Plant Tissues
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What are tissues?
Collection of specialized cells carrying out 1 function
4 ex of plant tissues
Meristems
Epidermis
Vascular tissues
Food storage tissues
3 categories of plant tissues
Dermal
Ground
Vascular
What are meristems?
Parenchyma
Cells that promote plant growth
Mitosis
Creates additional cells that typically have the same characteristics of the original cell
Three primary meristems develop from the….
apical meristem
What are the 3 primary meristems that develop from the apical meristem?
Protoderm (epidermal layers)
Ground meristem (pith and cortex)
Procambium (primary xylem and phloem)
Lateral meristems are responsible for growth in girth of what 2 things?
Stems
Roots
Lateral meristems produce secondary tissues of…
Vascular cambium (secondary xylem and phloem)
Cork cambium (bark)
What are the 3 ground tissue types?
Parenchyma
Collenchyma
Sclerenchyma
3 characteristics of parenchyma
Spherical
Thin-walled
Living, metabolizing tissue
Location of parenchyma
Throughout the plant
3 functions of parenchyma
Photosynthesis and respiration
Storage
Regeneration
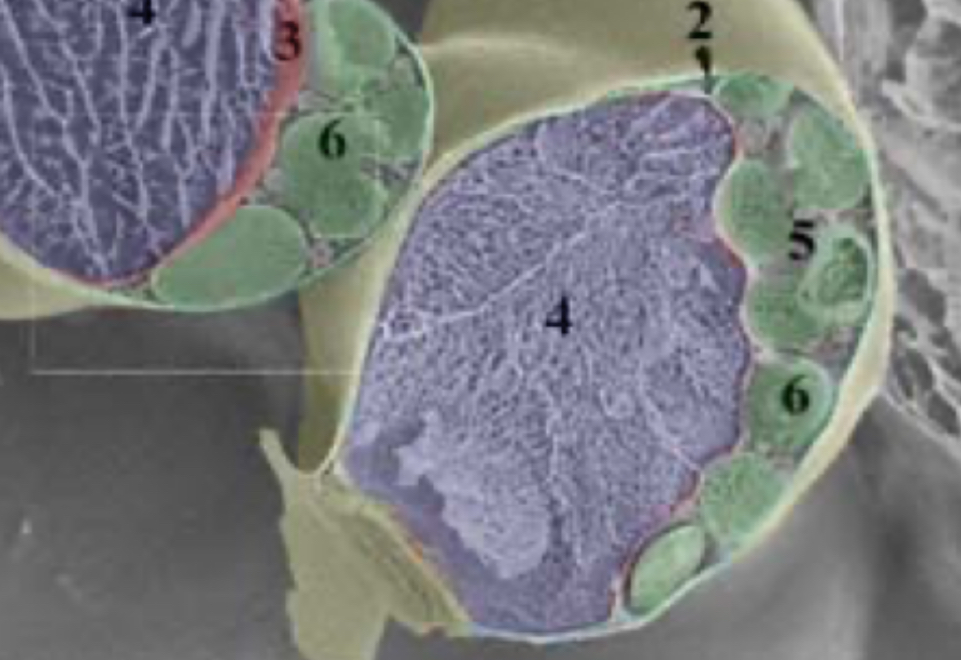
Parenchyma
2 characteristics of collenchyma (what are the walls like and are they dead or alive at maturity)?
Elongated cells with unevenly thickened cell walls
Alive @ maturity
Location of collenchyma
Beneath the epidermis in young stems and leaf veins
Function of collenchyma
Flexible support system
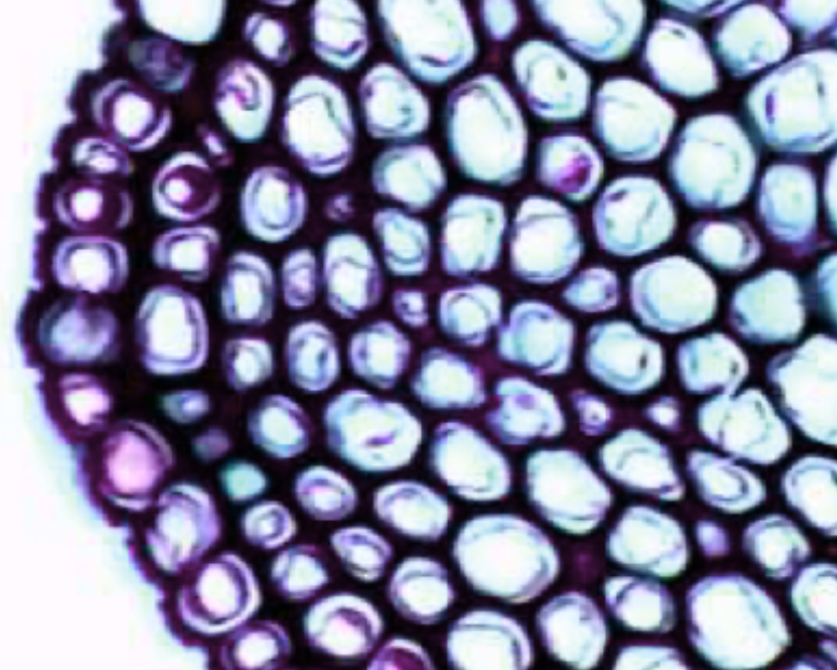
Collenchyma
2 characteristics of sclerenchyma
With primary + secondary walls
Dead @ functional maturity
2 locations of sclerenchyma
Fibers in wood, bark, leaves, stems
Sclereids in fruits and seeds
Function of sclerenchyma
Structural support
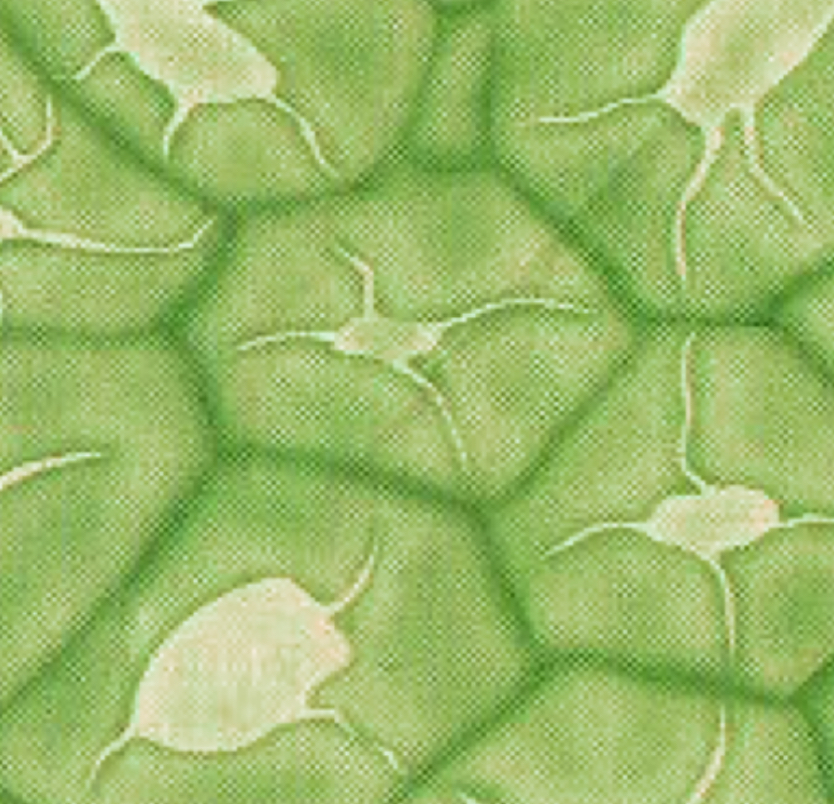
Sclerenchyma
Where are ground tissues found?
Leaves
Stems
Fruits
Flowers
Roots
All plant parts
Vegetable example of parenchyma tissue
Potato
Vegetable example of collenchyma tissue
Celery
Fruit example of sclerenchyma tissue
Pear
Epidermis
Single layer of exterior (parenchyma) cells
Protects various plant organs (leaves, stems, flowers, roots)
Root cap
Protects root meristem (parenchyma)
Replenished daily by root meristem
Leaves
Outer layer (parenchyma cells)
Protects inner contents of leaf
Guard cells
Differentially thickened cells that become turgid during the day
Expand to form pores called stomata
2 types of vascular tissues
Xylem
Phloem
Where are guard cells located?
Primarily on the underside of leaves
2 functions of guard cells
Gas exchange
Regulate water loss
Xylem function
Conduct water + dissolved minerals
Cells in xylem
Sclerenchyma
Phloem function
Transports sugars, amino acids, hormones
Cells in phloem
Parenchyma
How are vascular tissues arranged?
Bundles
Epidermis function in roots
Protection
Epidermis cells in roots
Parenchyma
Cortex function in roots
Food storage
Cortex cells in roots
Parenchyma
Endodermis function in roots
Controls water movement to xylem
Covered with a wax coating (casperian strip)
Endodermis cells in roots
Parenchyma
Pericycle function in roots
Cell division
What cells make up the pericylce in roots?
Parenchyma cells
What type of cells make up the cortex in a dicot seed?
Collenchyma
Cambium function in dicot stems
Produces new vascular cells and tissues
Cambium cells in dicot stems
Parenchyma
Pith function in dicot stems
Structure
Arrangement of tissues: monocot stems
Scattered vascular bundles
No secondary growth
Increases in diameter
Secondary growth
Bark
What is secondary growth?
Thickening of stems and roots (in many cases, the production of wood)
Cork cambium is located just inside the…
epidermis
Most tissues are composed of what type of cells?
Mature
Most tissues are composed of mature cells except…
Meristem tissues
Combinations of tissues make up organs such as…
Leaves
Purpose of cuticle (leaf tissue)
Waxy coating over the episdermis
Protection from water loss
Epidermis purpose + cell type(leaf tissue)
Protection
Parenchyma
The palisade parenchyma (or palisade layer) is a group of ________ cells in the leaf that are the main site of __________
parenchyma
photosynthesis
Spongy (leaf tissue)
Secondary site for photosynthesis
Loosely packed
Parenchyma
A vascular bundle is a group of what 2 tissues?
Xylem
Pholem
What are the 3 primary meristems develop from the APICAL MERISTEM:
1.Protoderm (epidermal layers)
2. Ground meristem (pith and cortex)
3. Procambium (primary xylem and phloem)
LATERIAL MERISTEMS produce secondary tissues of what 2 things?
1. Vascular cambium (secondary xylem and phloem)
2. Cork cambium (cork = bark)