Module 7 — Complexation and Precipitation Reactions and Titrations
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms






The concentration of chloride ions in an unknown sample was determined by Mohr's method. A standard solution of 0.1000 M silver nitrate solution was used to titrate with a sample solution using potassium chromate as indicator. 25.0 mL of the sample solution required 22.00 mL of the silver nitrate solution to reach the end point in the titration. Calculate the concentration of chloride ions in the sample solution.
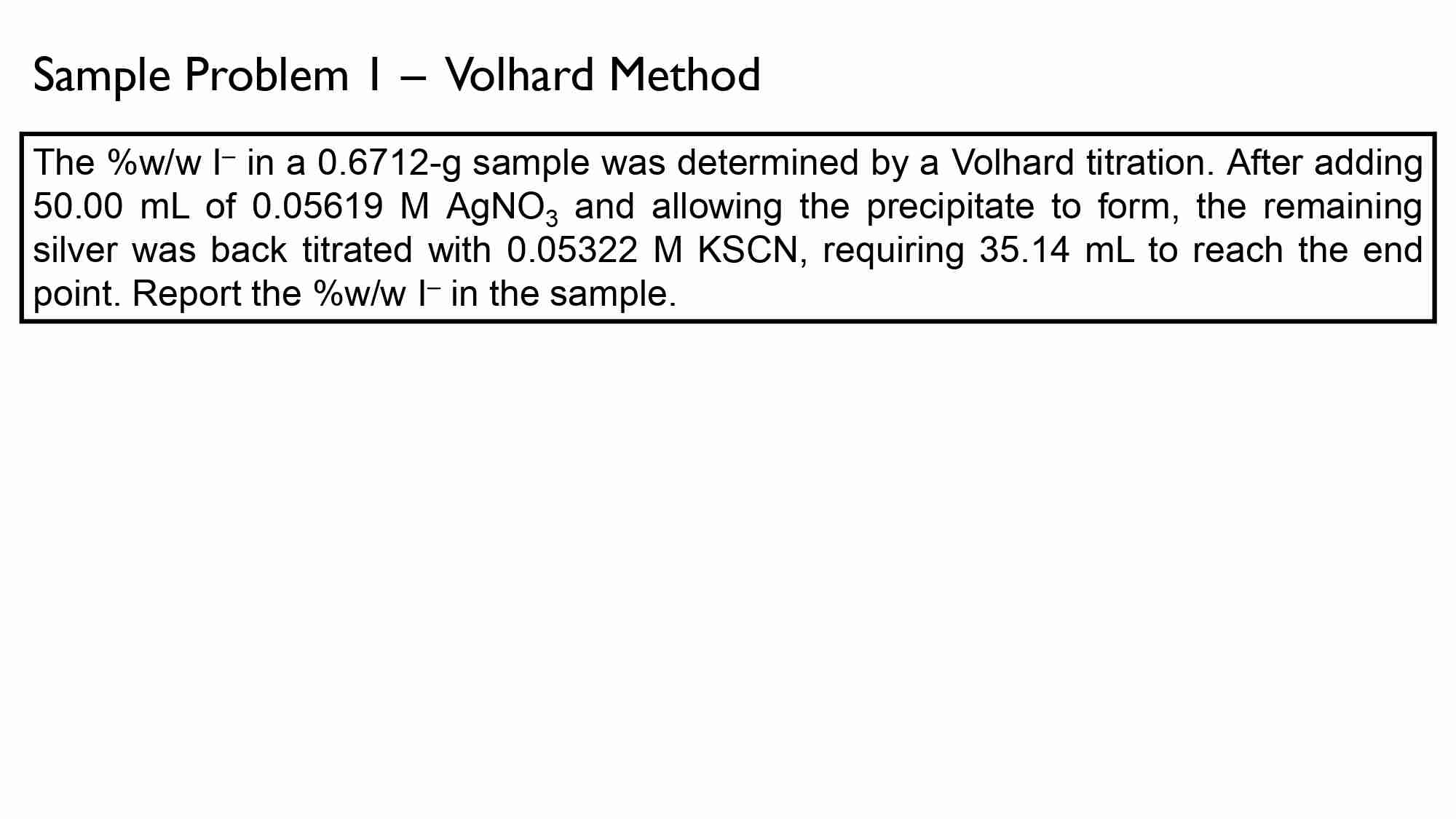
In a routine Volhard analysis, s student dissolved a 1.2319-g sample of an unknown in 100 mL of distilled water and then added 100.00 mL of 0.1045M AgNO3. The mixture was then back titrated with 0.1096 M KSCN and 28.65 mL was required to reach the end-point. Calculate the mass percentage of NaBr in the unknown.
Measured: Ag+ + Br «» AgBr
Excess: Ag+ + SCN- «» AgSCN
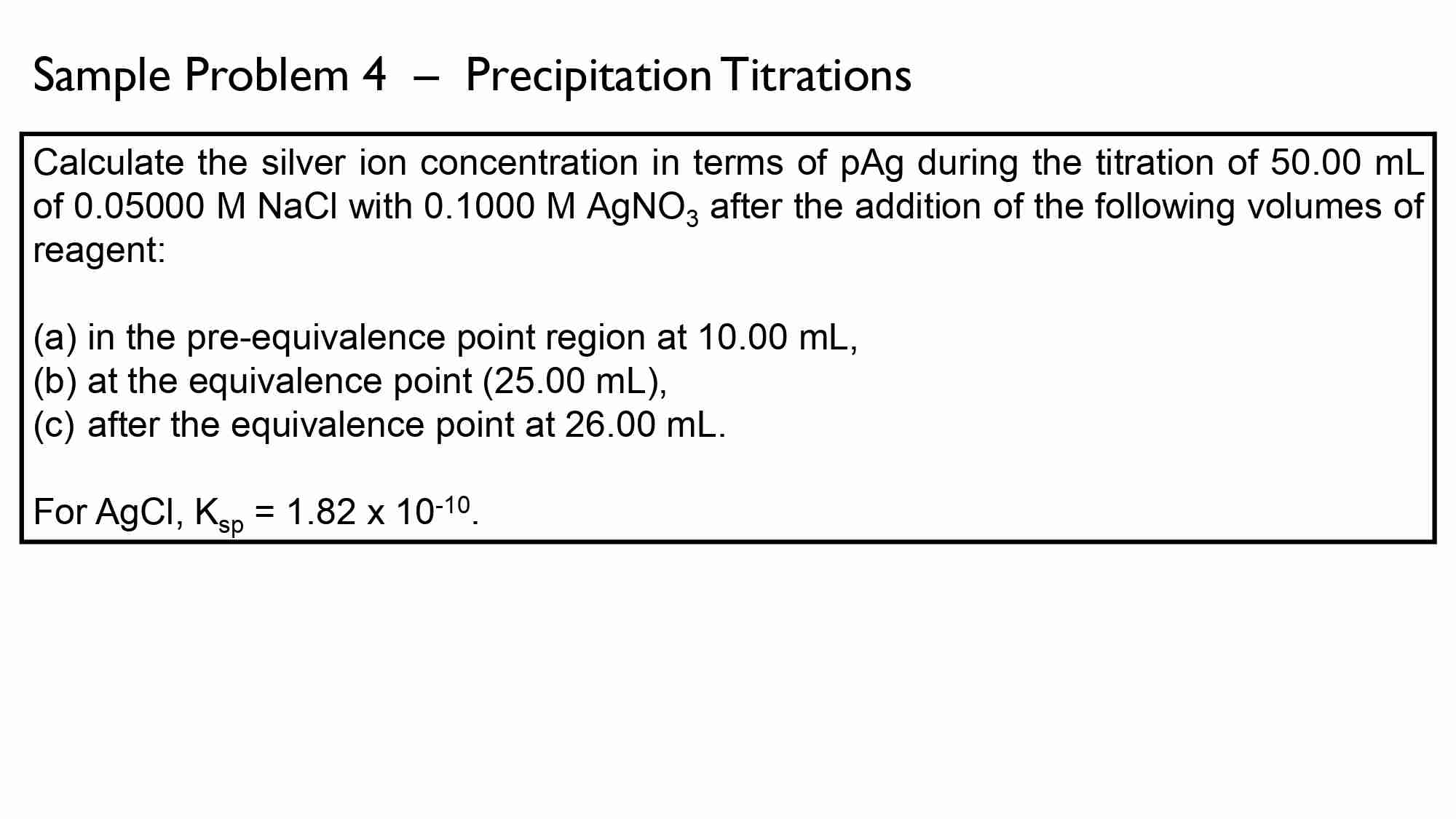
A Fajans titration of a 0.7908-g sample required 45.32 mL of 0.1046 M AgNO3. Express the results of this analysis in terms of the percentage of Cl-.
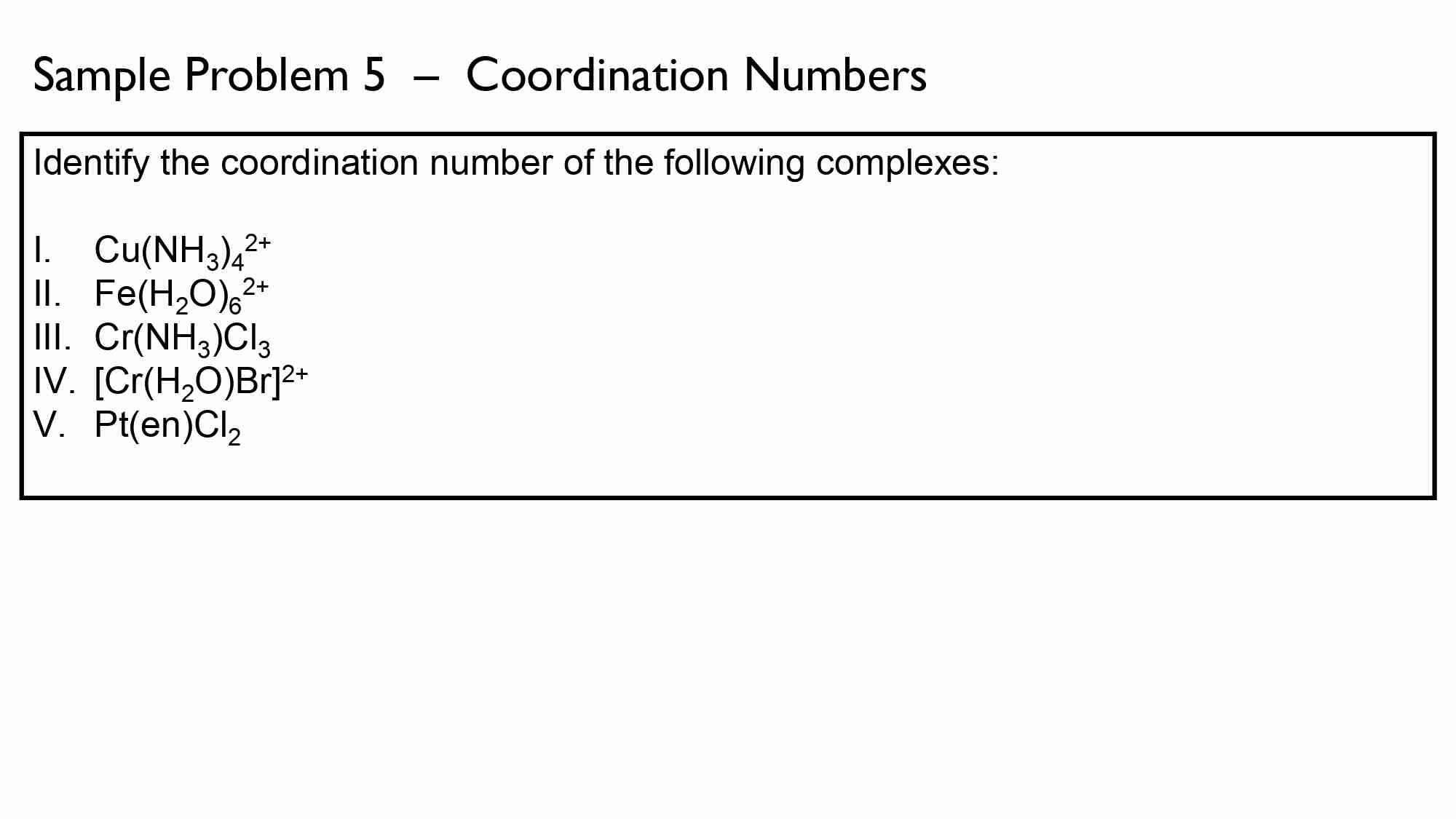
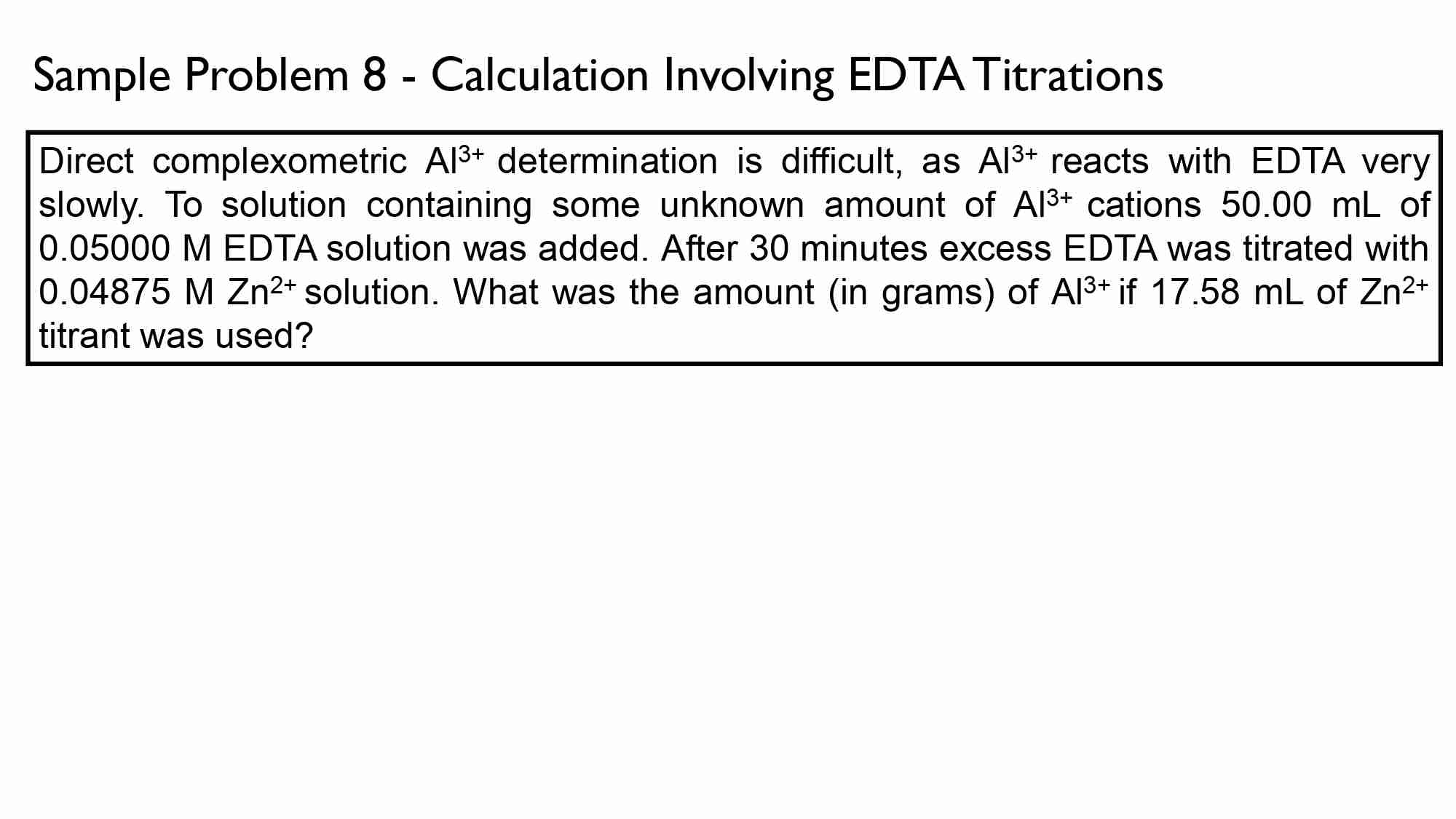
The Zn in a 0.7457-g sample of foot powder was titrated with 22.57 mL of 0.01639 M EDTA. Calculate the percent Zn in this sample.
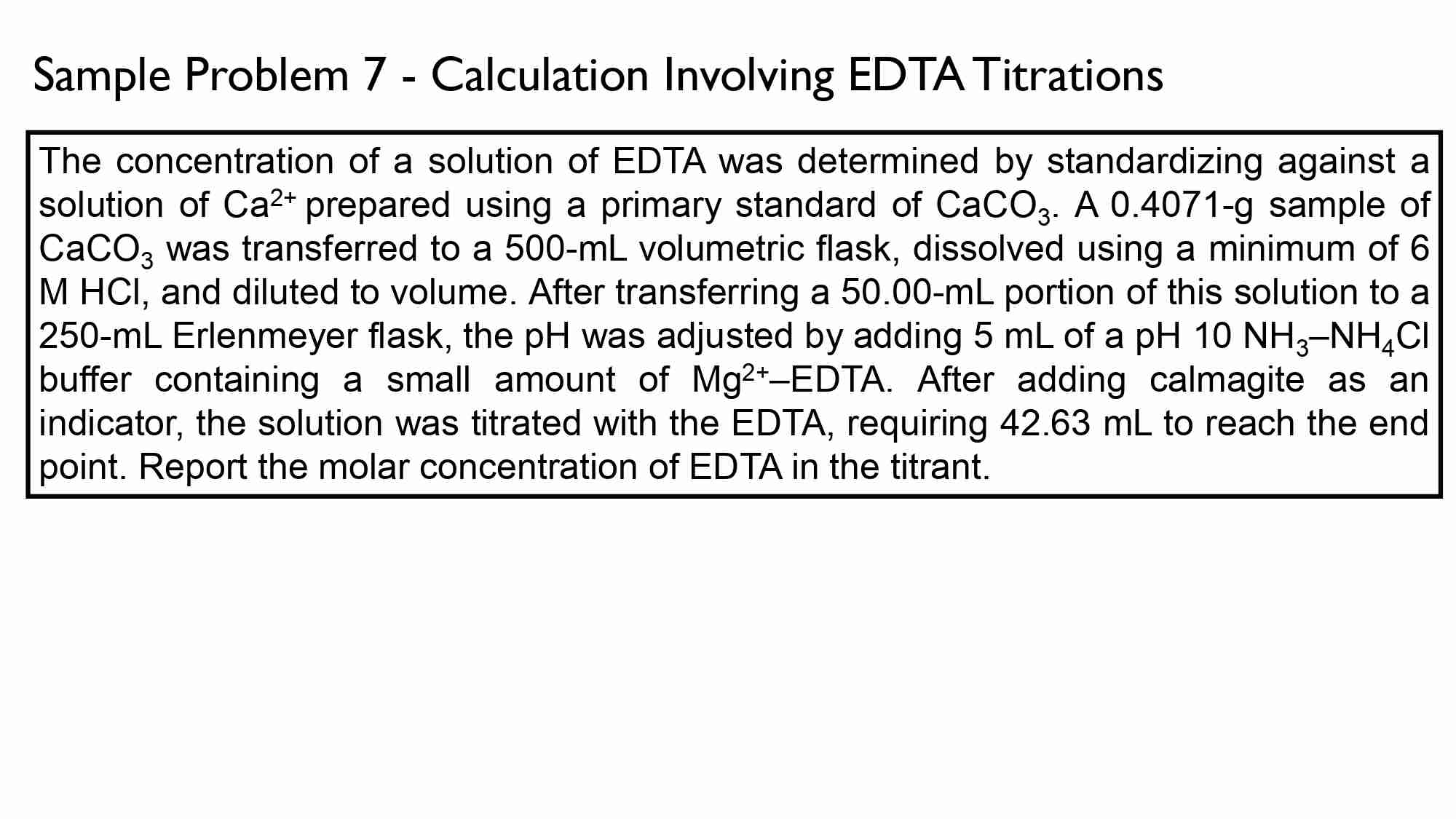
Calculate the hardness (in ppm of CaCO3) of a water sample with calcium concentration of 5.3 x 10^-4 M and magnesium concentration is 4.6 × 10^-4 M.