chpt 10 to 13 power point gen astronomy
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What are sunspots?
Dark spots visible on the Sun’s surface that are difficult to see without a telescope.
Who created sketches of sunspots in the mid 17th century?
Galileo.
Why are sunspots cooler than their surroundings?
They are cooler but also more energetic.
What do spectra taken around sunspot locations show?
Light consistent with charged particles in a magnetic field.
What is the effect of a sunspot's magnetic field on convection?
It suppresses convection, preventing heat from rising.
How does the Sun's rotation differ between the equator and poles?
The Sun rotates faster around the equator than at the poles.
What happens to the sun's magnetic field during its rotation?
The magnetic field gets dragged by the surface and twisted up, then slowly breaks free.
What is the cycle duration for the Sun's magnetic activity?
It repeats on an 11-year cycle.
What is a solar prominence?
A loop of material stuck on the solar magnetic field emerging from the surface, fairly stable.
What occurs during a solar flare?
When the magnetic field snaps, charges on the Sun’s surface can be ejected, which is highly energetic.
What are Coronal Mass Ejections (CME)?
Events where the magnetic field creates free bubbles carrying charge outward.
What components have we seen that can create a magnetic field?
Actual metals (Iron, Nickel), Liquid Metallic Hydrogen, and 'dirty' water (salt, hydrogen).
What is a significant method that the Sun uses to create its magnetic field?
Brute force to churn charges, specifically protons (H+).
Why is the Radiative Zone unlikely to be a source of the Sun's magnetic field?
There can’t be much churn in the Radiative Zone because H+ can’t move.
What is the significance of the Convective Zone in relation to the Sun's magnetic field?
The Convective Zone is characterized by churn, potentially contributing to the magnetic field.
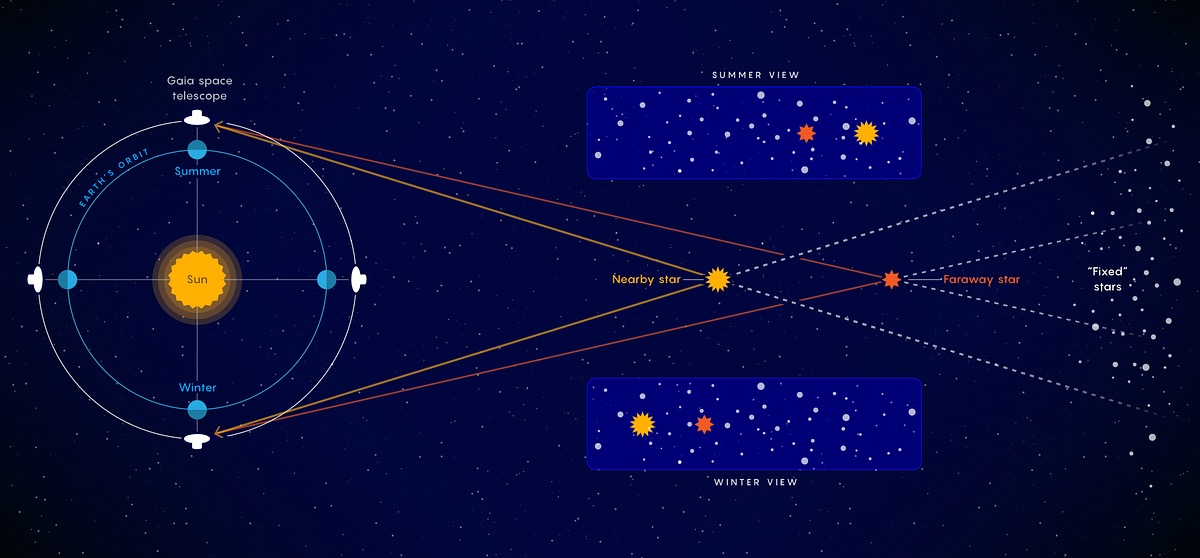
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
A plot of luminosity vs. color/temperature that categorizes stars into different classes.
Main Sequence Stars
Stars that fuse hydrogen into helium in their cores and lie along a diagonal band in the H-R diagram.
CNO Cycle
An alternative method of hydrogen to helium fusion that uses carbon as a catalyst; more efficient at higher temperatures.
Supergiants
Very large stars that have higher luminosities and can have radii significantly larger than the Sun.
Nuclear Fusion
The process where two light atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing energy.
Stellar Instability
The condition in which a star experiences varying luminosity due to alternating core and shell fusion.
Variable Stars
Stars whose luminosity fluctuates, often due to dynamic equilibrium being unstable.
RR Lyrae
A type of variable star with lower mass and shorter periods of less than a day.
Cepheid Variables
Higher mass variable stars that exhibit longer periods of luminosity ranging from 1 to 100 days.
Electron Degeneracy
The phenomenon that occurs when electrons resist compression due to quantum effects, halting gravitational collapse.
Baryon Degeneracy
A state reached when protons and neutrons in a stellar core resist further compression due to gravity.
Type II Supernova
An explosive end-of-life event for massive stars after the iron core collapses and triggers a rapid shock wave.
Iron Core Collapse
The stage when the core of a high-mass star collapses due to the cessation of fusion reactions, leading to a supernova.
Neutrinos
Subatomic particles released during the nuclear reactions in a star, contributing to energy driving shockwaves during supernova.
Luminosity
The intrinsic brightness of a star, measured relative to the Sun in the H-R diagram.
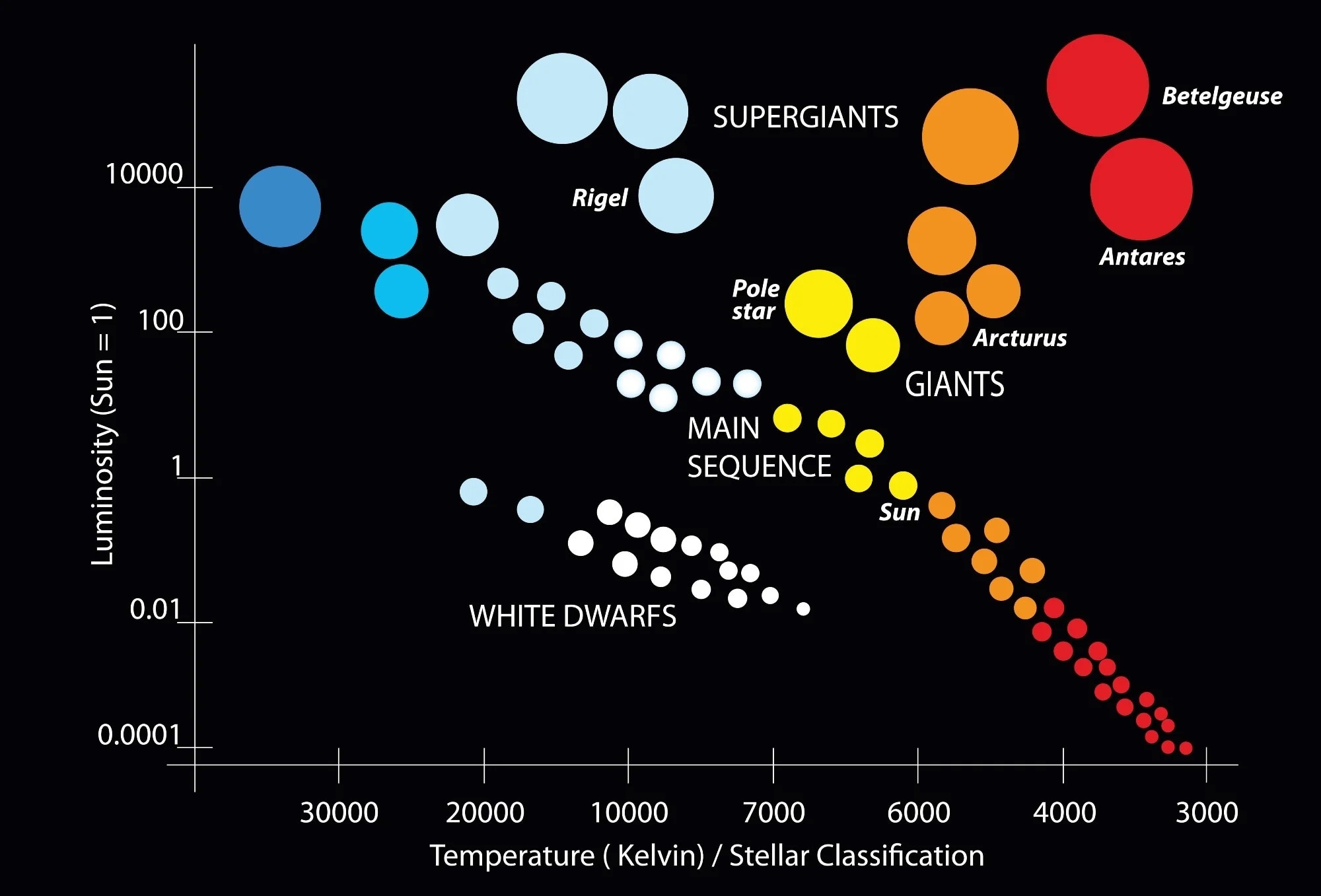
What does the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram illustrate?
The relationship between a star's luminosity and temperature.
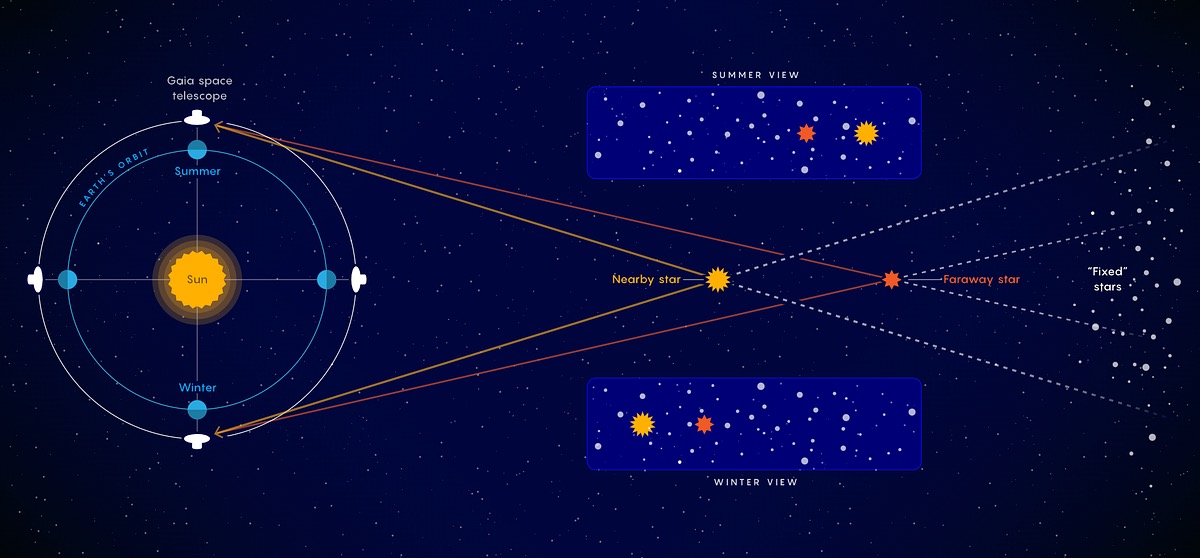
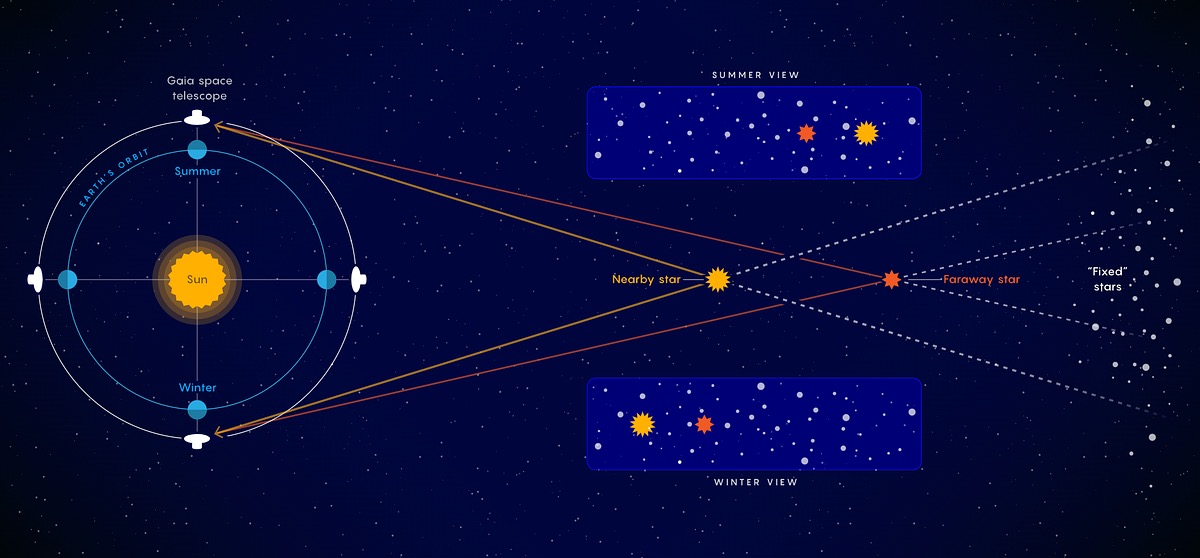
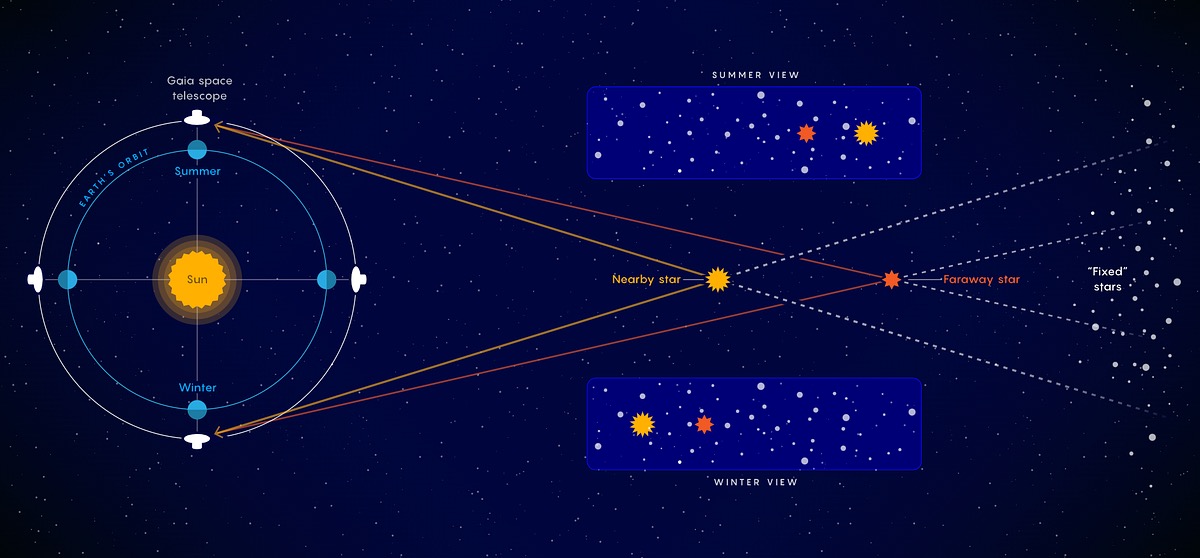
What is stellar parallax?
The apparent shift in a star's position due to the Earth's orbit around the Sun, used to calculate the distance to nearby stars.
What are the key properties of stars?
Luminosity, temperature, and mass.
How is the temperature of a star determined?
By its color; hotter stars appear bluer, and cooler stars appear redder.
What are the main zones of the Sun's structure?
Core, radiative zone, and convective zone in its interior; photosphere, chromosphere, and corona in its atmosphere.
How does the Sun generate energy?
Through nuclear fusion in its core, specifically the proton-proton chain converting hydrogen into helium.
What are sunspots?
Dark, cooler regions on the photosphere caused by magnetic activity.
What is solar wind?
A stream of charged particles flowing outward from the corona of the Sun.
What triggers a supernova in high-mass stars?
The collapse of the iron core after burning through their fuel much faster than low-mass stars.
What is a planetary nebula?
The outer layers expelled by low-mass stars during their evolution, after becoming an asymptotic giant branch star.
What forms from the collapse of the most massive stars?
Black holes, where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape.
What is a neutron star?
The incredibly dense core left behind after a massive star's supernova, which can be observed as pulsars.
Why is a star's initial mass important?
It is the most important factor in determining its fate and lifetime, with less massive stars having longer lifetimes.
What does the HR Diagram represent?
It is a plot of Luminosity versus Color/Temperature of stars.
What color are hot stars on the HR Diagram?
Hot stars are bluer.
What color are cool stars on the HR Diagram?
Cool stars are redder.
What happens when a star starts H+ → He2+ fusion?
A star is born and it lives on the Main Sequence.
What is the effect of a star's mass on its lifetime?
More mass leads to a shorter life due to faster consumption of hydrogen.
What indicates a star's evolution when helium 'ashes' build up?
Increased pressure and temperature are needed for hydrogen fusion.
What occurs when low mass stars run out of hydrogen fuel?
Gravity causes the star to collapse and heat up.
How does gravity stop the collapse of a low mass star?
Not by heat/pressure, but by electron degenerate matter.
What is the consequence of the quantum mechanics effect in low mass stars?
The star cools down and fades after collapse.
What are the typical stellar lifetimes based on mass?
High mass stars die quickest, medium mass stars have medium lifetimes, and low mass stars live the longest.
Luminosity
The actual brightness or light output of a star.
Flux
The amount of light received per unit area, which decreases with distance.
Parallax
The method of measuring the distance to nearby stars based on their apparent shift in position.
Parsec
A unit of distance in astronomy, equal to approximately 3.26 light years.
Temperature Classifications
System of classifying stars from hot to cool, including classes O, B, A, F, G, K, M.
Doppler Shift
The change in frequency of light or sound from a source moving relative to an observer.
Binary Stars
Stars that are in orbit around each other; over 50% of bright stars are binary.
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
A plot of star luminosity against temperature or color, showing the relationship between these properties.
What is the approximate age of the Sun according to the lecture notes?
The Sun is approximately 4.5 billion years old.
What two forces are in a state of Dynamic Equilibrium in the Sun?
Gravity and pressure are in Dynamic Equilibrium, where gravity pulls inward and pressure from heat pushes outward.
What is required for fusion to occur in the Sun?
Fusion requires high temperature and pressure, specifically about 15 million degrees Celsius at the core.
What are the four fundamental forces mentioned in the lecture?
The four fundamental forces are Gravity, Weak Force, Electromagnetic Force, and Strong Force.
What is the equation relating mass and energy mentioned in the lecture?
The equation is E=mc², showing the relationship between mass and energy.
How long does it take for energy to radiate out from the core of the Sun?
It takes approximately 100,000 to 1,000,000 years for energy to escape from the Sun's core to the surface.
What particle provides almost real-time information about the Sun?
Neutrinos provide almost real-time information because they can escape the Sun easily.
Describe the structure of the Sun as outlined in the lecture.
The Sun has three main layers: the Core (where H+ fusion occurs), the Radiative Zone (where energy emerges as light), and the Convective Zone (where H+ can move in convection cells).
What evidence is provided in the notes for the existence of convection cells on the Sun?
Granules on the surface of the Sun show patterns where hot gas rises and cooler gas sinks, supported by Doppler shift data.
What is the main product of the fusion process in the Sun?
The main product of fusion in the Sun is helium (He₂) along with energy and neutrinos.