Phonatory System
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
larynx
the structure that hangs off the hyoid bone and includes the folds, cartilages, muscles, and joints, 2-4 inches long
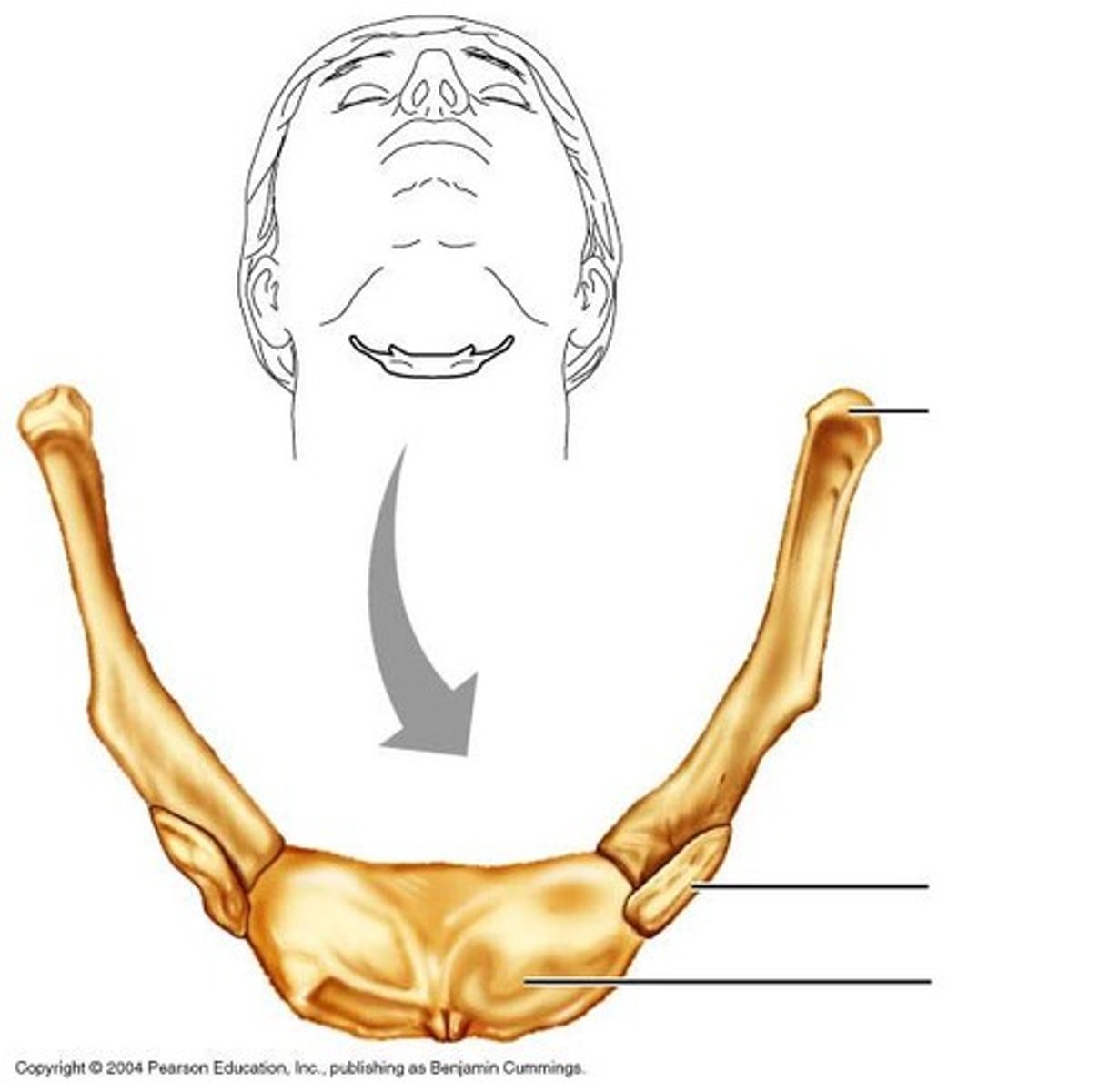
hyoid
the floating bone that is sort of part of the larynx but is definitely what the larynx hangs off of.
greater cornu (horns)
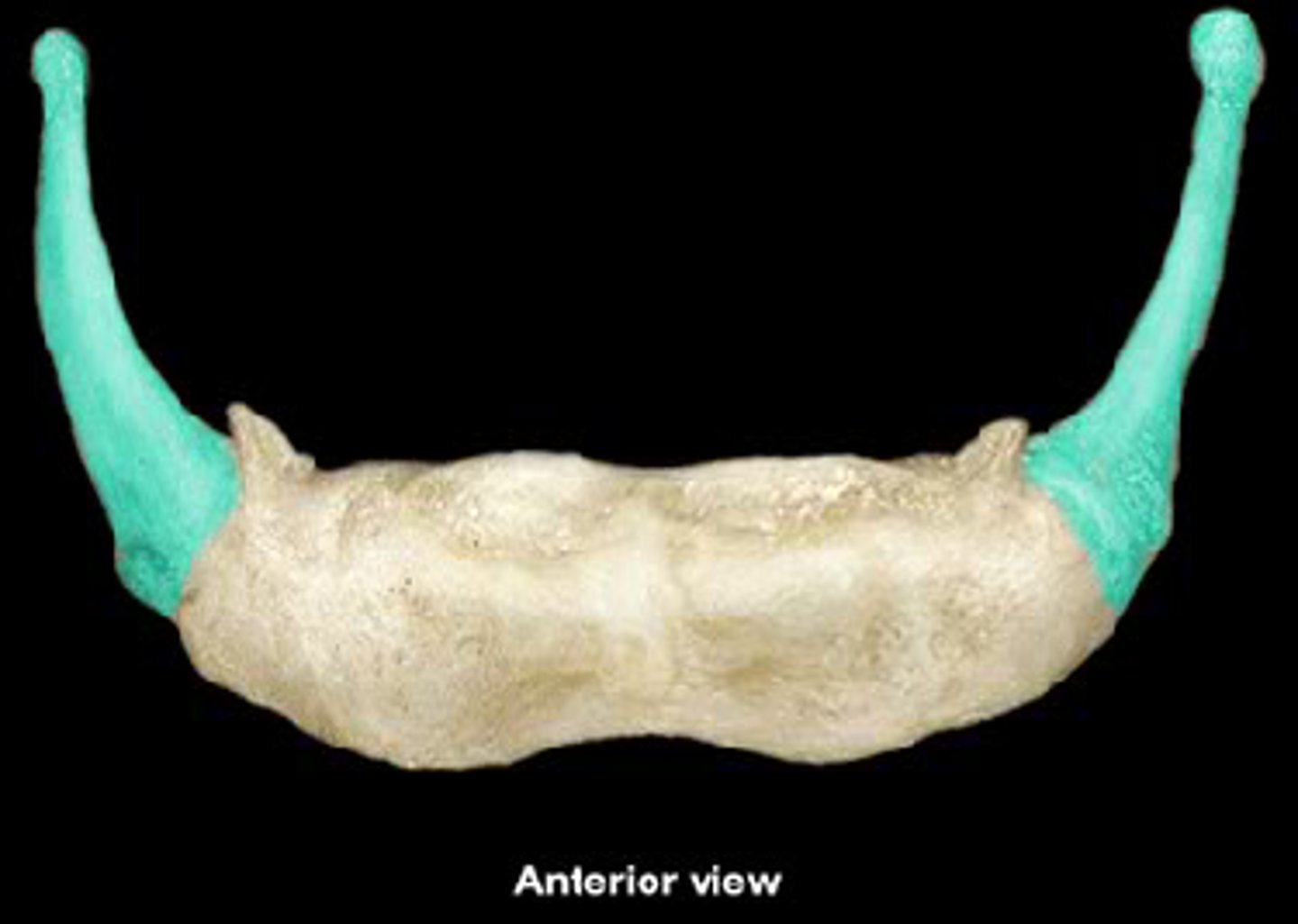
lesser cornu (horns)
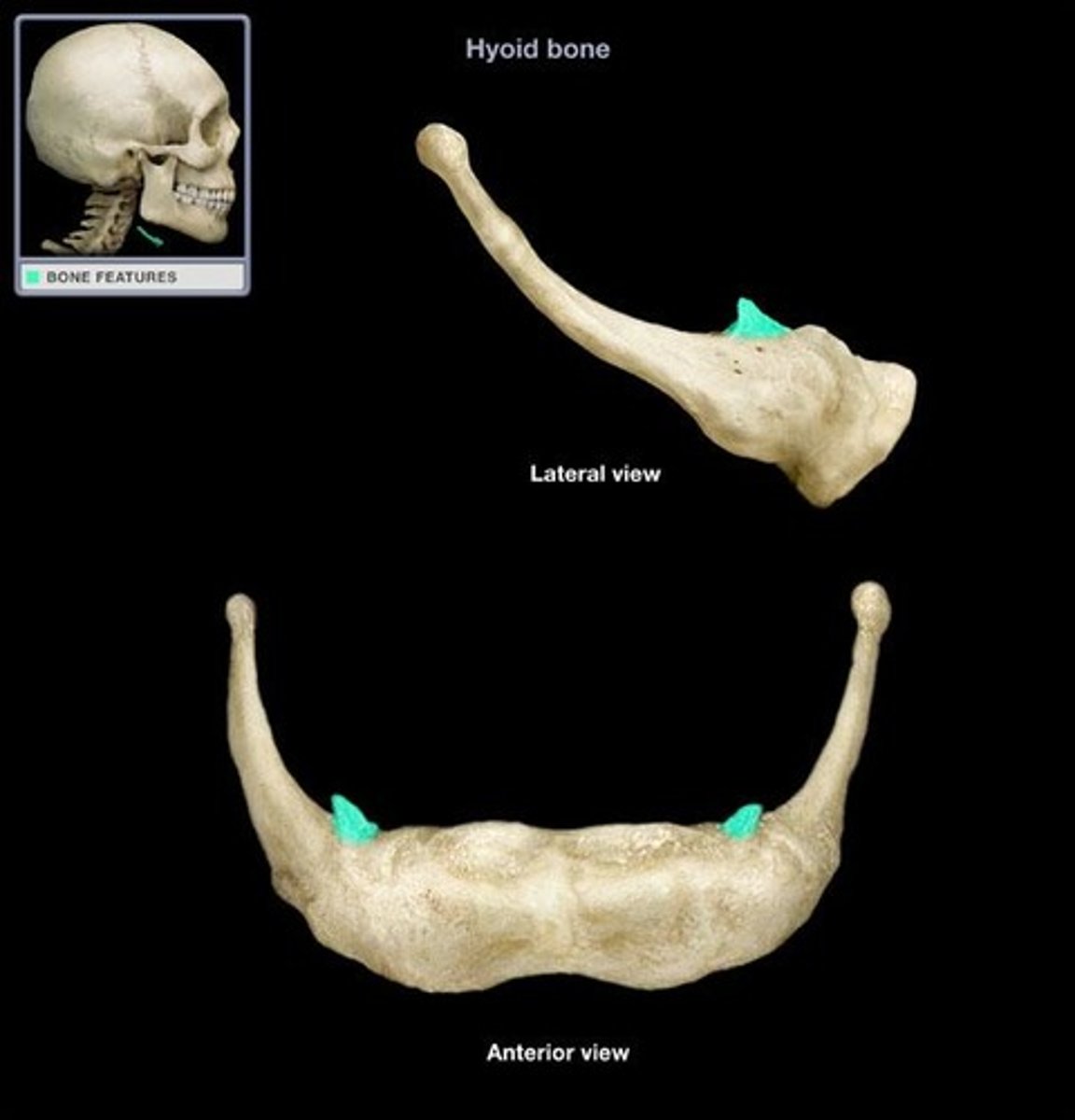
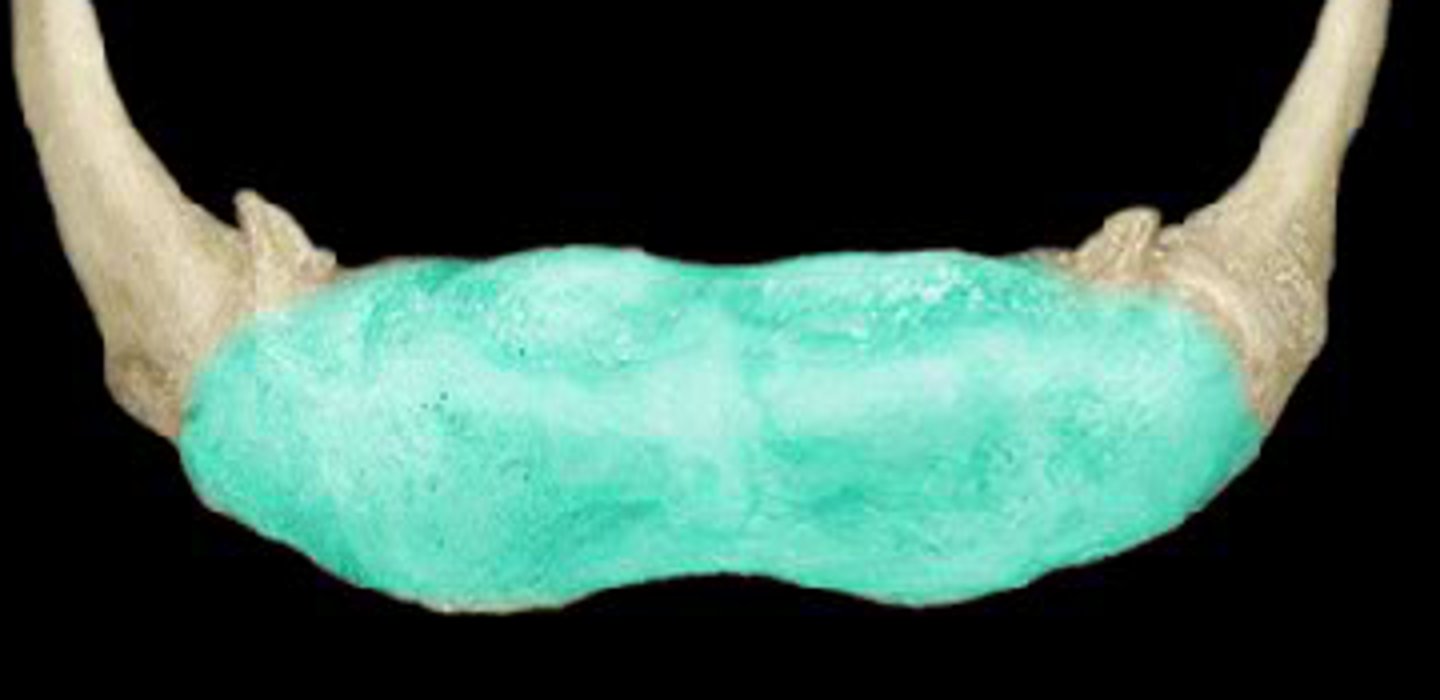
body (corpus)

thyrohyoid membrane
the larynx is suspended from the hyoid bone by this structure
cartilage
a firm, elastic, flexible fibrous type of connective tissue
thyroid
directly attached to the thyroid membrane and to the hyoid bone by ligaments
thyroid laminae
thyroid notch
where the thyroid laminae are fused at an angle
superior cornu
horns that project upward from the thyroid and attach to the hyoid bone by ligaments
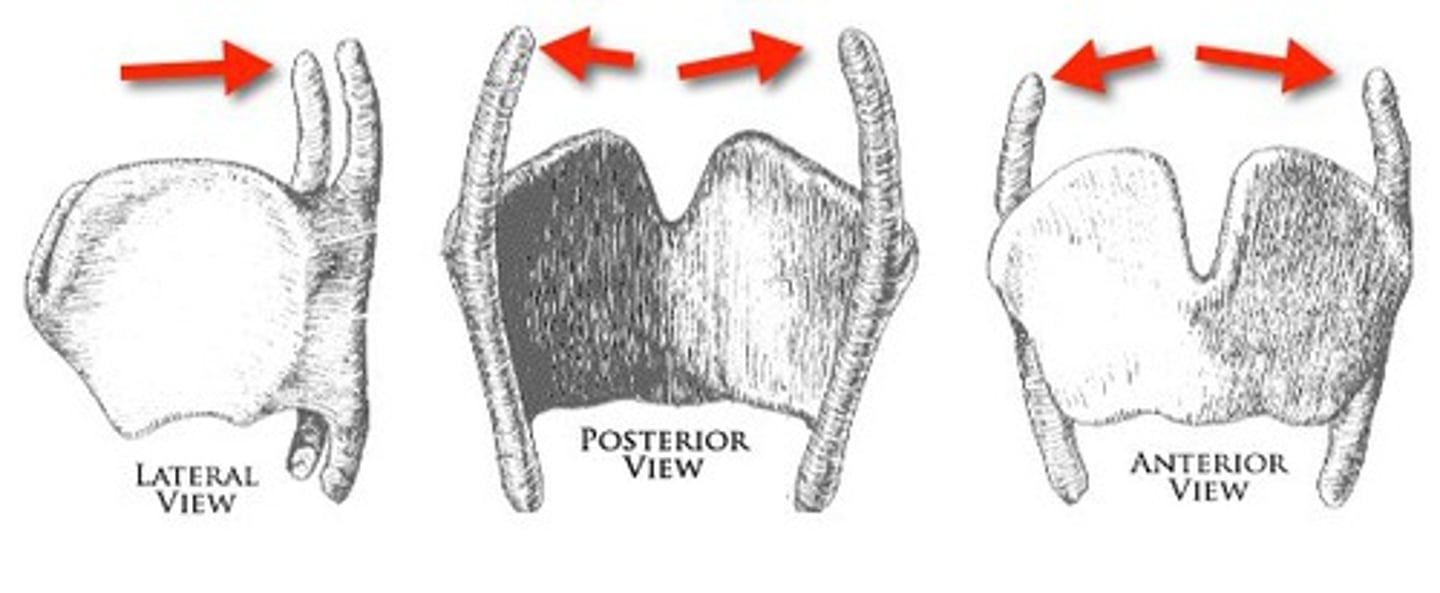
inferior cornu
horns that project downward from the thyroid and join with the sides of the cricoid cartilage
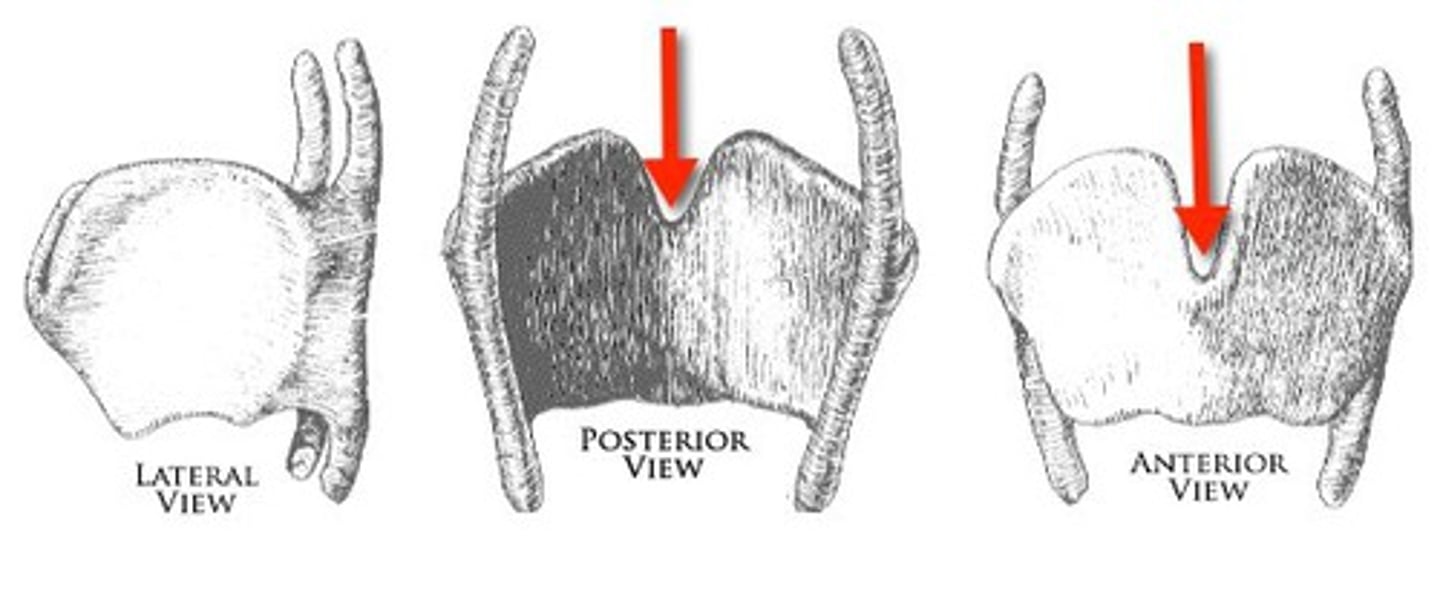
cricoid
complete ring at the base of the larynx, narrow at the front, wider in the back
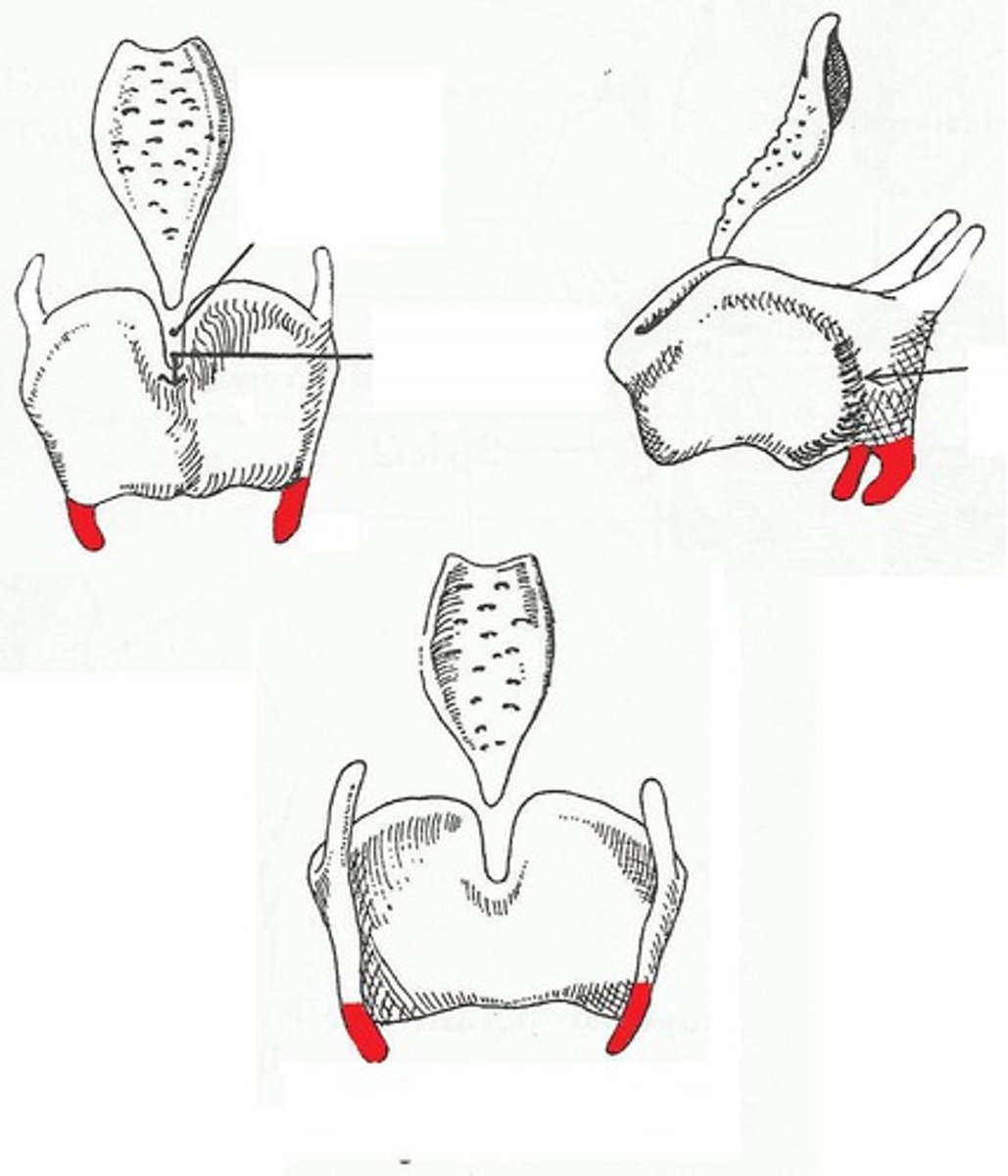
cricoidthyroid membrane
attaches the cricoid to the thyroid
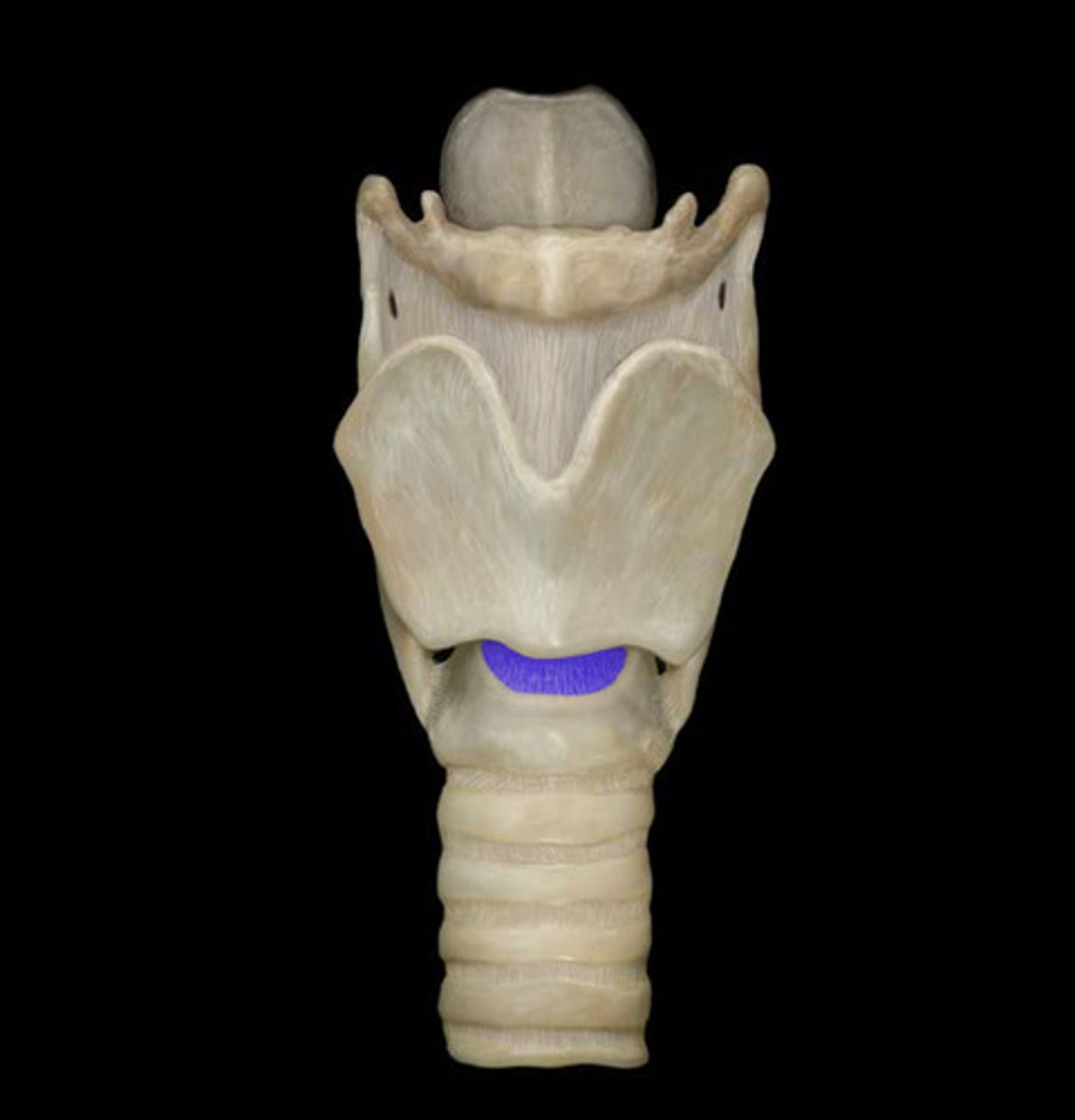
cricotracheal membrane
attaches the cricoid to the trachea
epiglottis
a broad, leaf shaped structure, which folds downward over the entrance of the larynx to prevent food from entering the trachea and direct food to the esophagus
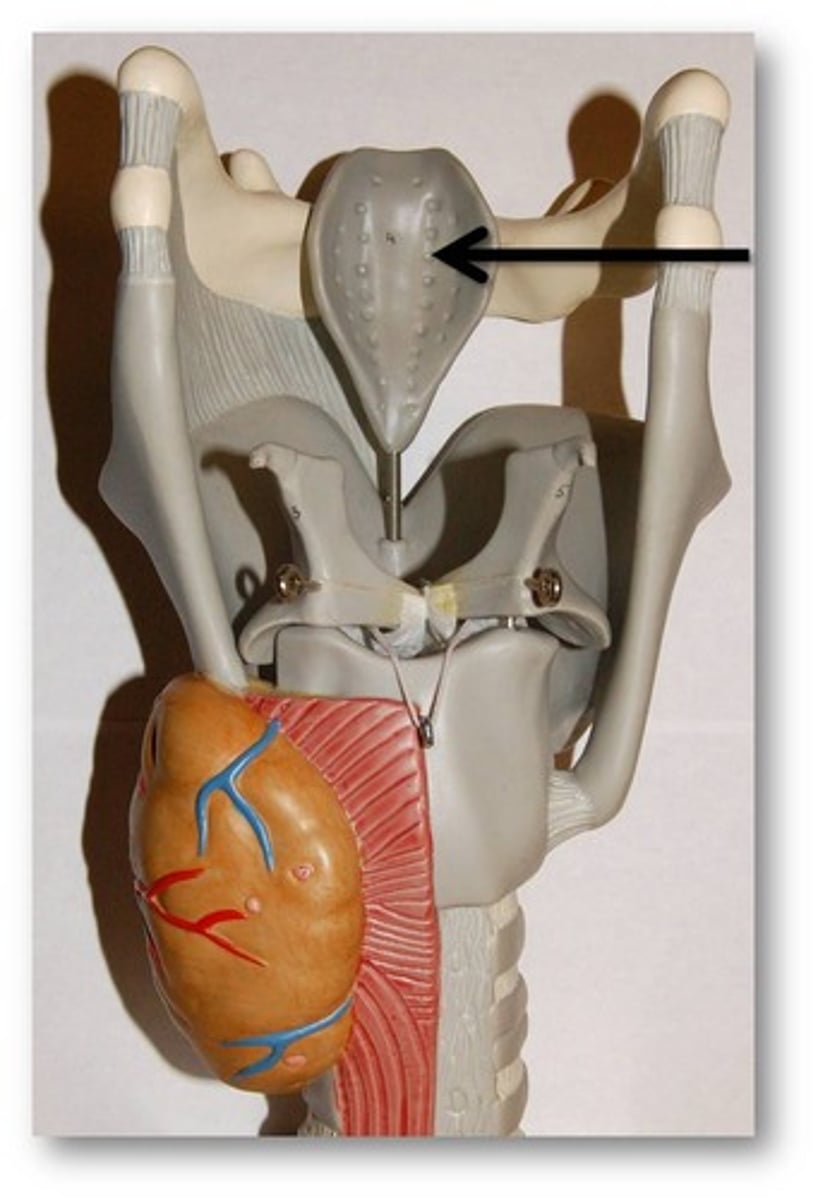
valleculea
the valley between the epiglottis and the tongue
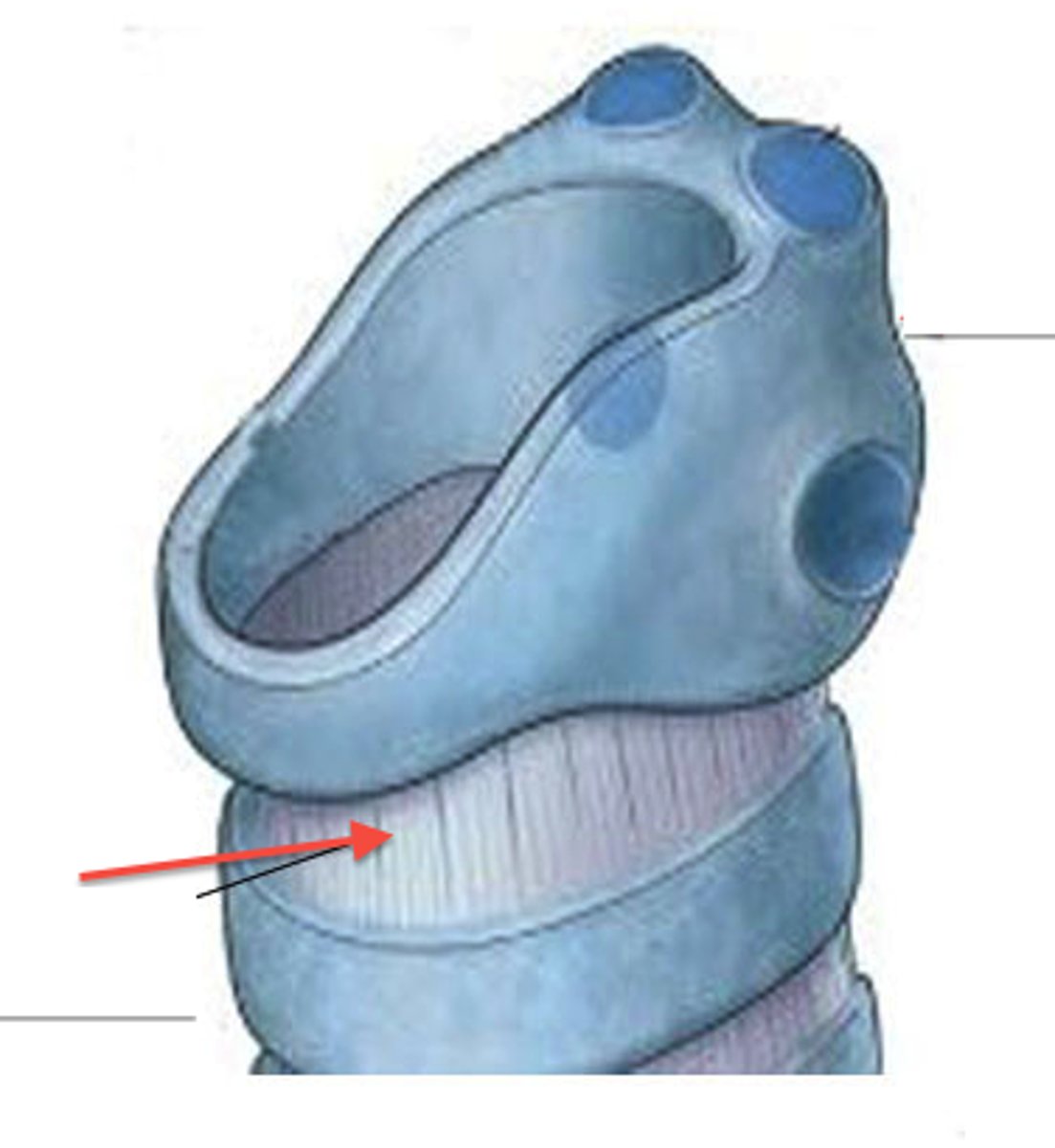
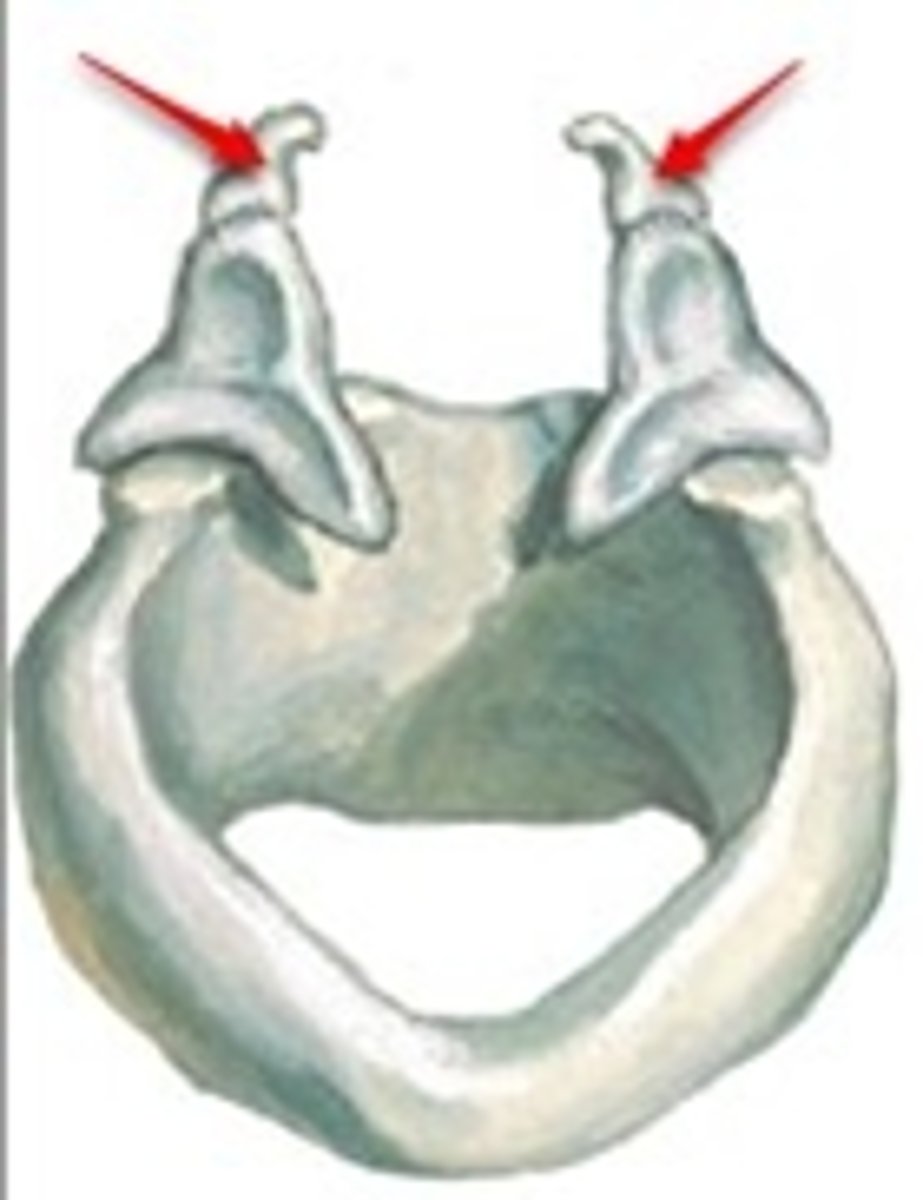
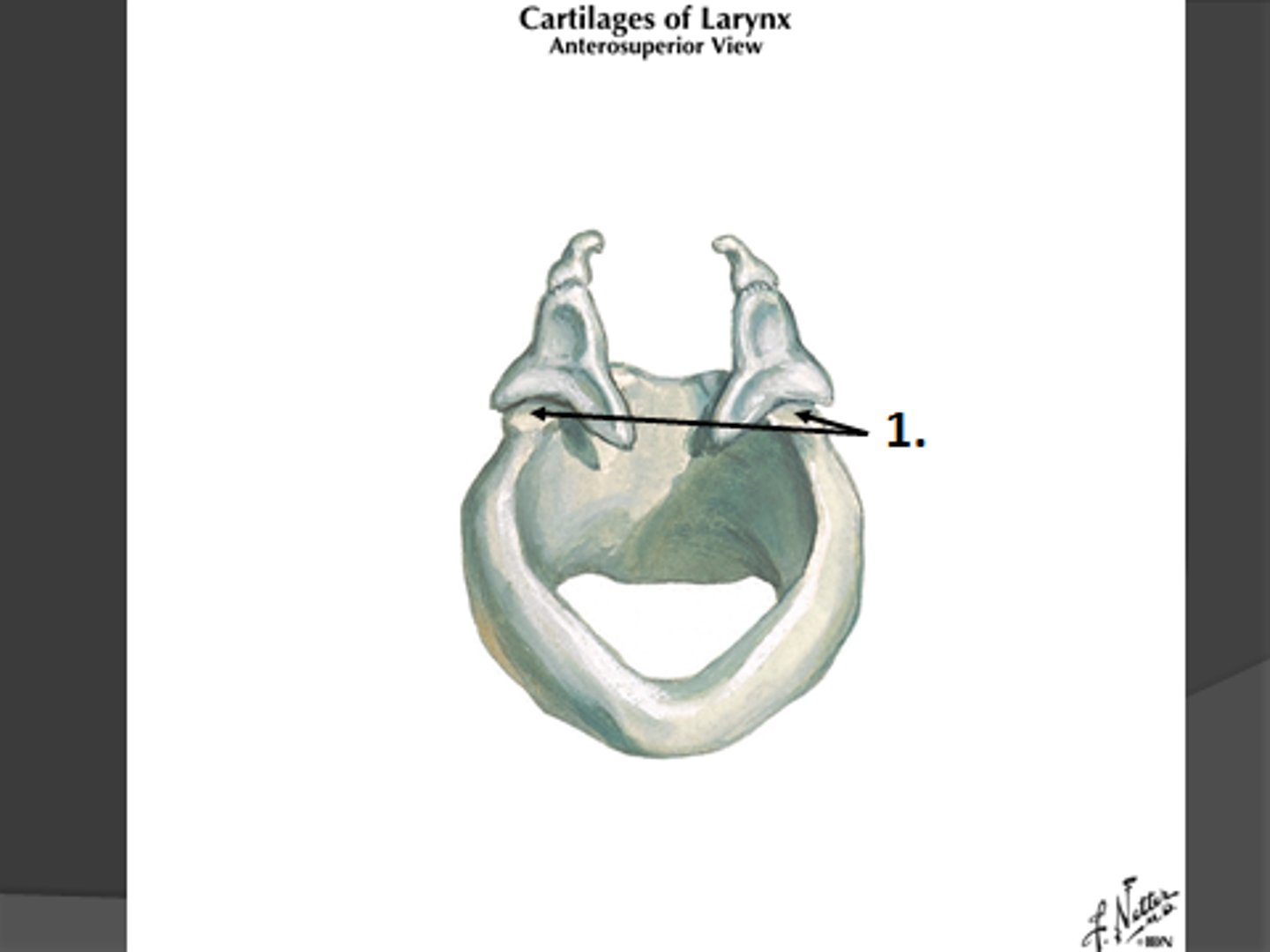
arytenoid
paired cartilages that forms the pyramidal structure on the superior and posterior surface of the cricoid. the vocal process extends out of this structure and is the attachment for the vocal folds
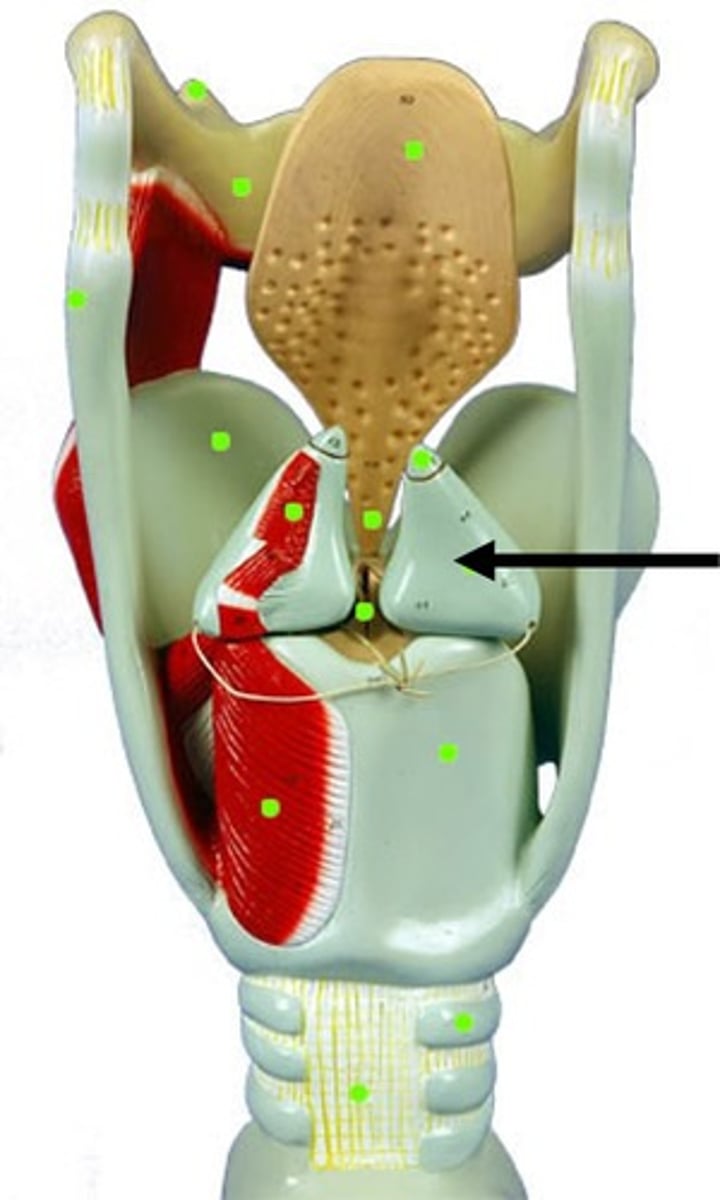
cuneiform cartilages
paired cartilages which are small rods of cartilage that aid in stiffening the aryepiglottic folds
corniculate cartilages
paired cartilages which are like horns or teeth on the top of the pyramid of the arytenoids. Create supraglottic constriction
cricoarytenoid joints
joints involved in adduction and abduction, medially, laterally, anteriorly and posteriorly of the vocal folds
cricothyroid joints
joints involved in lengthening and shortening the vocal folds to change pitch
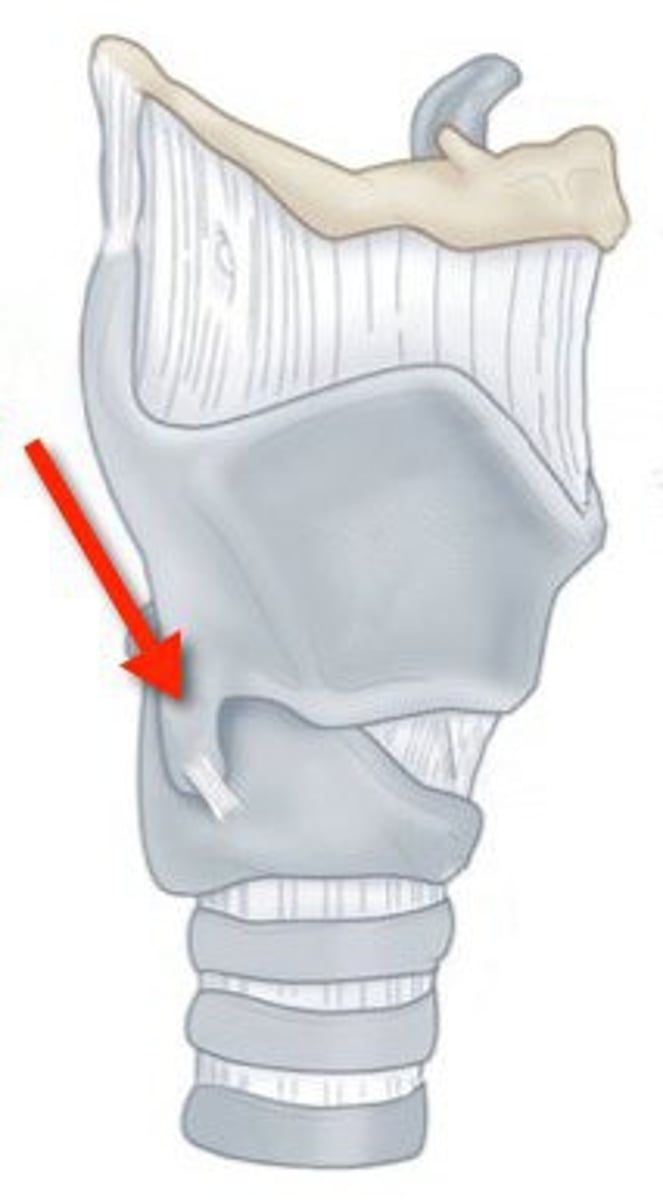
aryepiglottic folds
the tissue and muscle surrounding the epiglottis, where contracted it pulls the epiglottis posteriorly closing the larynx
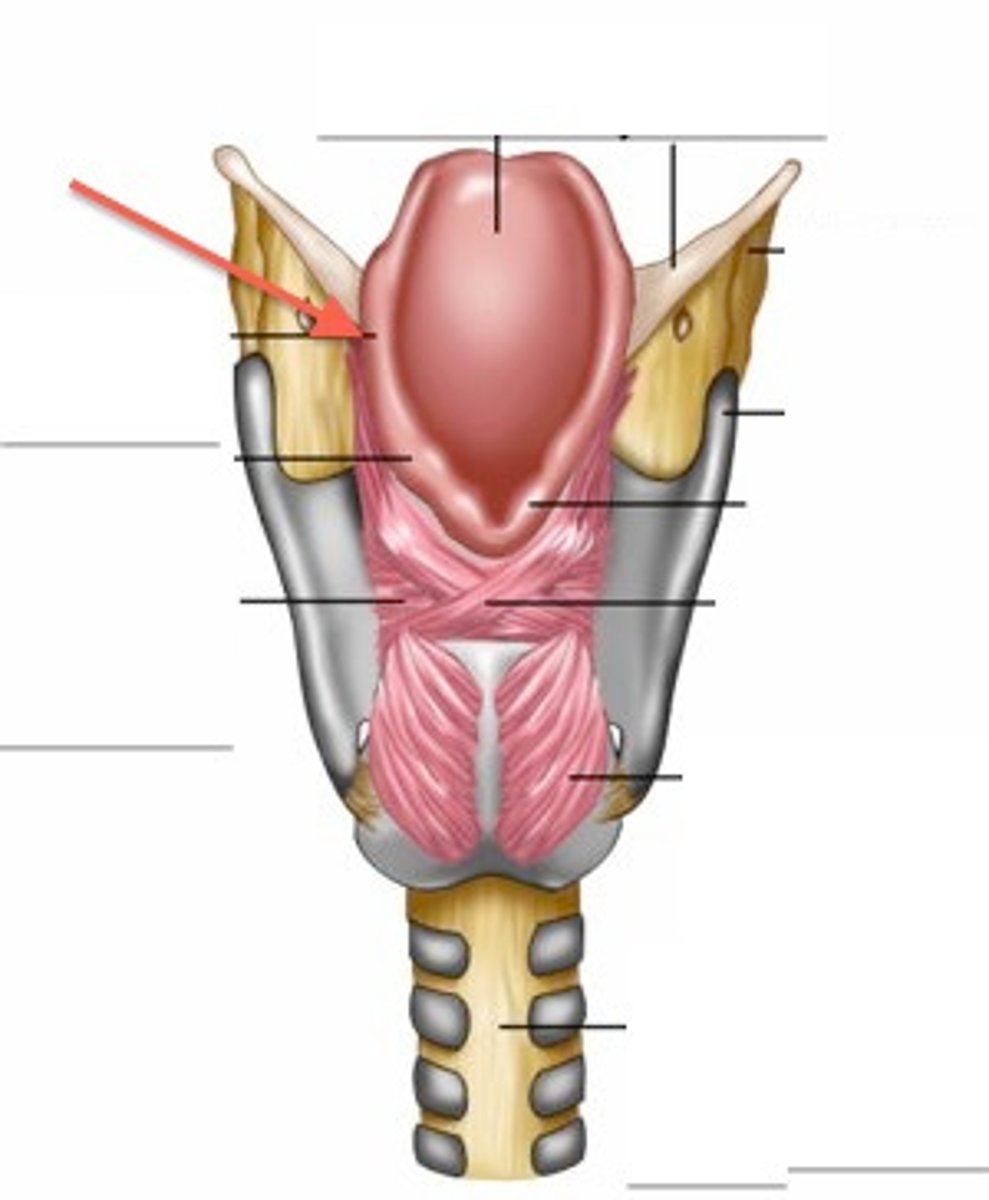
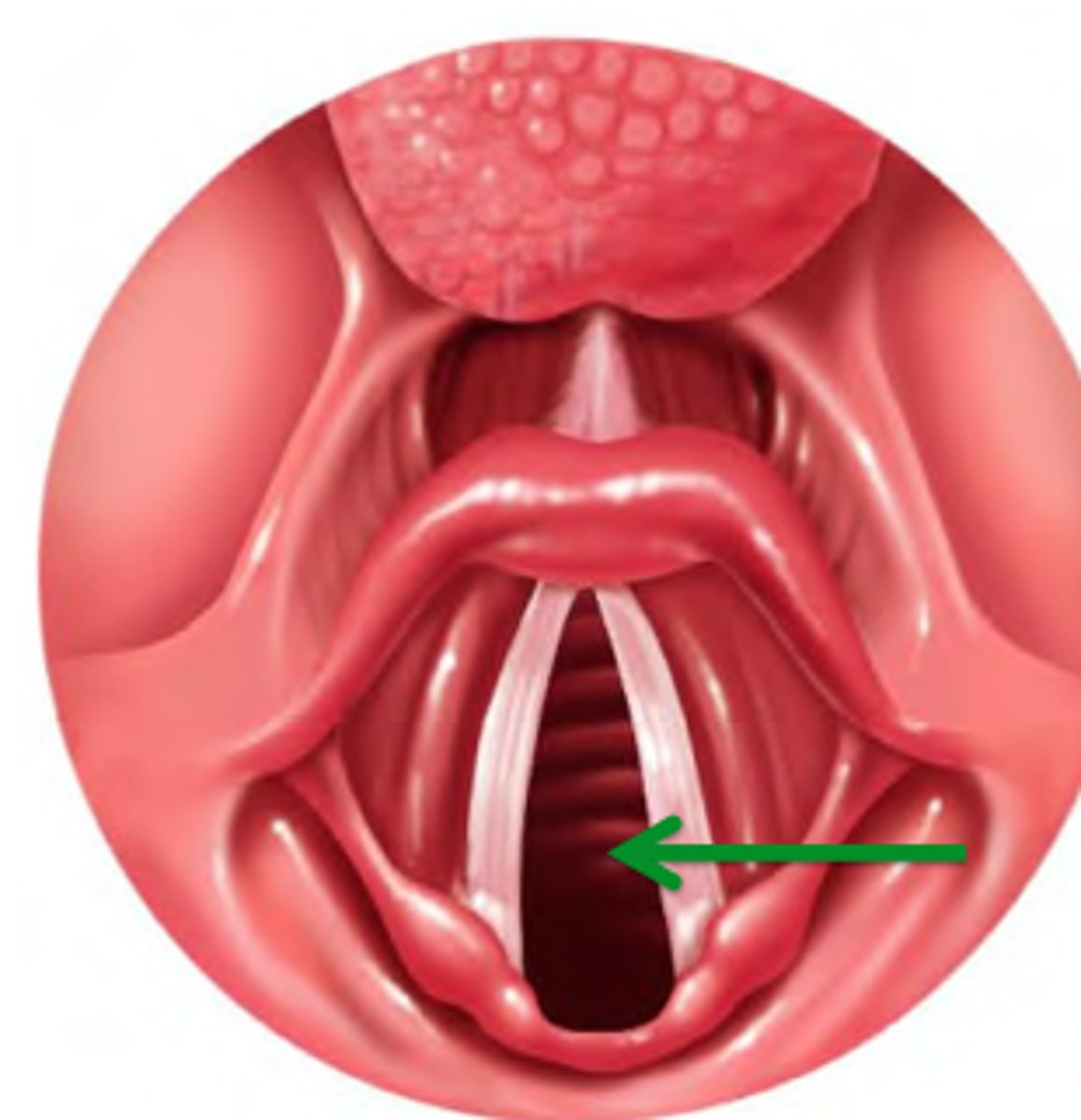
false vocal folds
AKA ventricular or vestibular folds. close during swallowing.
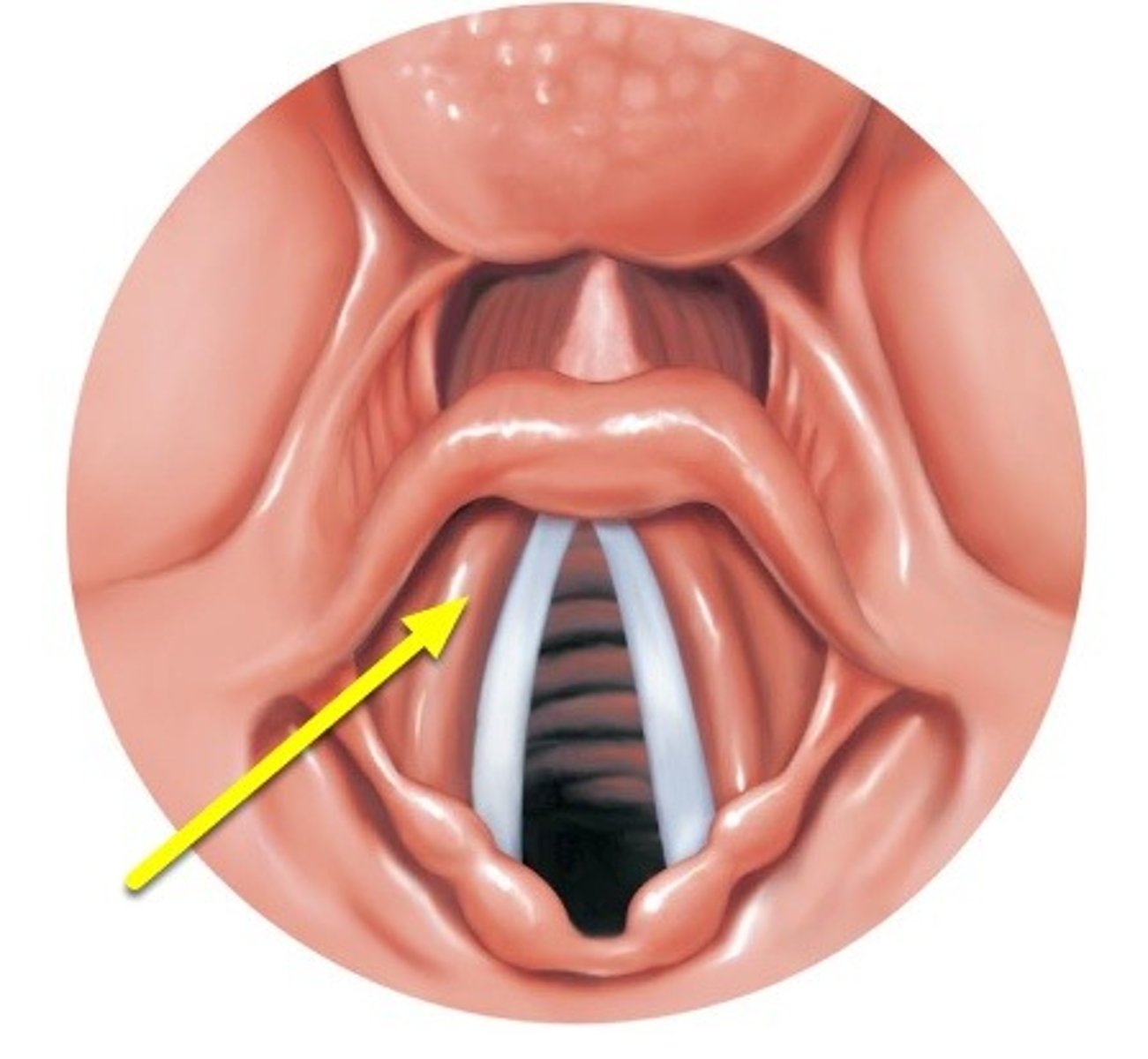
vocal folds
layers of tissue and muscle that vibrate to create phonation, attach anteriorly to the thyroid notch
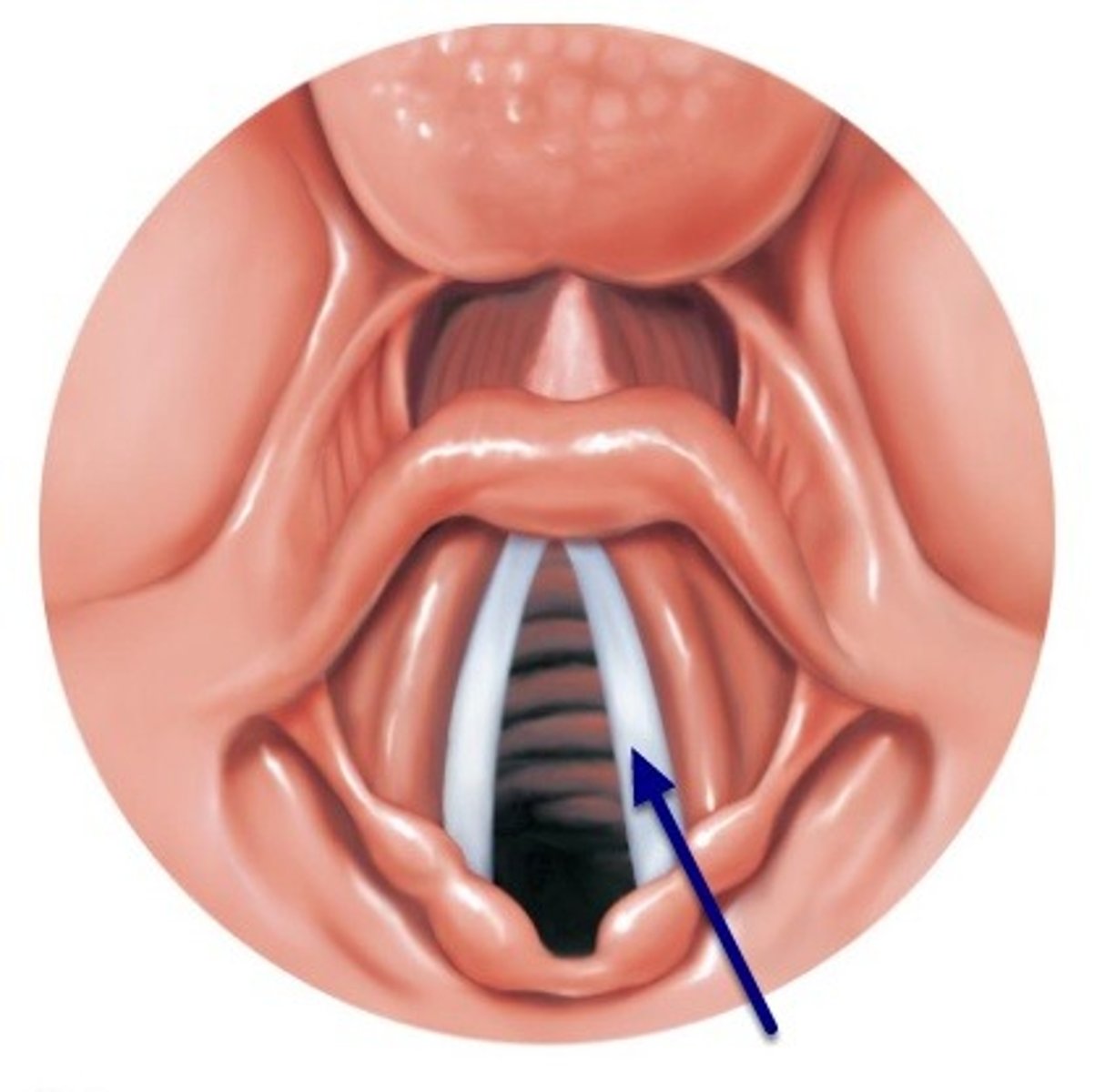
anterior commisure
the location where the vocal fold attach to the thyroid
epithelium
the layer of cells most superficial on the vocal folds
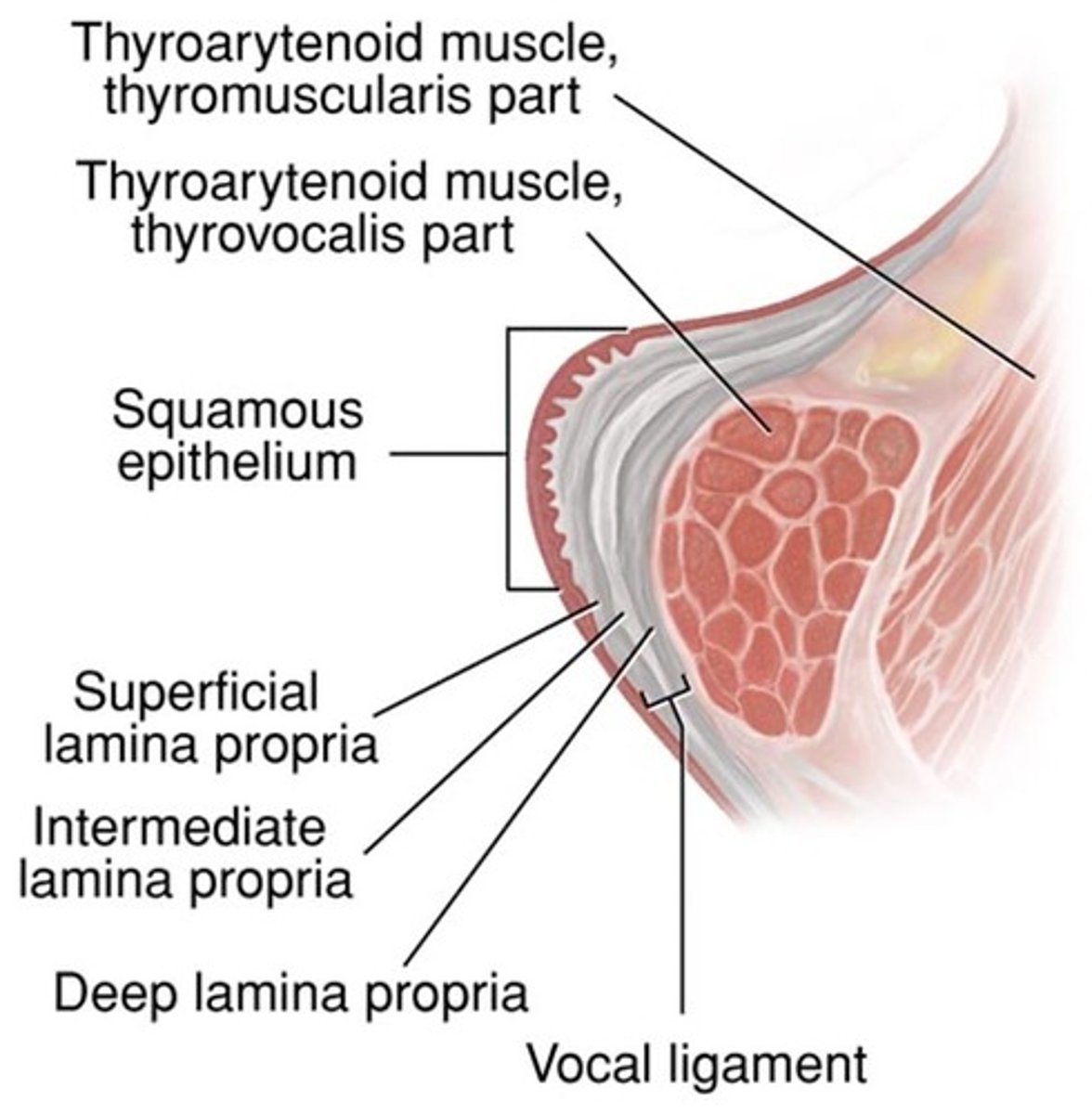
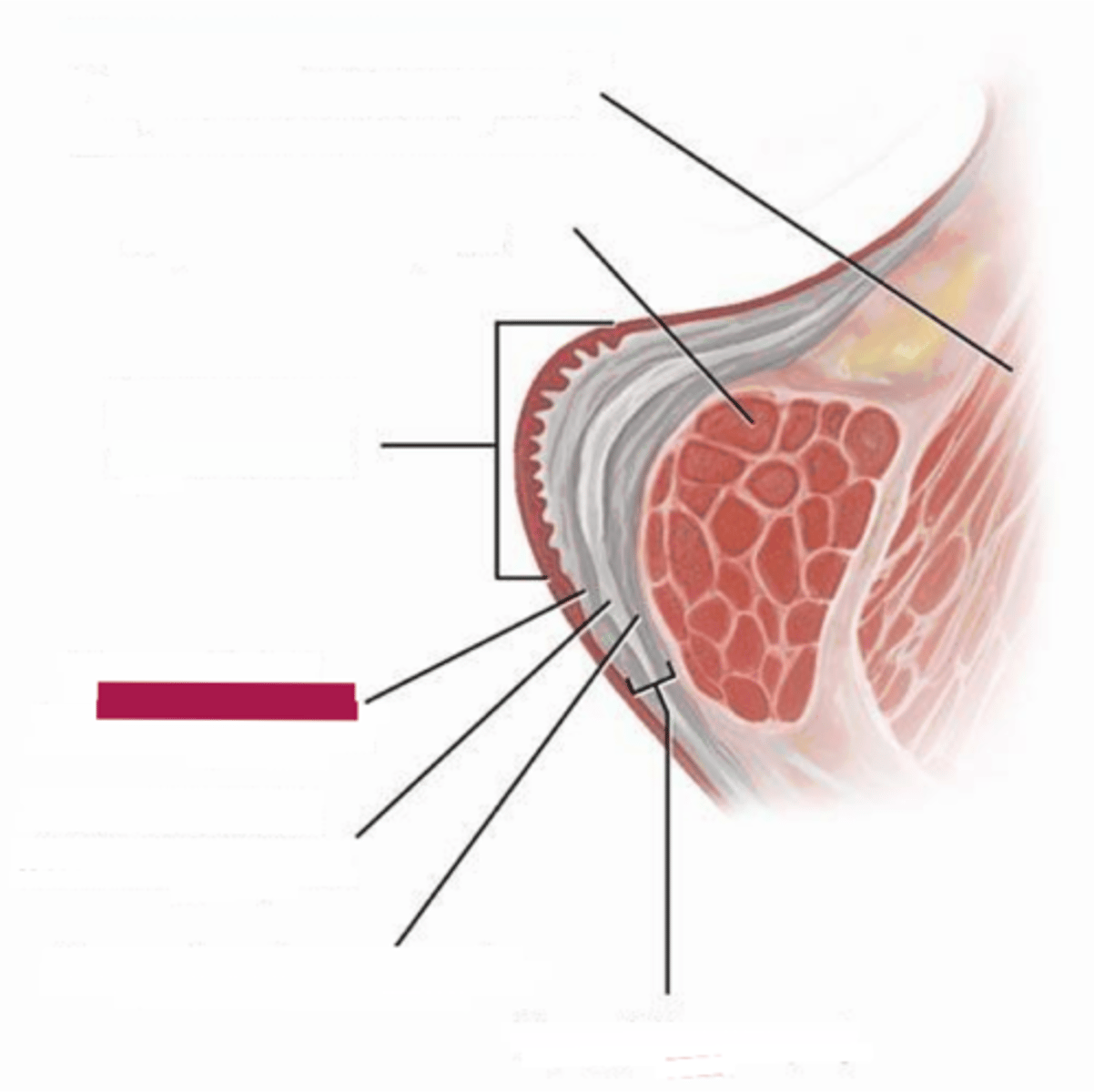
superficial lamina propria
the superficial layer of the three middle layers of the vocal folds
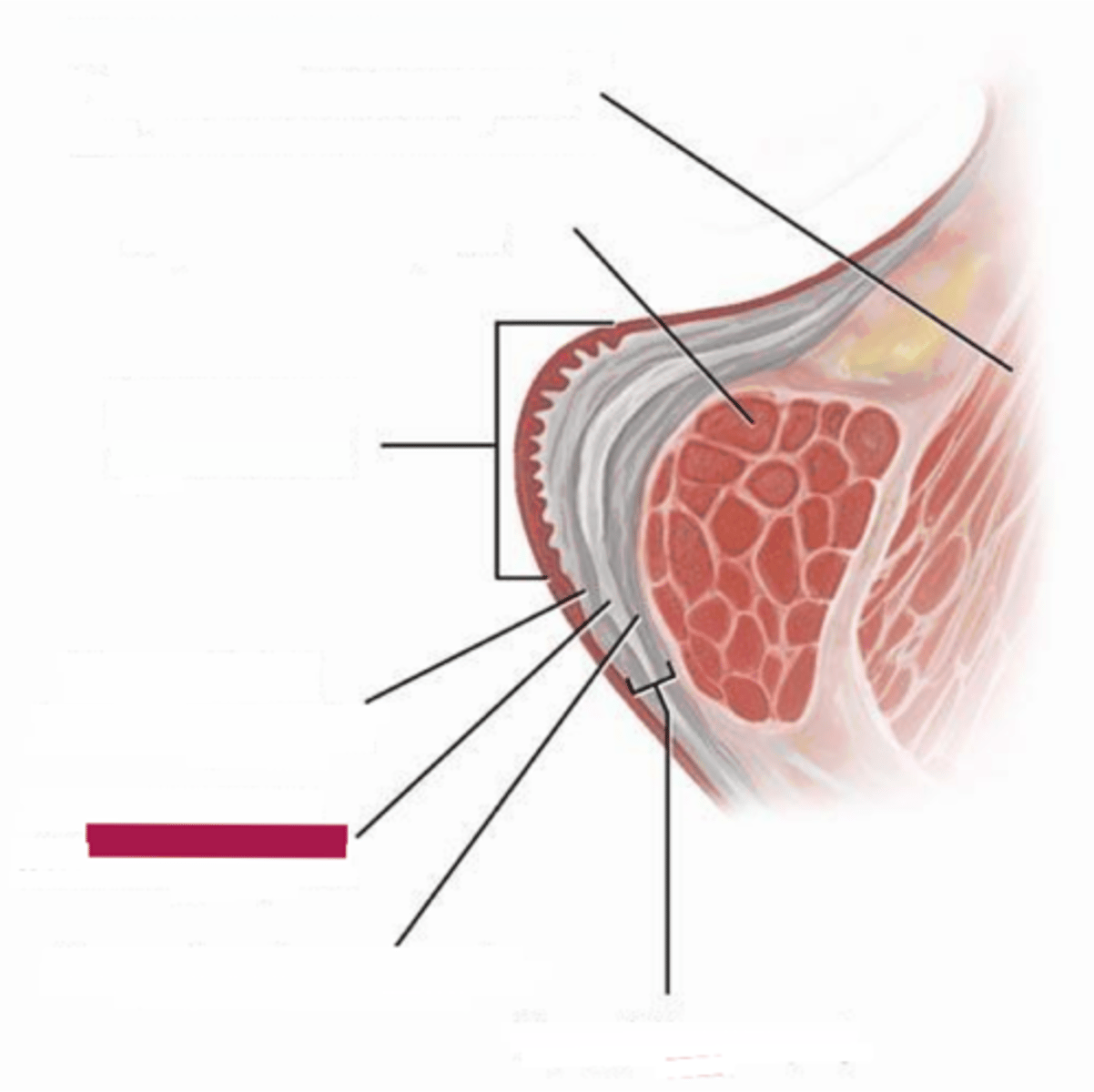
intermediate lamina propria
the middle layer of the three middle layers of the vocal folds
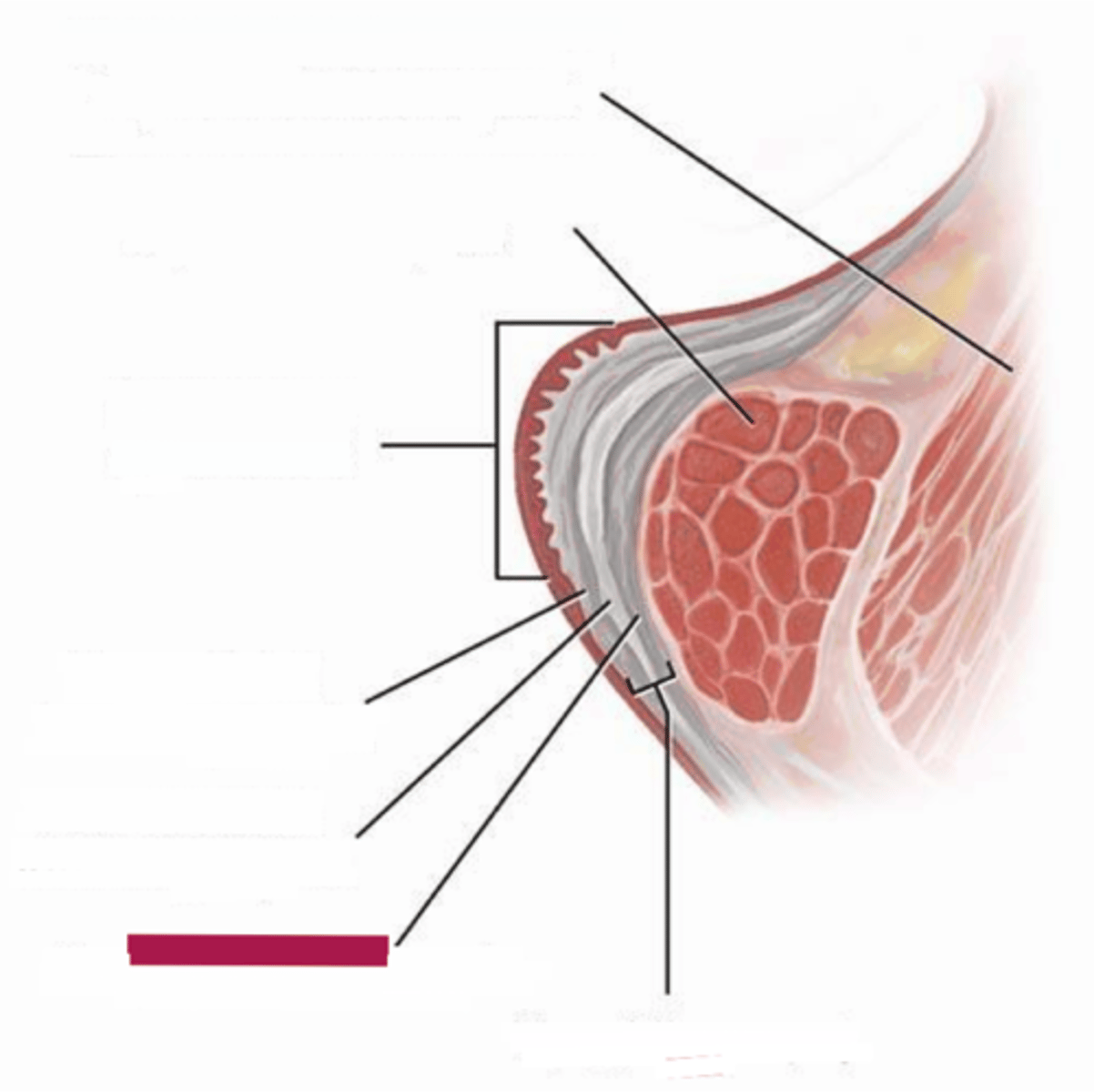
deep lamina propria
the deep layer of the three middle layers of the vocal folds
vocalis
a muscle that is the most deep layer of the lamina propria
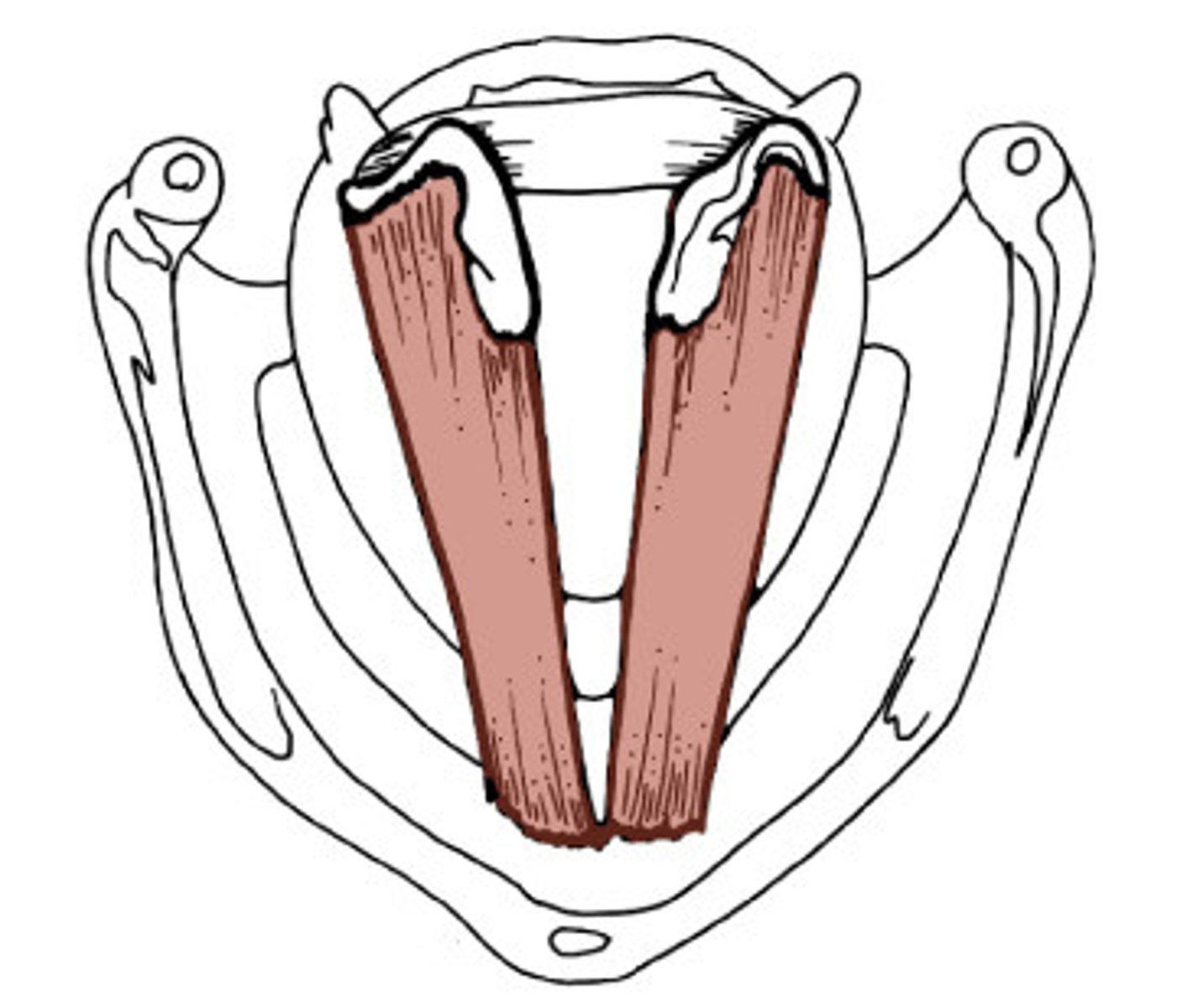
glottis
the space between the vocal folds
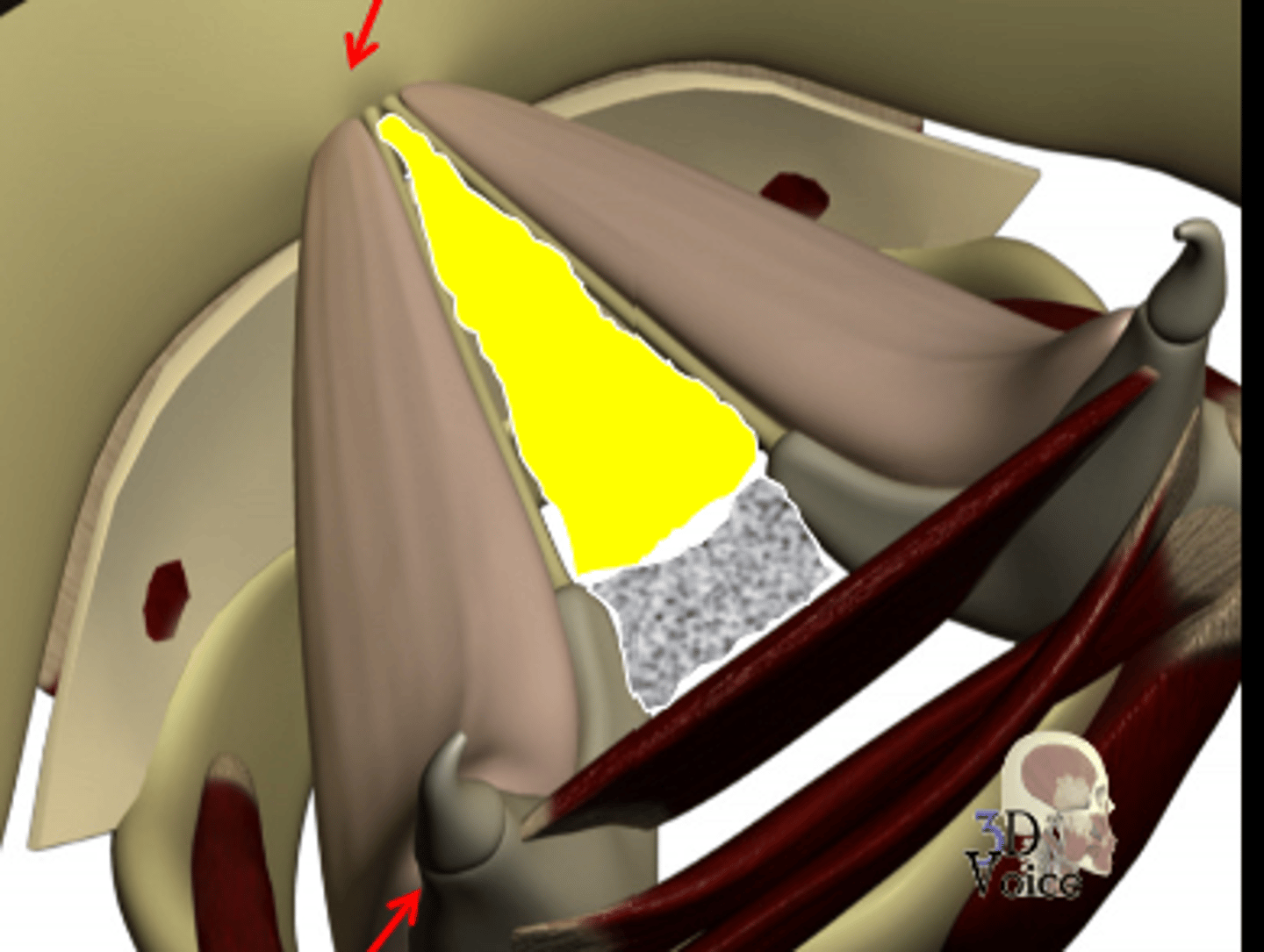
membranous glottis
the anterior space between the vocal ligament, yellow bit

cartilaginous glottis
the posterior space between the arytenoids, gray bit
laryngeal cavities
supraglottal cavity, subglottal cavity, laryngeal ventricles
supraglottal cavity
the large cavity above the vocal folds
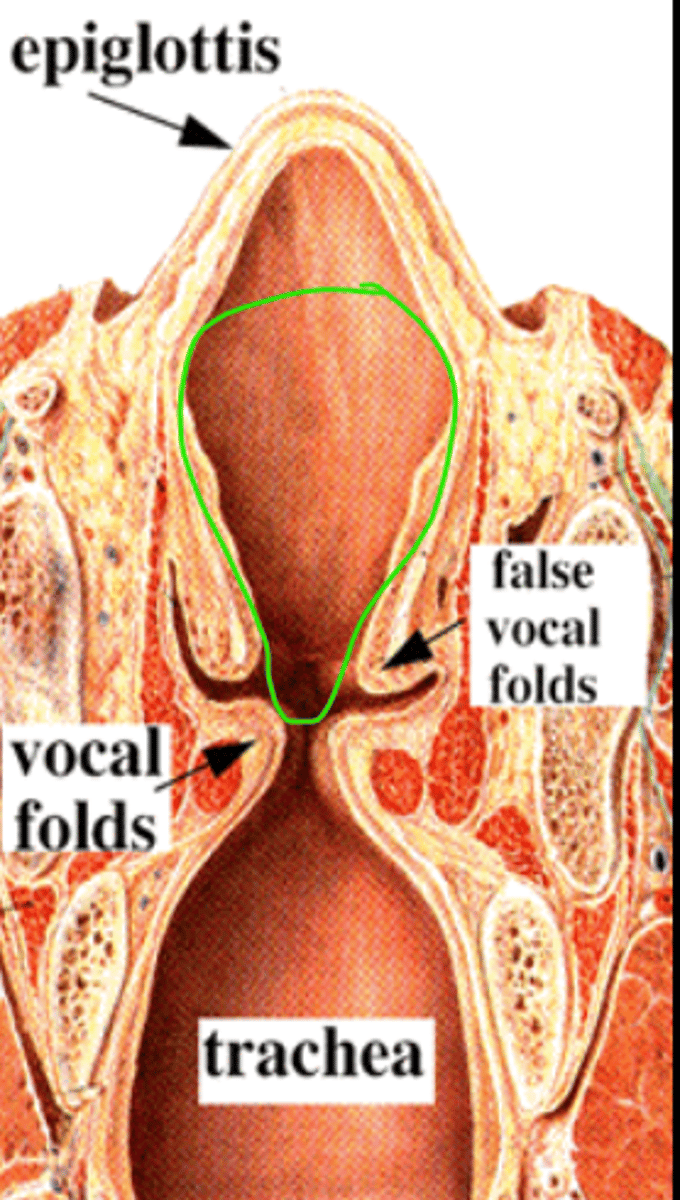
subglottal cavity
the cavity below the vocal folds and above the first tracheal ring
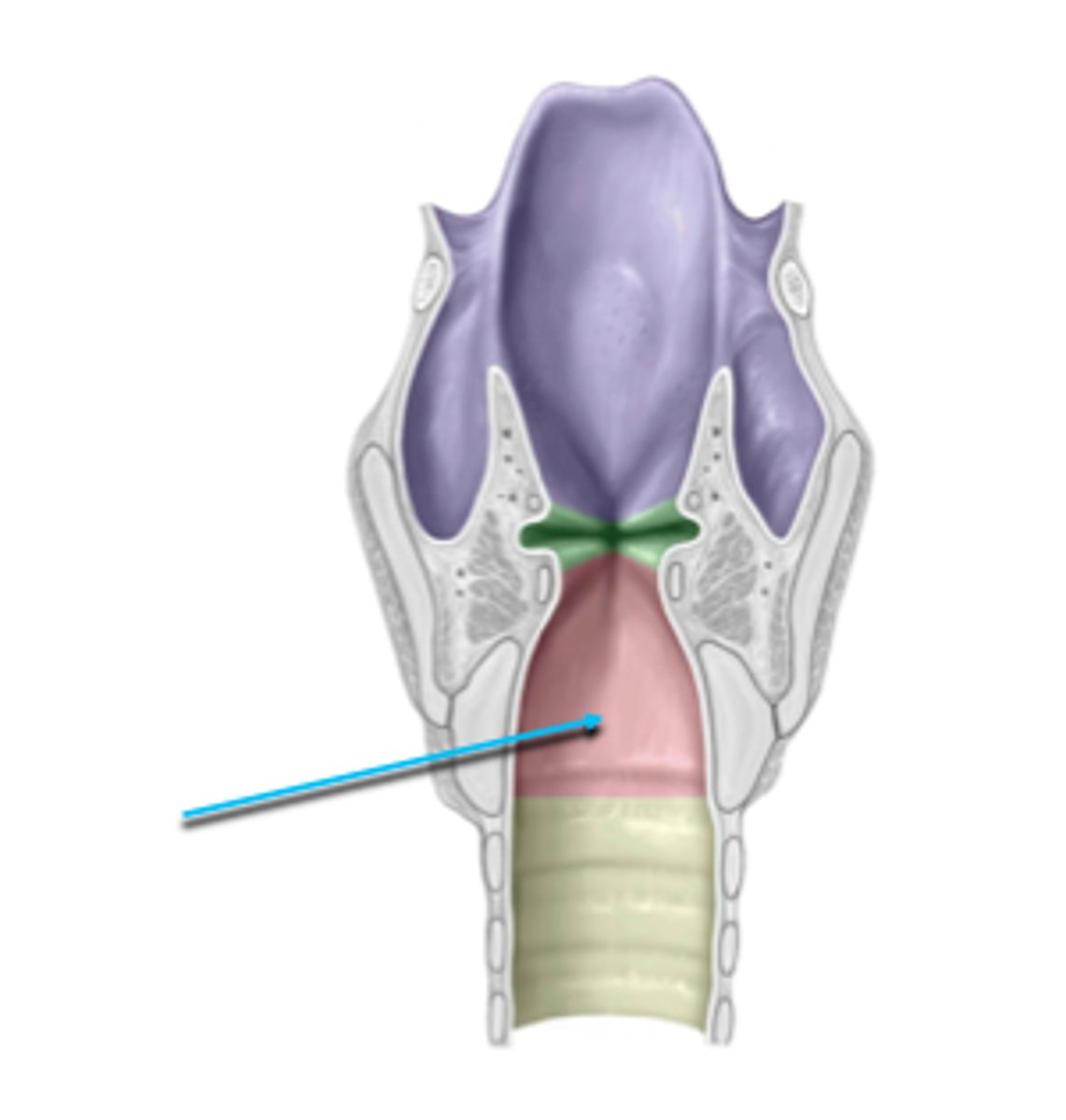
laryngeal ventricles
the small cavity on the lateral sides of the false vocal folds, there are glands here the produce fluid to lubricate the vocal folds
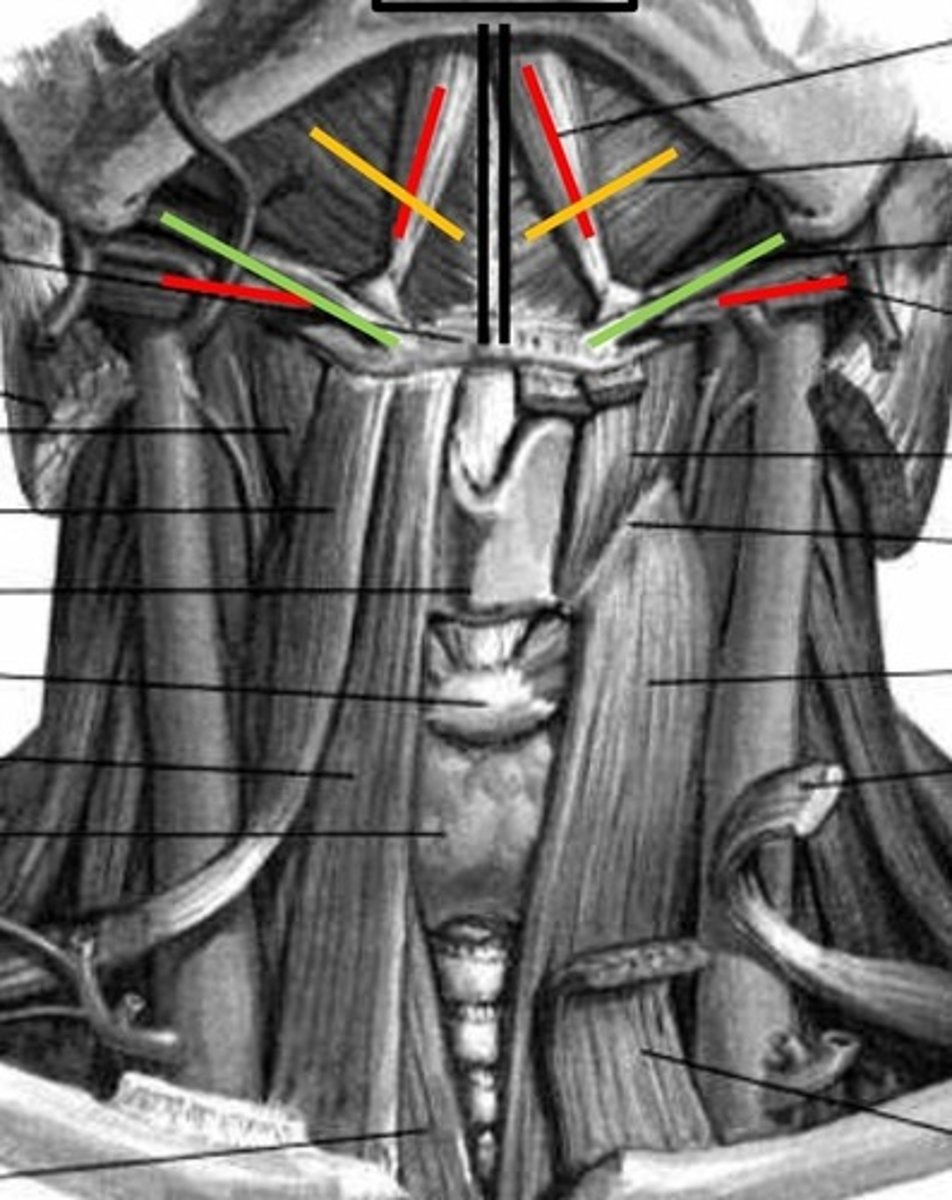
suprahyoids
extrinsic muscles: digastric, stylohyoid, mylohyoid, geniohyoid
digastric
anterior and posterior belly, red lines
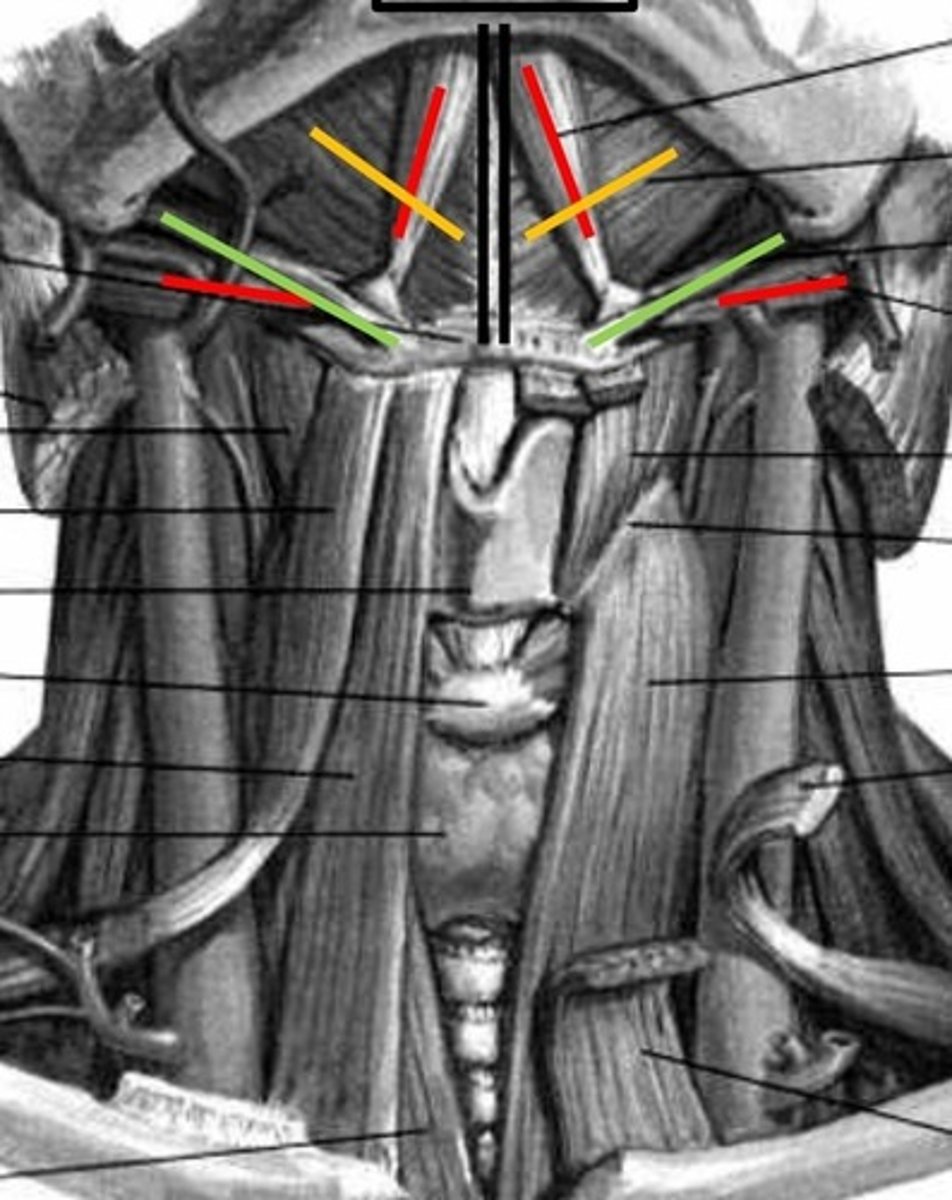
stylohyoid
Green lines
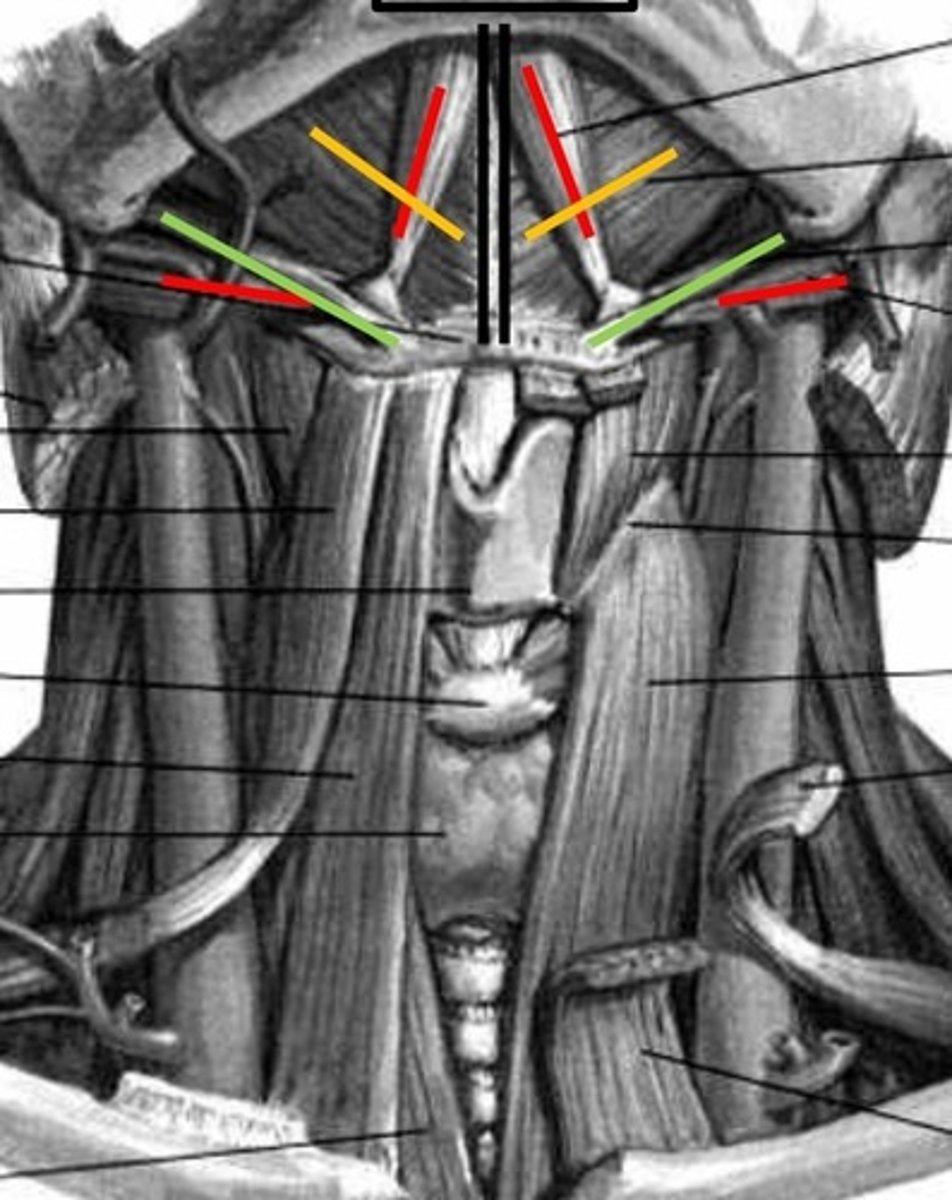
mylohyoid
yellow lines
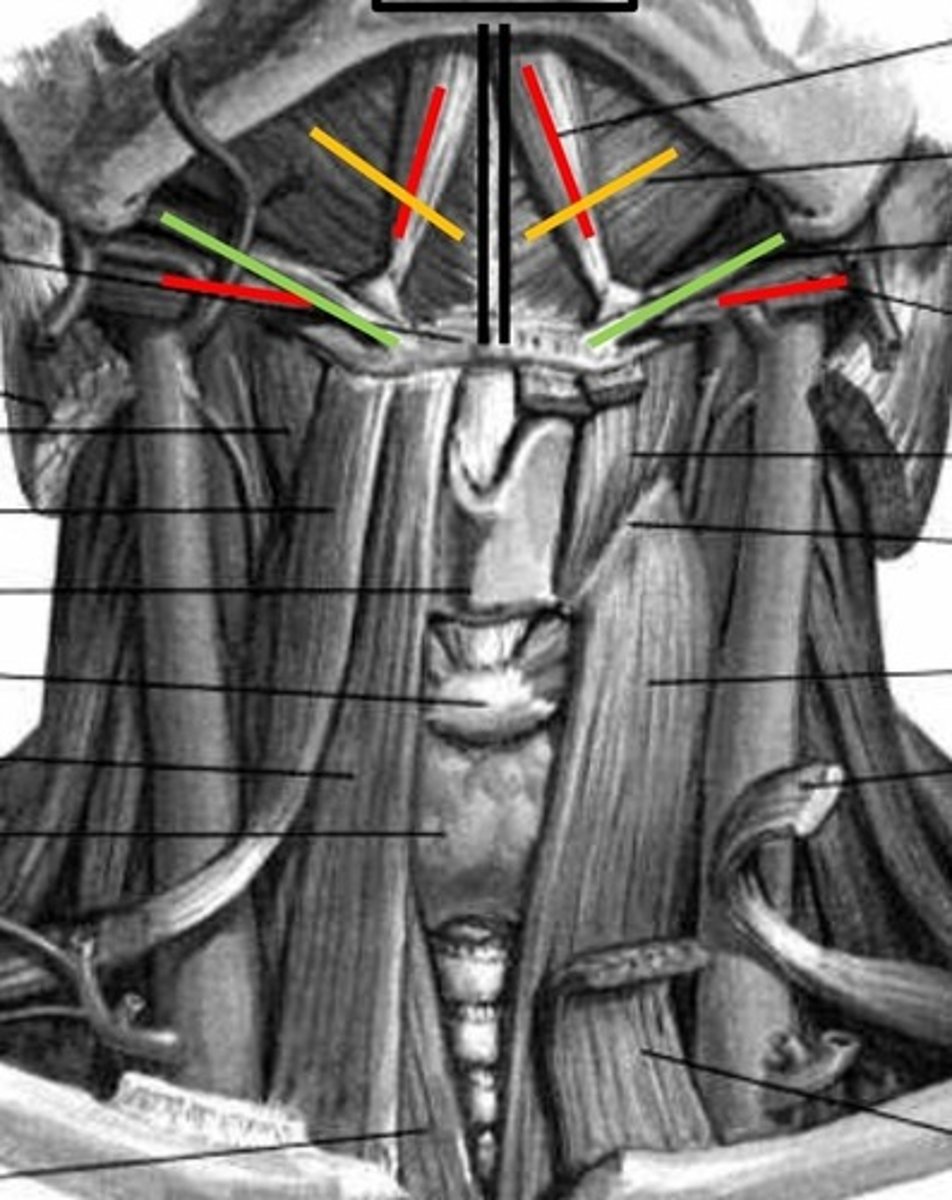
Geniohyoid
black lines
infrahyoids
extrinsic muscles: sternohyoid, omohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid
sternohyoid
Green lines
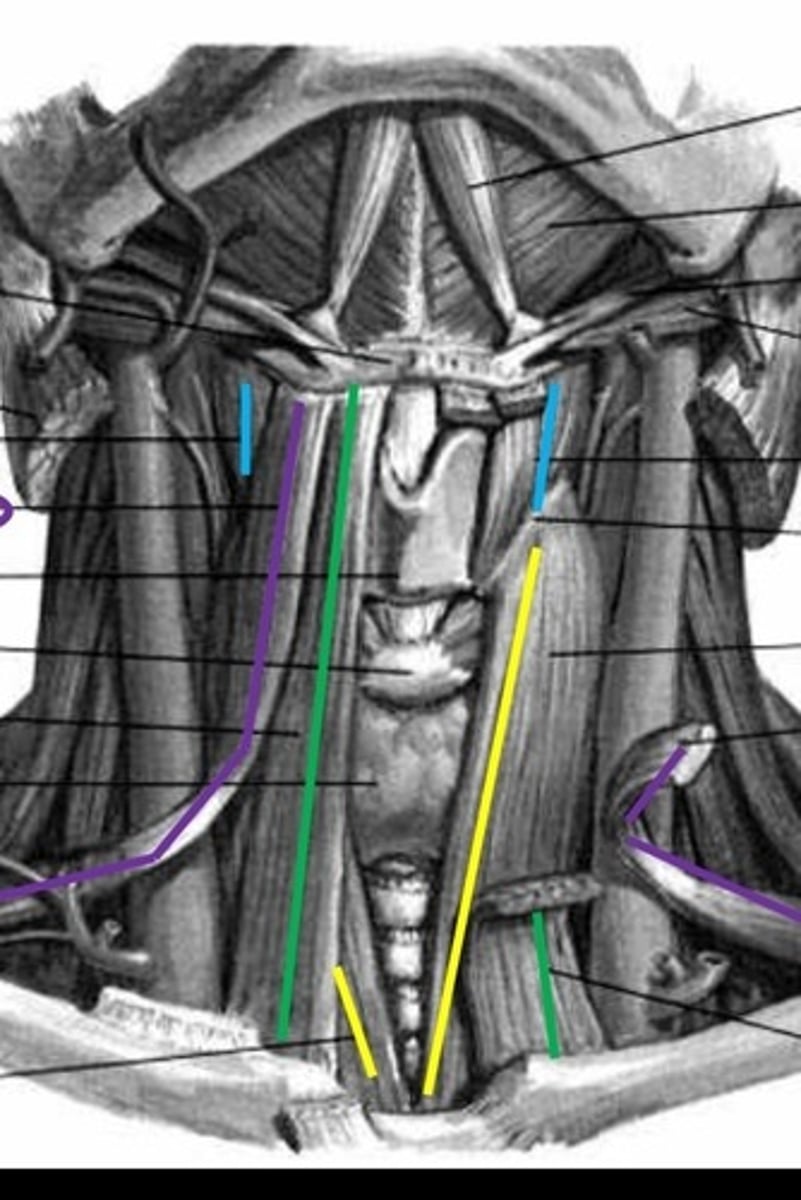
omohyoid
purple lines
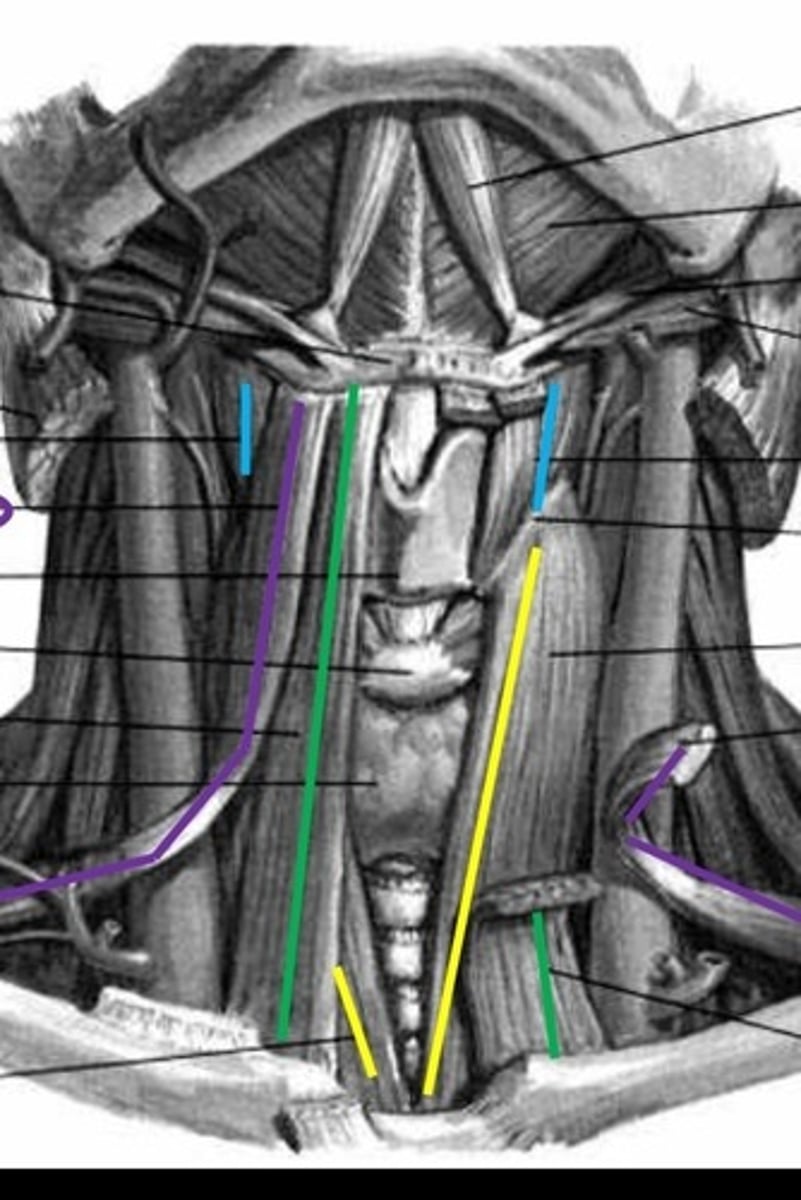
sternothyroid
yellow lines
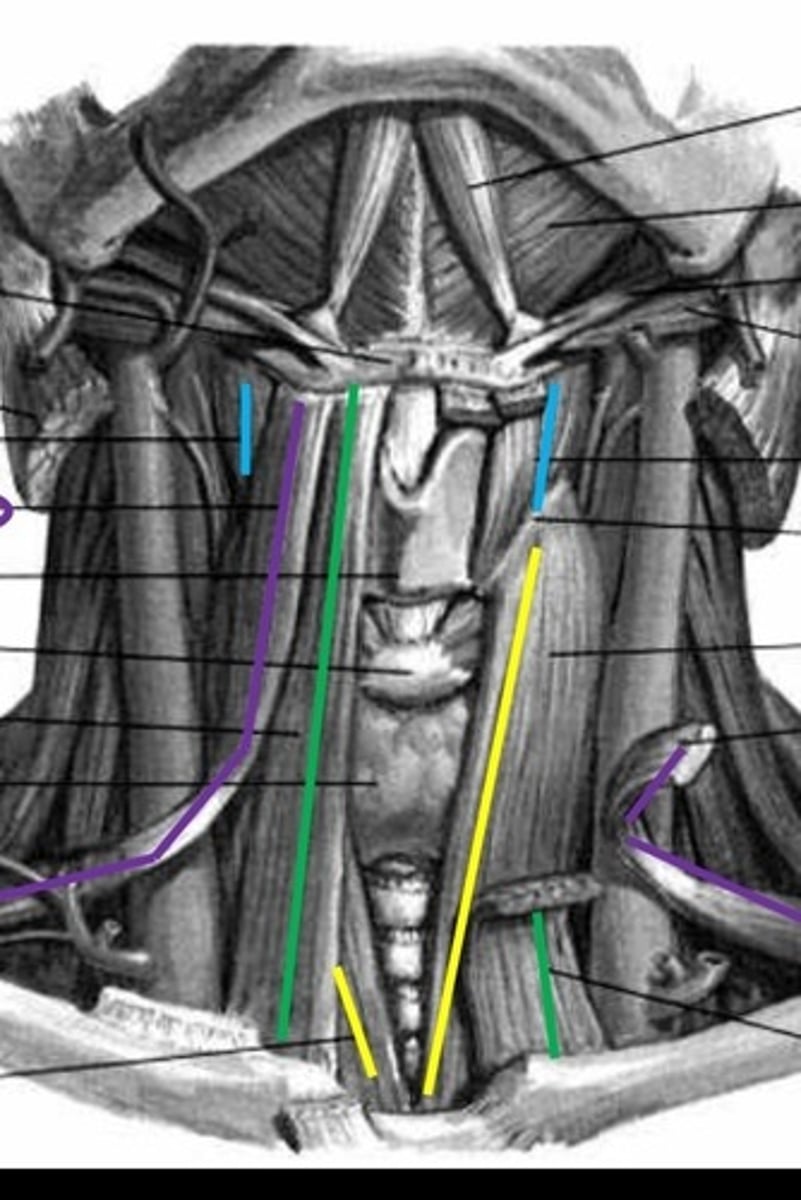
thyrohyoid
blue lines
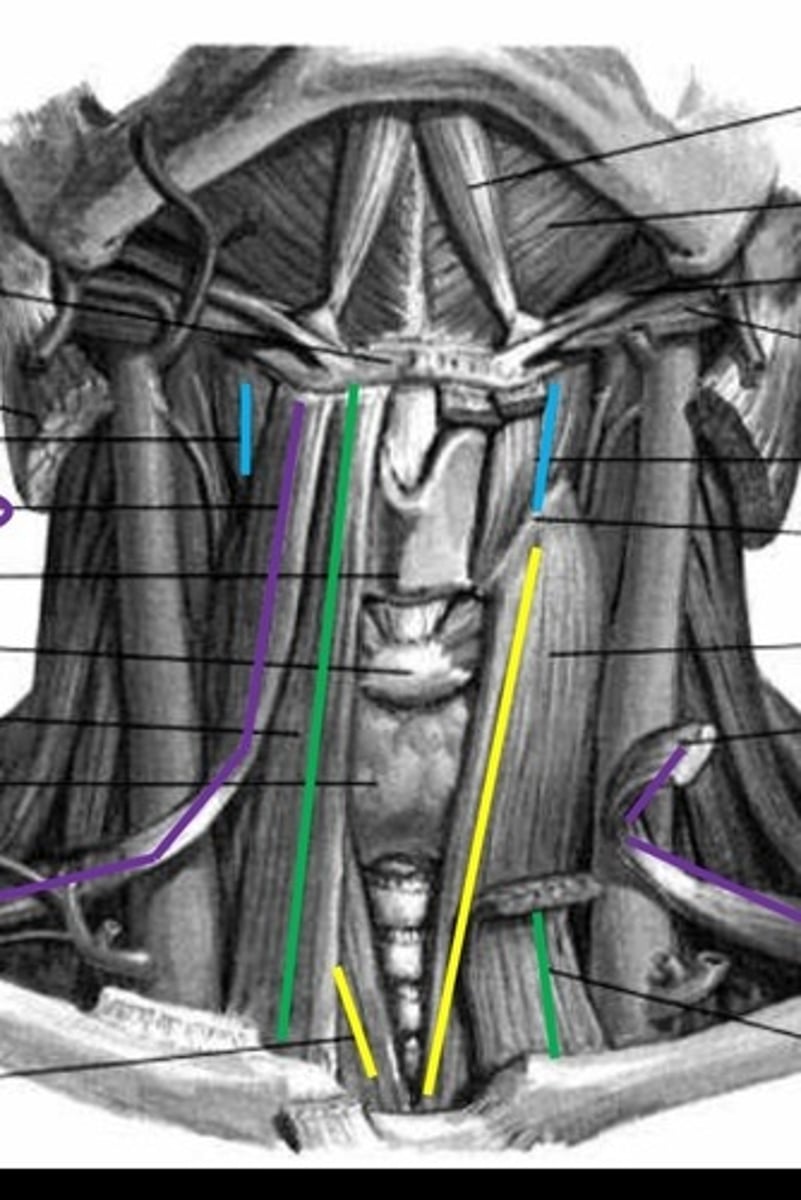
lateral cricoarytenoids
red
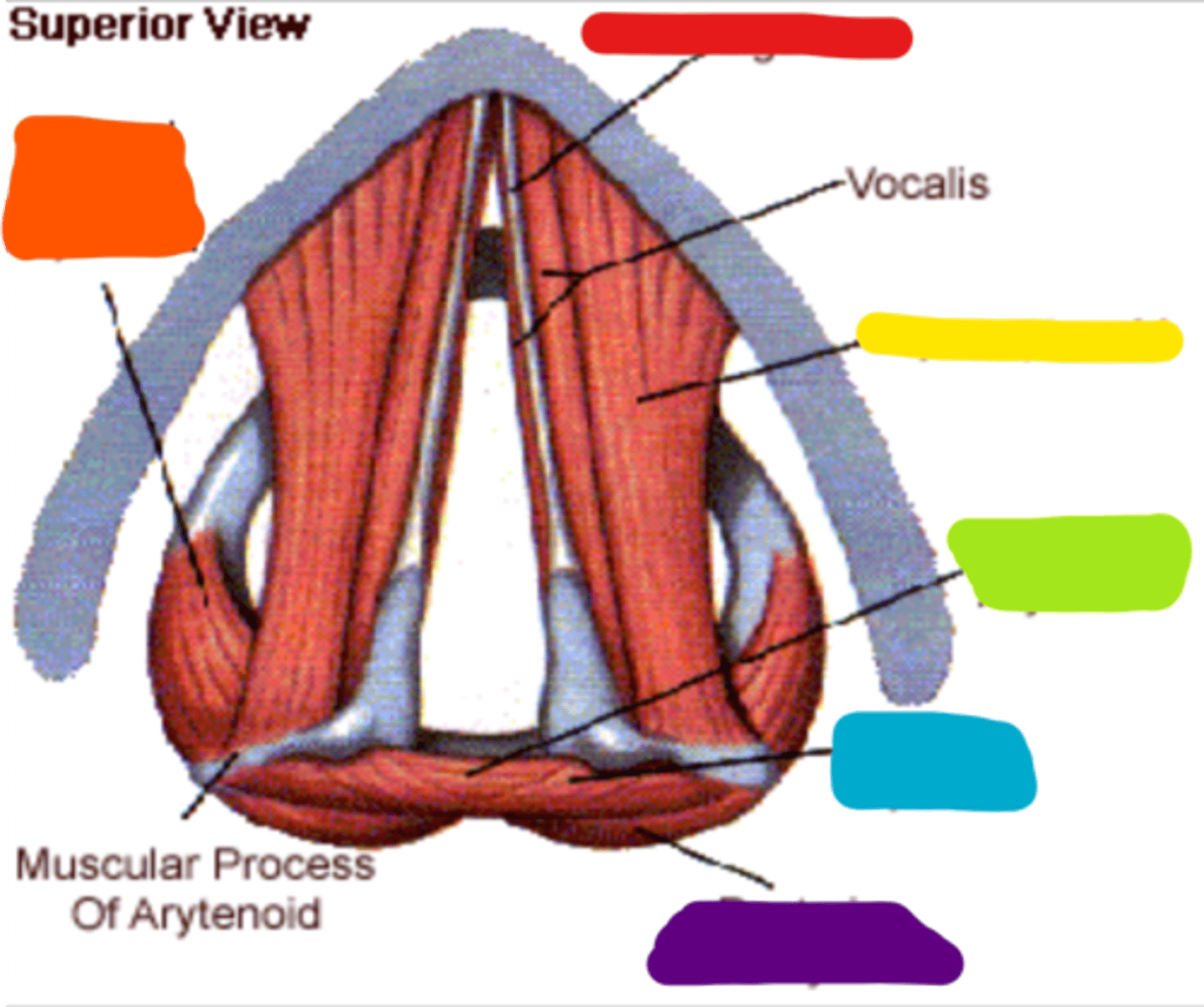
posterior cricoarytenoids
purple
transverse interarytenoid
ɡreen
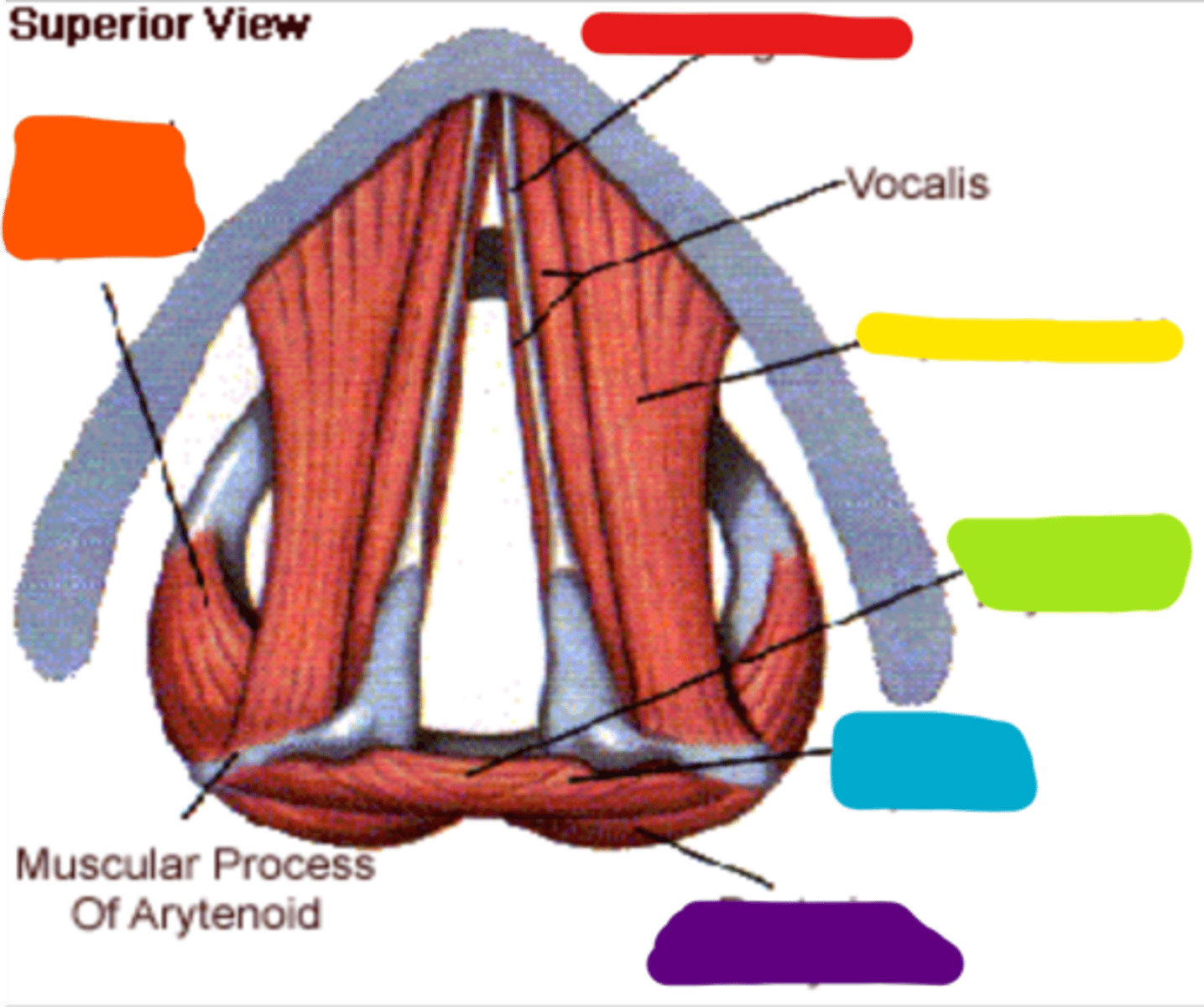
oblique interarytenoids
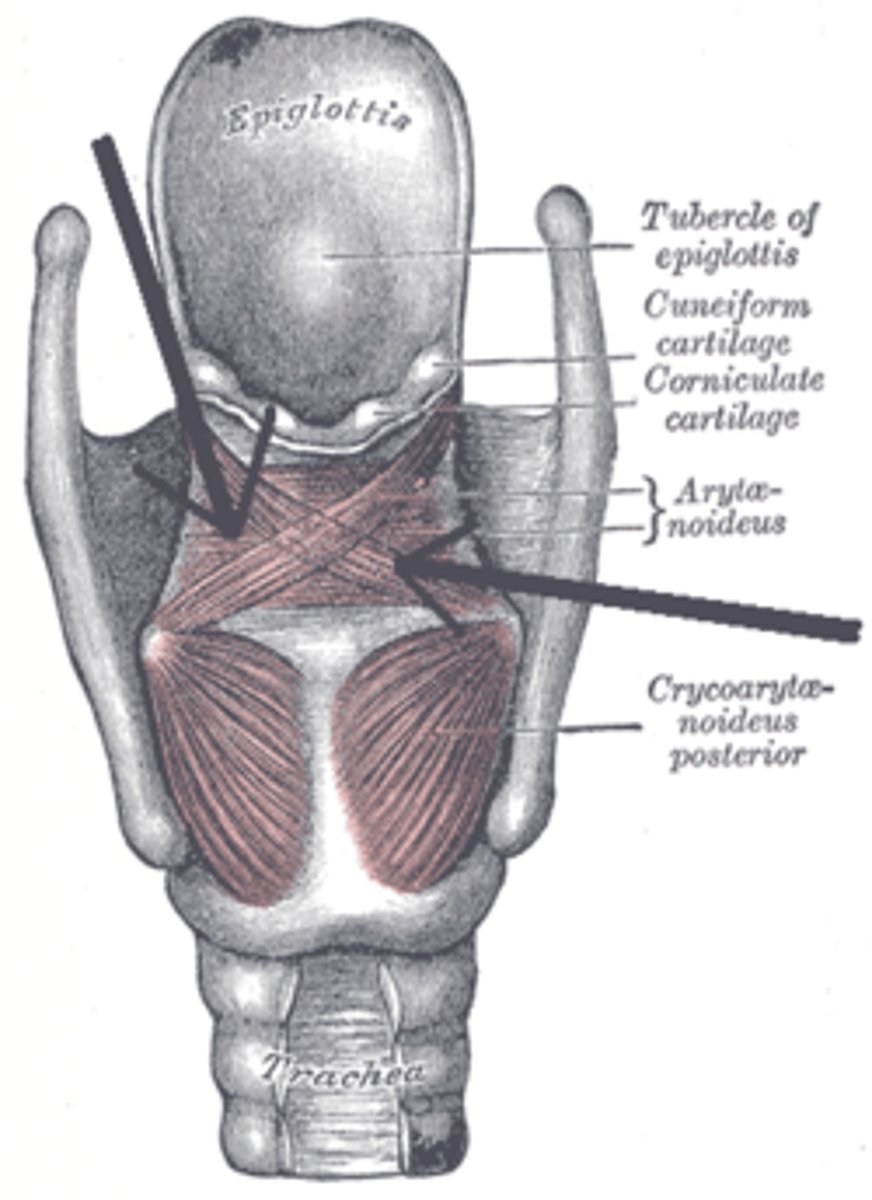
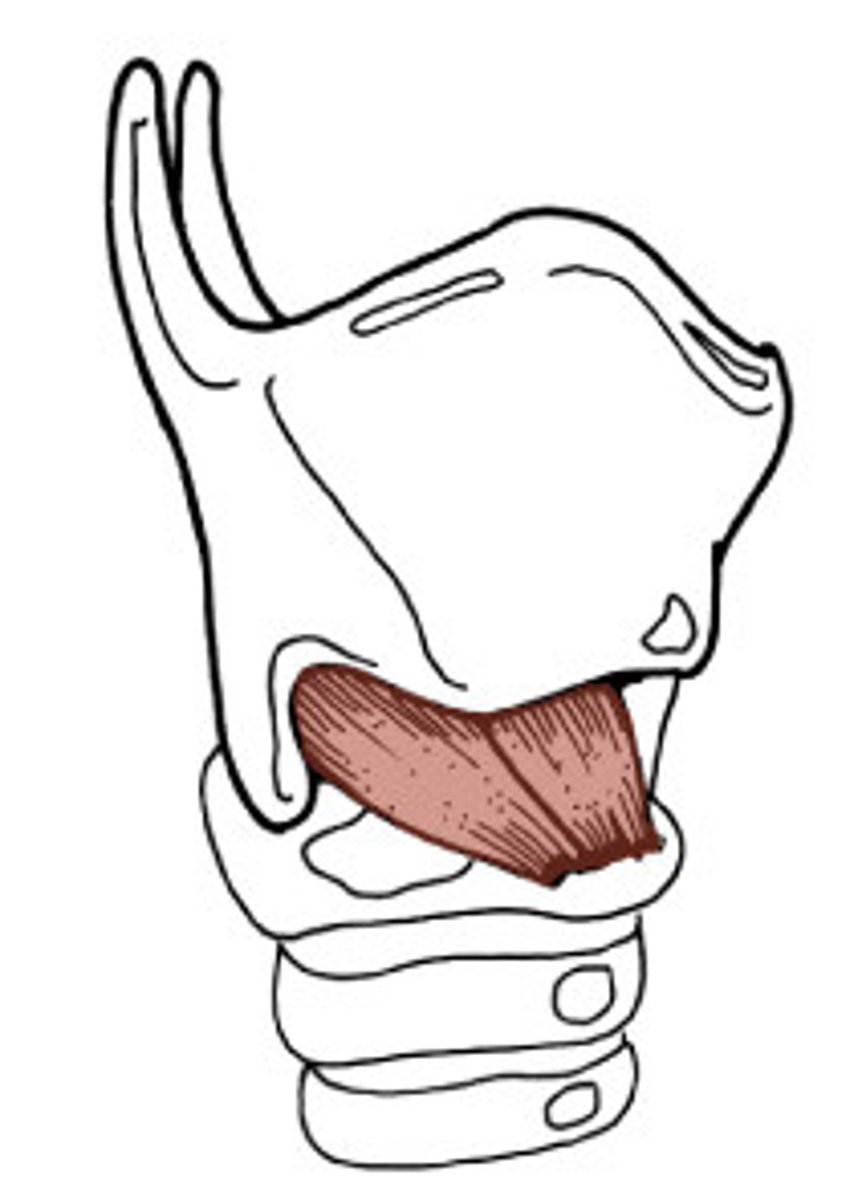
cricothyroids
thyroarytenoids
thyrovocalis and thyromuscularis
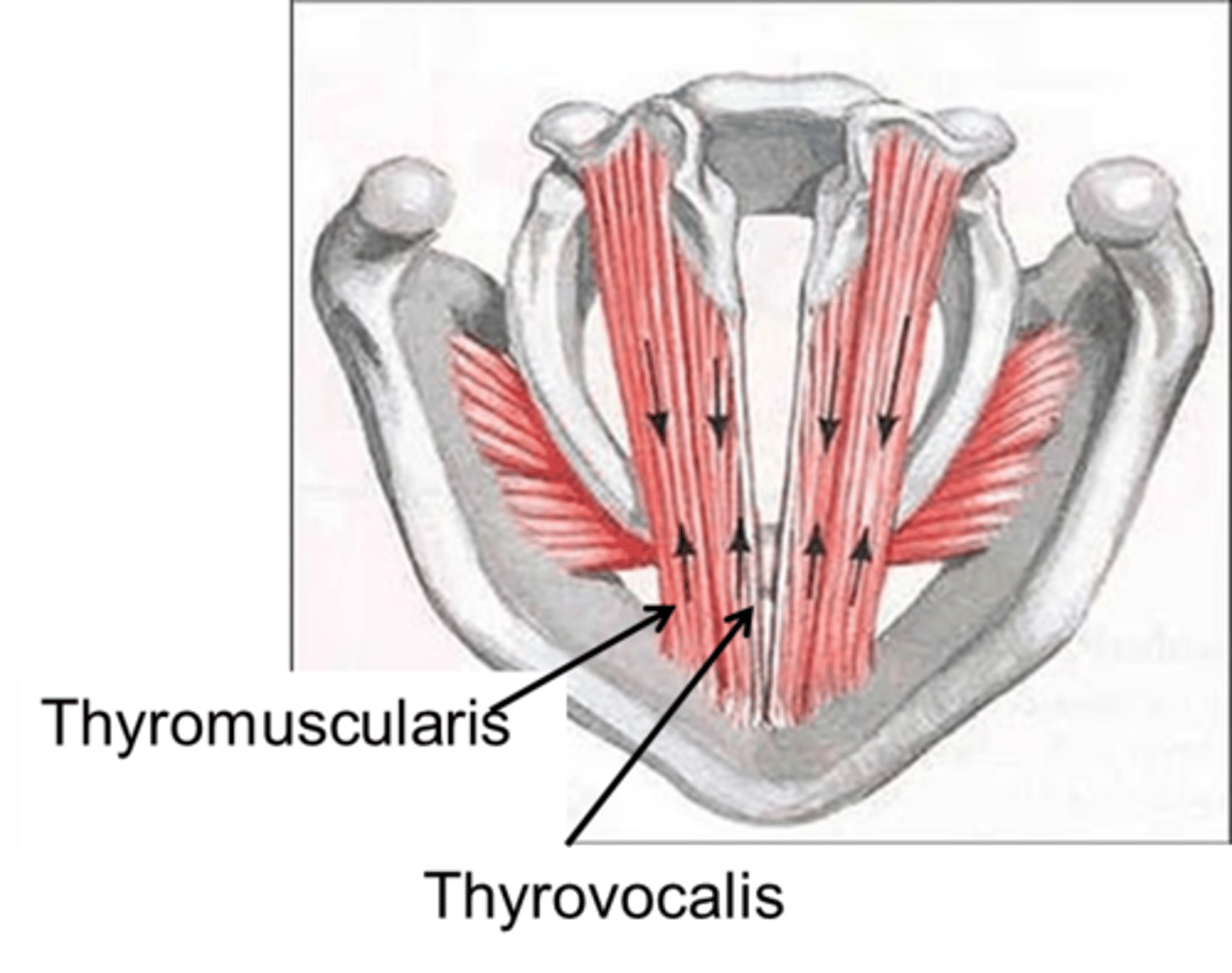
thyrovocalis
ɡreen
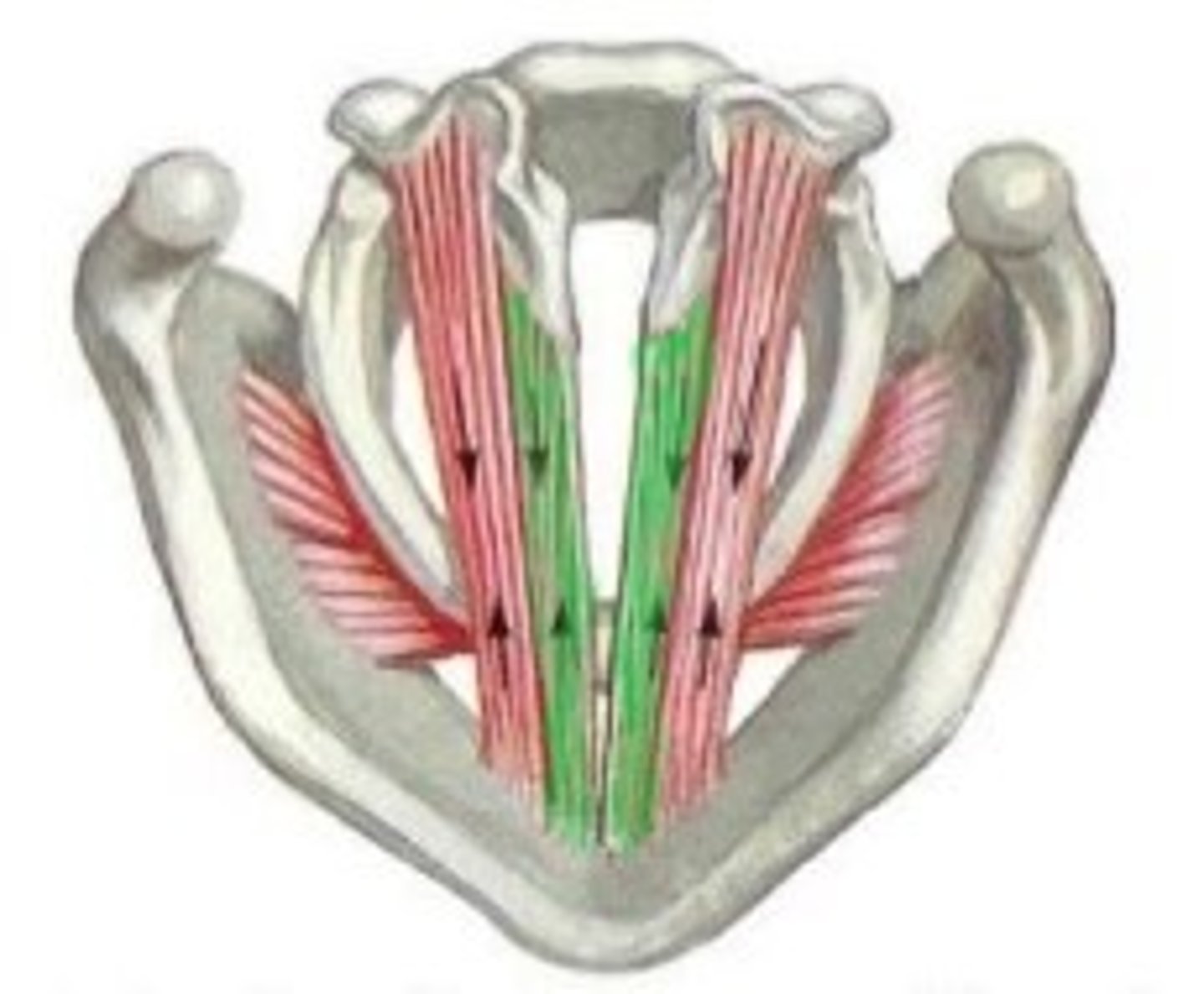
thyromuscularis
recurrent laryngeal nerve
lateral cricoarytenoid, posterior cricoarytenoid, transverse interarytenoid, oblique interarytenoid, thyroaryenoid
superior laryngeal nerve
cricothyroid
vocal fold cover
the 4 most superficial layers of the vocal folds
The Transition
layers 3 and 4 of the vocal folds
vocal folds body
the vocalis muscle. Thicker and denser than the other layers with nerve innervation.
myloelastic
muscle elasticity
aerodynamic
changes in air pressure and airflow
phases of VF vibration
closed, opening, open, closing
closed phase
lateral cricoarytenoid muscles and internal arytenoid muscles to close the VF and subglottic pressure builds beneath VF
opening phase
subglottal pressure builds and becomes stronger than the resistance of the closed VF,
closing phase
due to the elasticity of the VF and they recoil back, airflow speeds up to get through the narrow opening and the decrease in pressure pulls VF back together
Bernoulli principle
an aerodynamic law stating that an increase in the velocity of air decreases the air pressure