ORG 302 – Midterm 2
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Things that describe what employees are like
big five taxonomy
other personality taxonomies
cultural values
generally personality and cultural values
what are the big five
Conscientiousness (gewissenhaftigkeit)
Agreeableness
Neuroticism (emotionale mitgenommenheit?)
Openness
Extraversion
Examples for adjectives related to the big 5
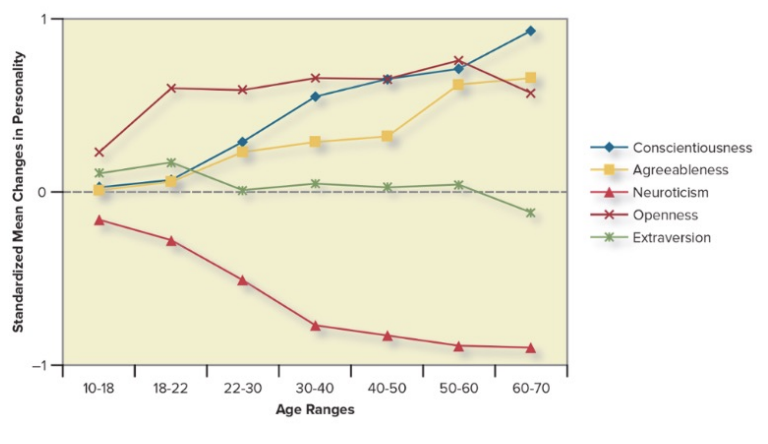
How do the Big 5 change as life progresses? do they stay the same?
Extraversion remains quite stable throughout a person’s life.
Openness to experience also remains stable, after a sharp increase from the teenage years to college age.
The other three dimensions, however, change quite significantly over a person’s life span.
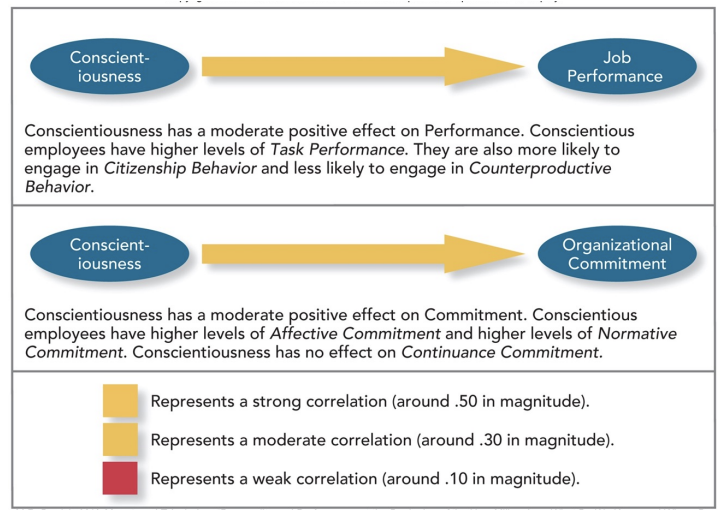
Which personality characteristics has the biggest influence on job performance?
Conscientiousness
Neuroticism (in a bad way)
Relevant aspects of conscientiousness
Dependable,
organized,
reliable,
ambitious,
hardworking,
persevering
related to
career success
good health
accomplishment striving (desire to complete task related goals)
Relevant aspects of agreeableness
Warm,
kind,
cooperative,
sympathetic,
helpful,
courteous
Not related to performance in all occupations
communion striving - strong desire to obtain acceptance in personal relationships
Relevant aspects of Extraversion
Talkative,
sociable,
passionate,
assertive,
bold,
dominant
status striving - wants power and influence
correlated with leadership emergence and job satisfaction
positive affectivity - tendency to experience pleasant engaging moods such as enthusiasm excitement and elation
Relevant aspects of Neuroticism
nervous
moody
emotional
insecure
jealous
counterproductive for most jobs
low levels job satisfaction and happiness in general
external locus of control
Differential exposure—being more likely to appraise day-to-day situations as stressful
Differential reactivity—being less likely to believe that one can cope with the stressors experienced on a daily basis
What does the Gripe index evaluate?
If you have positive or negative affectivity
Relevant aspects of Openness
Curious,
imaginative,
creative,
complex,
refined,
sophisticated
not related to job performance in all kinds of jobs
this and cognitive ability lead to creative thoughts and consequently creative performance
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
Extraversion – Intraversion
Sensing – Intuition
Thinking – Feeling
Judging – Percieving
Helpful for team building not predicting job perfprmance
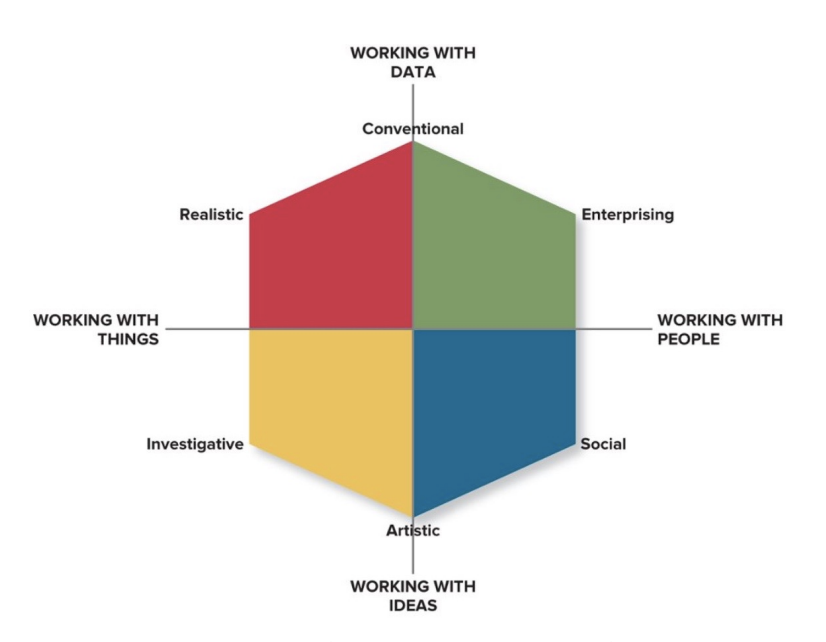
RIASEC Model
Realistic
Investigative
Artistic
Social
Enterprising
Conventional
to predict what job would be suitable
Hofstede
categorizes Cultural Values
Individualistic – Collectivistic
Power Distance
Uncertainty Avoidance
Masculine – Feminine
Short Term – Long Term Oriented
What is Project GLOBE
An ongoing international research effort to examine the impact of culture on leadership attributes, behaviors, and practices
Uses 9 dimensions to summarize cultures:
Power distance
Uncertainty avoidance
Institutional collectivism
Ingroup collectivism
Gender egalitarianism
Assertiveness
Future orientation
Performance orientation
Humane orientation
coutnries are being clustered
relevance of collectivism job setting
Higher levels of task performance and citizenship behaviors in work team settings
Lower levels of counterproductive and withdrawal behaviors
Greater commitment to employers
Preference for group rewards versus rewards tied to individual achievement
How Can We Describe What Employees Are Like?
Personality:
Big 5
Myers-Briggs
RIASEC
Culture:
Hofstede
Project GLOBE

Effects of Conscientiousness on Performance and Commitment
How Important Are Personality and Cultural Values? 2
Not much when a lot is at stake, but in “weak situations” the personality shows, also when there are cues that trigger it.
Team types
categorized by
purpose,
length of existence
Types:
Work teams (Produce goods or provide services, eg: sales team)
Management teams (Integrate activities of subunits across business functions, eg: top management)
Parallel teams (Provide recommendations and resolve issues, eg: advisory council)
Project teams (Produce a one-time output (product, service, plan, design, etc.), eg: Product design team)
Action teams (Perform complex tasks that vary in duration and take place in highly visible or challenging circumstances, eg: sports team, musical group, surgery team)
What influences team’s effectiveness?
autonomy
communication modes (virtual or irl)
experience together
Stages of team developement
Forming
Storming
Norming
Performing
Adjourning
What’s Punctuated equilibrium?
development in which not much gets done until the midway point of a project, and then the team increases effectiveness to meet its deadline
Team interdependence forms
task interdependence
goal interdependence
outcome interdependence
What’s Task interdependence/forms of it?
Refers to the degree to which team members interact with and rely on other members for the information, materials, and resources needed to accomplish work for the team
different possible variations:
pooled (work seperately, throw together in the end
sequential ( permutation schedule essentially)
reciprocal interdependance (everyone has a specialized task but interacts with others for help)
conprehensive (high degree of interaction)
What’s goal interdependance
Exists when team members have a shared vision of the team’s goal and align their individual goals with that vision as a result
What’s outcome interdependence?
The degree to which team members share equally in the feedback and rewards. sharing bonuses, recognition etc
high levels → more information shared among members
What are teh 5 aspects of team composition?
member roles
member ability
member personality
team diversity
team size
What are the different team role categories?
A role is the pattern of behavior a person is expected to display in a given context
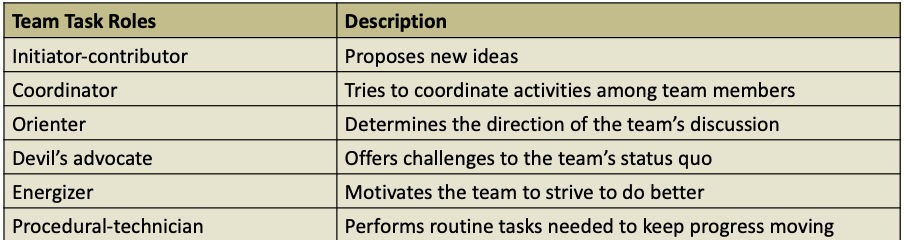
team task role: behaviors that directly influence outcomes
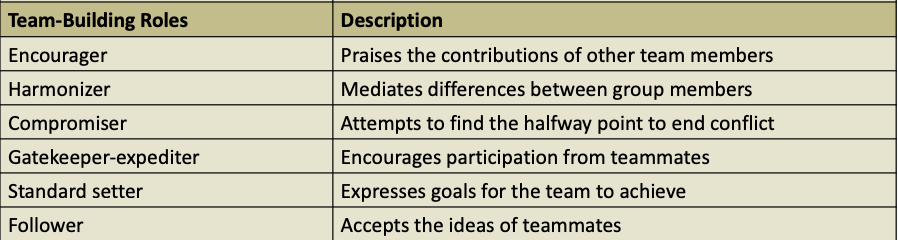
team building roles: refer to behaviors that influence social climate
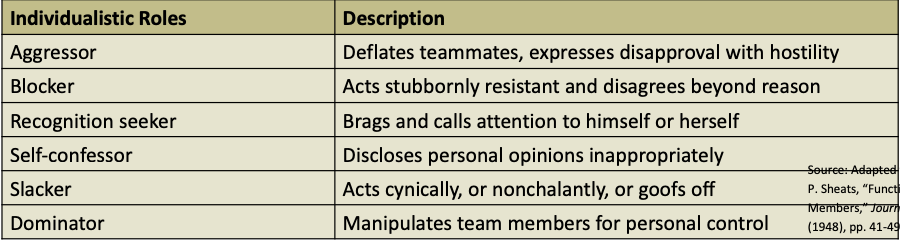
individualistic role: behaviors that benefit individual at the expense of team
Team Task Roles
Team Building Roles
Individualistic roles
Which personality traits are more important in the team setting? (Think about Big 5)
agreeable
conscientious
extraverted
What are the two different theories related to diversity in teams?
diversity beneficial because larger pool of knowledge (Value in diversity problem-solving approach)
people tend to avoid contact with people that are different from them (Similarity-attraction approach)
Impact of team viability and task independence
Team viability refers to the likelihood that the team can work together effectively into the future.
Task performance is moderately higher in teams in which members work closely together than when members work independently.
Task interdependence does not significantly increase team commitment.
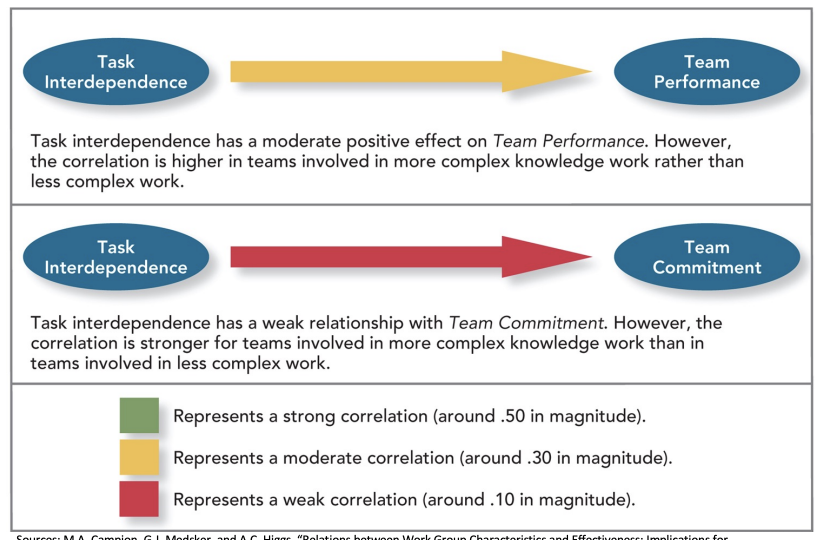
Why Are Some Teams More Than the Sum of Their Parts?
Process Gain / Synergy is getting more from the team than you would expect according to the capabilities of its individual members.
Process loss is the opposite
Causes of process loss
Coordination loss: time to coordinate and waiting for eachother and stuff
motivation loss: example social loafing (feeling less accountable for team outcome compared with individual work)
Components of Taskwork Processes nedir?
Creative Behavior (brainstorming)
Decision Making
Boundary Spanning
Factors in Team Decision making
Decision informity (do people know what they have to do?)
Staff validity (recs from staff to leader good?)
hieriarchal sensitivity (leader weighs recommendations of team well?)
Boundary spanning
= taskwork processes with outsiders
eg:
ambassador does communications that are intended to protect the team, persuade others to support the team, or obtain important resources for the team
task coordinator activities involve communications that are intended to coordinate task-related issues with people or groups in other functional areas.
scout activities refer to things team members do to obtain information about technology, competitors, or the broader marketplace.
Teamwork processes
facilitate accomplishment but don’t directly involve task accomplishment, they are creating the setting or context
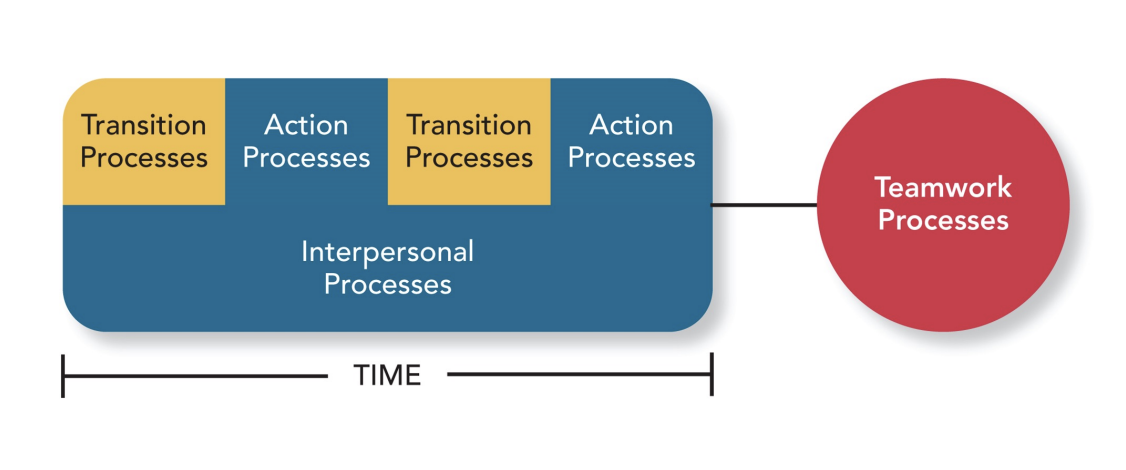
What activities happen in the transition process?
mission analysis (task analysis, challenges are being looked at, ressources are being checked)
strategy formulation (exactly what it sounds like)
Goal specification (exactly what it sounds like)
What activities happen in the action process?
monitoring towards goals (document accomplishments)
system monitoring (document if necessary things are still available)
helping
coordinating
Communication nedir?
The process by which information and meaning get transferred from a sender to a receiver
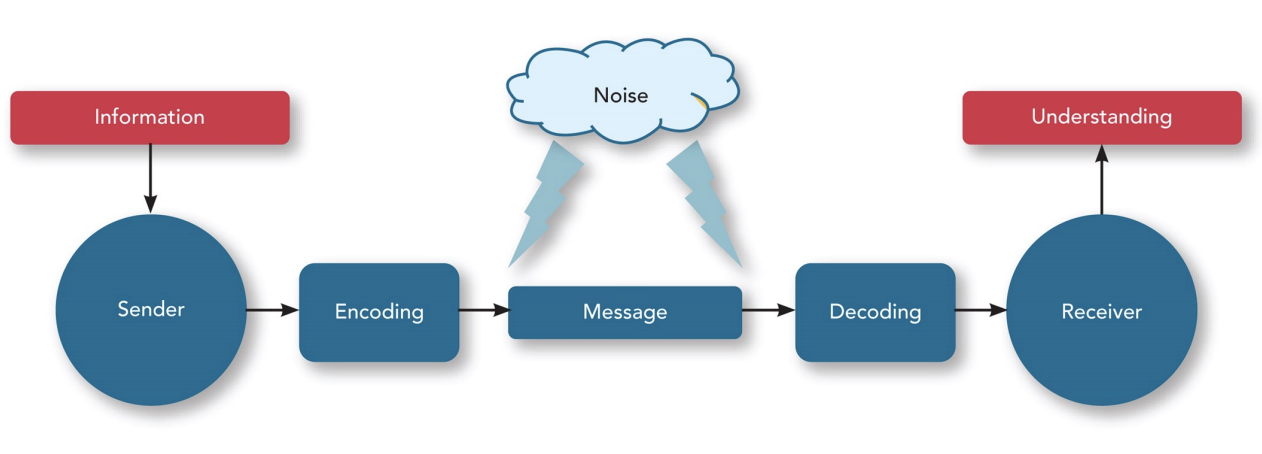
Issues in Communication
Communicator based
Communicator competence yetersiz
Emotions and emotional intelligence of team members yetersiz
Noise
Distance
Obstructions
Physical noise
Infromation Richness
amount of depth in information. also through body language, facial expressions, tone of voice
Network Structures within teams
All channel (decentralized)
circle
y (one central persont that strings are attached to)
Wheel (everyone has same contact person) (centralized)
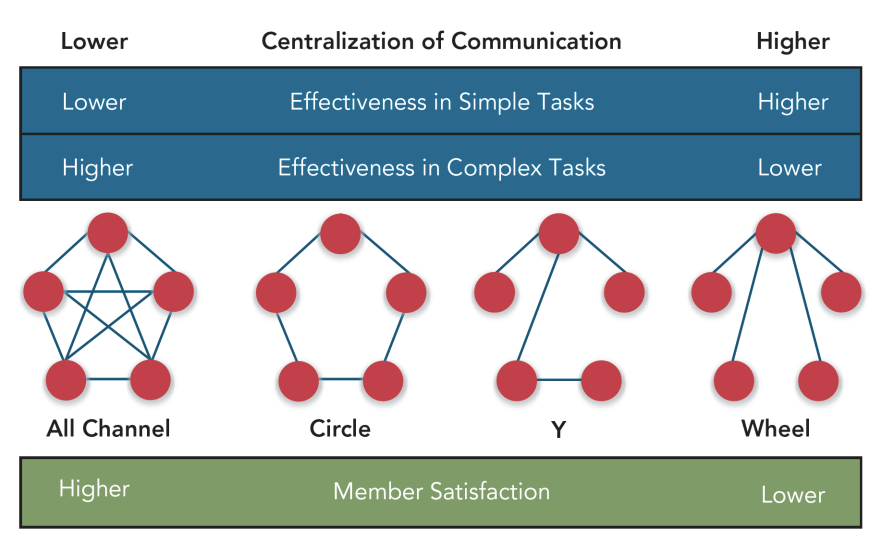
What are team states?
specific types of feelings and thoughts that coalesce in the minds of team members because of their experience working together
cohesion Possible negative outcome: groupthink
potency (high if they are confident they can be effective across a variety of situations, can be too high)
mental models (level of common understanding among team members about how to resolve conflict etc)
transactive memory (meta knowledge and specialized knowledge)
Effects of teamwork processes on performance and commitment
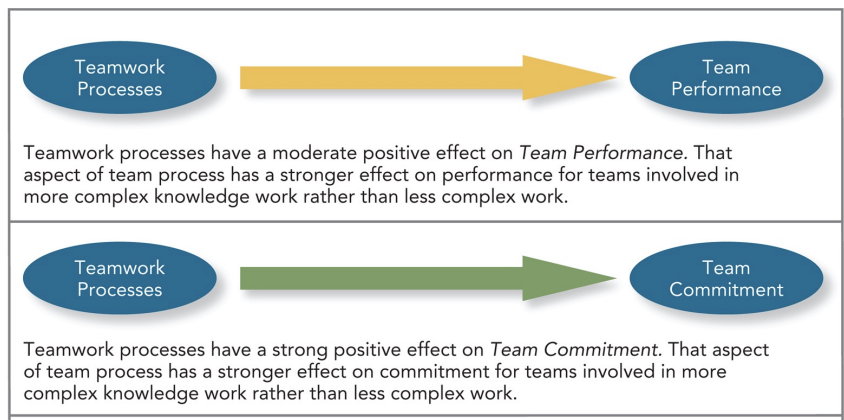
Cross training
when people are being taught what their team members are doing. can either be that they just learn what their tasks are (personal clarification), that they also watch how they’re doing it (positional modeling) or that they’re actually being trained in order to be able to execute those tasks (positional rotation)
What is Team Process Training?
use of team experiences so that they act more efficiently as unit

What’s Work specialization?
The degree to which tasks in an organization are divided into separate jobs
high specialization leads to:
increased efficiency
reduced flexibility by loss of other skills
lower motivation because of lack of variety
chain of command nedir?
Answers the question of “who reports to whom?” and signifies formal authority relationships
Span of control nedir?
Represents how many employees each manager in the organization has responsibility for
Dictates how flat or tall a hierarchy is. there is an optimum to it
Centralization
Refers to where decisions are formally made in organizations
only top management vs low level employees able to make decisions
Formalization
The degree to which rules and procedures are used to standardize behaviors and decisions in an organization
Mechanistic Vs Organic
Mechanistic organizations are efficient, rigid, predictable, and standardized organizations that thrive in stable environments.
Organic organizations are flexible, adaptive, outwardfocused organizations that thrive in dynamic environments.
What does choice of Organizations structure depend on?
Business environment: Customers, Suppliers, Competitors, anything outside. are they stable or not?
Company strategy: low cost focus often mechanistic to get that done, differentiators organic
Technology: more routine in technology → more need for mechanistic structures
Company size: The bigger the more mechanistic
Differentiate SImple / Bureaucratic structures
Simple: most common, A small organization with one person at the top who is the owner/manager, companies with simple structures have little specialization or formalization
Bureaucratic: designed for efficiency, high level of work specialization, formalization, centralization of authority, rigid and well-defined chains of command, narrow spans of control
Functional structures: employees grouped by function
multi divisional structures: groups based on
products,
geography,
clients
Matrix structure: two structures at the same time. Flexible? two chains of command
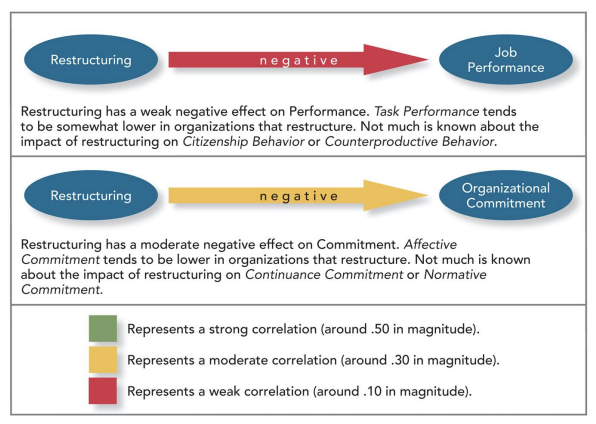
Effects of Organizational Structure on Performance and Commitment
Organizational Culture nedir
culture but within organization, aquired from other employees, system of control over employees
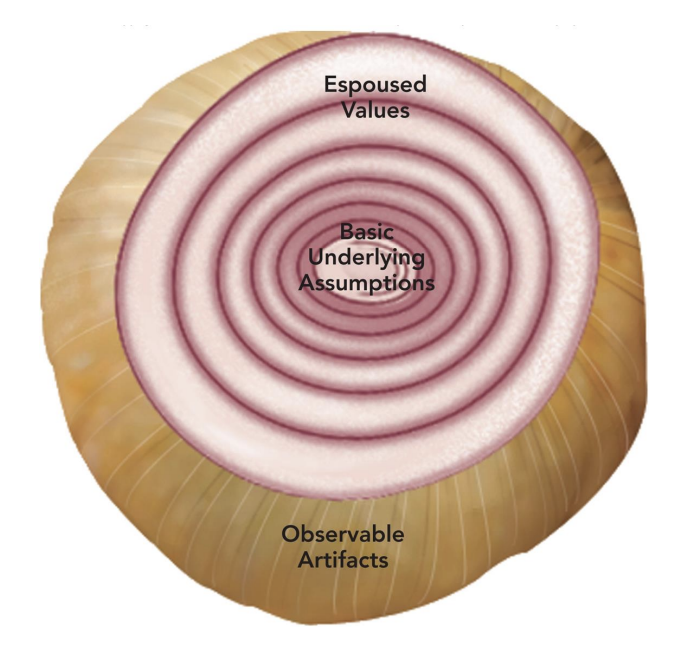
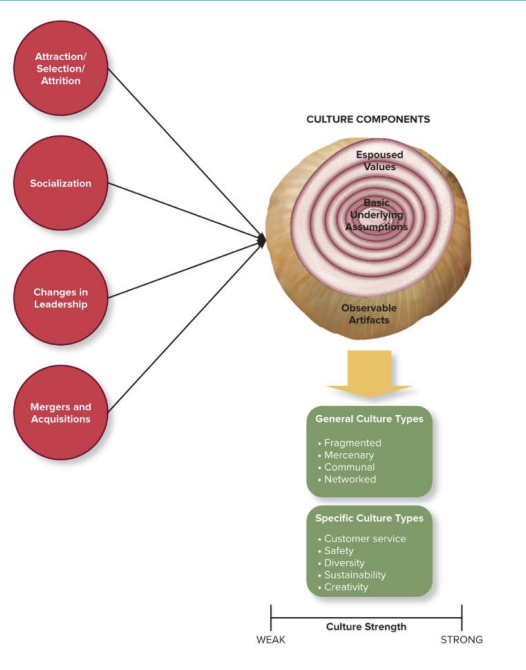
Different layers of Organizational Culture
Observable Artifacts
Language
Rituals
Stories
Symbols
Espoused Values
more mental beliefs
philosophies
norms that are being explicitly stated
Basic Underlying Assumptions
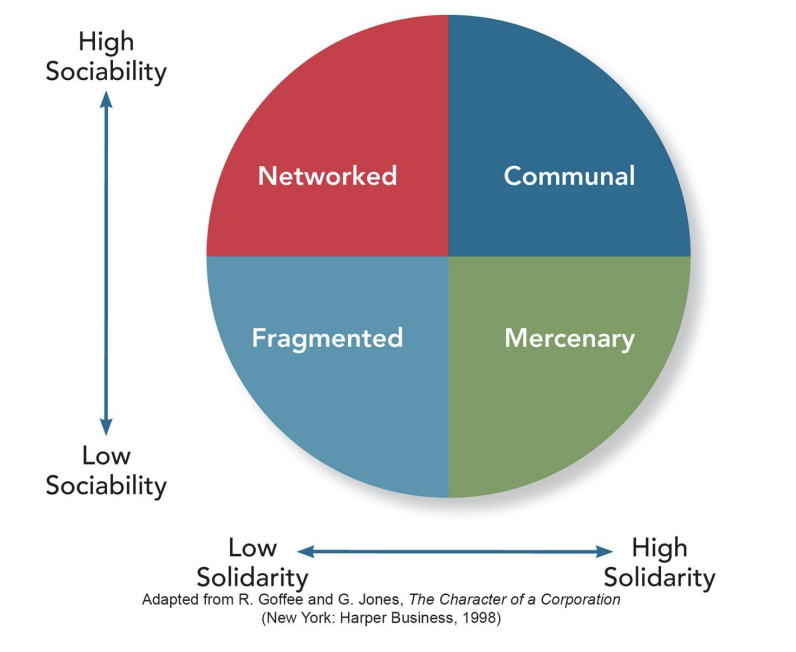
General Culture Types
Solidarity: degree to which members think and act alike
Sociability: represents how friendly employees are to one another
Service Culture Process
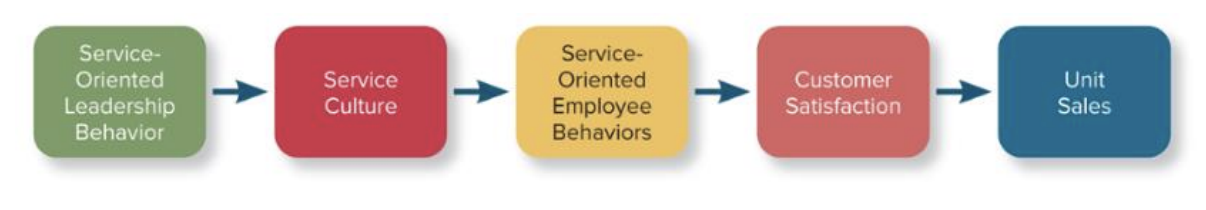
Negative and positive aspects of a strong organizational culture
plus sides:
Differentialtes organization from others
employee can identify with organization
facilitates desired behaviors among employees
stability withing org
cons:
merging with other orgs difficult
limited diversity among team cause attracts people who think alike
can foster extreme behavior
makes adapting to environment more difficult
What is ASA (Attraction-Selection-Attrition)
theory that employees will be drawn to orgs that have cultures that are like their personality
What are the stages of Socialization (getting to know culture)?
anticipatory stage before employment
Encounter stage when employment begins (may include reality shock)
understanding and adaptation when you accept those things
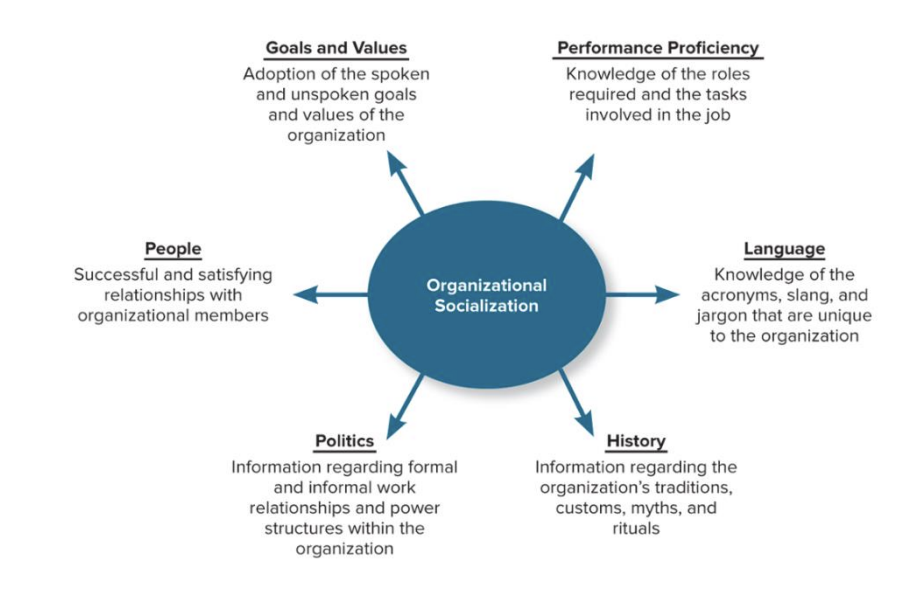
What are Dimensions Addressed in Most Socialization Efforts?
Goals and Values
Performance and Proficiency
People
Language
Politics
History
How could you change company culture?
Changes in leadership (optimal if leadership style is different from company's culture
Mergers and acquisitions (when you merge two companies i guess)
Why Do Some Organizations Have Different Cultures Than Others?
Impact of Person-organization culture fit
Strong correlation to organizational commitment
Weak correlation to job performance
Forms of power
Oragnizational Power
Legitimate Power (Role says you have power)
Reward power (based on controlling ressources other people want)
Coercive Power (ability to punish)
Personal Power
Expert power (based on skill)
Referent power (When people wanna be seen with you)
What are contingency factors in the context of power?
substitutability (alternative to get resources is available)
Discretion (have right to make decisions on their own)
Centrality (how integral a person’s job is)
VIsibility (aware that this person is in control of those resources)
Leaders can use power petter if the have
high discretion
high centrality
high visibility
low substitutability
What are the tactics that are commonly used by leaders to influence others?
Most effective:
Rational persuasion
Inspirational appeal (trigger emotional reaction through appealing values)
Consultation (allow target to take part in decision making)
Collaboration (work together)
Moderately effective:
Ingratiation (favors and compliments and stuff)
Personal appeal (using friendship or loyalty)
Apprising (explain benefit for target)
Least effective:
Exchange tactic (offering reward or something in return)
Coalations (enlisting others to help influence the target)
pressure (use coercive power)
Possible reactions to influence tactics
Internalization: both behavior and attitude shift towards agreement
Compliance: Behavior shifts but attitude does not
Resistance: neither shift
most effective obviously internalization
What are organizational politics?
whatever furthers personal interests
Networking ability nedir?
is an adeptness at identifying and developing contacts.
Social astuteness
is the tendency to observe others and accurately interpret their behavior
Interpersonal influence
involves having a personal style that’s flexible enough to adapt to different situations.
Apparent sincerity
involves appearing to others to have high levels of honesty and genuineness
Negative effects of organizational politics (if too much)
lower job satisfaction
increase in strain
lower job performance
increased turnover intentions
lower organizational commitment
What fosters organizational politics?
Personal Cahracteristics like:
need for power
high self monitors (people who adapt to situations heavily)
machiavellianism (being a manipulative bitch basically)
Organizational characteristics like:
Limited/changing resources
Ambiguity in roles
high performance pressure
unclear performance evaluations
Two factors that conflict resolution is influenced by
how assertive leaders want to persue their own interests
how cooperative they are with regard to the concerns of others
What are five different styles of conflict resolution?
competing (high assertive low cooperative)
avoiding (low assertive low cooperation)
accomodating (low assertive high cooperation)
collaboration (high assertive high cooperation)
compomise (moderate assertive moderate cooperation)
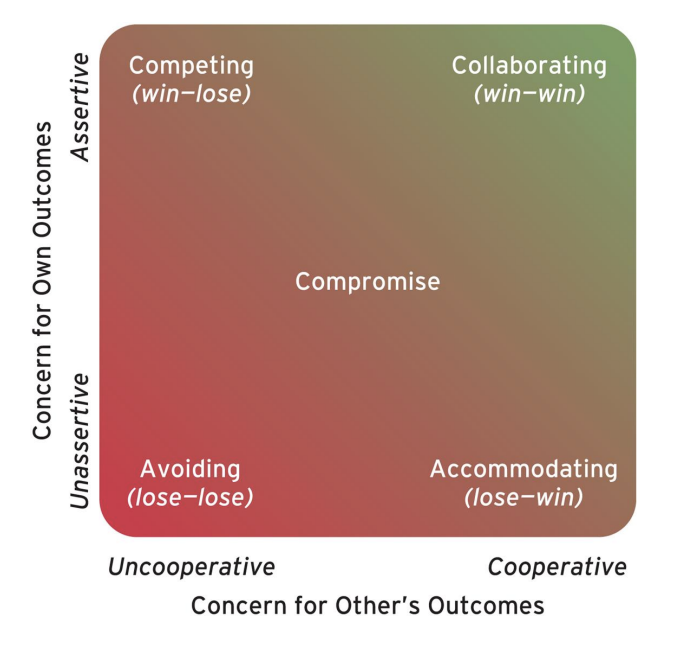
when to use which style
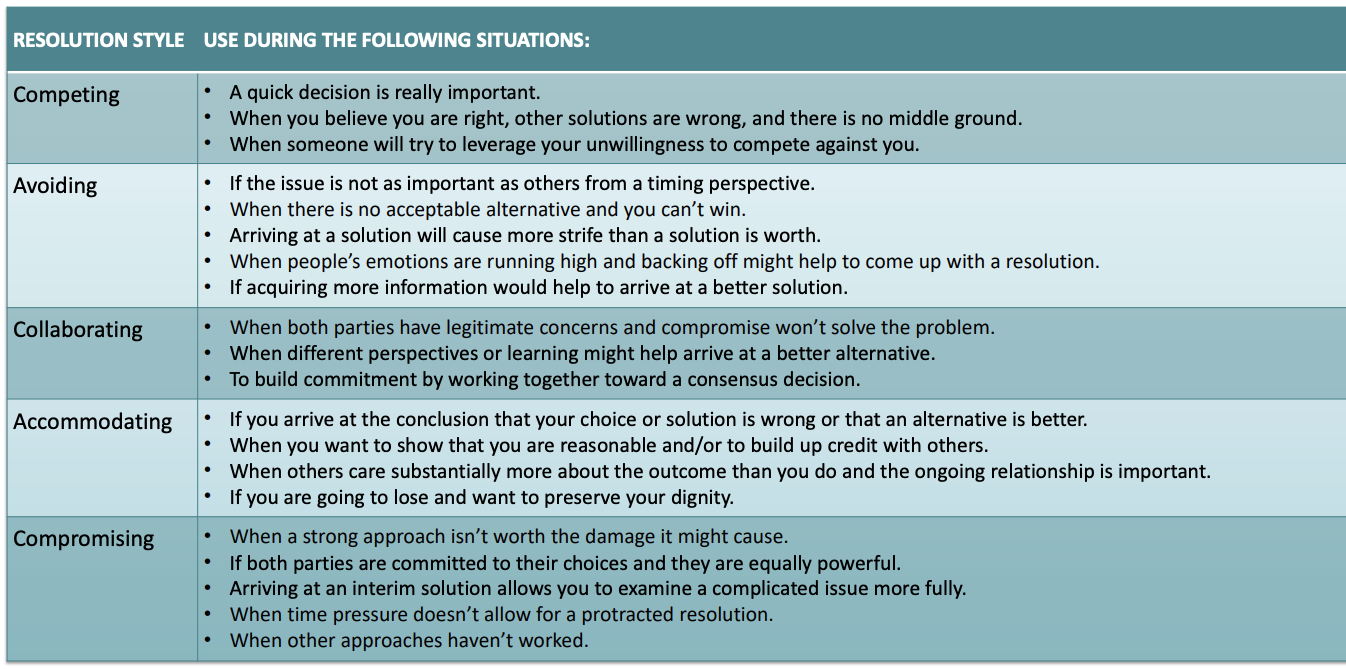
What is negotiation?
A process in which two or more interdependent individuals discuss and attempt to come to an agreement about their different preferences
What are two negotiation strategies?
Distributive bargaining (win lose style with fixed pie zero sum conditions)
Integrative bargaining (winwin style utilizing mutual respect and problem solving)
WHat are the 4 negotiation stages?
preperation stage ( each party determines goals and alternatives)
exchanging information (each party makes a case for its position)
Bargaining (both parties must likely make concessions)
closing and commitment (agreement is formalized)
What are negotiation biases?
when power relationship is too big so the outcome is likely to be a distributive approach in favor of the higher power party
positive emotions may lead to agreeing too quickly
negative emotions may lower judgement accuracy
effects of power and influence on performance and commitment
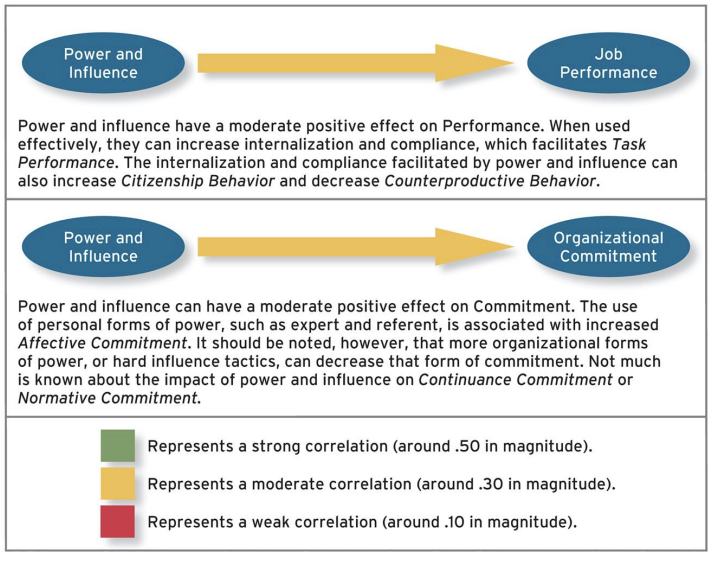
Mediation nedir?
requires a third party to facilitate the dispute resolution process, though this third party has no formal authority to dictate a solution.
what’s arbitration?
occurs when a third party determines a binding settlement to a dispute
traditionally comes after mediation, if that has failed. some research suggests other way around might be more useful
Describe leader-member relationship development over time
Role taking phase: leader provides employee with job expectations and follower tries to meet them
Role making phase: exchange of opportunities and resources based on follower voicing expectations for the relationship
the relationships that result out of this employer-employee interaction can either bei high quality in-group dyads or low quality out-group dyads. basically: it can lead to the employee differentiating wether the leader is the ingroup or outgroup.
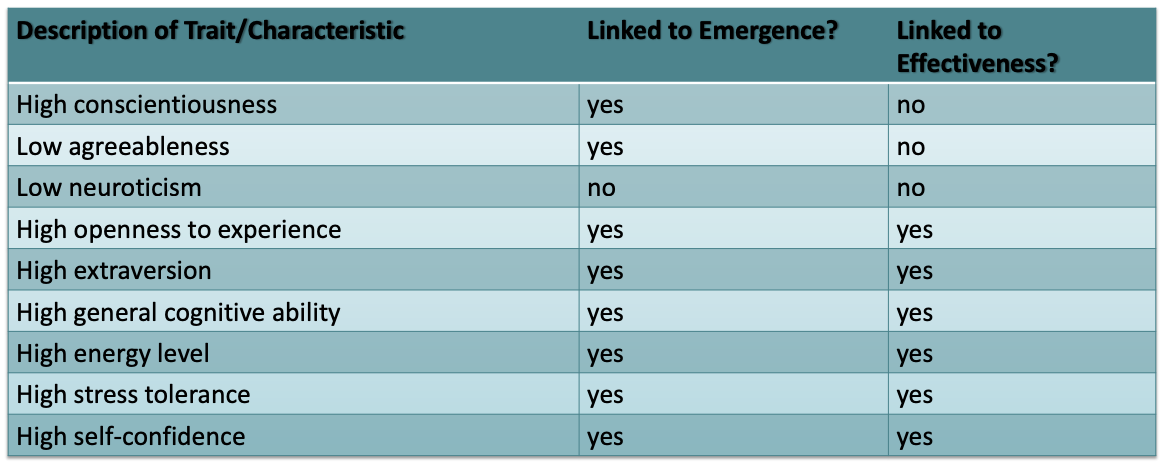
What traits are associated with leadership emergence and effectiveness?
What four different decision making styles are there?
autocratic (leader only decision maker)
consultative (asks for opinions but decides himself)
facilitative (everyones opinion weighed the same)
delegative (gives off decision to other(s))
What does the time-driven model of leadership say?
Provides 7 factors which decide what type of decision making style should be applied. It’s that fun matrix or table or whatever
What are the 7 factors in the Time Driven Model of leadership?
Decision significance
Importance of commitment (Is it important that employees “buy in” to the decision?)
leader expertise
likelihood of commitment (How likely is it that employees will trust the leader’s decision and commit to it?)
shared objectives
employee expertise
teamwork skills
What do leaders even do yani?
many behaviors in these categories:
Initiation
Organization
Production
Membership
Integration
Communication
Recognition
Representation
What are two broad dimensions that encompass day-to-day leadership behaviors?
initiating structure (includes initiation, organization and production factors. has a strong impact on employer motivation)
Consideration (includes building trust, respect, considerating employees feelings etc, strong impact o employees motivation, job satisfaction and percieved leadership effectiveness)
What is readiness in the context of Life Cycle Theory of leadership?
the degree to which employees have the ability and the willingness to accomplish their specific tasks