BIO 120.42 | Module 0: Lab Safety Guidelines & Operating Procedures
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
4 important aspects of Lab Safety Guidelines & Operating Procedures
rmam
Risk groups and biosafety levels
Microbiology lab SOP
Aseptic technique
Media prep calculations
Which risk group?
Could be of local / exotic origin
Involves respiratory transmission and can cause serious or lethal diseases where treatment and/or vaccines may or may not be available
e.g., Bacillus anthracis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Risk group 3
Which risk group?
Commonly encountered in the community
Poses moderate environmental and/or health hazard
Causes opportunistic/nosocomial infections
Associated with treatable human diseases
e.g., sspvlc
Salmonella, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, Listeria, Campylobacter
Risk group 2
Which risk group?
Has great potential for lethal infection
Aerosol / droplet spread
e.g., Ebola virus
Risk group 4
Which risk group?
Nonpathogenic
Poses minimal threat to environment / lab personnel
e.g., B. subtilis, E. coli
Risk group 1
Set of minimum standards and practices established to ensure safe handling of microorganisms in lab environments
Biosafety levels
Biosafety levels are determined based on which 2 factors
pp
Potential risks associated with the microorganisms being handled
Protective measures needed to safeguard lab personnel, people outside the lab, environment lpe
Which BSL?
srsb
Special ventilation system
Restricted access
Specially trained personnel
BSC
Can be used to handle RG1,2,3
BSL-3
Which BSL?
Standard microbial practices
Handle in the open
No special equipment
Can be used to handle RG1
BSL-1
Which BSL?
ispb
Isolated lab (strictly controlled access, ventilation, waste management)
Specially trained personnel
Wearing positive pressure one-piece body suit
BSC
Can be used to handle RG1,2,3,4
BSL-4
Which BSL?
BSC: only if splashes or aerosols are generated
Signages posted
Designated waste container for biohazards
Autoclave (which may not necessarily be within the room but near it)
Can be used to handle RG1, RG2
BSL-2
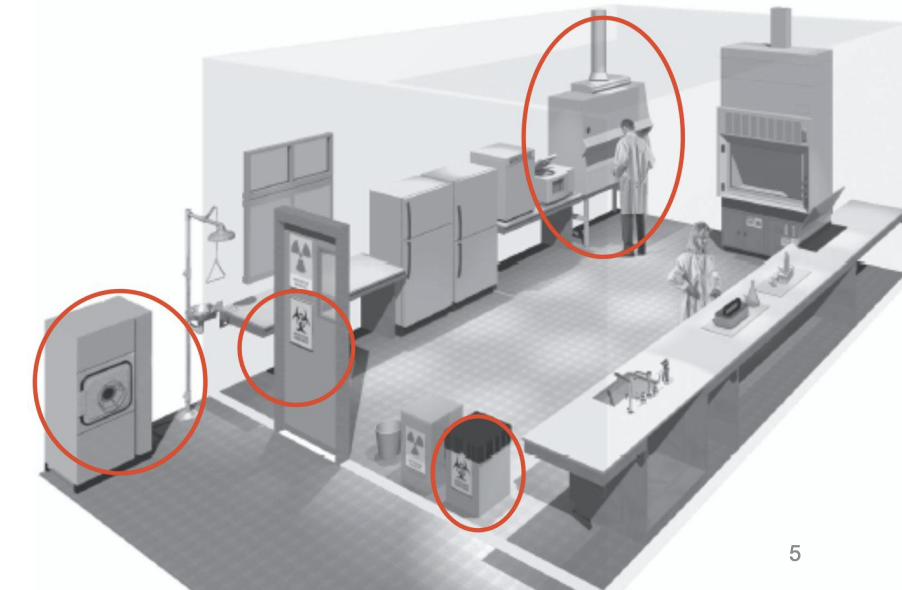
Which BSL?
BSL-2
BSC
Signages
Biohazards waste container
Autoclave (not necessarily within room but near it)
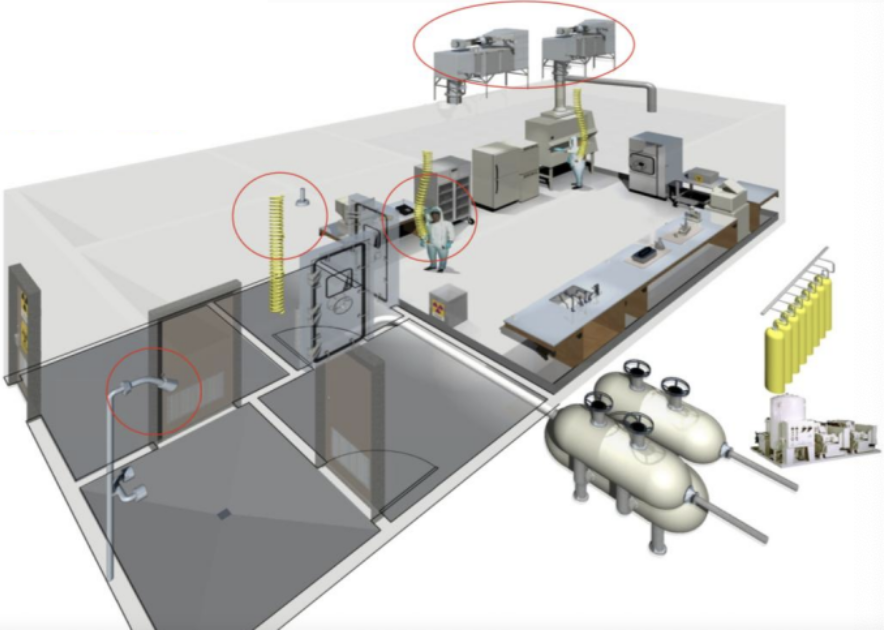
Which BSL?
BSL-4
Isolated lab (strictly controlled access, ventilation, waste management)
Specially trained personnel
Positive pressure one-piece body suit
BSC
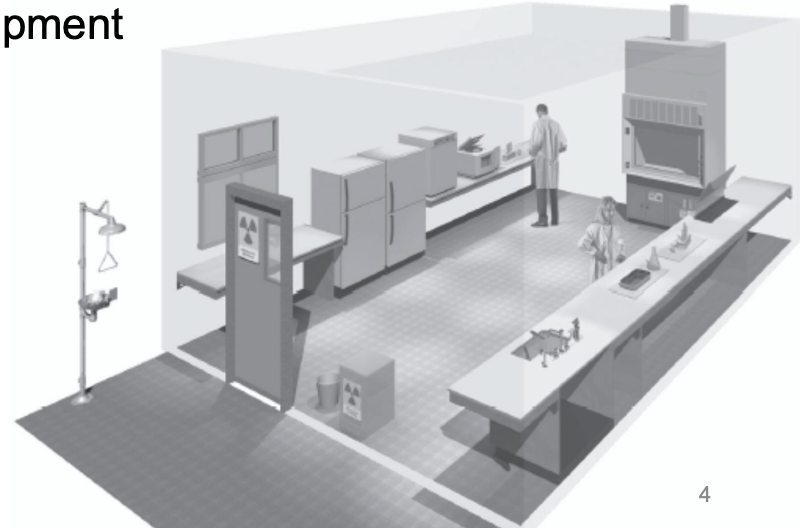
Which BSL?
BSL-1
Handle in the open
No special equipment
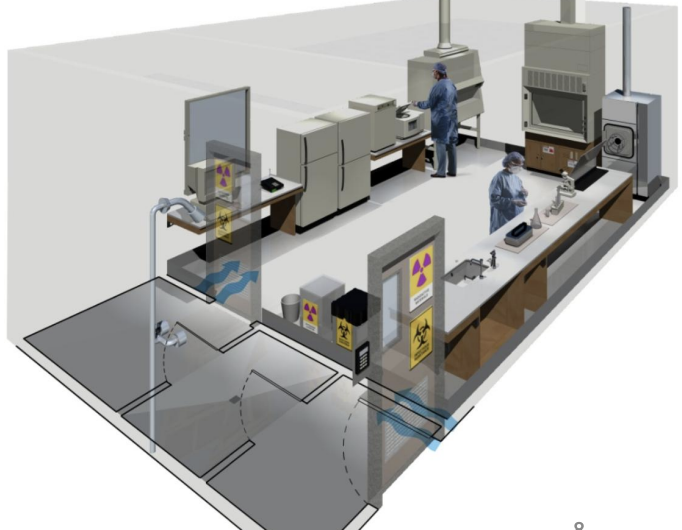
Which BSL?
BSL-3
Special ventilation system
Restricted access
Specially trained personnel
BSC
5 safety equipment that must be present in lab (Microbio Lab SOP)
3 fire ee first
Fire extinguisher
Fire blanket
Fire exit
Emergency shower
Eye-wash station
First aid kit
Enumerate some Microbiology Lab SOP
Refrain from working in the lab when immunocompromised (e.g., undergoing chemotherapy treatment, organ transplant, have autoimmune conditions, pregnant)
No eating
No applying makeup
No smoking
No using of contact lenses
No running/horseplay
No sleeping
Cover wounds with a band-aid, especially if on the hands
Keep equipment and materials away from the edge of lab benches
Do not let electrical cords hang over the edge
Keep the floor free of slip hazards
Accident resulting from inadvertent contact with fixed object
Trips

Accident resulting from slip, trip, or fall from height
Falls

Accident resulting from loss of traction between shoe and walking surface
Slips

Never leave any _ unattended
If alcohol in a beaker ignites, put out the fire by _
Do not try to _
Treat all chemicals as _, unless your instructor tells you otherwise
Heat source
Smothering or covering with petri plate top cover
Move the fire into the sink
Poisonous, corrosive, flammable pcf
Do not take cultures _
When transporting cultures to incubator, use _
Treat all cultures as _
Out of the lab
Plastic tub / test tube rack
Potentially pathogenic
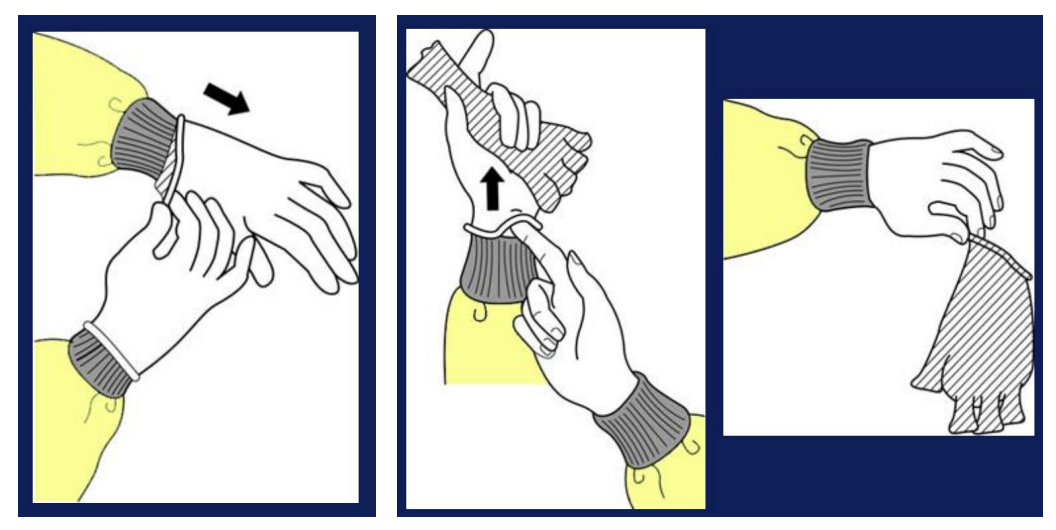
How to remove gloves properly
Spray gloved hands first with disinfectant, preferably 10% bleach
Pull out 1 glove by pinching from outside of glove and removing it out of your hand
Then insert ungloved hand into the inside of the other gloved hand, pull the hand free from the gloves, and make a bag out of the glove
Discard gloves in the regular trash
How to dispose chemical waste
Discard chemical waste in designated waste containers
This includes alcohol-stain waste but ensure there’s no culture media to prevent contamination or unintended chemical reactions
Collected waste is then sent for hauling and treatment
How to dispose contaminated pipette tips & Pasteur pipette
Autoclave or use 10% bleach (30 - 60 mins contact time)
Discard in sharps container
How to dispose needles and syringes
Discard in sharps container
Do not recap needles by hand
Do not remove needles from syringes by hand
Do not bend or break needles by hand
Do not manipulate needles by hand
How to dispose broken glassware
Discard in broken glassware container
How to dispose liquid waste
Autoclave or use 10% bleach (30 - 60 mins contact time)
Discard in sink as regular waste
How to dispose solid waste
Autoclave
Discard as regular waste
How to dispose contaminated tissue
Preferably 10% bleach (30 - 60 mins contact time) to ensure all tissue surfaces are disinfected since bleach will be able to penetrate all throughout (instead of autoclaving)
Discard as regular waste
#1 rule in decontamination of lab waste
Do it ASAP (no later than 8 days after generation when stored above freezing temperature)
Refers to the killing or removal of all viable organisms, including endospores and viruses
Decontamination
2 methods of decontamination
Using moist heat (autoclaving)
Using chemicals (10% bleach)
Decontamination method that denatures most macromolecules of microorganisms
Autoclave
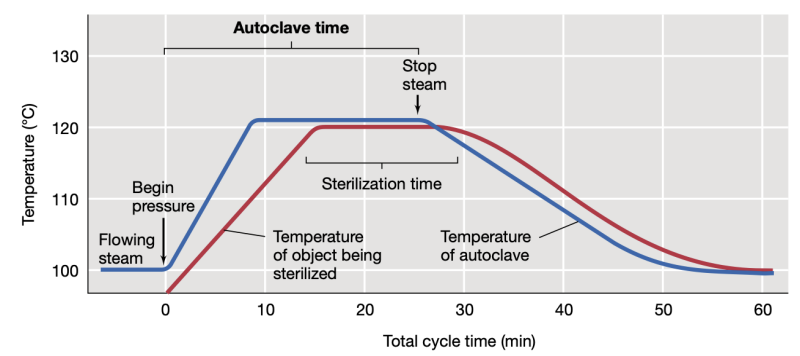
Autoclave setting for decontamination
121 C, 15 psi, 30 mins
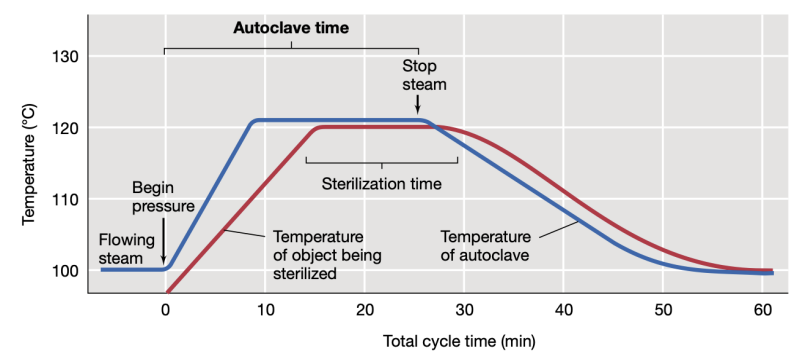
Autoclave setting for sterilization
121 C, 15 psi, 15 mins
What should you not autoclave?
fracer
Flammable material
Radioactive materials
Acids
Chlorine-based products / chlorine
Explosive material
Reactive, corrosive, toxic material
How to sterilize BSC / Laminar Flow Hood
Turn on BSC (warm up)
Turn on UV lamp (default time = 10 - 15 mins)
10% fresh bleach solution
Cover all surfaces
10-min contact time
Evaporate or wipe it dry before using ethanol because when bleach + ethanol mixes, chloroform forms, which is corrosive
Do not stick your head in the unit
70% ethanol
Cover all surfaces
10-min contact time
Evaporate or wipe dry
Do not stick your head in the unit
How to decontaminate BSC / Laminar Flow Hood
10% fresh bleach solution
Cover all surfaces
10-min contact time
Evaporate or wipe dry
Do not stick your head in the unit
70% ethanol
Cover all surfaces
10-min contact time
Evaporate or wipe dry
Do not stick your head in the unit
Turn on UV lamp (default = 10 - 15 mins)
Turn off BSC
How to handle biological spill
Cover any spilled cultures with paper towel
Spray disinfectant generously (starting from edges to avoid further spreading spillage across surface)
Allow 30 - 60 mins contact time
Work concentrically to clean up absorbent material (from the outer edge of the spill towards the center)
Report all spills and accidents to instructor (incident report form)
Set of procedures followed in handling microbial cultures to prevent contamination of scsoe source of culture, culture media, self, other lab workers, and the environment
Aseptic technique
Aseptic technique refers to the set of procedures followed in handling microbial cultures to prevent contamination of _
scsoe
Source of culture
Culture media
Self
Other lab workers
Environment
Give examples of aseptic techniques
Washing your hands thoroughly before and after every experiment
Disinfecting your work area using tissue and ethanol before and after every experiment
Turning off electric fans
Ensuring proper ventilation system within the lab
Removing bags, notebooks, gadgets, etc. from work benches
Following a “clean-to-dirty” workflow to ensure contamination from dirty areas does not spread to clean areas
Position nondominant hand closest to the clean station; dominant hand nearest to the dirty station
e.g., If you’re right-handed, then the clean station should be to your left and you start working there, while dirty station should be to your right.
Once an item is used in dirty station, avoid bringing it back to clean station.
Properly labeling cultures
Working near an alcohol lamp when doing isolation techniques outside of BSC (convection current)
Holding loop/needle at an angle of 60 degrees (to heat large SA of wire), passing the entire length of loop/needle through flame until red-hot, then cooling this for 10 secs before use
Culture media prep
Volume of agar plate
Volume used for calculations
15 - 20 mL/plate
20 mL (this gives it a room for error)
When do you have to add 10% extra to culture media volume?
When culture media is to be dispensed into different containers (room for error)
Culture media prep
Volume of test tubes
Volume used for calculations
5 mL/tube
5 mL/tube + 10% (total volume)
When do you not add 10% extra to volume of media?
When media will not be dispensed into different containers
T/F: You heat media only if agar is dispensed after sterilization
FALSE
Heat media only if agar is to be dispensed before sterilization (e.g., when making NA tubes)
Culture media prep
Maximum volume for flask/bottle
50 - 70% of max capacity
When do you have to heat media?
Media is heated if agar is to be dispensed prior to sterilization (e.g., when making NA tubes)
T/F: You add 10% extra to culture media volume if media is to be dispensed in different containers
TRUE
Why must media be heated if agar is to be dispensed before sterilization?
This is done to dissolve components and ensure that they are mixed thoroughly
What must be the total volume of dH2O added to your media if you have to make 10 NA plates?
1 plate = 20 mL / plate
20 mL/plate x 10 plates = 200 mL dH2O
What should be the amount of ff. components to prepare 200 mL of cultured media?
dH2O = 1 L
Beef extract = 3 g
Peptone = 0.5%
Agar = 17 g
Beef extract
3g / 1000 mL x 200 mL = 0.6 g
Peptone
0.5 g / 100 mL x 200 mL = 1.0 g
Agar
17 g / 1000 mL x 200 mL = 3.4 g
Formula for dilution vs. dilution factor
Dilution (D) = vol transferred / total volume
raise to negative 10-n
Dilution factor (DF) = 1 / D
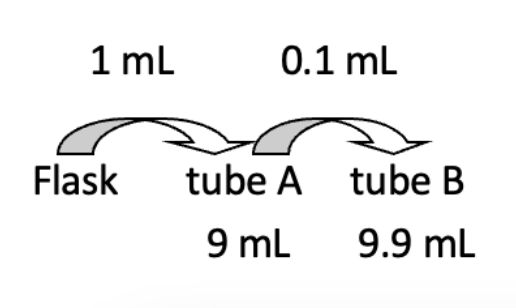
Compute for the dilution (D) and dilution factor (DF) of tubes A and B
Tube A
DA = vol transferred / total vol
1 mL / 10 mL = 0.1 = 10-1
DFA = 1 / D
1 / 0.1 = 10
Tube B
DB = Prev D (vol transferred / total vol)
10-1 (0.1 / 10 mL) = 0.001 = 10-3
DFB = 1 / D
1 / 10-3 = 1000 = 103
General formula for concentration computations
C1V1 = C2V2
Formula for anhydrous / hydrous form substitution computations
Weight anhydrous / MW anhydrous = Weight hydrous / MW hydrous
MW = No. of atoms of each element x Atomic weight of element
C = 12
H = 1
O = 16
N = 14
Prepare 500 mL of 0.1 g / 100 mL reagent from a 2 g / 10 mL reagent
C1V1 = C2V2
2g/10 mL (V1) = 0.1g/100mL (500 mL)
V1 = 0.1g/100mL (500 mL) / 2g/10mL
V1 = 0.5 g / (2g/10mL)
V1 = 2.5 mL
Total vol = 2.5 mL of 2g/10mL reagent + 497.5 mL dH2O
You need the unhydrated form (12 g MgSO4), but only the hydrated form (MgSO4 × 5H2O) is available.
MW of MgSO4 = 120.366 g/mol
MW of H2O = 18.015 g/mol
Weight anhydrous / MW anhydrous = Weight hydrous / MW hydrous
12 g MgSO4 / 120.366 g/mol = Weight hydrous / (120.366 g/mol + 5 × 18.015 g/mol)
Weight hydrous = (12 g MgSO4 / 120.366 g/mol) (120.366 g/mol + 5 × 18.015 g/mol)
Weight hydrous = 20.980 g = 21 g of hydrated form (MgSO4 × 5H2O)
Formula for computing for moles
Weight solute / MW solute
Formula for computing for molarity
moles solute / L solution
(Weight solute / MW solute) / vol of soln (L)
Molarity problem
Given
200 mL dH2O
2 M solution
MW = 56.11 g/mol
Compute for the amount of solute (g)
Molarity (M) = moles / L
M = (Weight solute / MW solute) / vol (L)
2 M = (Weight solute / 56.11 g/mol) / 0.200 L
2 mol/L (0.200 L) (56.11 g/mol) = Weight solute
Weight solute = 22.44 g
Conversion units 10-1 → 10-18
dcmunpfa
deci = 10-1
centi = 10-2
milli = 10-3
u (micro) = 10-6
nano = 10-9
pico = 10-12
femto = 10-15
atto = 10-18
Conversion units 101 → 1018
dhk mg tph
deca = 101
hecto = 102
kilo = 103
mega = 106
giga = 109
tera = 1012
peta = 1015
hexa = 1018
Conversion
ug → _ → _
uL → _ → _
ug → mg → g
uL → mL → L
Convert 900 ug → kg
900 ug (1 mg / 103 ug) (1 g / 103 mg) (1 kg / 103 g) = 9×10-7 kg
Fill in the conversion table for % w/w, % w/v, % v/v
w/w | w/v | v/v | |
pph or % | |||
parts per thousand | |||
ppm | |||
ppb | |||
ppt |
w/w | w/v | v/v | |
pph or % | g / 100 g | g / 100 mL | mL / 100 mL |
parts per thousand | g / kg | g / L | mL / L |
ppm | mg / kg | mg / L | uL / L |
ppb | ug / kg | ug / L | nL / L |
ppt | ng / kg | ng / L | pL / L |