Lesson 7: Interphase nucleus
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Characteristics
Membranous organelle, characteristic of eukaryotic cells, which contains the genetic material and allows the compartmentalization of DNA
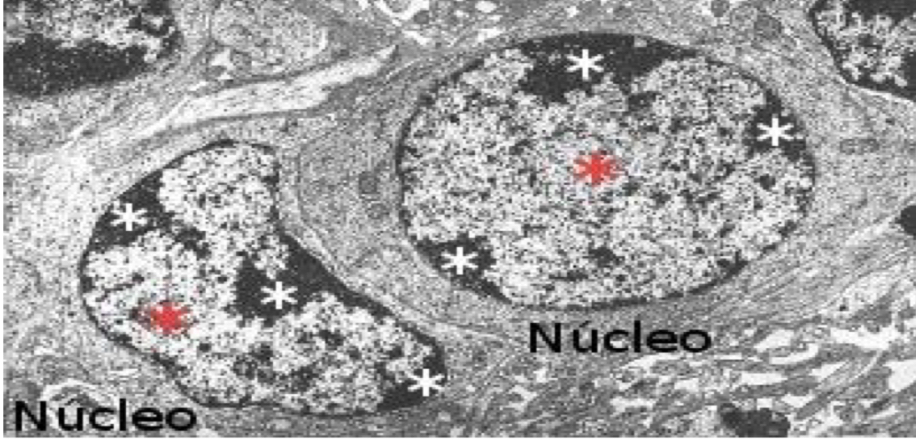
Types of chromatin
2 types of chromatin:
• Euchromatin: Dispersed chromatin, grey colour:
active transcription
• Heterochromatin (90%): Condensed chromatin, darker:
silenced genes, no transcription
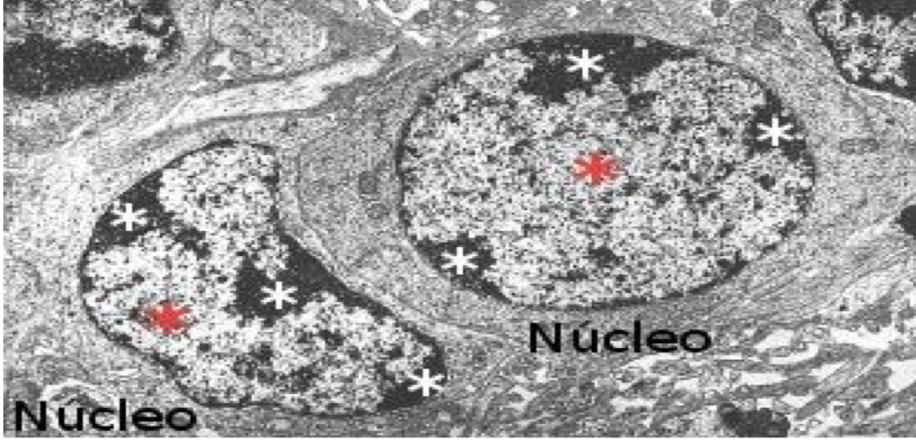
Types of heterochromatin
Constitute - always inactive
Facultative - can get active
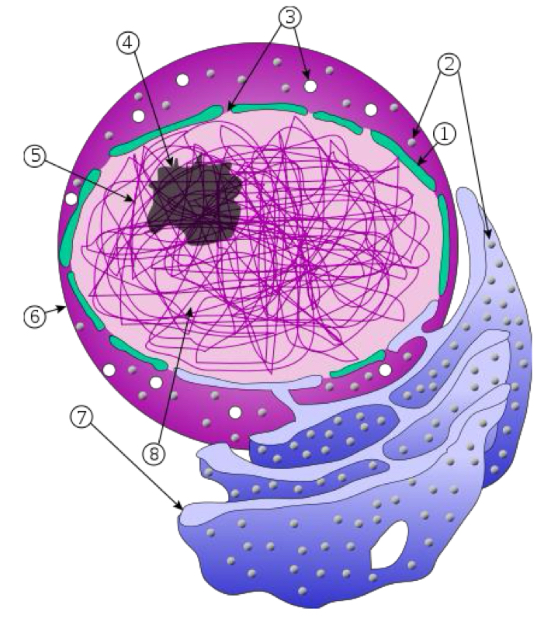
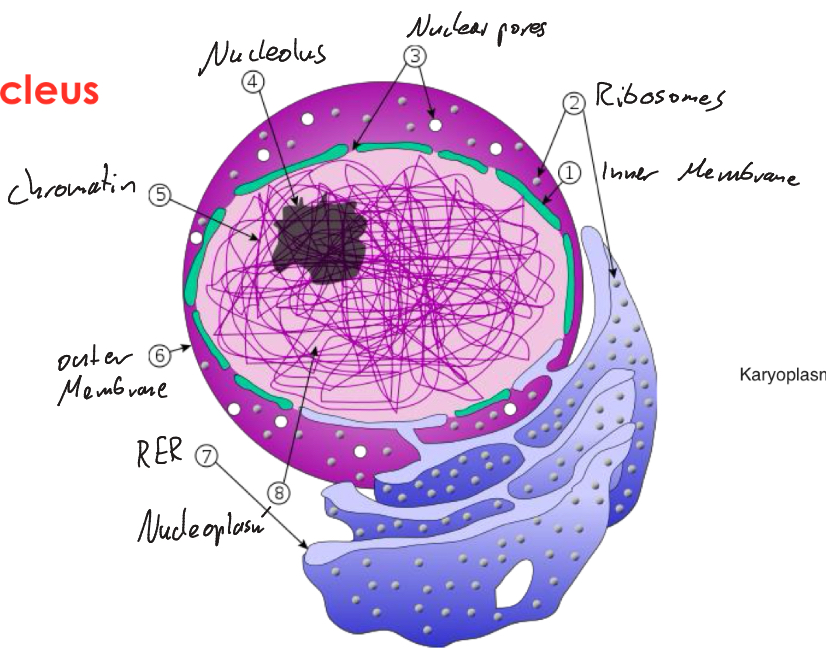
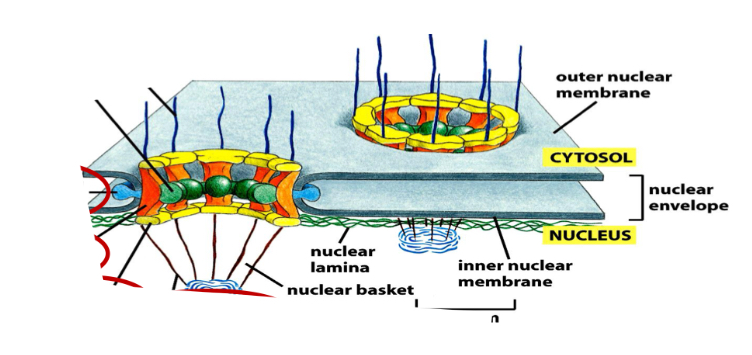
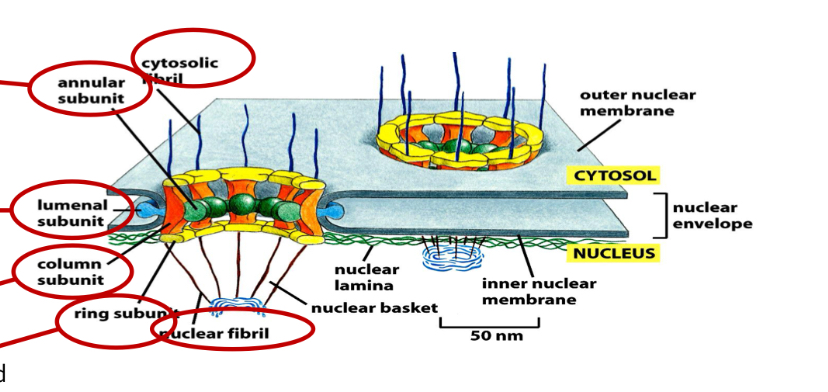
Nuclear envelope
Protein network formed by intermediate filaments inside the nucleus.
Consists of:
Outer/Inner Membrane
Perinuclear space
Nuclear lamina: formation of chromosomes from chromatin and cell division
Nuclear pores: allow transport RNA and proteins
Nucleoplasm/Karyoplasm
Contains nuclear components
Similar to cytosol
Placenta of Replicationa nd transcription
Chromatin
Constituted by DNA, histones and RNA
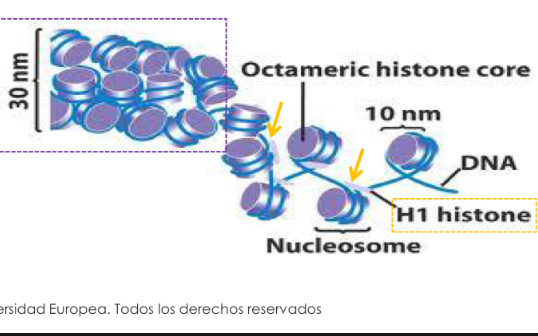
Chromatin compaction level: First level
Nucelosomes
Not tight
Second level: Chromatin fibre
Very tigh
Nucleolus
Main function: synthesis of rRNA and Asse,Bly of ribosomal subunits
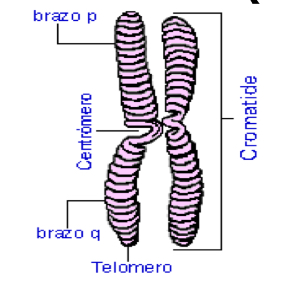
Difference nucleus interphase and mitosis
Interphase: Chromosomes are replicated, chromatin less condensed
Mitosis: chromatin very condensed and chromosomes distributed into 2 daughter cells