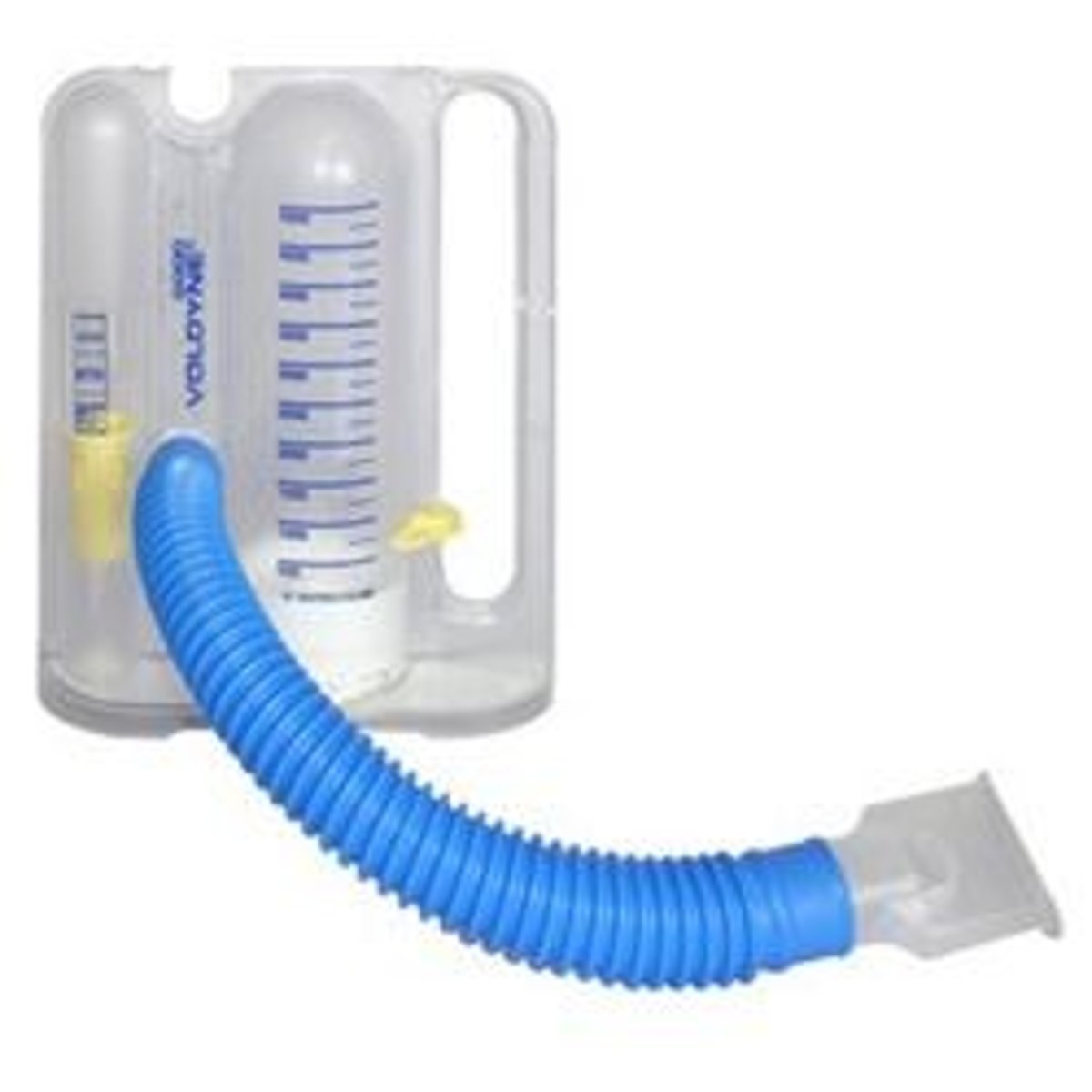
Incentive Spirometer
- encourages deep breathing
- promotes lung expansion
- patient inhales through mouthpiece
- 9-10 times per hour while awake
suctioning can be done
orally, nasally, endotracheal, and to clear airway of hypoxic patients
chest physiotherapy, requires Dr orders
- percussion
- vibration
- postural drainage
all to loosen secretions within the lungs
- contraindicated in pregnancy, head or neck injury, recent abdominal surgery or bleeding disorders
- 1 hour before or two hours after a meal
- monitor for aspiration
collaborative respiratory interventions
- oxygen therapy to increase FiO2
- can apply oxygen in emergencies and then call provider
- with every L of O2 FiO2 increases by 4%
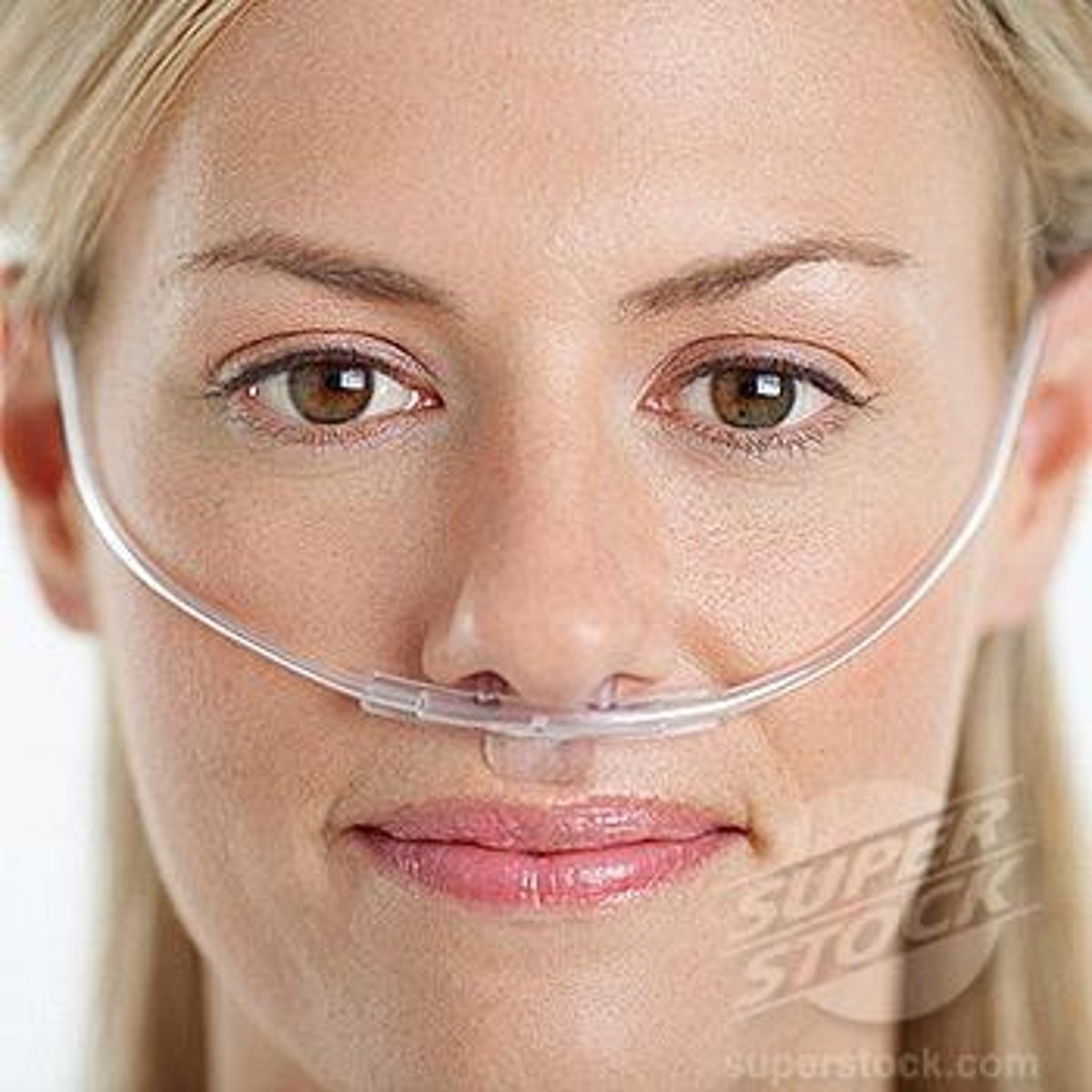
nasal cannula
A device that delivers low concentrations of oxygen through two prongs that rest in the patient's nostrils.
disadvantages:
- 1-6 L per minute
- 24-44% fiO2
- skin breakdown behind ears, on cheekbones, and under nose

simple face mask
an oxygen-delivery apparatus used for patients who require a moderate flow rate for a short period of time via a plastic mask that fits snugly over the mouth and nose
- 6-12 L per min
- 35-50% FiO2
disadvantages:
- impaired eating and drinking
- anxiety in claustrophobic pts
- skin breakdown around border of mask and strap
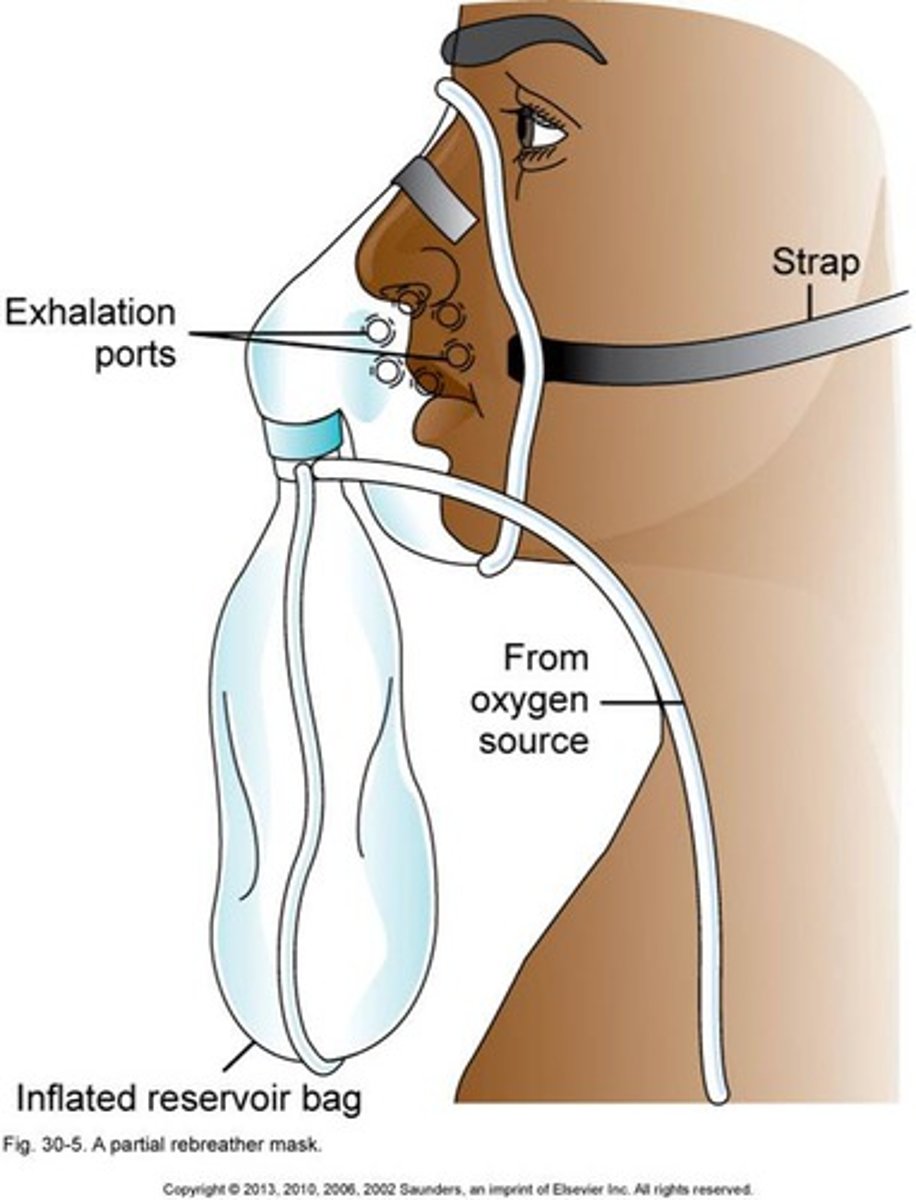
non-rebreather mask
allows higher levels of oxygen to be added to the air taken in by the patient
- 10-15 L/min
- up to 100% FiO2
- humidification required
- provides the highest amount of oxygen
Venturi
- High flow system
- Delivers 24-50% oxygen
- 4-12 L/min
- most precise delivery system
The oxygen mixes with the air
Clients receive constant O2
concentration regardless of rate or depth of respirations
with oxygen therapy do not use
petroleum based products to prevent burns and combustion
Humidification is requires for oxygen therapy above
4L per minute
atelectasis is most often associated with general anesthesia, pay particular attention to patients that
have had surgery in the last 1-2 days
for dyspneic patients
raise head of bed, asses, intervene, assess, then apply O2 if needed
1. Oxygenation is the name of the game for ABC's
- Airway - get the air in and out
- Breathing - get the air down to the alveoli for gas exchange
- Circulation - perfuse the body's tissues with oxygenated blood and get rid of carbon dioxide
Do not avoid opioid pain medications because of fear of respiratory depression because
- Pain will cause more long-term lung complications in the long run
- Be the patient advocate - provide comfort and be watchful to avoid harm (in other words, be a good nurse!)
Oxygenation
hemoglobin being loaded with oxygen
Oxygenation problems
COPD, pneumonia, pulmonary edema, anything affecting lungs
Oxygenation Assessment
pulse oximetry, respiratory rate, LOC, SOB, arterial blood gasses are the most accurate representation of oxygenation
Circulation definition
blood traveling to and from all tissues in body
Circulation problems
- occlusions/ blood clots
- sickle cell anemia
- bed rest / restricted movement
- low blood volume
- dehydration
- heart problems
Circulation assessment
capillary refill, peripheral pulses, cyanosis
Perfusion problems
heart dysfunction, ischemia progressing to infarction progressing to necrosis
Assessment of perfusion
- decreased temperature
- cyanosis
- decreased LOC
- altered mental function with decreased perfusion in the brain
blood pressure is measured as
systolic/diastolic
factors that increase blood pressure
- increased age
- stress
- ethnicity (African Americans)
- certain medications
- obesity
- smoking
factors that can lower blood pressure
- certain medications
- consistent exercise
Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR)
- constriction / dilation of arteries
- SVR increases (constriction)=blood pressure increases
- SVR decreases (dilation) = blood pressure decreases
pulse sites
- carotid, brachial, and femoral are central pulses
- radial
- popliteal
- posterior tibial
- dorsalis pedis ( pedis)
pulse strength
reflects the volume of blood ejected against the arterial wall with each contraction of the heart (stroke volume)
how to take pulse rate for an adult
- measured in BMP
- for regular pulse, count for 30 seconds and multiply by 2
- for irregular pulse, count for a full minute
scale for pulse strength
0= absent
1= diminished
2= normal
3= increased and strong
4= bounding
Tachycardia
- more than 100 BMP
- causes: cardiac dysrhythmias, exercise, anxiety, pain, hypovolemia, hypoxemia
bradycardia
- less than 60 BMP
- S/S: dizziness, hypotension, decreased LOC
- causes: cardiac dysrhythmias, medications, exercise, relaxation, ect.
Apical Pulse/Pulse Deficit
- auscultate apical pulse for 1 full minute
- simultaneously palpate the radial pulse and auscultate the apical pulse to check for deficit
cardiac output=
stroke volume x heart rate
blood pressure=
cardiac output x systemic vascular resistance
stroke volume increases
HR decreases
cardiac output and blood pressure remails the same
stroke volume decreases
heart rate increases
cardiac output and blood pressure remains the same
when stroke volume decreases and heart rate increases too much
the heart does not have time to properly fill with blood
cardiac output and blood pressure decreases
heart sounds
S1 and S2
anything else is abnormal
S1
lub
ventricle systole/ contraction
bicuspid and tricuspid valves
S2
dub
ventricle diastole/ relaxation
pulmonic and aortic valves
Diaphragm of stethoscope
high pitched heart sounds
Bell of stethoscope
low pitched sounds
unexpected heart sounds and bruits
thrill
palpable vibration caused by turbulent blood
bruits
whooshing sound caused by obstructed or turbulent blood
heart failure / broken pump causes
decreased circulation / oxygenation and decreased perfusion
right sided heart failure
think body
- fatigue
- increased peripheral venous pressure
- asities
- enlarged liver and spleen
- distended jugular veins
- GI distress
- weight gain
- dependent edema
left sided heart failure
think lungs
- pulmonary congestion
- restlessness
- dyspnea
- tachycardia
- fatigue
- exertional dyspnea
- cyanosis
arterial blood
- high oxygen
- bright red
- moves distally from the heart
- blockage= ischemia/ infarction
S/S of arterial problem
- pain
- pallor
- pulses diminished / absent
- paresthesia ( abnormal feeling can lead to paralysis)