Mental wellbeing continuum
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What does the mental wellbeing continuum describe
The progression of levels of mental health
What are the three stages of the mental wellbeing continuum
Mentally healthy
Mental health problem
Mental health disorder
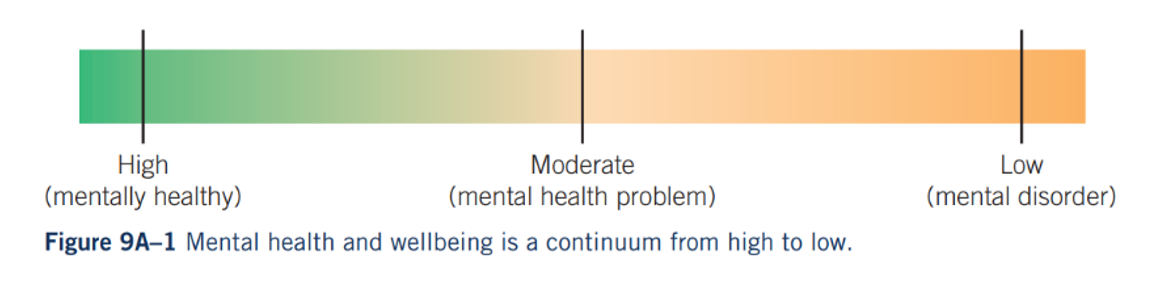
How is mental wellbeing defined
the current state of a person’s psychological wellbeing and functioning
What does mental wellbeing involve
A state of emotional and social wellbeing in which individuals can cope with normal stresses of life, work productively, and contribute to their community
What are some key factors influencing mental wellbeing
Social and emotional wellbeing
Environmental quality
Self-management skills
Physical health
Is mental wellbeing static or changing
It is not static; it constantly fluctuates over time, placing individuals at different points on the mental health continuum
What is the purpose of the Mental Wellbeing Continuum
It is a tool used to track the progression and fluctuation of mental wellbeing, ranging from high levels of wellbeing to low levels
What does high levels of mental wellbeing mean
The current state of psychological wellbeing and functioning where a person is functioning at a satisfactory level
What can individuals at the high end of the mental wellbeing continuum do
They can independently and effectively function in everyday life, coping with demands without excessive distress or dysfunction
What are the characteristics of a mentally healthy person
High levels of functioning
Ability to cope with stress
Ability to meet demands of everyday life and be productive
Displays resilience
Maintains positive relationships with others
Regulates and appropriately expresses emotions
Do mentally healthy individuals ever experience negative emotions like stress, sadness, or anger
Yes — but they are considered mentally healthy because they can cope with these experiences, regulate their emotions, and express them appropriately
What do moderate levels of mental wellbeing involve
A degree of disturbance or dysfunction that reduces an individual’s ability to function at an optimal level
How does moderate mental wellbeing impact daily functioning
It can have a considerable impact, but it is less profound than a mental health disorder and is typically temporary
What are the characteristics of moderate levels of mental wellbeing
Not functioning at an optimal level
Temporary impact on mental wellbeing
Experiencing amplified emotions and high levels of stress
Difficulty concentrating and experiencing irrational thought patterns
What do low levels of mental wellbeing involve
Severe and profound disturbances to an individual’s ability to function
Why are individuals with low levels of mental wellbeing not considered mentally well
Show high levels of distress
Unable to independently complete tasks
Unable to meet the demands of their environment
How might behaviour appear in individuals with low levels of mental wellbeing
They may display behaviour that does not meet societal norms and may be deemed inappropriate
How long are people typically impacted by low levels of mental wellbeing, and how are mental health disorders treated
Impact is extended (more than two weeks); mental health disorders are diagnosable and may be treated through psychotherapy or medication
Does the nature and course of mental disorders vary between individuals
Yes — some people experience only one short-lived episode and fully recover, while others may struggle with a mental disorder throughout their life
What characterises anxiety disorders
Extreme levels of distress that significantly disrupt daily functioning and the ability to cope with everyday demands
What experiences might individuals with anxiety disorders have
Panic attacks and irrational thoughts, placing them at the low end of the mental wellbeing continuum
What is mental health according to the Mental Wellbeing Continuum
The psychological state of someone who is functioning at a satisfactory level of emotional and behavioural adjustment
What are the characteristics of someone with good mental health
Able to manage feelings and emotions
Able to cope with normal stressors
Physically and socially active
Psychological wellbeing
Few sleep difficulties
What is a mental health problem
Disruption to an individual's usual level of social and emotional wellbeing, negatively impacting their abilities
What are the characteristics of someone experiencing a mental health problem
Difficulties in coping
Difficulty concentrating
Some changes in appetite
Mild to moderate stress
Temporary impairment
What is mental illness
The psychological state characterised by significant emotional, cognitive, or social difficulties serious enough to require psychiatric intervention
What are the characteristics of someone with a mental illness
Withdrawal from and avoidance of social situations
Marked distress
Psychological dysfunction
Excessive anxiety
Ongoing impairment
What are some tips for maintaining mental wellbeing
Look after physical health: diet, sleep, exercise
Be social: create connections with people
Do something you enjoy: hobbies, creative pursuits, learning
Have some time to yourself
Take notice: be aware of and take action regarding your emotions
What are internal factors in mental wellbeing
Influences that originate inside or within a person, stemming directly from the individual and changing over time, affecting their placement on the mental wellbeing continuum
What are the two main types of internal factors
Biological factors and psychological factors
What are biological factors
Physiologically based or determined influences, often not under our control, such as:
Genes we inherit
Sex (male/female)
Neurotransmitter balances or imbalances
Substance use
Physiological response to medication
Brain and nervous system functioning
Hormonal activities
Fight–flight–freeze and other bodily stress responses
What are psychological factors
Influences associated with mental processes, such as:
Thoughts, ways of thinking, beliefs, attitudes
Skills in interacting with others
Prior learning and perceptions of self, others, and environment
How we learn, make decisions, solve problems
Understanding and experiencing emotions
Responding to and managing stress
Reconstructing memories
Give an example of how internal factors can affect mental wellbeing
If an individual has a family history of a particular mental health disorder, they may have an increased likelihood of developing this disorder
How can internal factors maintain high levels of mental wellbeing
Optimistic thought patterns, effective stress responses, or other internal strengths can help individuals view difficult situations positively, protecting their mental wellbeing
Give an example of internal factors maintaining high mental wellbeing
Mei Zhen views school assessments as opportunities to learn and improve, which helps her maintain high levels of mental wellbeing during stressful times
How can internal factors lead to low levels of mental wellbeing
A genetic predisposition (family history) to a mental health disorder can increase the likelihood of developing a disorder, leading to lower levels of mental wellbeing
Give an example of internal factors contributing to low mental wellbeing
Mei Zhen has a family history of anxiety disorders, and her mother experienced panic attacks.
This may have contributed to Mei Zhen developing significant anxiety after university, resulting in low mental wellbeing.
What are external factors in mental wellbeing
Influences that originate outside a person, linked to their environment, and can positively or negatively impact placement on the mental wellbeing continuum
What are some examples of external factors
School- and work-related factors
Interpersonal relationships
Support from others
Exposure to stressors
Level of education and employment history
Level of income
Housing and risks of violence
Access to healthcare and community resources
Exposure to social stigma
Cultural influences (values and traditions)
How can external factors maintain high levels of mental wellbeing
Adequate access to support systems, such as friends, family, or professional support, helps individuals cope with challenges and maintain high mental wellbeing
How can external factors lead to low levels of mental wellbeing
Loss of significant relationships or difficulties in certain environments (e.g., work or school) can negatively impact mental wellbeing if not adequately addressed
Give an example of external factors maintaining mental wellbeing
Mei Zhen had strong support from friends, family, and school, which helped her maintain high levels of mental wellbeing during stressful periods like SACS
Give an example of external factors helping recovery after low mental wellbeing
After experiencing significant anxiety post-university, Mei Zhen accessed a psychologist, which supported her recovery and helped maintain her mental wellbeing