Thyroid Hormones
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
location of the thyroid gland
below the larynx and on either side of and anterior to the trachea
structures of the thyroid gland
thyroid hormones
thyroxine
triiodothyronine
calcitonin or thyrocalcitonin
T4 is known as
Thyroxine
T3 is known as
Triiodothyronine
secretory cell of th
secretory cell of calcitonin or thyrocalcitonin
thyroid parafollicular cells
stimulator for T3 and T4
exposure of animal to low environmental temperature (cold)
inhibitor for T3 and T4 secretion
conditions that stimulate the sympathetic nervous system
excitement
anxiety
Regulation of Thyroid Hormone Secretion
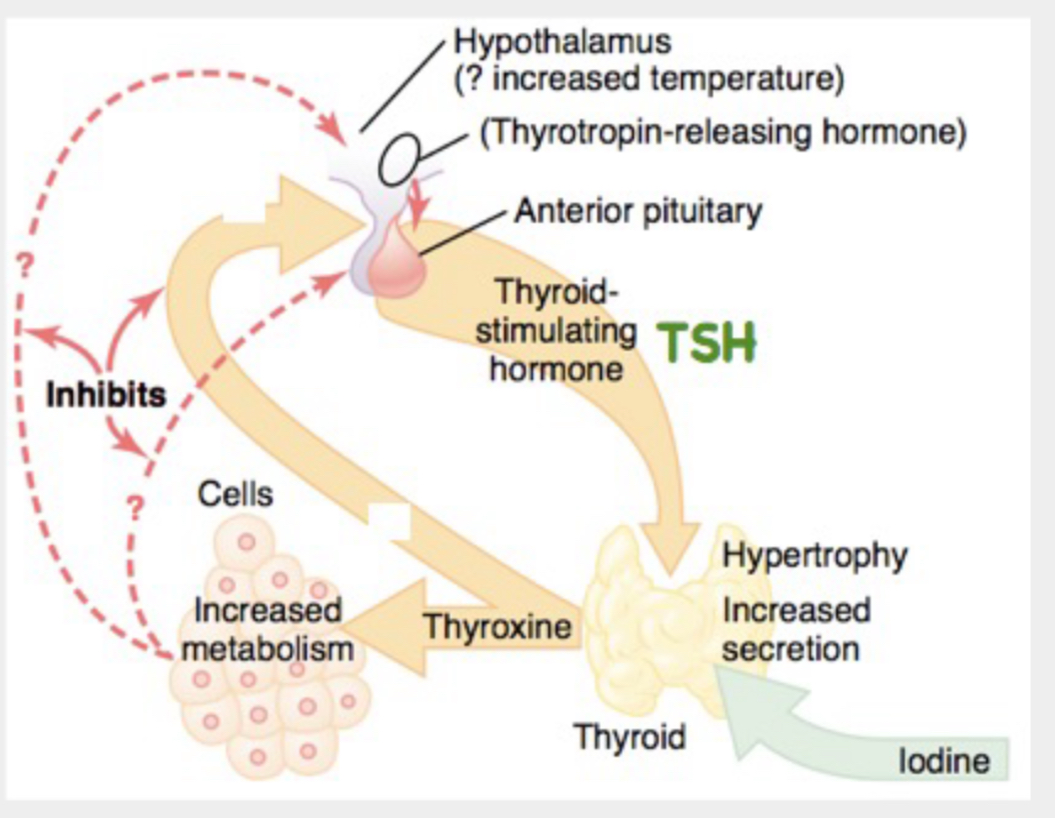
TSH Signaling Pathway of Thyroid Follicular Cells
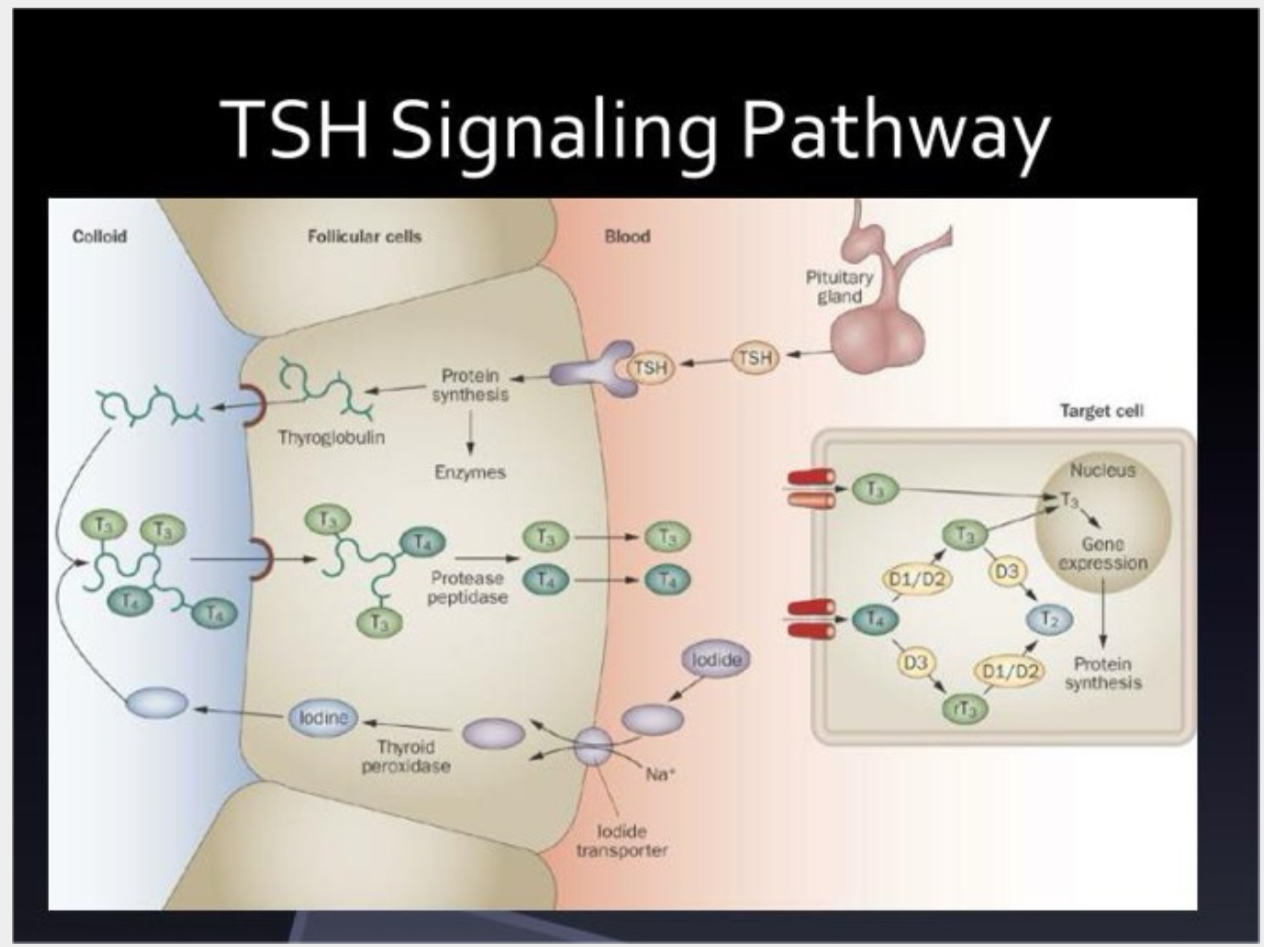
Synthesis of T3 and T4 by Thyroid Follicular Cells
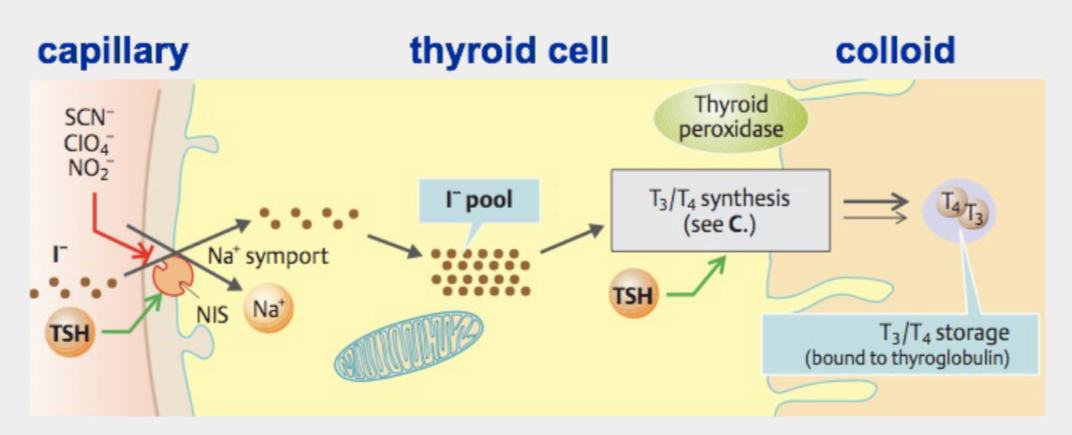
Iodide Trapping
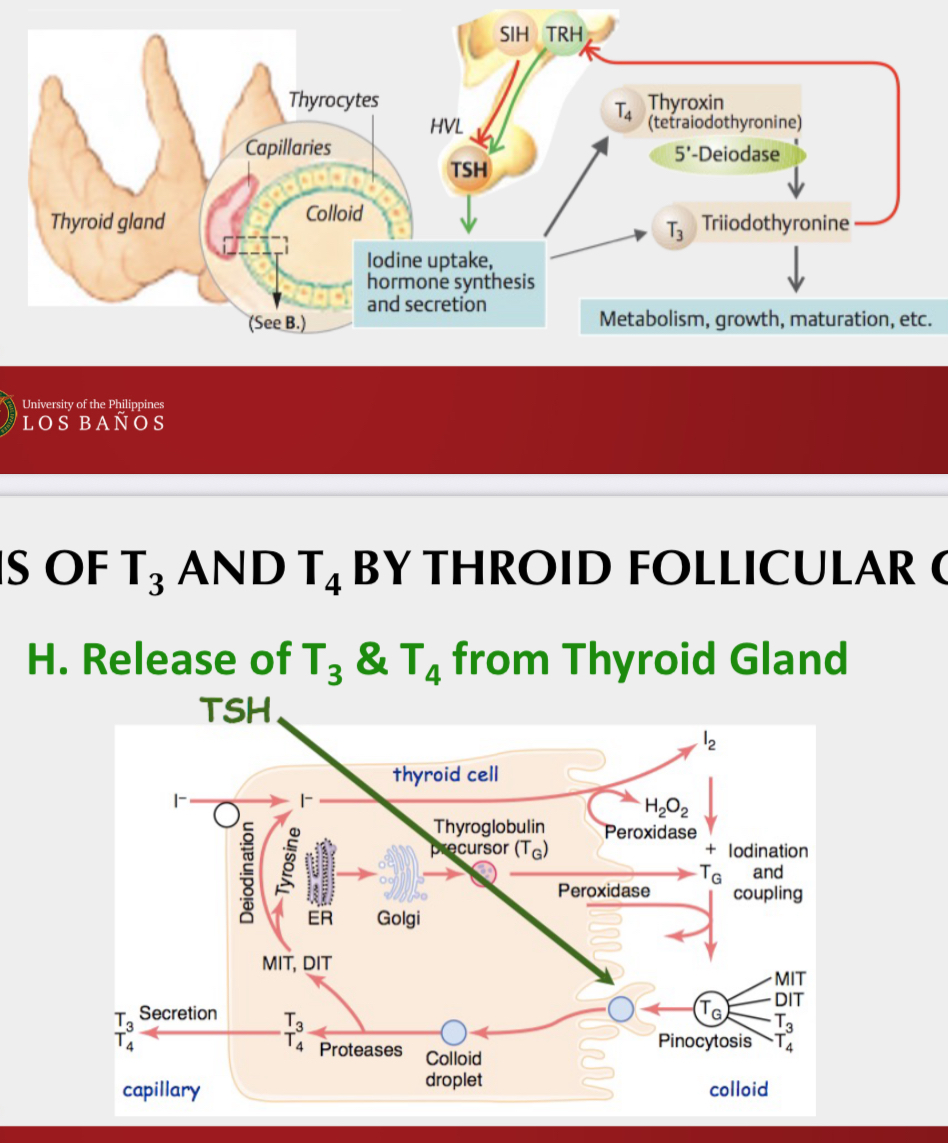
Formation & Secretion of Thyroglobulin
Oxidation of Iodide Ions
Iodination of Tyrosine & Formation of Thyroid Hormones or Organification of Thyroglobulin
Coupling Reaction
Storage of T3 and T4
Release of T3 and T4 from Thyroid Gland
Iodide Trapping Mechanism
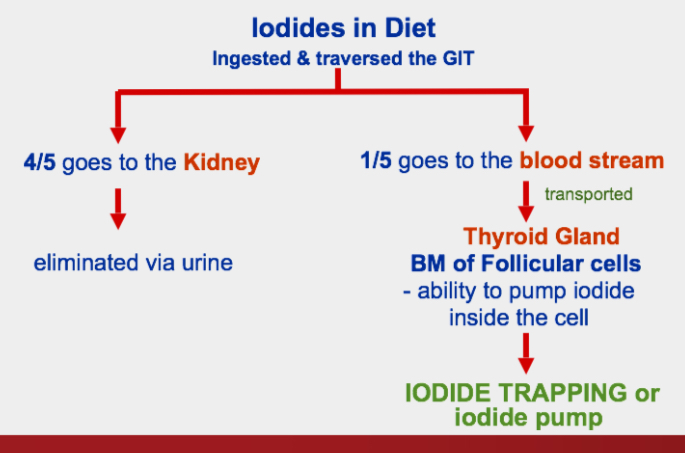
Formation & Secretion of Thyroglobulin
Oxidation of Iodide Ions

Iodination of Tyrosine & Formation of Thyroid Hormones
or
Organification of Thyroglobulin
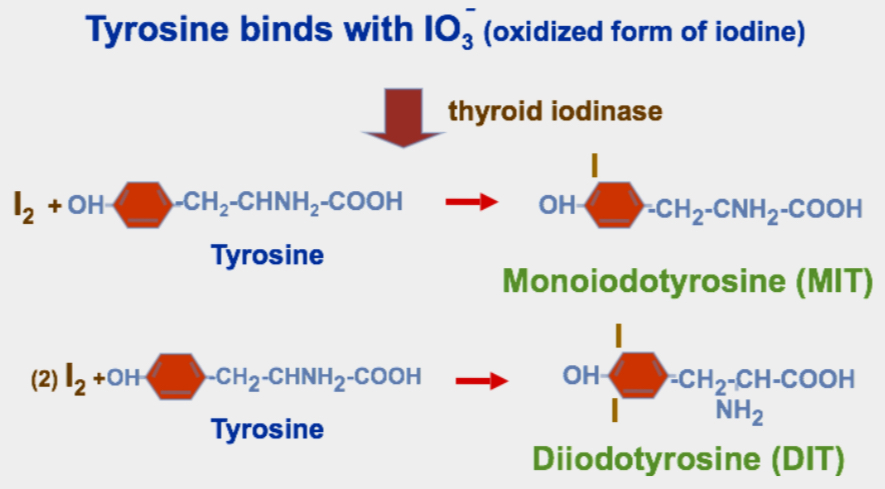
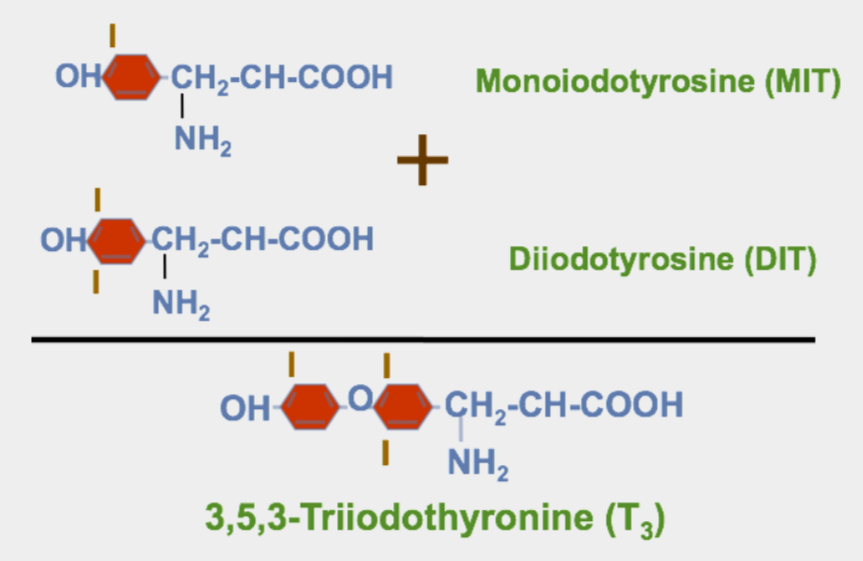
chemical name of T3
3,5,3-triiodothyronine
Coupling Reaction (T3)
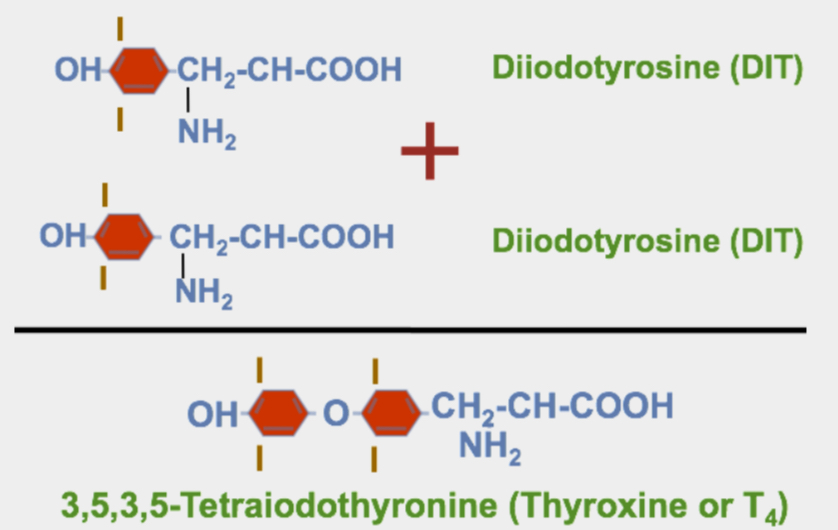
chemical name of T4
3,5,3,5-tetraiodothyronine
Coupling Reaction (T4)
Storage of T3 and T4 Hormones
how many molecules of T3 and T4 in a thyroglobulin molecule
T3 - 1 molecule
T4 - 1-3 molecules
Release of T3 and T4 from Thyroid Gland
plasma proteins which bind to T3 and T4
thyroxine binding globulin (TBG)
thyroxine binding prealbumin
albumin
binding affinity of thyroxine binding globulin
high affinity for thyroxine
binding affinity of thyroxine binding prealbumin
binds T3 and T4
binding affinity of albumin
binds T3 and T4
percentage of T3 and T4 in free form
<0.05% of T3 and <0.05% of T4
features of T3 and T4 in bound form (in dogs)
TBG - high affinity for T4
prealbumin & albumin - low affinity T3 and T4
features of T3 and T4 in bound form (in cats)
prealbumin - high affinity T3 and T4
Features of T3 and T4
blood level
potency
duration of action
binding with plasma proteins
how much is released in x days
T3
blood level 7%
potency 4x higher
duration short
binding with plasma proteins
weakly bound
½ released in 1 day
T4
blood level 93%
potency 4x lesser
duration long
binding with plasma proteins
strongly bound
½ released in 6 days

monodeiodination of T4
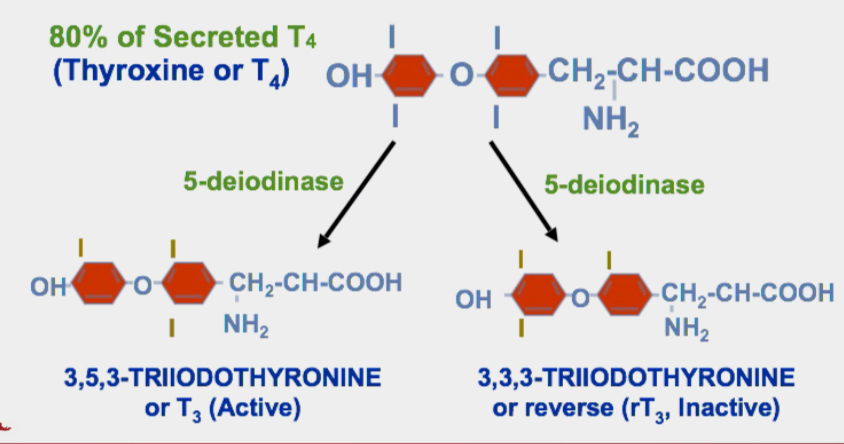
site of monodeiodination
liver & kidney
Thyroid Hormone Receptors in Target Cells
TRa
TRa1
TRa2
TRa3
TRb
TRb1
TRb2
TRb3
distribution of TRa1
all tissues, abundant in heart, skeletal muscle, brown adipose tissue, brain
distribution of TRb1
liver & kidneys
distribution of TRb2
anterior pituitary gland
hypothalamus
inner ear
developing brain
distribution of TRb3
kidney
liver
lungs
Effect of Thyroid Hormones on Different Body Systems
maintains normal basal metabolic rate (BMR)
effect on metabolism
maintains normal blood lipid levels
maintains normal body weight
increases formation of enzymes or co-enzymes essential for vitamin formation
promotes growth of animals
effect on circulatory system
increases respiratory function
increases food intake, appetite, digestion
increases brain cerebration
promotes muscle to react with vigor
promotes good sleep
maintains normal body temperature
needed for normal reproduction
maintains normal basal metabolic rate (BMR)
hyperthyroidism vs hypothyroidism
increases metabolism in almost all cells
hyperthyroidism - increases BMR by 60-100%
hypothyroidism - decreases BMR by 30-50%
effect on metabolism
carbohydrates (CHO)
promotes glucose absorption in GIT
promotes glucose uptake by cell through stimulation of insulin secretion
deficit in glucose
glycogenolysis
gluconeogenesis
fats
mobilize fats in adipose
lipolysis
promotes utilization of cholesterol for bile acid formation
activates lipoprotein lipase
catalyze hydrolysis of chylomicrons (TG) into glycerol + FA
protein
protein anabolism
formation of enzymes
formation of structural proteins
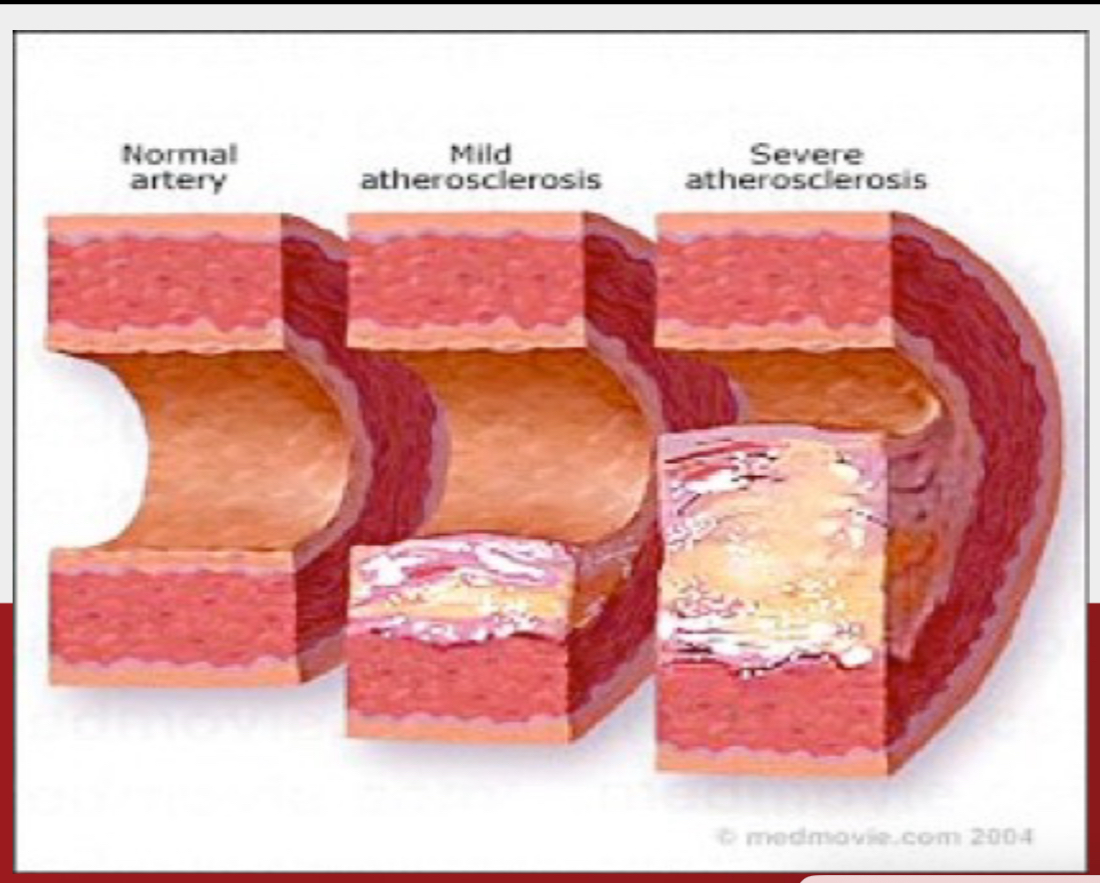
maintains normal blood lipid levels
hyperthyroidism vs hypothyroidism
hyperthyroidism
low plasma cholesterol, phospholipids, TAG
hypothyroidism
high plasma cholesterol, phospholipids, TAG
fatty liver
development of atherosclerosis
due to high blood cholesterol level
maintains normal body weight
hyperthyroidism vs hypothyroidism
hyperthyroidism
decrease in body weight
weight loss
hypothyroidism
increase in body weight
develops obesity
increases formation of enzymes/co-enzymes essential for vitamin formation
hyperthyroidism vs hypothyroidism
chronic hyperthyroidism
initially increases vitamin formation then deficiency in vitamins occur
chronic hypothyroidism
vitamin deficiency
promotes growth of animals
hyperthyroidism vs hypothyroidism
bone, brain, muscles, etc.
chronic hyperthyroidism
early closure of epiphyseal plate
rapid bone maturation
chronic hypothyroidism
stunted growth
retarded brain development
effects on circulatory system
increases blood flow to tissues
increased BMR
increases O2 utilization by tissues
increases cardiac output
increased O2 demand
increases heart rate
increased O2 demand
arterial vasodilation
increase transport of blood to the tissues
development of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
heart function abnormality
hyperthyroidism vs hypothyroidism
chronic hyperthyroidism
tachycardia
cardiac murmurs
chronic hypothyroidism
bradycardia
slow heart sound
arrythmia
increases respiratory function
hyperthyroidism vs hypothyroidism
increases RR due to increased O2 consumption and CO2 formation by cells (due to increased BMR)
chronic hyperthyroidism
high RR
fast shallow breathing
chronic hypothyroidism
low RR
slow, deep breathing
increases food intake, appetite, digestion
hyperthyroidism vs hypothyroidism
increases appetite and feed intake
increases GIT motility & digestive juice secretions
chronic hyperthyroidism
diarrhea
chronic hypothyroidism
constipation
increases brain cerebration
hyperthyroidism vs. hypothyroidism
chronic hyperthyroidism
extreme nervousness
anxiety
chronic hypothyroidism
lame
inactive disposition
promotes muscle to react with vigor
hyperthyroidism vs. hypothyroidism
chronic hyperthyroidism
fine muscle tremors
*more muscle proteins catabolized - leads to muscle weakness
chronic hypothyroidism
muscle sluggish
muscle relax slowly
promotes good sleep
hyperthyroidism vs. hypothyroidism
chronic hyperthyroidism
difficulty in sleeping
short sleep hours
exhaustion of brain and skeletal muscles
chronic hypothyroidism
extreme somnolence
12-14 hours sleep per day
maintains normal body temperature
hyperthyroidism vs. hypothyroidism
chronic hyperthyroidism
high body temp
heat production
sweating, panting
chronic hypothyroidism
difficulty to maintain normal body temp
cold intolerance - skin feels cold
heat seekers - blankets, TV, fridge
needed for normal reproduction
hyperthyroidism vs. hypothyroidism
chronic hyperthyroidism
male
impotence
female
irregular estrous cycle
infertility
chronic hypothyroidism
male
loss of libido
poor sperm quality
testicular atrophy
female
loss of libido
irregular estrous cycle
prolonged anestrus
low fertility & conception rates
high abortion rate
thyroid hormone abnormalities
hyperthyroidism
hypothyroidism
etiology of hypothyroidism
deficiency in thyroid hormone secretion
types of hypothyroidism
congenital and acquired
hypothyroidism is common in what age of dogs
young to middle aged dogs
hypothyroidism can be observed in what species
dogs
cats
cattle
sheep
goat
poultry
horse
hypothyroidism
dog breeds
high risk
moderately at risk
low risk
high risk
edit
moderately at risk
shetland sheepdog
miniature schnauzer
beagle
dachshund
pomeranian
cocker spaniel
airedale terrier
low risk
German shepherd
mixed breed

types of congenital hypothyroidism in dogs
primary congenital hypothyroidism
secondary congenital hypothyroidism
etiology of primary congenital hypothyroidism
thyroid dysgenesis
thyroid hypoplasia, athyreosis
dyhormonogenesis
inherent inability to synthesize T3 and T4
thyroid not responding to TSH
clinical signs of primary congenital hypothyroidism
goiter
underdeveloped long bones
epiphyseal dysgenesis
short vertebral bodies
etiology of secondary congenital hypothyroidism
cystic rathke’s pocket
congenital deficiency in TSH
breed predilection of secondary congenital hypothyroidism
giant schnauzers
german shepherd
clinical signs of secondary congenital hypothyroidism
pituitary dwarfism
disproportionate dwarfism
lethargy
constipation
gait abnormalities
types of acquired hypothyroidism in dogs
primary acquired hypothyroidism
secondary acquired hypothyroidism
tertiary acquired hypothyroidism
lymphocytic thyroiditis
idiopathic thyroid follicular atrophy
autoimmune thyroiditis
type of hypothyroidism of thyroid origin
primary acquired hypothyroidism
95% of clinical cases in animals
type of hypothyroidism of pituitary origin
secondary acquired hypothyroidism
rare in animals
type of hypothyroidism of hypothalamic origin
tertiary acquired hypothyroidism
rare in animals
etiology of primary acquired hypothyroidism
lymphocytic thyroiditis
idopathic thyroid follicular atrophy
autoimmune thyroiditis
neoplasm of thyroid
iodine deficiency
iatrogenic (drugs)
radioactive iodine treatment Tx
signs of primary acquired hypothyroidism
insensitive to TSH
high TSH; low
etiology of secondary acquired hypothyroidism
pituitary gland tumor
infection of the pituitary gland
inflammation of the pituitary gland
iatrogenic (drugs, hormones)
signs of secondary acquired hypothyroidism
low TSH levels
low T3 and T4
etiology of tertiary acquired hypothyroidism
tumors of the hypothalamus
trauma of the hypothalamus
inflammation of the hypothalamus
signs of tertiary acquired hypothyroidism
low TRH levels
low TSH levels
low T3 and T4
immune mediated thyroid atrophy
lymphocytic thyroiditis
similar to human hashimoto’s disease
lymphocytic thyroiditis
non-inflammatory destruction of the thyroid
idiopathic thyroid follicular atrophy
autoimmune destruction of the thyroid
autoimmune thyroiditis
production of autoantibodies against the thyroglobulin
lymphocytic thyroiditis
humoral & cell-mediated destruction of the thyroid
idiopathic thyroid follicular atrophy
lymphocytic thyroiditis (mechanism)
diffused infiltration of lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages
destruction of thyroid follicles and secondary fibrosis
idiopathic thyroid follicular atrophy
loss of thyroid parenchyma and replacement by adipose tissue
autoimmune thyroiditis is prevalent in what dog breeds
doberman
pinscher
beagle
akita
golden retriever
types of hypothyroidism in cats
primary congenital hypothyroidism
primary acquired hypothyroidism
*secondary and tertiary congenital & acquired hypothyroidism not documented
etiology of primary congenital hypothyroidism (cats)
thyroid dysgenesis
dyshormonogenesis
thyroid not responding to TSH
etiology of primary acquired hypothyroidism (cats)
after radioactive iodine treatment Tx for hyperthyroidism
surgical thyroidectomy
use anti-thyroid drugs
common cause of cases in cats
primary acquired hypothyroidism
signs of primary congenital hypothyroidism (cats)
insensitive to TSH
high TSH
low T3
signs of primary acquired hypothyroidism (cats)
insensitive to TSH
high TSH
low T3 and T4
goitrogenic substances mechanism of action
inhibits iodide trapping
goitrogenic substances
thiocyanates
complex anions
examples of thiocyanates
cabbage
lentils
peanuts
soybeans
turnips
examples of complex anions
perchlorate
pernechnetate
perhennate
tetrafluoroborate
anti-thyroid drugs
thiocarbamids
propylthiouracil
sulfonamides
thiocarbamids mechanism of action
inhibits peroxidase