Coordination and response
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Stimulus
Changes in internal and external environment
Homeostasis
Maintains internal conditions
Optimal conditions for enzymes and cell function
Factors controlled by homeostasis
Water content
Temperature
pH
Blood pressure
Blood glucose concentration
2 main communication systems
Endocrine system
Nervous system
Where is body temperature maintained and controlled
Thermoregulatory centre
Types of control responses
Nervous
Chemical
Components of the control system
A stimulus
A receptor
A coordination centre which receives and processes information from receptors
An effector (a muscle or gland), which brings about responses to restore optimum levels
Positive tropism
Growth towards the stimuls
Negative tropism
Growth away from the stimulus
Phototropism
Response to light
Geotropism
Response to gravity
Auxin
Plant growth regulators that control directional growth responses
Where is auxin produced
Tips of growing shoots and diffuses to the region just below the tip, where cell division occurs.
Only the area behind the tip can contribute to growth by cell division and elongation.
How does the nervous system transmit information
Sent as electrical impulses through neurons at very high speeds
How does the endocrine system transmit information
Sends information as hormones, which are carried by the blood and can circulate throughout the body.
Main features of the nervous system
Made up of nerves, brain, and spinal cord.
It uses electrical impulses, with fast action and a short duration.
Main features of the endocrine system
Made up of glands.
It uses chemical hormones, with slower action and a longer duration.
The human nervous system consists of
Central nervous system (CNS) – the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – all of the nerves in the body
Nerve
Bundle of neurons
The pathway through the nervous system
stimulus → sensory neurone → relay neurone → motor neurone → effector → response
Synapse
A synapse is a junction between two neurones where their dendrites meet. It is a very small gap known as the synaptic cleft
How is the signal transferred across a synapse
The electrical signal is converted into neurotransmitters that crosses the synaptic cleft, then back into an electrical impulse when it meets the neurone on the other side.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical signalling molecules used to transfer the signal between neurons at a synapse
Process of how an impulse is passed across a synapse.
The electrical impulse travels along the presynaptic neurone.
This triggers the release of neurotransmitters from vesicles.
Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind with receptor molecules on the postsynaptic membrane.
This stimulates the second neurone to generate an electrical impulse.
The neurotransmitters are destroyed to prevent continued stimulation.
Why do synapses ensure impulses only travel in one direction?
To avoid confusion within the nervous system
Reflex arc
Pathway of a reflex response taken by an electrical impulse
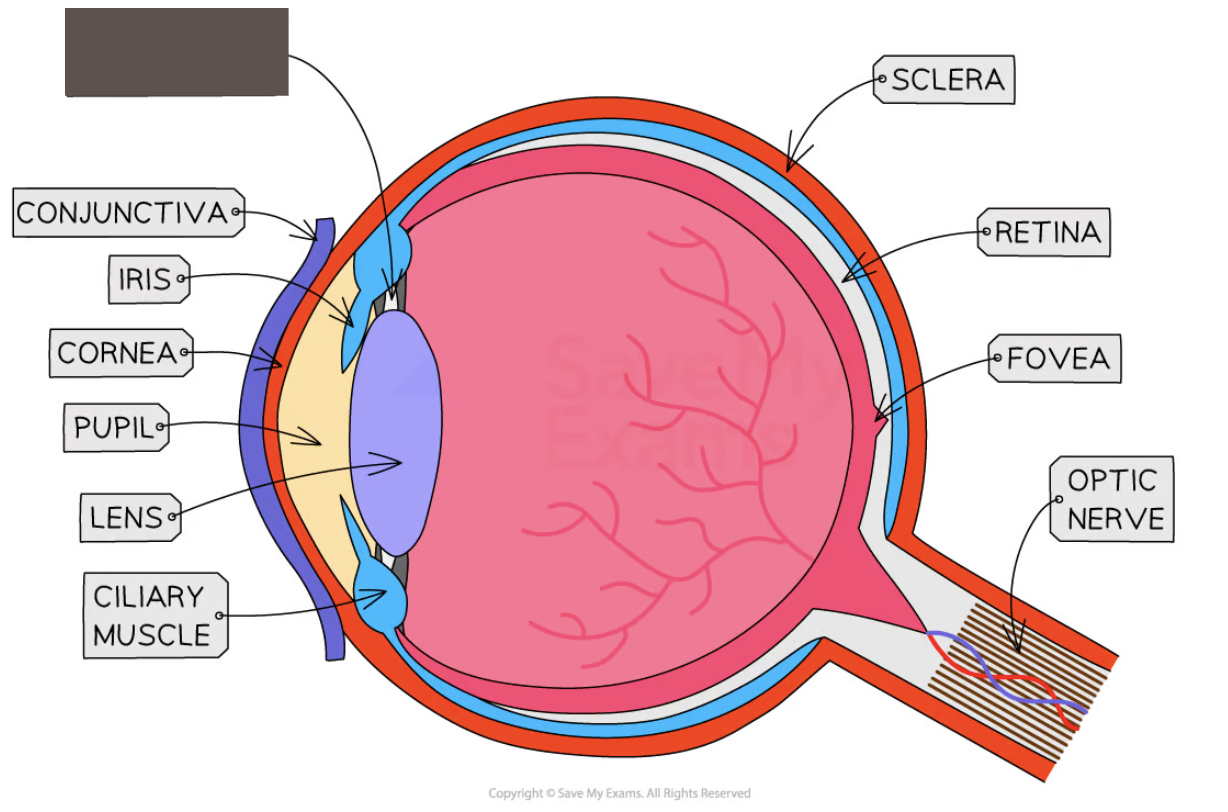
Label the structure and its function
Suspensory ligament
Ligaments that connect the ciliary muscle to the lens
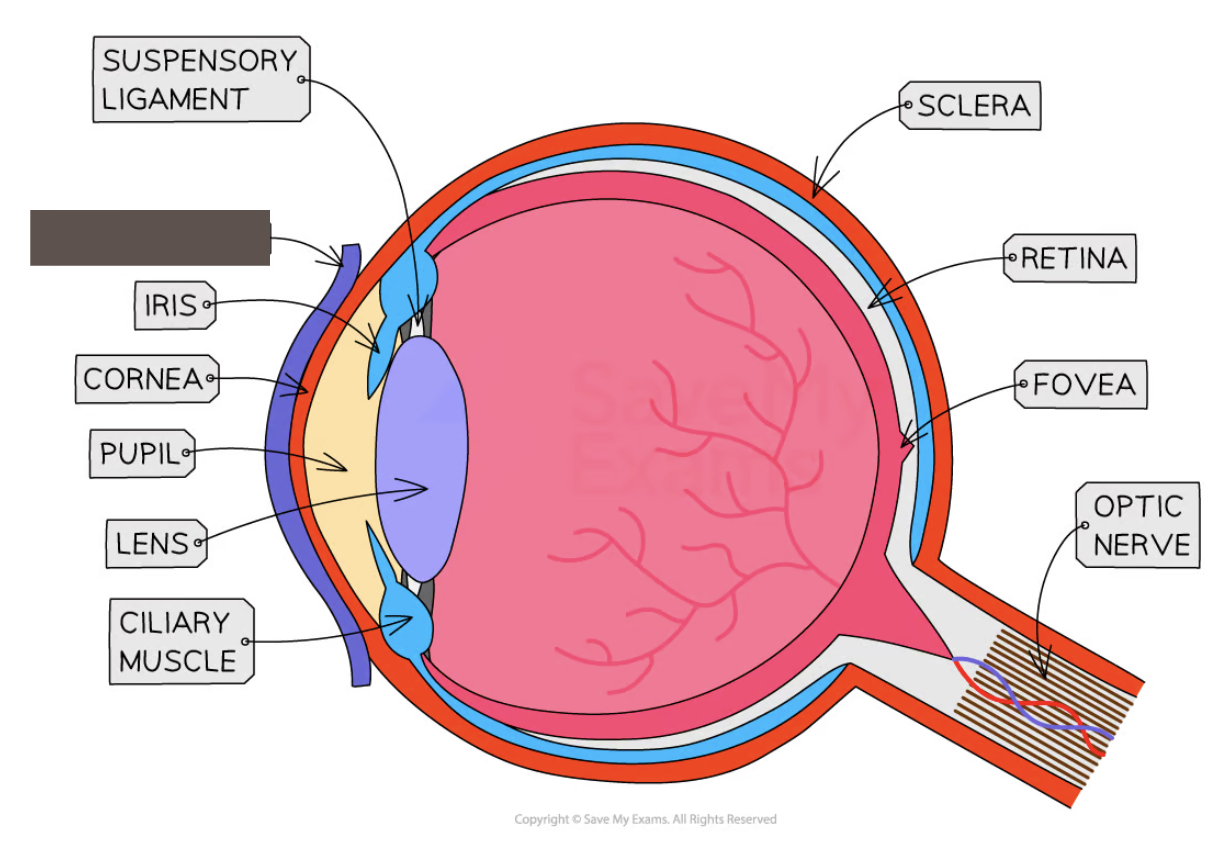
Label the structure and its function
Conjunctiva
A clear membrane that covers the white of the eye and the inside of the eyelids; it lubricates the eye and provides protection from external irritants
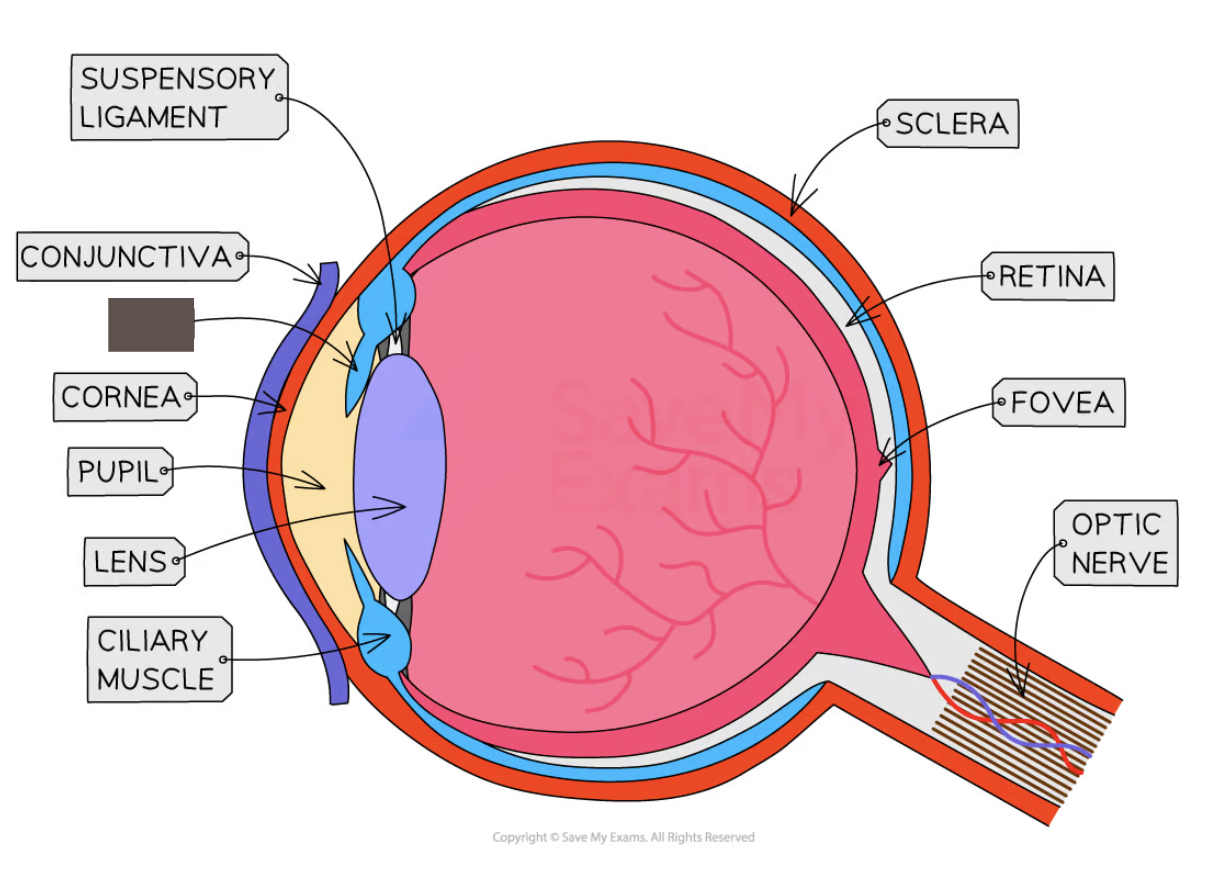
Label the structure and its function
Iris
controls how much light enters the pupil
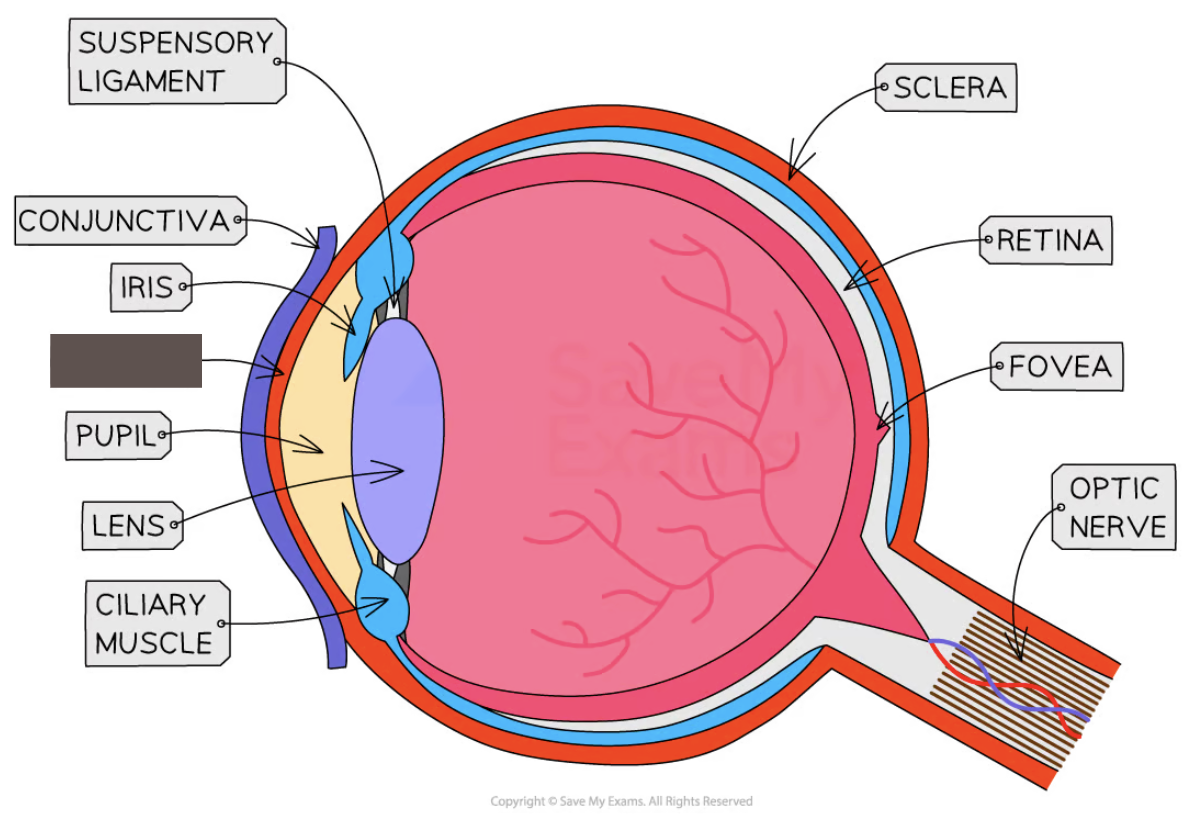
Label the structure and its function
Cornea
transparent lens that refracts light as it enters the eye
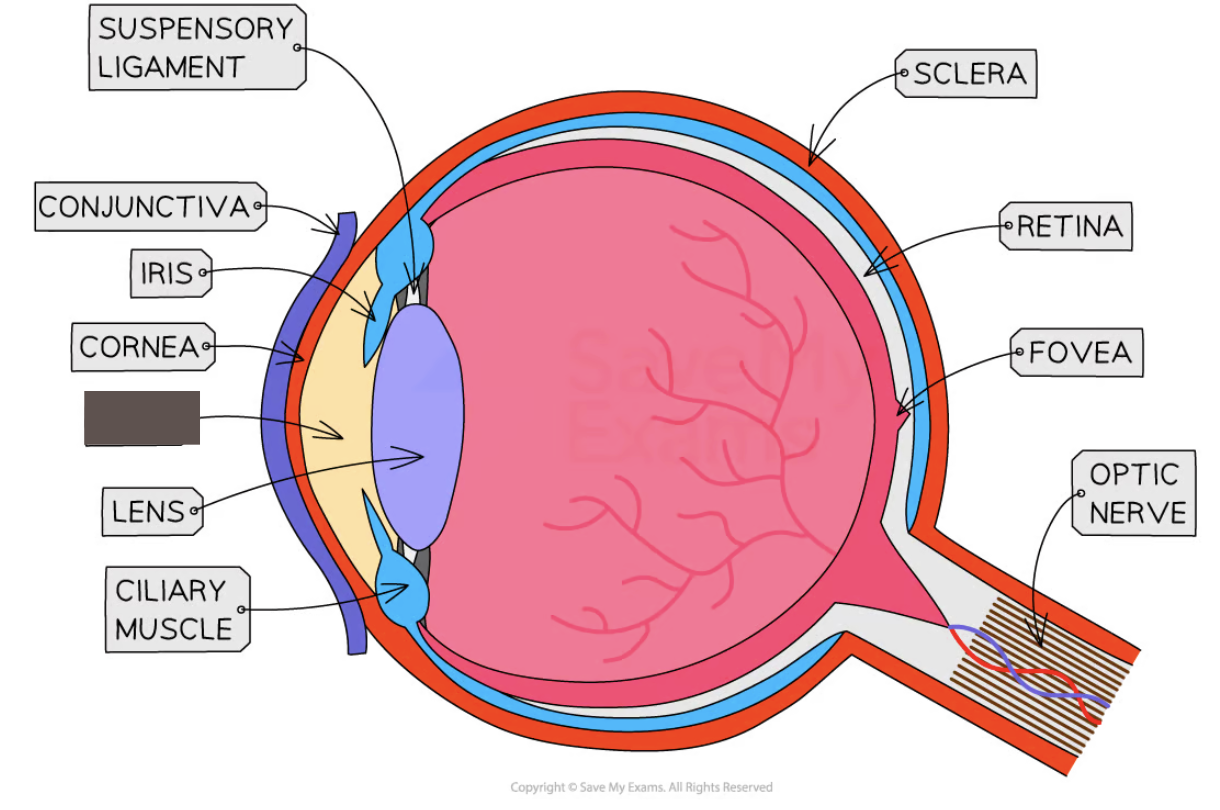
Label the structure and its function
Pupil
Hole that allows light to enter the eye

Label the structure and its function
Lens
transparent disc that can change shape to focus light onto the retina
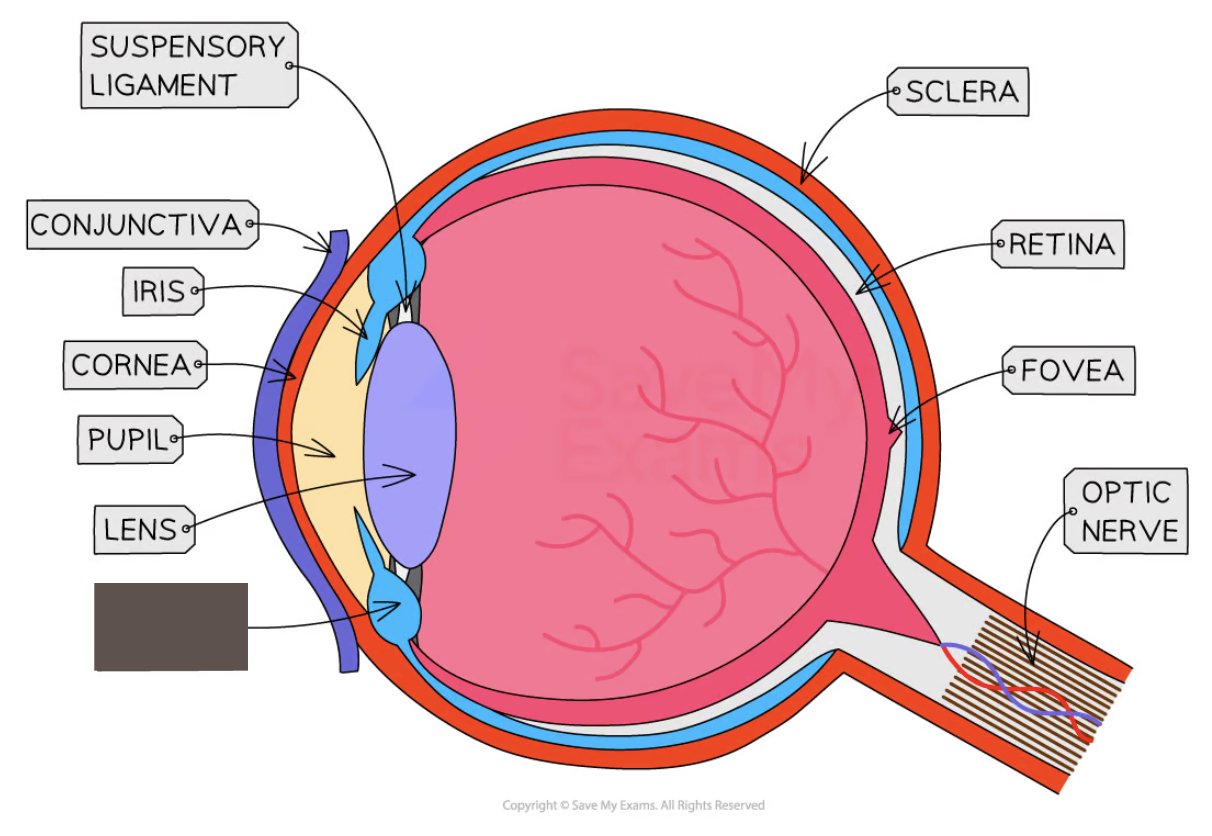
Label the structure and its function
Ciliary muscle
A ring of muscle that contracts and relaxes to change the shape of the lens
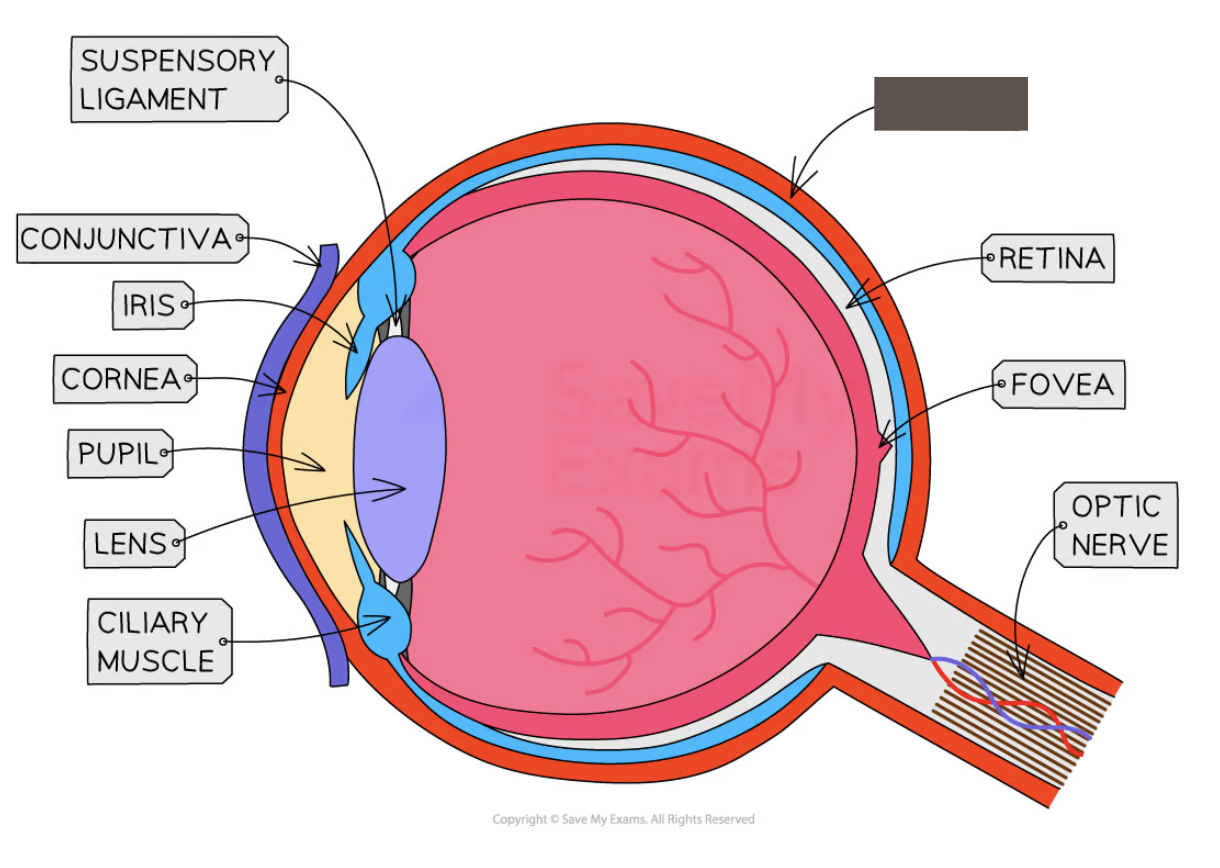
Label the structure and its function
Sclera
The strong outer wall of the eyeball that helps to keep the eye in shape and provides a place of attachment for the muscles that move the eye
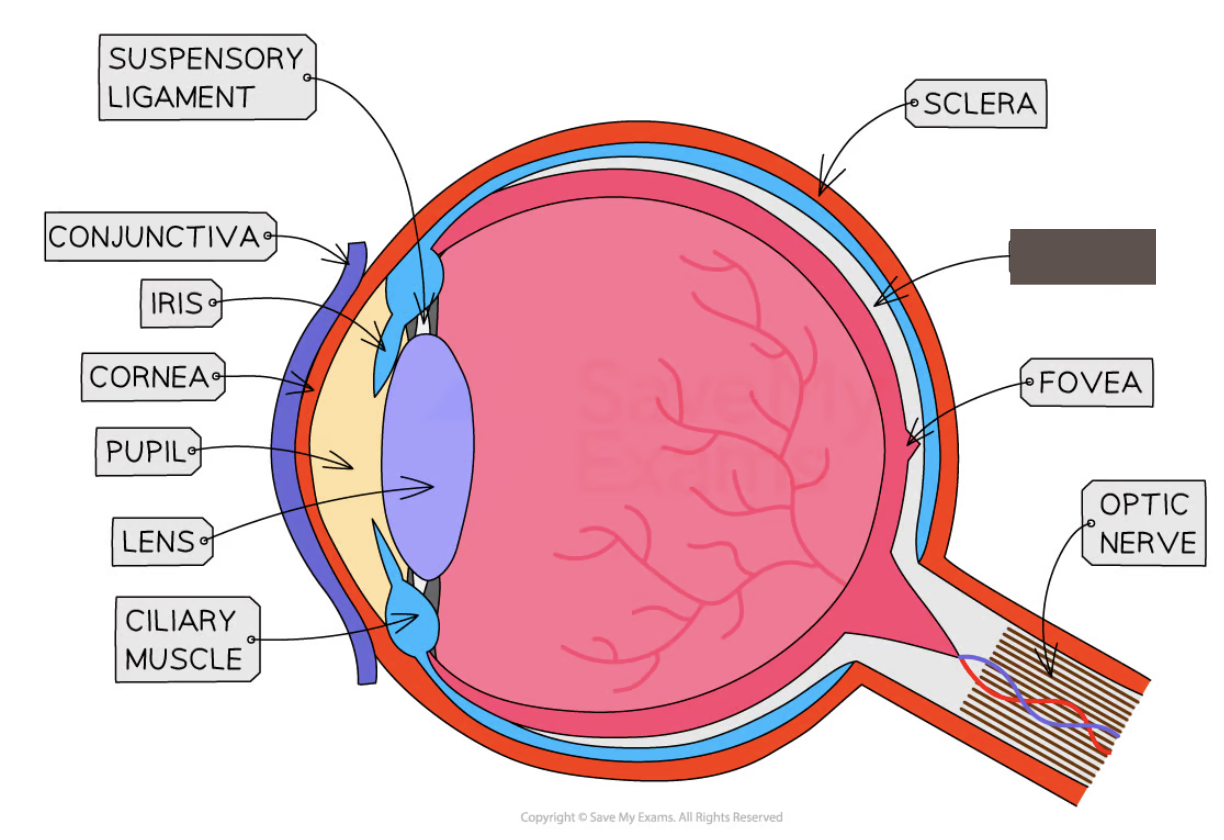
Label the structure and its function
Retina
contains light receptor cells – rods (detect light intensity) and cones (detect colour)
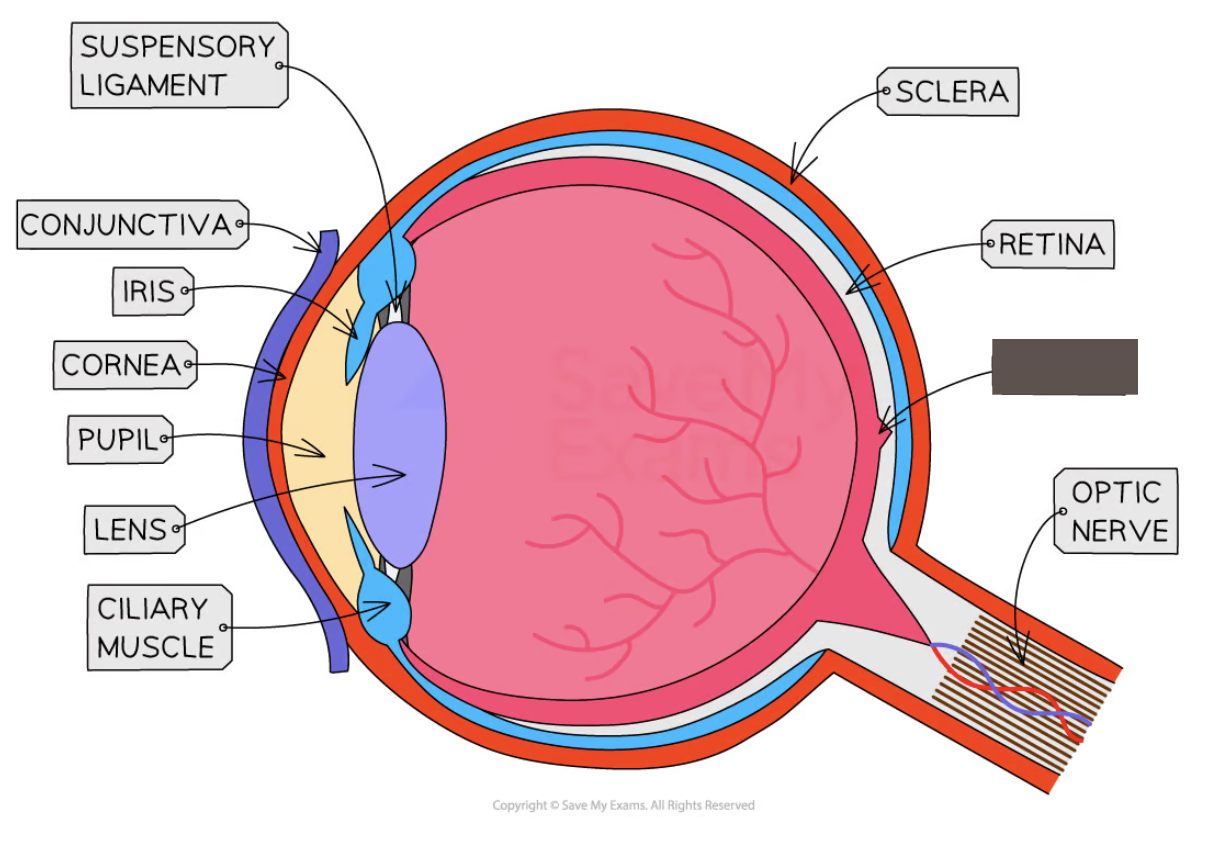
Label the structure and its function
Fovea
A region of the retina with the highest density of cones (colour detecting cells) where the eye sees particularly good detail
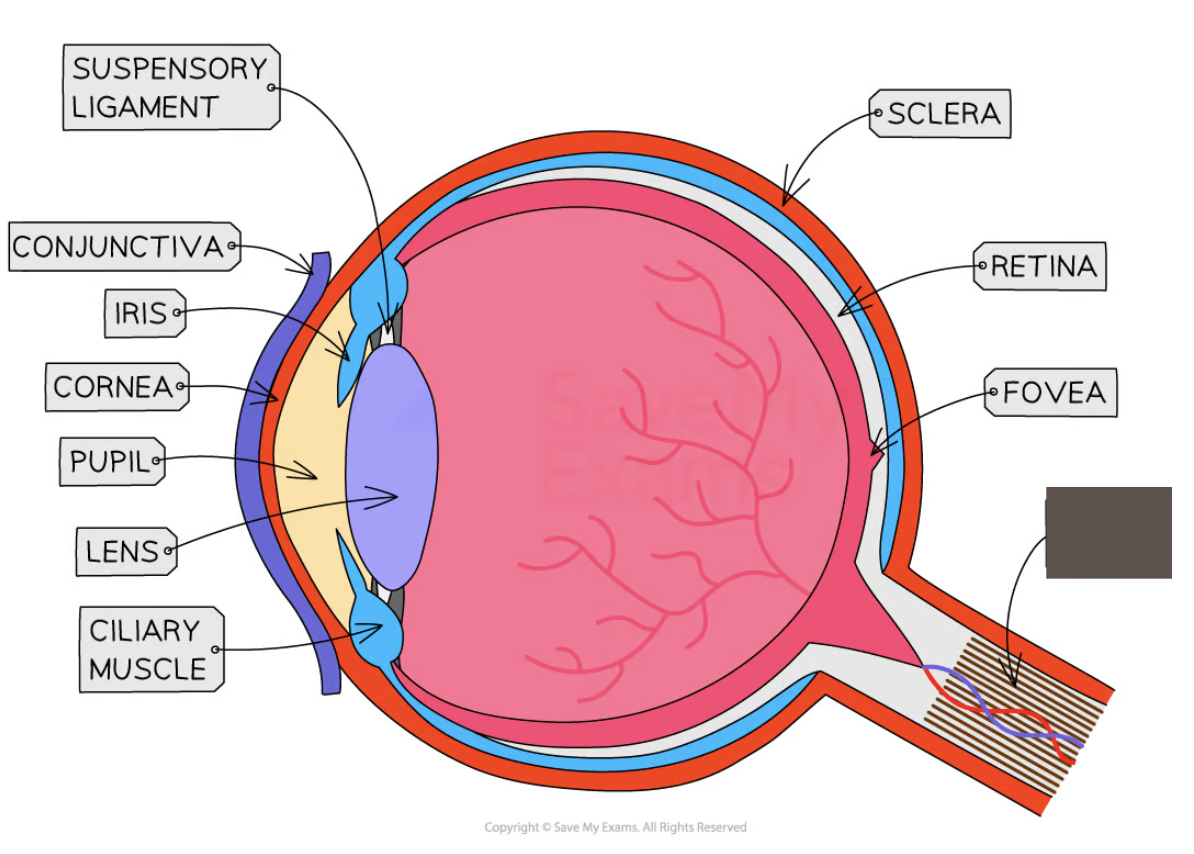
Label the structure and its function
Optic nerve
sensory neuron that carries impulses between the eye and the brain
rod cells
Sensitive to light
Cone cells
Sensitive to colour
Blind spot
The point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye, where there are no receptor cells
In bright light
Radial muscles relax
Circular muscles contract
Pupil constricts
In dim light
Radial muscles contract
Circular muscles contract
Pupil dilates
Focusing on near objects
Ciliary muscles contract
Suspensory ligaments loosen
Lens gets fatter
Focusing on distant objects
Ciliary muscles relax
Suspensory ligaments tighten
Lens is pulled thin
Cooling mechanisms
Vasodilation
Sweating
Flattening of hairs
Vasodilation
Increase heat loss is to supply the capillaries in the skin with a greater volume of blood, which then loses heat to the environment via radiation
Sweating
Sweat is secreted by sweat glands
This cools the skin by evaporation
Flattening of hairs
The hair erector muscles in the skin relax, causing hairs to lie flat
This stops them from forming an insulating layer by trapping air and allows air to circulate over the skin and allows heat to leave by radiation
Warming mechanisms
Vasoconstriction
Shivering
Erection of hairs
Vasoconstriction
The capillaries in the skin are supplied with a smaller volume of blood, minimising the loss of heat to the environment via radiation
Shivering
This is a reflex action in response to a decrease in core body temperature
Muscles contract in a rapid and regular manner to warm the blood
Erection of hairs
The hair erector muscles in the skin contract, causing hairs to stand on end
This forms an insulating layer over the skin's surface by trapping air between the hairs and stops heat from being lost by radiation
Adrenaline
Readies the body for a 'fight or flight' response
Increases heart and breathing rate
Adrenaline- Source
Adrenal gland
Insulin
Lowers blood glucose levels
Causes excess glucose in the blood to be taken up by the muscles and liver and converted into glycogen for storage
Insulin- source
Pancreas
Testosterone
Main sex hormone in males
Development of male reproductive organs and secondary sexual characteristics (eg facial hair, deep voice)
Testosterone- source
Testes
Progesterone
Maintains pregnancy
Maintains the uterus lining to cushion the fertilised egg and allow it to develop
Progesterone- source
Ovaries
Oestrogen
Main sex hormone in females
Development of female secondary sexual characteristics and regulation of the menstrual cycle